Therapeutic Modalities
What are Therapeutic Modalities?
Therapeutic Modalities (also known as physical agents or electrophysical agents) refer to the various types of energy and physical forces applied to the body's tissues to elicit a therapeutic effect (1, 2). They are commonly used by physical therapists, occupational therapists, athletic trainers, and other healthcare professionals as part of a comprehensive rehabilitation program.
While often used adjunctively alongside exercise, manual therapy, and patient education, modalities can play a significant role in managing pain, controlling inflammation and swelling, facilitating tissue healing, improving circulation, and modulating muscle function (1, 3).
Their application can be beneficial in treating a wide range of conditions affecting the nervous system (central and peripheral), the musculoskeletal system (muscles, tendons, ligaments, joints, bones), and in managing post-operative or post-traumatic recovery (2).
Goals and Physiological Effects
The primary goals for using therapeutic modalities typically include (1, 2, 3):
- Pain Management: Modulating pain signals (e.g., gate control theory, opioid release), reducing nerve sensitivity.
- Inflammation and Swelling Control: Altering blood flow, cell membrane permeability, and inflammatory mediator activity.
- Tissue Healing Facilitation: Stimulating cellular activity (e.g., fibroblast proliferation, collagen synthesis), increasing circulation to deliver nutrients and remove waste.
- Muscle Tone Modulation: Reducing muscle spasm/hypertonicity or facilitating muscle contraction/re-education.
- Increased Circulation: Vasodilation to improve blood flow.
- Increased Tissue Extensibility: Heating tissues prior to stretching.
- Drug Delivery Enhancement: Using electrical currents (iontophoresis) or ultrasound (phonophoresis) to drive medication through the skin.
Improved regional circulation, reduced edema, and modulation of metabolic processes contribute to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects often seen with these treatments (3).
Common Types of Therapeutic Modalities
Modalities can be broadly categorized based on the type of energy used (1, 2):
Thermal Modalities (Heat/Cold)
- Superficial Heat: Hot packs, paraffin wax, fluidotherapy, infrared lamps (IT). Used to decrease pain/stiffness, increase blood flow, promote relaxation, increase tissue extensibility.
- Deep Heat: Ultrasound, Shortwave Diathermy (SWD). Heat deeper tissues to achieve similar effects as superficial heat but at greater depths.
- Cryotherapy (Cold): Cold packs, ice massage, vapocoolant sprays, cold water immersion. Used primarily to reduce pain, inflammation, swelling (edema), and muscle spasm, especially in acute injuries. Causes vasoconstriction.
Electrical Modalities (Electrostimulation)
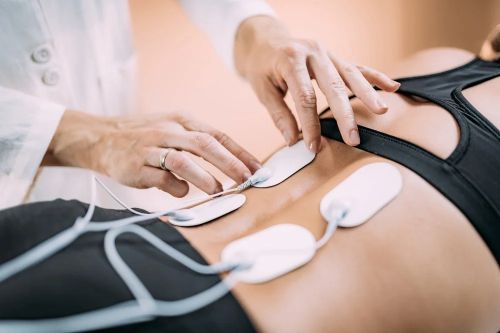
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Uses low-voltage electrical currents applied via skin electrodes primarily for pain relief (sensory analgesia via gate control or opioid release mechanisms) (1, 4).
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES): Uses parameters designed to cause muscle contraction. Used for muscle strengthening/re-education, preventing atrophy, reducing spasm, or improving range of motion (1, 4). Sometimes referred to as myostimulation or neurostimulation depending on target.
- Interferential Current (IFC): Uses two medium-frequency currents that interfere to create a lower beat frequency within the tissues. Often used for deeper pain relief and potentially edema reduction (1).
- High Voltage Pulsed Current (HVPC): Used for pain control, edema reduction, and wound healing (1).
- Iontophoresis: Uses low-level direct current (galvanic current - GT) to drive ionized medications (like dexamethasone or lidocaine) through the skin for localized anti-inflammatory or anesthetic effects (1).
- Sinusoidal Modulated Current (SMC) / Diadynamic Currents (DDT): Older forms of electrical stimulation used primarily for pain relief and muscle stimulation (effects similar to TENS/IFC/NMES depending on parameters).
Electromagnetic Modalities
- Shortwave Diathermy (SWD): Uses high-frequency electromagnetic energy to generate deep heat within tissues (1).
- Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMF): Uses non-thermal electromagnetic fields, primarily investigated for bone healing and pain/inflammation reduction (1).
- Microwave Diathermy (MWD): Uses microwaves for deep heating (less common than SWD) (1).
- Ultrahigh Frequency (UHF): (As mentioned in original text) - Falls under high-frequency electromagnetic therapy, similar principles to SWD/MWD, aims to generate heat in tissues (1).
Mechanical Modalities
- Therapeutic Ultrasound: Uses high-frequency sound waves. Can produce thermal effects (deep heating) or non-thermal effects (e.g., increased cell membrane permeability, acoustic streaming) thought to facilitate tissue healing (1, 2). Phonophoresis uses ultrasound to enhance transdermal drug delivery.
- Traction (Cervical/Lumbar): Application of mechanical force to distract spinal segments, aiming to reduce pressure on nerves or joints (1).
- Compression Therapy: Intermittent pneumatic compression devices or compression bandaging used to manage edema (1).
- Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT): High-energy acoustic waves used primarily for chronic tendinopathies and conditions like plantar fasciitis (1).
Light-Based Modalities
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) / Photobiomodulation: Application of specific wavelengths of light (laser or LED) to stimulate cellular processes, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue healing and pain relief (1, 5). Example: Multiwave Lock System (MLS) Laser Therapy utilizes specific wavelengths (e.g., 808nm for anti-inflammatory/anti-edemic effects, 905nm for analgesic effects) aiming for deeper tissue penetration (5).
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Used primarily for dermatological conditions (less common in standard PT).
Indications for Therapeutic Modalities
The choice of modality depends on the specific therapeutic goal, the stage of healing (acute vs. chronic), the target tissue depth, and patient-specific factors. General indications include management of symptoms associated with (1, 2, 3):
- Pain Relief: Acute pain, chronic pain, neuropathic pain (neuralgia), musculoskeletal pain (lumbago, myalgia).
- Inflammation and Edema: Acute injuries (sprains, strains, bruises), post-surgical swelling, bursitis, tendinitis/tenosynovitis.
- Muscle Spasm/Hypertonicity: Often associated with back pain, neck pain, or postural strain.
- Limited Range of Motion: Due to pain, stiffness, swelling, or contracture (e.g., adhesive capsulitis). Heat can increase tissue extensibility before stretching.
- Tissue Healing: Promoting healing of soft tissue injuries, wounds, or fractures (specific modalities like ultrasound, laser, PEMF).
- Muscle Weakness/Dysfunction: Neuromuscular re-education, preventing atrophy after injury/surgery (nerve injuries like neuropathy, neuritis).
- Arthritis/Arthrosis: Managing pain and stiffness in arthritis (e.g., rheumatic ailments), coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis.
- Specific Conditions: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Epicondylitis, Plantar Fasciitis, TMJ Dysfunction, pain from disc herniation, osteochondrosis, Ankylosing Spondylitis (symptom management).
Contraindications and Precautions
Each modality has specific contraindications and precautions. General considerations include (1, 2):
- General Contraindications (may apply to many modalities):
- Over areas with active malignancy (cancer).
- Over electronic implants (pacemakers, defibrillators, neurostimulators - especially for electrical/electromagnetic modalities).
- Over pregnant uterus.
- Over areas of active hemorrhage or thrombophlebitis (blood clot).
- Over infected tissues (unless specifically indicated, e.g., some wound care modalities).
- Over impaired sensation or mentation (patient cannot provide feedback).
- Specific Precautions/Contraindications:
- Heat: Avoid over areas of acute inflammation, impaired circulation, bleeding disorders.
- Cold: Avoid over areas of impaired circulation (e.g., Raynaud's disease), cold hypersensitivity/urticaria, open wounds.
- Electrical Stim/Ultrasound: Avoid over carotid sinus, anterior neck, eyes, transcranially, damaged skin (relative).
- Diathermy: Avoid near metal implants or moist dressings.
A thorough assessment by a qualified healthcare professional is essential before applying any therapeutic modality to ensure it is safe and appropriate for the individual patient and condition.
References
- Michlovitz SL, Bellew JW, Nolan TP Jr. Modalities for Therapeutic Intervention. 6th ed. F.A. Davis Company; 2016. (Comprehensive textbook on modalities)
- Prentice WE. Therapeutic Modalities in Rehabilitation. 5th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016. (Widely used textbook)
- Watson T. Electrophysical agents: contraindications and precautions: an evidence-based approach to clinical practice in physical therapy. Physiotherapy. 2000;86(10):515-526. doi:10.1016/S0031-9406(05)60870-1
- Johnson MI, Paley CA, Howe TE, Sluka KA. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for acute pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(6):CD006142. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006142.pub3 (Focus on TENS)
- Chow RT, Johnson MI, Lopes-Martins RA, Bjordal JM. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in the management of neck pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo or active-treatment controlled trials. Lancet. 2009;374(9705):1897-1908. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61522-1 (Focus on LLLT)