Hip joint osteoarthrosis (coxarthrosis)
Hip Osteoarthritis (Coxarthrosis): Overview & Causes
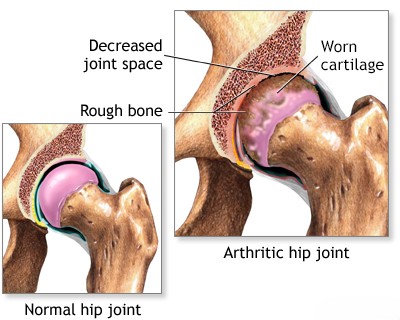
Hip Osteoarthritis (OA), also known as coxarthrosis, is a degenerative condition affecting the hip joint [1, 2]. It is primarily characterized by the breakdown and loss of articular cartilage covering the femoral head and the acetabulum (hip socket) [1, 2]. This leads to subsequent bony changes including marginal osteophyte (bone spur) formation, joint space narrowing, and subchondral bone sclerosis (hardening), ultimately causing joint deformation, pain, stiffness, and impaired hip function [1, 2].
Coxarthrosis is fundamentally a degenerative process ("wear and tear"), often influenced by biomechanical factors, aging, and genetics, rather than being primarily driven by systemic inflammation or metabolic disorders causing salt deposition, although secondary inflammation can occur [1, 2]. While metabolic bone diseases exist, typical OA involves cartilage degeneration, not necessarily salt deposition as the primary driver. Common risk factors for developing hip OA include [1, 2]:
- Age: Risk significantly increases with age.
- Genetics: Family history plays a role.
- Obesity: Increased mechanical load on the hip joint.
- Previous Hip Injury: Fractures involving the joint, dislocations, labral tears.
- Developmental Hip Conditions: Such as developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) or Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, which alter joint mechanics.
- Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): Abnormal contact between the femur and acetabulum during movement.
- Occupational Factors: Activities involving heavy lifting or repetitive stress.
Hip Osteoarthritis (Coxarthrosis): Diagnosis
To accurately diagnose hip osteoarthritis (coxarthrosis) and assess the extent of joint changes, several steps are usually necessary [1, 2]:
- Clinical Evaluation: Includes a detailed medical history focusing on hip or groin pain (location, character, aggravating/relieving factors), stiffness (especially after rest), functional limitations (walking, stairs, dressing), and risk factors. Physical examination assesses range of motion (often limited internal rotation and flexion), gait, pain with specific movements, and tenderness.
- Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: Weight-bearing anteroposterior (AP) pelvis and lateral views of the affected hip are standard. Key findings confirming OA include joint space narrowing (especially superior or superolateral), osteophyte formation (bone spurs around the femoral head and acetabulum), subchondral sclerosis (increased bone density below cartilage), and subchondral cyst formation [1, 2, 3].
- MRI of the hip joint: Not typically required for routine OA diagnosis but useful for evaluating associated soft tissue problems (labral tears, tendon issues), assessing cartilage status in detail, detecting early signs of avascular necrosis (AVN) which can mimic OA pain, or ruling out other causes of hip pain [3].
- CT of the hip joints: Primarily used for detailed bony assessment, such as characterizing complex anatomy (e.g., FAI morphology) or planning for surgery [3].
- Laboratory Tests (Complete Blood Count, etc.): Generally normal in primary OA and mainly used to rule out inflammatory arthritis or other systemic conditions if suspected based on clinical presentation [1, 2].
Differential Diagnosis of Hip Pain
| Condition | Key Features / Distinguishing Points | Typical Investigations / Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Hip Osteoarthritis (Coxarthrosis) | Gradual onset groin/anterior hip/buttock pain, worse with activity/weight-bearing, improves with rest. Morning stiffness (<30 min). Limited internal rotation/flexion. Older age common. | X-ray: Joint space narrowing (esp. superior), osteophytes, sclerosis, cysts. Labs normal. |
| Inflammatory Arthritis (e.g., RA, SpA) | Pain often present at rest, prolonged morning stiffness (>30-60 min). May affect other joints. Systemic symptoms possible. | Elevated ESR/CRP. Specific autoantibodies (RF, anti-CCP, HLA-B27). X-ray may show erosions, uniform joint space narrowing. MRI shows synovitis. |
| Trochanteric Bursitis / Gluteal Tendinopathy | Pain localized to the lateral aspect of the hip (over greater trochanter). Worse when lying on affected side, walking, climbing stairs. | Point tenderness over greater trochanter. Pain with resisted hip abduction. Hip joint ROM usually normal. Ultrasound/MRI can show bursitis/tendon tears. X-ray normal usually. |
| Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of Femoral Head | Groin pain, often sudden onset or rapidly progressive. May have risk factors (steroid use, alcohol, trauma, sickle cell). Pain often severe, present at rest. | X-ray may be normal initially, later shows femoral head changes (crescent sign, collapse). MRI is most sensitive for early diagnosis. |
| Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) / Labral Tear | Often younger/active adults. Activity-related anterior hip/groin pain, clicking, catching, limited flexion/internal rotation (positive impingement tests). | Clinical exam (FADIR test). X-ray may show cam/pincer morphology. MRI/MR Arthrography confirms labral tear, cartilage damage. |
| Lumbar Spine Radiculopathy / Referred Pain | Pain radiating from back down into buttock/hip/leg (often posterior/lateral). May have associated back pain, numbness, tingling, weakness. Hip joint exam usually normal. | Clinical exam suggests lumbar spine origin (straight leg raise test, neuro exam). Lumbar spine MRI confirms nerve root compression (disc herniation, stenosis). |
| Hip Fracture (Femoral Neck / Intertrochanteric) | History of trauma (often fall in elderly). Severe pain, inability to bear weight. Leg often shortened and externally rotated. | X-ray confirms fracture. MRI/CT for occult fractures. |
| Meralgia Paresthetica | Burning pain, numbness, tingling isolated to the anterolateral thigh (sensory only). Due to lateral femoral cutaneous nerve entrapment. | Clinical diagnosis based on typical sensory distribution. Normal hip exam/imaging. Nerve conduction studies may help. |
Hip Joint Osteoarthritis (Coxarthrosis): Treatment
Depending on the degree of damage to the hip joint from osteoarthritis (coxarthrosis), the following therapeutic actions may be indicated [1, 2]:
- Drug therapy: NSAIDs, analgesics (e.g., acetaminophen). Opioids used cautiously for severe pain. Duloxetine sometimes used.
- Intra-articular injections: Corticosteroids for temporary relief of pain/inflammation; hyaluronic acid (viscosupplementation) may provide some benefit; platelet-rich plasma (PRP) effectiveness is still under study.
- Manual therapy: Myofascial release and joint mobilization techniques for improving mobility and reducing pain.
- Physiotherapy: Modalities like heat/cold, ultrasound (UHF), TENS (SMC - Sinusoidal Modulated Currents likely refers to TENS/Interferential), for symptom management.
- Therapeutic Exercise: Essential component including strengthening (hip abductors, extensors, core), flexibility, and low-impact aerobic exercise (swimming, cycling). Weight loss if overweight.
- Surgery: For moderate-to-severe OA unresponsive to conservative management [4]:
- Arthroscopy: Very limited role; primarily for associated mechanical issues like labral tears or loose bodies.
- Osteotomy: Less common now; primarily for younger patients with specific deformities.
- Arthroplasty (Total Hip Replacement - THR): Highly effective standard surgical treatment for end-stage hip OA, providing significant pain relief and functional improvement.
References
- Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT, et al; American College of Rheumatology. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012 Apr;64(4):465-74. (Or newer ACR/EULAR guidelines).
- Skinner HB, McMahon PJ. Current Diagnosis & Treatment in Orthopedics. 5th ed. McGraw Hill; 2014. Chapter 2: Arthritis & Related Conditions & Chapter 6: Hip & Femur Trauma (Sections on OA).
- Resnick D, Kransdorf MJ. Bone and Joint Imaging. 3rd ed. Elsevier Saunders; 2005. Chapter on Hip Imaging.
- Canale ST, Beaty JH. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 13th ed. Elsevier; 2017. Section on Hip Arthroplasty and Arthritis.
See also
- Achilles tendon inflammation (paratenonitis, ahillobursitis)
- Achilles tendon injury (sprain, rupture)
- Ankle and foot sprain
- Arthritis and arthrosis (osteoarthritis):
- Autoimmune connective tissue disease:
- Bunion (hallux valgus)
- Epicondylitis ("tennis elbow")
- Hygroma
- Joint ankylosis
- Joint contractures
- Joint dislocation:
- Knee joint (ligaments and meniscus) injury
- Metabolic bone disease:
- Myositis, fibromyalgia (muscle pain)
- Plantar fasciitis (heel spurs)
- Tenosynovitis (infectious, stenosing)
- Vitamin D and parathyroid hormone