Back pain during pregnancy
- Understanding Back Pain During Pregnancy
- Causes of Back Pain in Pregnant Women
- Treatment and Management Strategies for Back Pain During Pregnancy
- Differential Diagnosis of Back Pain in Pregnancy
- When to Seek Medical Attention for Back Pain During Pregnancy
- Prevention of Back Pain During Pregnancy
- References
Understanding Back Pain During Pregnancy
Back pain is a very common and often anticipated discomfort experienced by many women at some point during their pregnancy. Alongside other common pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and the anticipation of labor pains, back pain can significantly impact a pregnant woman's quality of life. It is estimated that between 50% and 70% of expectant mothers will experience some form of back pain during their gestational period.
Prevalence and Onset
Often, back pain, particularly in the lower back (lumbar region) and sacrum, begins to manifest in the second half of pregnancy. This timing is largely due to the progressive physiological changes the body undergoes, including a significant increase in total body weight and a forward shift in the body's center of gravity. These changes place considerable additional mechanical stress on the spine and its supporting structures.
Common Location of Pain
Back pain during pregnancy is frequently perceived as a chronic, persistent ache or soreness in the lower back. It commonly occurs in younger women, those with multiple pregnancies (multiparity), or individuals who had pre-existing weak back muscles or a history of back pain before becoming pregnant. In the majority of pregnant women experiencing back pain, or those in the immediate postpartum period, the pain is often localized to the sacroiliac (SI) joints. These are the joints where the pelvic bones (ilia) articulate with the sacrum at the base of the spine. Pain originating from the SI joints can manifest as stiffness, particularly noticeable in the morning hours upon waking, and can develop into more pronounced soreness or aching as the day progresses and with increased activity.
Causes of Back Pain in Pregnant Women
Numerous physiological and biomechanical factors contribute to the development of back or spinal pain in pregnant women. Some of the most likely and well-recognized causes include:
Weight Gain
During a physiologically normal pregnancy, a woman typically gains between 11 to 16 kilograms (approximately 25 to 35 pounds), though this can vary. This additional body weight must be supported by the spine, placing increased mechanical load on the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and muscles of the back. This can lead to discomfort, strain, and pain, particularly in the lower back (lumbar region and sacrum). Furthermore, the growing weight of the baby and the increasing size of the uterus exert direct pressure on blood vessels and nerves within the pelvis and posterior abdominal wall, which can also contribute to back pain or referred pain sensations.
Postural Changes
As the uterus expands and becomes heavier with the growing fetus, a pregnant woman's center of gravity shifts forward. To compensate for this shift and maintain balance, women often unconsciously or consciously alter their posture and gait. This typically involves an increase in lumbar lordosis (the inward curve of the lower back) and a backward tilt of the upper torso. While these adjustments help maintain an upright stance, they can lead to increased strain on the muscles and ligaments of the lower back (psoas, paraspinal muscles) and stress on the facet joints, contributing to back pain.
Hormonal Changes (Relaxin)
During pregnancy, the body produces significantly increased levels of certain hormones, notably relaxin. Relaxin's primary role is to prepare the body for childbirth by increasing the laxity (looseness) of ligaments in the pelvic area, allowing the pelvic joints (especially the sacroiliac joints and pubic symphysis) to become more mobile and flexible. This facilitates the passage of the baby through the birth canal. However, relaxin affects ligaments throughout the body, not just in the pelvis. It can also weaken the ligaments that support the bones of the spine, leading to decreased spinal stability and potentially contributing to pain, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the sacroiliac joints and lumbar spine.
Muscle Separation (Diastasis Recti)
As the uterus enlarges significantly, especially in the later stages of pregnancy, the two parallel bands of muscles of the anterior abdominal wall (the rectus abdominis muscles, which run vertically from the ribs down to the pubic bone) may stretch and separate along their central tendinous seam (the linea alba). This condition is known as diastasis recti. The rectus abdominis muscles play an important role in core stability and supporting the spine. Their separation and weakening during pregnancy can reduce abdominal support for the back, potentially worsening or contributing to back pain by increasing the load on spinal structures.
Diastasis recti (separation of the rectus abdominis muscles) and stretching of the skin on the anterior abdominal wall (leading to striae or stretch marks) are common occurrences in some women during pregnancy. Wearing a special maternity support bandage or belt can sometimes help alleviate associated discomfort and provide abdominal support.
Stress
Emotional stress, anxiety, and fatigue, which can be heightened during pregnancy, can contribute to increased muscle tension throughout the body, including the muscles of the lower back. This chronic muscle tension can manifest as back pain or muscle spasms. As a result of stress, a pregnant woman may experience new or worsened pain in the lower back (lumbar region and sacrum) due to this increased muscle tightness and spasm.
Treatment and Management Strategies for Back Pain During Pregnancy
While back pain during pregnancy often subsides to a certain extent after childbirth, it can persist or even worsen in the postpartum period, especially if these pains in the lower back and sacrum were chronic even before the onset of pregnancy. Fortunately, in many cases, discomfort can be significantly alleviated or managed through various conservative measures during pregnancy.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular, appropriate exercise strengthens back and abdominal muscles, improves flexibility and posture, and can significantly relieve muscle tension in the lumbar spine that accumulates during pregnancy. Studies have shown that women who engage in exercise approximately three times a week during the second half of pregnancy often experience a significant reduction in the severity of back pain. Safe and beneficial exercises for most pregnant women include:
- Walking: A low-impact activity that improves circulation and cardiovascular health.
- Swimming or Water Aerobics: The buoyancy of water supports body weight, reducing stress on joints while allowing for effective exercise.
- Stationary Cycling (Exercise Bike): Provides a good cardiovascular workout with minimal impact.
- Prenatal Yoga or Pilates: Focuses on gentle stretching, strengthening core muscles, and improving posture and body awareness.
Obstetrician-gynecologists, neurologists (if nerve involvement is suspected), physical therapists, or certified prenatal exercise specialists can recommend specific exercises tailored to strengthen abdominal and back muscles safely during pregnancy. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen during pregnancy.
Application of Cold and Warm Compresses
After consultation with a doctor, the application of cold and warm compresses to painful areas may be recommended to relieve tension from strained muscles and increase local blood flow, thereby reducing pain. A common approach is to:
- Start with cold compresses (e.g., an ice pack or a bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a thin towel) applied to the painful areas for about 20 minutes, several times a day. This is often most helpful in the initial 24-48 hours of acute pain or after activity that aggravates pain.
- After 2-3 days of cold therapy (or if pain is more chronic and muscular), switch to warm compresses. Apply a heating pad (on a low setting), a warm water bottle, or a warm moist towel to the lower back to relax muscles and soothe soreness.
![]() Attention! Warm compresses or heating pads should generally **not** be applied directly to the abdomen during pregnancy, especially for prolonged periods, to avoid overheating the fetus. Focus heat application on the back.
Attention! Warm compresses or heating pads should generally **not** be applied directly to the abdomen during pregnancy, especially for prolonged periods, to avoid overheating the fetus. Focus heat application on the back.
Posture Correction and Ergonomics
Consciously correcting and maintaining good posture while working, sitting, standing, or sleeping can significantly help relieve pregnancy-related back pain. Key strategies include:
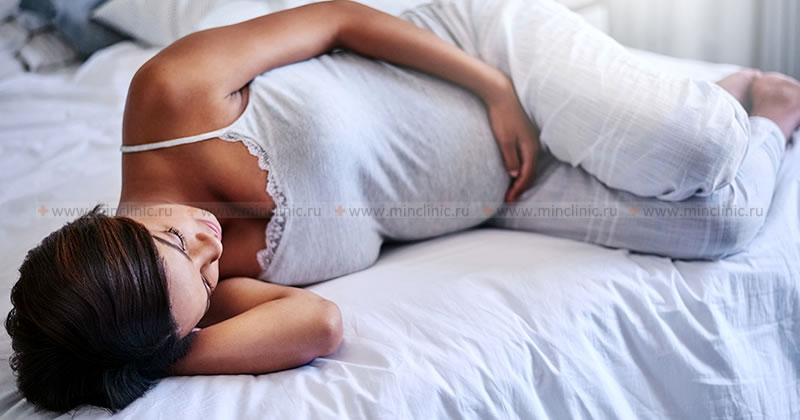
- Sleeping Position: Sleeping on your side (preferably the left side, which improves circulation to the fetus) with knees bent and a pillow placed between the knees helps to align the spine and relieve tension in the lower back. A pillow can also be placed under the abdomen for support.
- Sitting Posture: When sitting, especially for prolonged periods (e.g., at a desk), place a rolled-up towel or a small lumbar support pillow between the seat back and the curve of your lower back. Ensure feet are flat on the floor or supported by a footrest. Sit with your back straight and shoulders relaxed and back.
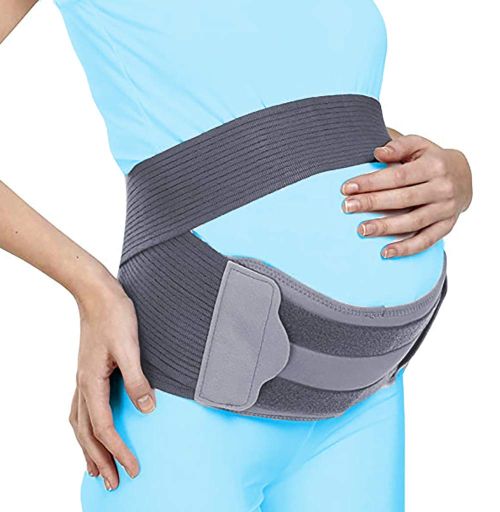
- Support Braces: Wearing a maternity support brace or belt can provide additional support to the abdomen and lower back, helping to alleviate pain and improve posture.
- Lifting: Avoid lifting heavy objects. If lifting is necessary, bend at the knees (squat) and keep the back straight, using leg muscles rather than back muscles. Avoid twisting while lifting.
- Footwear: Avoid wearing high-heeled shoes, as they can alter posture and increase strain on the back. Opt for comfortable, supportive, low-heeled shoes.
- Standing: If standing for long periods, try to rest one foot on a low stool periodically to reduce strain on the lower back.
- Avoid sleeping on your back with straight legs, especially in later pregnancy, as this can compress major blood vessels and may exacerbate back pain.
A variant of a semi-rigid lumbosacral corset or maternity support belt can be worn to help treat back and lower back pain experienced during pregnancy or in the postpartum period by providing external support.
Psychological Support and Stress Management
If back pain is significantly associated with muscle tension arising from emotional problems, stress, or anxiety, counseling with a psychotherapist or engaging in stress-reduction techniques (e.g., mindfulness, meditation, prenatal yoga) can be beneficial in reducing or completely eliminating these unpleasant sensations in the lower back and sacrum.
Acupuncture (Reflexotherapy)
Acupuncture, a practice originating in traditional Chinese medicine, involves the insertion of sterile, disposable needles into specific points on the skin to achieve a therapeutic effect. The use of acupuncture for back pain during pregnancy, when performed by a qualified and experienced practitioner specializing in prenatal care, has shown good clinical results for some women, often within several sessions, especially when combined with other therapeutic methods. The therapeutic effect of acupuncture is thought to be associated with a reflex response of the body, including the relaxation of tense muscles, improvement of local blood flow, and the release of endorphins (natural pain-relieving chemicals).
The application of acupuncture by a trained practitioner can be very effective in treating back pain, particularly in the lower back and sacral regions, experienced during pregnancy.
Manual Therapy (Osteopathy, Soft Tissue Techniques)
Manual therapy, encompassing techniques like soft muscle mobilization, osteopathic treatment, or gentle chiropractic adjustments, is based on specific manipulations of the back muscles and joints. When performed by a qualified healthcare provider experienced in treating pregnant women (e.g., a physical therapist, osteopath, or chiropractor specializing in prenatal care), manual therapy on the muscles of the lower back and joints of the sacrum can be a safe and effective component of treating back pain during pregnancy. Correctly conducted manual therapy (e.g., muscle energy techniques, osteopathy) aimed at relieving back pain is generally not contraindicated in women with uncomplicated pregnancies. However, it is essential that the possibility and appropriateness of using manual therapy be discussed with and approved by the obstetrician-gynecologist observing the pregnant woman.
Pharmacological Therapy (Medications)
If back pain during pregnancy is not adequately relieved by the non-drug methods listed above, the prescribing of medications by the observing obstetrician-gynecologist or a consulting neurologist may be necessary. It is crucial that any medication taken during pregnancy is deemed safe for both mother and fetus.
- Acetaminophen (Paracetamol, e.g., Tylenol): Generally considered safe for pain relief during all trimesters of pregnancy when used as directed for short periods. It is often the first-line analgesic.
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): Drugs such as aspirin, ibuprofen (e.g., Advil, Motrin), and naproxen (e.g., Aleve) are generally **not recommended** for back pain in pregnant women, especially during the third trimester, due to potential risks to the fetus (e.g., premature closure of the ductus arteriosus, kidney problems). Their use earlier in pregnancy should only be under strict medical supervision if benefits clearly outweigh risks.
- Other Pain Relievers or Muscle Relaxants: In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend other specific pain relievers or muscle relaxants that are considered relatively safe for use during pregnancy, but only after careful consideration of the individual's situation and potential risks. Opioids are generally avoided unless absolutely necessary for severe pain and under strict medical control due to risks of neonatal abstinence syndrome.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication during pregnancy.
Differential Diagnosis of Back Pain in Pregnancy
While most back pain in pregnancy is musculoskeletal and related to the physiological changes of gestation, it's important to rule out other, potentially more serious causes, especially if "red flag" symptoms are present.
| Condition | Key Differentiating Features |
|---|---|
| Common Pregnancy-Related Musculoskeletal Back Pain | Aching pain in lumbar/sacroiliac region, morning stiffness, often worse with activity or prolonged positions. No neurological deficits. Improves with rest, posture changes, gentle exercise. |
| Lumbar Disc Herniation / Sciatica | Sharp, radiating pain down the leg (sciatica), may have numbness, tingling, or weakness in a dermatomal pattern. Pain often worse with sitting, bending, coughing. May be pre-existing or exacerbated by pregnancy. |
| Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) / Pyelonephritis | Flank or low back pain (often unilateral for pyelonephritis), dysuria, urinary frequency/urgency, fever, nausea/vomiting. Urinalysis and culture confirm infection. |
| Preterm Labor | Rhythmic, cramping low back pain (like menstrual cramps), abdominal tightening, pelvic pressure, change in vaginal discharge. Occurs before 37 weeks. Requires urgent obstetric evaluation. |
| Vertebral Osteomyelitis / Discitis (rare) | Severe, localized back pain, fever, malaise, point tenderness over spine. Elevated inflammatory markers. MRI diagnostic. |
| Vertebral Compression Fracture (from osteoporosis or trauma) | Sudden onset of severe localized back pain, often after minimal trauma if osteoporosis present. Point tenderness. X-ray/MRI confirms. |
| Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction (SPD) / Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP) | Pain in pubic bone, groin, inner thighs, perineum, may radiate to back. Worse with weight-bearing, walking, straddle movements. |
When to Seek Medical Attention for Back Pain During Pregnancy
While mild back pain is common, pregnant women should contact their healthcare provider if they experience:
- Severe back pain.
- Back pain that starts suddenly.
- Rhythmic, cramping back pain (potential sign of preterm labor).
- Pain accompanied by fever, chills, or burning urination (suggesting UTI/kidney infection).
- Loss of sensation, numbness, or significant weakness in one or both legs or feet.
- Loss of bowel or bladder control (a neurological emergency).
- Back pain following a fall or trauma.
- Pain that does not improve or worsens despite self-care measures.
It's always best to discuss any persistent or concerning back pain with an obstetrician-gynecologist or other relevant healthcare professional to rule out serious conditions and receive appropriate advice and treatment.
Prevention of Back Pain During Pregnancy
While not all pregnancy-related back pain can be avoided, certain measures can help minimize its occurrence or severity:
- Pre-pregnancy Fitness: Strengthening core and back muscles before pregnancy can provide better support.
- Good Posture: Consciously maintaining good posture throughout pregnancy while sitting, standing, and walking.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Always bend at the knees and keep the back straight when lifting. Avoid lifting heavy objects.
- Appropriate Footwear: Wearing supportive, low-heeled shoes.
- Weight Management: Gaining a healthy amount of weight as recommended by the healthcare provider.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in pregnancy-appropriate exercises to maintain strength and flexibility.
- Supportive Sleep Environment: Using a firm mattress and supportive pillows.
References
- Katonis P, Kampouroglou A, Aggelopoulos A, Kakavelakis K, Lykoudis S, Makrigiannakis A, Alpantaki K. Pregnancy-related low back pain. Hippokratia. 2011 Jul;15(3):205-10.
- Ostgaard HC, Andersson GB, Karlsson K. Prevalence of back pain in pregnancy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991 May;16(5):549-52.
- Sabino J, Grauer JN. Pregnancy and low back pain. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2008 Jun;1(2):137-41.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Back pain during pregnancy. FAQ017. Published March 2022.
- Pennick V, Liddle SD. Interventions for preventing and treating pelvic and back pain in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 1;(8):CD001139.
- Wang SM, Dezinno P, Maranets I, et al. Low back pain during pregnancy: prevalence, risk factors, and outcomes. Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Jul;104(1):65-70.
- Stuge B, Hilde G, Vøllestad N. Physical therapy for pregnancy-related low back and pelvic pain: a systematic review. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2003 Nov;82(11):983-90.
See also
- Anatomy of the spine
- Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's disease)
- Back pain by the region of the spine:
- Back pain during pregnancy
- Coccygodynia (tailbone pain)
- Compression fracture of the spine
- Dislocation and subluxation of the vertebrae
- Herniated and bulging intervertebral disc
- Lumbago (low back pain) and sciatica
- Osteoarthritis of the sacroiliac joint
- Osteocondritis of the spine
- Osteoporosis of the spine
- Guidelines for Caregiving for Individuals with Paraplegia and Tetraplegia
- Sacrodinia (pain in the sacrum)
- Sacroiliitis (inflammation of the sacroiliac joint)
- Scheuermann-Mau disease (juvenile osteochondrosis)
- Scoliosis, poor posture
- Spinal bacterial (purulent) epiduritis
- Spinal cord diseases:
- Spinal spondylosis
- Spinal stenosis
- Spine abnormalities
- Spondylitis (osteomyelitic, tuberculous)
- Spondyloarthrosis (facet joint osteoarthritis)
- Spondylolisthesis (displacement and instability of the spine)
- Symptom of pain in the neck, head, and arm
- Pain in the thoracic spine, intercostal neuralgia
- Vertebral hemangiomas (spinal angiomas)
- Whiplash neck injury, cervico-cranial syndrome