Arthritis and osteoarthritis
Joint Disease: Arthritis vs. Osteoarthritis Overview
Diseases affecting joints and the surrounding tissues generally fall into two main categories: inflammatory conditions and degenerative (or metabolic) conditions [1].
Inflammatory Joint Diseases (Arthritis): These are characterized by inflammation within the joint (synovium, capsule) and sometimes surrounding tissues [1]. Inflammation is the body's response to injury or infection, but in many types of arthritis, it occurs inappropriately or persists chronically [1]. This group includes conditions often termed autoimmune diseases, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues [1]. Examples include rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, lupus arthritis, and gout [1, 2]. These conditions can sometimes affect other organs as well (e.g., the heart in rheumatic fever, kidneys in lupus, skin in scleroderma) [1].
Arthritis symptoms typically include joint pain (often present even at rest), swelling, stiffness (especially in the morning), redness, warmth, and limited range of motion [1, 2].
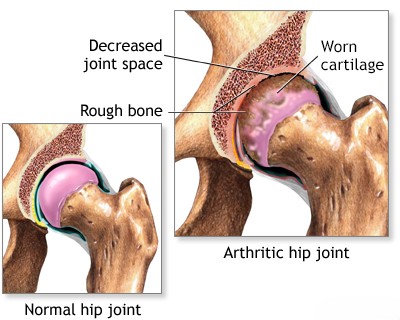
Degenerative Joint Diseases (Osteoarthritis/Osteoarthrosis): These conditions are primarily characterized by the breakdown and loss of articular cartilage, the smooth tissue covering the ends of bones in a joint [1, 2]. This leads to changes in the underlying bone (e.g., bone spurs - osteophytes), joint space narrowing, and altered joint mechanics [1]. While some secondary inflammation can occur, the primary process is degeneration ("wear and tear"), often related to aging, previous injury, genetics, or obesity [1, 2].
Osteoarthritis (OA), also called osteoarthrosis or degenerative joint disease (DJD), is the most common type [1, 2]. Common sites include:
- Hip (Coxarthrosis)
- Knee (Gonarthrosis)
- Hands (finger joints)
- Spine
- Shoulder (Glenohumeral arthritis or conditions like scapulohumeral periarthrosis, often involving surrounding tendons)
- Ankle (often post-traumatic after sprains or fractures)
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
OA symptoms typically include joint pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest, stiffness after inactivity (usually lasting less than 30 minutes), clicking or grinding sensations (crepitus), and sometimes swelling or bony enlargement [1, 2].
Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa, a fluid-filled sac that cushions areas where tendons or muscles glide over bone [1]. While related to joints, it's an inflammation of periarticular (around the joint) tissue, often caused by trauma or repetitive friction [1]. It presents with localized pain, swelling, and limited motion [1].
Arthritis & Osteoarthritis Diagnosis
Diagnosing joint diseases involves understanding the underlying process, whether inflammatory or degenerative [1, 2].
In degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis, metabolic changes within the joint tissues disrupt normal biochemical processes [1]. This leads to cartilage breakdown, degeneration, and sometimes deposition of salts or crystals [1]. These changes alter the joint surface and cartilage structure, leading to pain and dysfunction [1].
To determine the nature and extent of joint changes, a combination of diagnostic approaches is used [1, 2, 3]:
- Clinical Evaluation: Taking a detailed medical history (symptoms, onset, pattern of pain, stiffness, previous injuries) and performing a physical examination (checking range of motion, swelling, tenderness, crepitus, stability, alignment).
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests can help diagnose inflammatory arthritis (e.g., rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP antibodies for rheumatoid arthritis; ESR, CRP as markers of inflammation; uric acid for gout). Synovial fluid analysis (aspirating fluid from the joint) can differentiate inflammatory from non-inflammatory conditions and detect infection or crystals.
- Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: The standard initial imaging test. Can show joint space narrowing (cartilage loss), bone spurs (osteophytes), bone erosion (in inflammatory arthritis), cysts, and altered alignment. Arthrography (injecting contrast) is less common now.
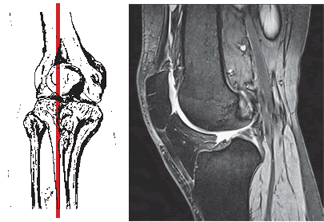
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including cartilage, ligaments, tendons, menisci, and bone marrow edema (inflammation). Excellent for assessing cartilage damage extent, early inflammatory changes, and associated soft tissue injuries.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Offers superior bony detail compared to X-ray, useful for assessing complex fractures, bone erosion, or planning surgery.
- Ultrasound: Can visualize soft tissues, effusions (fluid), synovitis (inflammation of the joint lining), and guide injections.
Arthritis & Osteoarthritis Treatment
Treatment strategies for arthritis and osteoarthritis aim to reduce pain, control inflammation (in arthritis), maintain or improve joint function, and slow disease progression [1, 2]. The approach depends on the specific diagnosis, severity, joints involved, and patient factors [1, 2].
Common Treatment Modalities:
- Pharmacological Therapy:
- Analgesics: Pain relievers like acetaminophen (paracetamol) [2].
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): Reduce pain and inflammation (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac) [2]. Available orally or topically. Use requires caution regarding potential side effects (gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, renal) [2].
- Corticosteroids: Powerful anti-inflammatory drugs [2]. Can be taken orally for systemic effects (in inflammatory arthritis, usually short-term or low-dose) or injected directly into the joint (intra-articular injections) for localized relief (often used in both OA and arthritis) [1, 2].
- DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs): Used for inflammatory arthritis (like rheumatoid arthritis) to slow disease progression and prevent joint damage (e.g., methotrexate, sulfasalazine) [2].
- Biologic Agents: Targeted therapies for specific inflammatory pathways, used for moderate-to-severe inflammatory arthritis (e.g., TNF inhibitors, IL-6 inhibitors) [2].
- Other Medications: Specific drugs for gout (e.g., allopurinol, colchicine), topical capsaicin [2].
- Physical & Occupational Therapy [1, 2]:
- Therapeutic Exercise (Gymnastics): Tailored programs to improve range of motion, strengthen muscles supporting the joint, and enhance overall function. Low-impact aerobic exercise (swimming, cycling) is often recommended.
- Physical Therapy Modalities: Heat, cold therapy, ultrasound (UHF), TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation), electrophoresis (using electrical current to deliver medication) may be used for symptom relief.
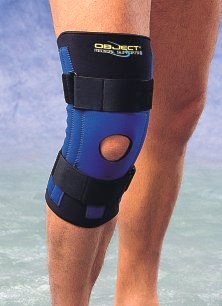
- Assistive Devices: Canes, walkers, braces, splints can reduce joint stress and improve stability.
- Occupational Therapy: Focuses on joint protection techniques, adaptive strategies for daily activities, and recommending assistive devices.
- Lifestyle Modifications [1, 2]:
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight significantly reduces stress on weight-bearing joints (hips, knees).
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that overload or excessively stress affected joints.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques like joint mobilization or manipulation may provide short-term pain relief and improve mobility for some patients, particularly with OA [1].
- Massage: Can help relieve muscle tension and soreness around affected joints [1].
- Surgical Treatment: Considered when conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief or function is severely limited [1, 2, 4].
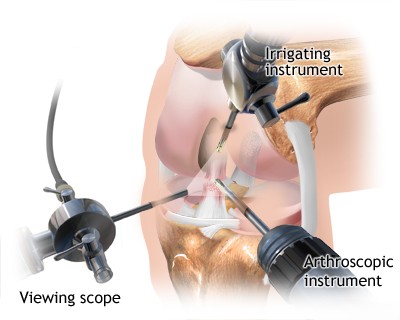
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive procedure to diagnose issues, remove loose bodies, debride damaged cartilage, or repair meniscal tears (primarily knee and shoulder). Its role in purely degenerative OA is limited.
- Osteotomy: Cutting and realigning bone to shift weight away from the damaged part of the joint (mainly knee).
- Arthrodesis (Joint Fusion): Surgically fusing the bones of the joint to eliminate pain but sacrifice motion (used for specific joints like ankle, wrist, spine).
- Arthroplasty (Joint Replacement): Replacing the damaged joint surfaces with artificial implants (prostheses). Highly successful for advanced OA or inflammatory arthritis of the hip and knee; also performed for shoulder, elbow, ankle, and finger joints.
In the acute phase of arthritis or post-injury, managing swelling and inflammation is key (e.g., RICE, NSAIDs, physiotherapy modalities like UHF) [1]. Maintaining muscle strength and joint mobility through appropriate exercise and physical therapy is crucial throughout the treatment course [1].
Bracing or splinting can provide support and reduce stress on the affected joint during activity [1].
Differential Diagnosis of Joint Pain
| Condition | Key Features / Distinguishing Points | Typical Investigations / Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis (OA) / Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD) | Pain worse with activity, improves with rest. Stiffness after inactivity (<30 min). Crepitus, bony enlargement. Typically affects weight-bearing joints, hands, spine. Gradual onset. | X-ray: Joint space narrowing, osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis/cysts. Labs (ESR, CRP, RF) usually normal. Synovial fluid non-inflammatory. |
| Inflammatory Arthritis (e.g., Rheumatoid Arthritis - RA, Psoriatic Arthritis - PsA, SLE, Spondyloarthritis) | Pain often present at rest, morning stiffness >30-60 min. Joint swelling, warmth, redness. Often affects multiple joints symmetrically (RA) or asymmetrically (PsA, SpA). Systemic symptoms (fatigue, fever, rash, etc.) possible. | Elevated ESR/CRP common. Specific autoantibodies (RF, anti-CCP for RA; ANA for SLE; HLA-B27 for SpA). X-ray: Erosions, joint space narrowing (later), periarticular osteopenia. Synovial fluid inflammatory. |
| Crystal Arthropathy (Gout, Pseudogout) | Acute, sudden onset of severe joint pain, swelling, redness, warmth (often monoarticular initially, esp. big toe MTP for gout). Can be recurrent attacks. | Synovial fluid analysis shows crystals (urate - gout; CPPD - pseudogout). Serum uric acid often elevated (gout). X-ray may show specific erosions (gout) or chondrocalcinosis (pseudogout). |
| Septic Arthritis | Acute onset severe pain, swelling, warmth, markedly limited range of motion (active & passive). Fever, chills common. Usually monoarticular. Medical emergency. | Joint aspiration diagnostic: very high WBC count, positive Gram stain/culture. Elevated blood WBC, ESR/CRP. |
| Bursitis | Pain, tenderness, swelling localized over a bursa (e.g., prepatellar, olecranon, trochanteric, retrocalcaneal). Pain often worse with specific movements stressing the bursa. | Clinical diagnosis based on location of tenderness/swelling. Ultrasound can confirm bursal fluid/thickening. X-ray usually normal. |
| Tendinopathy / Tendinitis | Pain localized along a tendon, worse with resisted movement involving that tendon. Tenderness over tendon. Swelling/thickening possible (tendinopathy). | Clinical exam. Ultrasound or MRI can show tendon thickening, degeneration, or tears. |
| Ligament Sprain/Tear | History of specific injury/mechanism. Pain, swelling, tenderness over ligament. Instability on stress testing. | Clinical exam. X-ray usually normal (may show avulsion). MRI confirms tear grade/location. |
| Fracture (Intra- or Peri-articular) | History of trauma. Localized bony tenderness, pain, swelling, deformity, inability to bear weight/use limb. Crepitus possible. | X-ray shows fracture line. CT for complex articular fractures. |
| Fibromyalgia | Widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, multiple tender points on exam. Joint exam usually normal (no swelling/inflammation). | Clinical diagnosis based on criteria. Labs/imaging typically normal. |
References
- Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR. Kelley & Firestein's Textbook of Rheumatology. 10th ed. Elsevier; 2017. Chapters on specific joint diseases (OA, RA, Gout, etc.).
- Skinner HB, McMahon PJ. Current Diagnosis & Treatment in Orthopedics. 5th ed. McGraw Hill; 2014. Chapter 2: Arthritis & Related Conditions.
- Resnick D, Kransdorf MJ. Bone and Joint Imaging. 3rd ed. Elsevier Saunders; 2005. Chapters on specific joints and disease processes.
- Canale ST, Beaty JH. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 13th ed. Elsevier; 2017. Relevant chapters on Arthritis, Arthroplasty, Arthroscopy.
See also
- Achilles tendon inflammation (paratenonitis, ahillobursitis)
- Achilles tendon injury (sprain, rupture)
- Ankle and foot sprain
- Arthritis and arthrosis (osteoarthritis):
- Autoimmune connective tissue disease:
- Bunion (hallux valgus)
- Epicondylitis ("tennis elbow")
- Hygroma
- Joint ankylosis
- Joint contractures
- Joint dislocation:
- Knee joint (ligaments and meniscus) injury
- Metabolic bone disease:
- Myositis, fibromyalgia (muscle pain)
- Plantar fasciitis (heel spurs)
- Tenosynovitis (infectious, stenosing)
- Vitamin D and parathyroid hormone