Radiography (X-ray)
- Radiography (X-ray) Imaging: An Overview
- Common X-ray Studies and Applications
- Indications for Radiography (Why a Doctor Orders an X-ray)
- Preparation for an X-ray Examination
- The X-ray Procedure: What to Expect
- Benefits and Advantages of X-ray Imaging
- Risks, Limitations, and Contraindications
- Interpreting X-ray Results
- Differential Diagnosis for Common X-ray Findings
- Conclusion: The Role of X-rays in Modern Diagnostics
- References
Radiography (X-ray) Imaging: An Overview
Radiography, universally known as an X-ray, is a cornerstone and one of the oldest forms of diagnostic medical imaging. It utilizes a controlled beam of X-rays, a type of electromagnetic radiation, which are passed through a specific part of the body. Different tissues absorb these X-rays to varying degrees based on their density. The X-rays that pass through the body strike a detector (historically photographic film, now often a digital sensor) to create an image, or radiograph. This process allows for the visualization of internal structures and is invaluable for detecting a wide range of pathologies in areas such as the spine, bones, joints, chest (lungs and heart), abdomen, pelvis, teeth, and mammary glands (mammography).
Basic Principles of X-ray Imaging
The fundamental principle behind X-ray imaging is differential absorption. Dense tissues like bone absorb more X-rays and thus appear white or light gray on the radiograph. Softer tissues, like muscle or fat, absorb fewer X-rays and appear in varying shades of gray. Air-filled spaces, such as the lungs, absorb very few X-rays and appear black. This contrast allows physicians to identify abnormalities like fractures, infections, tumors, or foreign objects.
Modern Digital Radiography Systems
Modern radiography suites, such as those found within specialized radiation diagnostics departments, are equipped with advanced digital radiography (DR) systems. These systems offer significant advantages over older film-based methods, including improved image quality, lower radiation doses, faster image acquisition, and easier image storage, retrieval, and sharing. For example, a state-of-the-art digital radiography system like the STEPHANIX (France) X-ray diagnostic complex might feature a remote-controlled patient table (e.g., Evolution table), a sophisticated digital image processing system, and a full-size flat-panel digital detector. Such equipment provides an accessible and high-quality imaging option for a diverse range of clinical conditions.
Patients can typically schedule an X-ray examination by phone if they have a referral from another specialist, or directly following a consultation with one of the clinic's doctors who determines the necessity of the study.
An example of an X-ray examination of the spine viewed in a direct (anteroposterior or front-to-back) projection, allowing assessment of vertebral alignment and bone structure.
Advanced features of modern digital systems include capabilities like electronic tomography (tomosynthesis) directly on the detector, without the need for mechanical synchronization of the X-ray tube and detector. This allows for the creation of cross-sectional "slices" with slice thickness being set manually or programmatically. Additionally, features such as a motorized compression system (useful in mammography or for certain specialized views) and the X-ray tube's ability to rotate ±180° horizontally can significantly enhance diagnostic capabilities during patient examinations.
Accompanying sophisticated software (e.g., MedRadio) provides radiologists with powerful image processing and analysis tools, streamlining the diagnostic workflow. Key software features often include:
- Customizable patient worklist displays and filtering options (by radiologist, date, organization).
- Dynamic windowing for optimal contrast and brightness adjustment.
- Dynamic zoom, panning, and customizable magnifying glass settings.
- Measurement tools for distances, angles (including multiple angles).
- Pre-set or custom annotations, and tools for adding arrows, circles, and lines to highlight findings.
- Image manipulation capabilities (horizontal/vertical flip, 90-degree rotation).
- Inverted video display (negative view) for enhanced perception of certain details.
- Multi-patient display and image comparison functionalities.
- Flexible printing options (DICOM and standard Windows formats) with customizable print stamp settings.
- Ability for simultaneous modification of multiple selected images.
- Multi-tasking display capabilities and user-defined display optimization.
- Full-resolution image "flashing" for quick review.
- Versatile image storage formats (DICOM, JPEG, TIFF, AVI) and easy import/export options (CD, DVD, USB).
- Multi-user software access with appropriate security.
- Integrated remote service support for system maintenance.
- STITCHING programs for reconstructing panoramic or full-length images (e.g., full spine or long leg X-rays) from multiple smaller, overlapping images.
- Integrated patient radiation dose measurement and recording systems, crucial for monitoring and optimizing patient safety.
Video illustrating the basic principles of Radiography (X-ray imaging), explaining how images are generated and interpreted.
Common X-ray Studies and Applications Performed at the Clinic
X-ray facilities equipped with modern digital systems can support a diverse range of diagnostic radiographic procedures, catering to various medical specialties. These include, but are not limited to:
Fluorography (Often Referring to Chest X-ray)
While "fluorography" historically referred to a specific technique of photographing a fluoroscopic screen image (often for mass chest screening), in modern contexts, it often colloquially refers to standard chest X-ray (CXR). Chest radiography is an essential examination focused on the organs within the thorax, primarily the lungs and heart. It is invaluable for diagnosing a wide array of lung conditions (e.g., pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung cancer, pneumothorax, pleural effusion) and heart conditions (e.g., cardiomegaly, congestive heart failure). Chest X-rays are known for being highly informative, widely accessible, relatively inexpensive, and, with modern equipment, involving a low radiation dose, making them a safe and routine diagnostic tool.
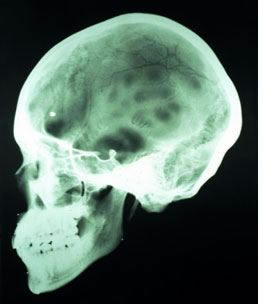
Radiography (X-ray) of Skull Bones
Skull radiography is used to evaluate the bones of the cranium and face. It helps in diagnosing conditions such as:
- Fractures (linear, depressed, basilar).
- Certain bone diseases or tumors affecting the skull.
- Evaluation of paranasal sinuses (though CT is often preferred for detailed sinus assessment).
- Assessment of sella turcica (for pituitary gland abnormalities).
Different views (projections), such as anteroposterior (AP or direct front view), lateral (side view), Towne's view (occipital), Waters' view (facial bones/sinuses), and Caldwell view (frontal/ethmoid sinuses), along with specialized angles, are employed to effectively visualize specific anatomical areas of the skull. Skull X-rays are often requested by ENT specialists, neurosurgeons, neurologists, ophthalmologists, or trauma specialists.
Example of a skull X-ray taken in the lateral (side) projection, useful for assessing cranial vault fractures and general bone structure.
Radiography (X-ray) of Bones and Joints (Extremities and Axial Skeleton)
Radiography is a primary tool for evaluating the health and integrity of bones and joints throughout the body. X-rays of bones near major joints (e.g., shoulder, elbow, wrist, hand, hip, knee, ankle, foot) allow assessment of:
- Fractures and dislocations.
- Arthritis (e.g., osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis), showing joint space narrowing, osteophytes, erosions.
- Bone infections (osteomyelitis) or tumors (benign or malignant).
- Congenital bone abnormalities or developmental disorders.
- Metabolic bone diseases (e.g., signs of osteoporosis, Paget's disease).
- The articular surfaces (bone ends within the joint) and the joint space itself.
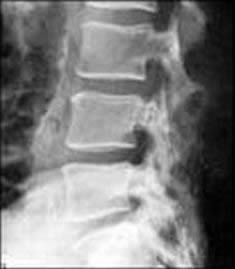
Radiography (X-ray) of the Spine (Spondylography)
Spine X-rays, technically known as spondylography, allow for detailed examination of the vertebral structures at different levels (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal). This includes visualization of:
- Vertebral bodies (for compression fractures, lytic/blastic lesions).
- Transverse processes and spinous processes.
- Articular processes (facet joints, for signs of arthropathy).
- Intervertebral joints and disc spaces (for disc space narrowing, a sign of degenerative disc disease).
- Intervertebral foramina (openings for spinal nerves, best seen on oblique views).
- Spinal alignment (scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis).
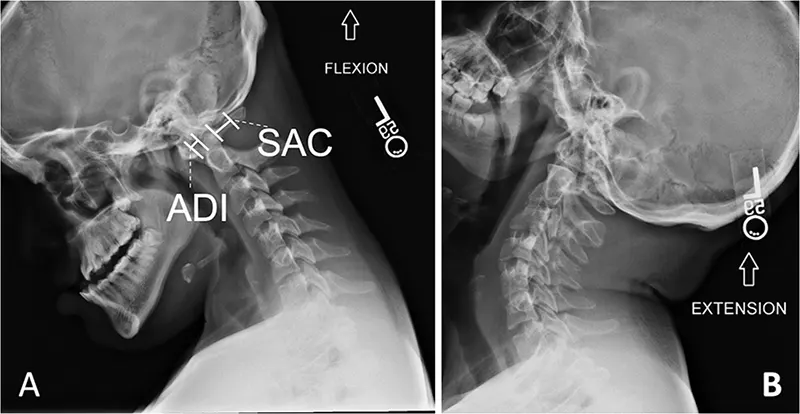
Spine X-rays can also include functional studies (dynamic views), such as flexion and extension views, particularly for the cervical and lumbar spine. These are taken while the patient bends forward and backward to assess for spinal instability, abnormal movement between vertebrae (e.g., spondylolisthesis), or limitations in range of motion. Such studies are valuable for evaluating deformities, vertebral displacements, subtle fractures, and overall segmental stability without causing excessive discomfort during the assessment of an injury.
Cervical spine (neck) radiography is mandatory for any suspected significant damage or fracture, regardless of the severity of neurological symptoms, and is a standard part of the initial evaluation for all unconscious trauma patients to rule out unstable cervical spine injury.
Radiograph of the lumbosacral spine in the lateral projection. This view can demonstrate abnormalities such as a straightening or loss of the normal inward curve (lordosis) of the lumbar spine.
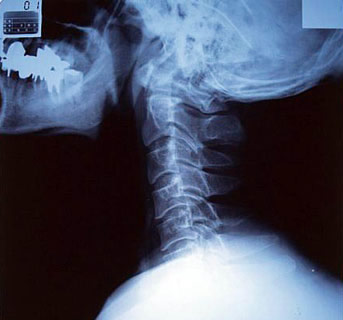
Radiograph of the cervical spine in the lateral projection. This image shows a straightening of the normal cervical curve (lordosis), which can be associated with muscle spasm or degenerative changes.
Dynamic flexion and extension views of the lateral cervical spine are crucial for assessing ligamentous instability or abnormal motion between vertebrae, particularly after trauma or in degenerative conditions.
Cervical spine flexion and extension X-rays involve taking images while the patient actively (or sometimes passively, with caution) bends their neck forward (flexion) as far as comfortable, and then backward (extension) as far as comfortable. These dynamic views are particularly useful for evaluating suspected neck injuries or ligamentous instability. Common reasons a doctor might order these views include:
- Assessment of Whiplash Injury or other ligamentous injuries: To assess potential damage to ligaments or intervertebral joints resulting from sudden neck movements (acceleration-deceleration injuries).
- Detection of Cervical Instability: To detect abnormal or excessive movement between vertebrae, which can occur in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, Down syndrome, certain congenital anomalies, or following trauma.
- Evaluation of Degenerative Disc Disease or Spondylosis: To identify if abnormal motion or malalignment contributes to pain or neurological symptoms caused by wear and tear on the cervical spine.
- Post-Surgery Evaluation: To check the stability of the spine after previous cervical fusion surgery or other spinal operations.
- Trauma Assessment: To evaluate for subtle fractures, subluxations, or ligamentous injuries after head or neck trauma, especially if static X-rays are inconclusive but clinical suspicion remains.
The decision to utilize flexion and extension views is based on the individual patient's clinical situation, symptoms, and the findings of initial static X-rays, and will be determined by the healthcare provider. These views are contraindicated if a grossly unstable fracture is already identified or strongly suspected.
Contrast Studies of the Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract
X-rays using contrast agents (typically barium sulfate or water-soluble iodinated contrast) are employed to visualize the lumen of the GI tract. Common studies include:
- Esophagogram (Barium Swallow): Evaluates the esophagus for swallowing difficulties (dysphagia), strictures, tumors, reflux, or motility disorders.
- Upper GI Series (Barium Meal): Examines the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum for ulcers, tumors, inflammation, or structural abnormalities. Double-contrast techniques (using both barium and air) can provide enhanced detail of the mucosal lining.
Intestinal Irrigoscopy (Barium Enema)
This is a contrast X-ray examination of the large intestine (colon and rectum). A barium sulfate suspension is introduced into the colon via the rectum (retrograde filling). Air may also be introduced (double-contrast barium enema) to distend the colon and provide better mucosal detail. Irrigoscopy is used to detect polyps, tumors, diverticulosis, inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease), or strictures.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
HSG is a specialized contrast X-ray study of the female reproductive system. A contrast agent is injected through the cervix into the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. It is primarily used to:
- Evaluate fallopian tube patency in the investigation of infertility.
- Detect uterine abnormalities (e.g., fibroids, polyps, congenital anomalies, adhesions).
Excretory Urography (Intravenous Pyelogram - IVP)
(Note: Largely replaced by CT Urography in many centers, but still has some applications). This is a contrast X-ray examination that assesses the structure and function of the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, and bladder). An iodinated contrast agent is injected intravenously and is excreted by the kidneys. A series of X-rays are taken at timed intervals to visualize the contrast filling the renal pelvicalyceal systems, ureters, and bladder, allowing for detection of stones, obstructions, tumors, or anatomical anomalies.
Specialized spine and spinal cord radiography techniques using contrast agents also exist, such as myelography (see separate article if available), for visualizing the spinal canal and nerve roots.
For specific preparations required before any X-ray procedure (e.g., fasting for GI studies, bowel prep for barium enema), patients should consult with the radiography department staff or their referring physician at the clinic.
Indications for Radiography (Why a Doctor Orders an X-ray)
A doctor may order an X-ray for a multitude of reasons, depending on the patient's symptoms and suspected condition. Common indications include:
- Detecting Fractures and Dislocations: Evaluating bone injuries after trauma.
- Diagnosing Bone and Joint Diseases: Identifying arthritis, infections (osteomyelitis), tumors, or congenital abnormalities.
- Assessing Lung Conditions: Diagnosing pneumonia, bronchitis, emphysema, lung cancer, pneumothorax, or pleural effusion.
- Evaluating Heart Size and Shape: Detecting cardiomegaly or signs of heart failure.
- Investigating Abdominal Pain: Looking for bowel obstruction, perforated viscus (free air), or certain types of kidney/gallstones.
- Locating Foreign Objects: Identifying swallowed or inserted foreign bodies.
- Dental Examinations: Detecting cavities, impacted teeth, or jaw problems.
- Mammography: Screening for and diagnosing breast cancer.
- Monitoring Disease Progression or Treatment Response: E.g., tracking fracture healing or changes in arthritic joints.
- Guiding Certain Medical Procedures.
Preparation for an X-ray Examination
Preparation for an X-ray varies depending on the type of examination being performed:
- Most Bone X-rays: Usually require no special preparation. Patients may be asked to remove jewelry, eyeglasses, and any metal objects or clothing that might interfere with the X-ray images.
- Contrast Studies (e.g., GI series, IVP, HSG, Barium Enema): Require specific preparation, which may include:
- Fasting for several hours before the exam.
- Bowel preparation (laxatives, enemas) for barium enemas to clear the colon.
- Drinking a contrast agent or having it injected.
- Pregnancy: It is crucial for female patients of childbearing age to inform the technologist or doctor if there is any possibility they might be pregnant, as X-rays are generally avoided during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary due to potential risk to the fetus.
Patients will receive specific instructions from the clinic or radiology department prior to their scheduled X-ray if special preparation is needed.
The X-ray Procedure: What to Expect
The X-ray procedure itself is generally quick and painless:
- The patient will be positioned by a radiologic technologist so that the body part being examined is between the X-ray machine and the image receptor (digital detector or film cassette).
- The technologist may use pillows or sandbags to help the patient hold the correct position.
- The patient will be asked to remain very still and may need to hold their breath for a few seconds while the X-ray image is taken to prevent blurring.
- The technologist will go behind a protective screen or into an adjacent room to activate the X-ray machine.
- Multiple images from different angles may be taken.
The entire procedure for a simple X-ray usually takes only a few minutes, though more complex studies or those involving contrast can take longer.
Benefits and Advantages of X-ray Imaging
- Widely Available and Relatively Inexpensive: Compared to other advanced imaging modalities like CT or MRI.
- Quick and Non-Invasive (for most standard X-rays).
- Excellent for Visualizing Bones: Highly effective for detecting fractures, dislocations, and many bone diseases.
- Good for Chest Imaging: Provides valuable information about the lungs, heart, and major blood vessels.
- Low Radiation Dose (for standard diagnostic X-rays): Especially with modern digital systems.
- Painless.
Risks, Limitations, and Contraindications
Radiation Exposure and Safety
X-rays involve exposure to ionizing radiation. While the radiation dose from a single diagnostic X-ray is generally very low and the risk of harmful effects is small, repeated exposure over time can accumulate. The principle of ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) is always followed to minimize radiation dose.
Specific risks include:
- Slightly Increased Cancer Risk: Very high or frequent exposure to radiation can theoretically increase the lifetime risk of developing cancer, though the risk from typical diagnostic X-rays is considered minimal.
- Risk to Fetus: Radiation exposure during pregnancy can potentially harm a developing fetus, which is why X-rays are generally avoided in pregnant women unless medically essential.
Lead aprons or shields may be used to protect parts of the body not being imaged, especially radiosensitive organs like the gonads or thyroid.
Limitations of X-ray Imaging
- Limited Soft Tissue Detail: X-rays are not as effective as MRI or ultrasound for visualizing soft tissues like muscles, ligaments, tendons, or internal organs in detail.
- Overlapping Structures: Being a 2D projection of a 3D structure, overlying tissues can obscure abnormalities.
- Not All Conditions are Visible: Some fractures (e.g., subtle stress fractures, some skull base fractures) or early stages of certain diseases may not be visible on plain X-rays.
Contraindications
- Pregnancy: This is a relative contraindication. X-rays are generally avoided, especially during the first trimester, unless the benefits clearly outweigh the potential risks to the fetus. If an X-ray is necessary, measures are taken to minimize fetal exposure.
- Allergy to Contrast Media: For X-ray studies that require iodinated contrast agents, a known severe allergy to such agents is a contraindication or requires careful premedication and management.
Interpreting X-ray Results
After the X-ray images are taken, they are reviewed and interpreted by a radiologist, a physician specially trained in interpreting medical images. The radiologist will prepare a report detailing their findings, which is then sent to the referring doctor. The referring doctor will discuss the results with the patient and integrate them with other clinical information to make a diagnosis or guide further management.
Differential Diagnosis for Common X-ray Findings
X-rays help differentiate various conditions based on their appearance:
| Common X-ray Finding | Potential Diagnoses / Conditions |
|---|---|
| Fracture Line / Bone Discontinuity | Acute fracture, Old healed fracture (with callus), Stress fracture (may be subtle initially), Pathological fracture (through diseased bone). |
| Joint Space Narrowing / Osteophytes | Osteoarthritis, Degenerative joint disease. |
| Bone Erosions / Periarticular Osteopenia | Inflammatory arthritis (e.g., Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis). |
| Lung Opacity / Consolidation (Chest X-ray) | Pneumonia (bacterial, viral, fungal), Pulmonary edema, Atelectasis, Lung tumor/mass, Pleural effusion (if blunting costophrenic angle). |
| Pneumothorax (Chest X-ray) | Presence of air in the pleural space, causing lung collapse. Visible pleural line. |
| Cardiomegaly (Chest X-ray) | Enlarged heart silhouette. Can be due to various cardiac conditions (heart failure, valvular disease, hypertension). |
| Lytic or Blastic Bone Lesions | Metastatic disease, Multiple myeloma (lytic), Benign bone tumors, Osteomyelitis (can be lytic or sclerotic). |
| Soft Tissue Swelling / Gas | Trauma, Infection (cellulitis, abscess with gas formation). |
| Radiopaque Foreign Body | Swallowed or inserted metallic objects, some types of glass, gravel. |
Conclusion: The Role of X-rays in Modern Diagnostics
Despite the advent of more advanced imaging technologies like CT and MRI, radiography (X-ray) remains a fundamental, widely accessible, and cost-effective diagnostic tool in medicine. Its ability to quickly and clearly visualize bony structures and certain soft tissue abnormalities makes it indispensable for a vast range of clinical applications, from diagnosing fractures and pneumonia to screening for breast cancer and guiding certain interventions. Modern digital systems have further enhanced its utility by improving image quality and reducing radiation exposure.
References
- Bushberg JT, Seibert JA, Leidholdt EM Jr, Boone JM. The Essential Physics of Medical Imaging. 3rd ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012.
- Webb WR, Brant WE, Major NM. Fundamentals of Body CT. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2019. (Provides context for X-ray principles as foundational to CT).
- American College of Radiology (ACR). ACR Practice Parameters and Technical Standards. (Refer to specific guidelines for different X-ray examinations, e.g., Chest Radiography, Skeletal Surveys). Accessed [Current Date].
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP). NCRP Report No. 160: Ionizing Radiation Exposure of the Population of the United States. NCRP; 2009. (Provides data on medical radiation exposure).
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Various publications on radiation protection in medicine (e.g., ICRP Publication 103, ICRP Publication 105).
- Mettler FA Jr, Huda W, Yoshizumi TT, Mahesh M. Effective doses in radiology and diagnostic nuclear medicine: a catalog. Radiology. 2008 Jul;248(1):254-63.
- European Commission. Radiation Protection No. 180: Medical Radiation Exposure of the European Population. Publications Office of the European Union; 2014.
- Squire LF, Novelline RA. Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology. 6th ed. Harvard University Press; 2004.