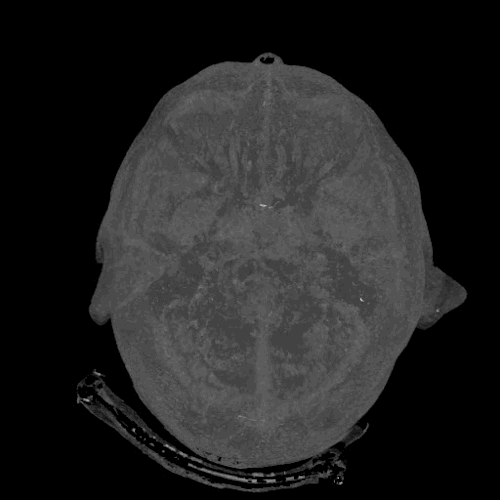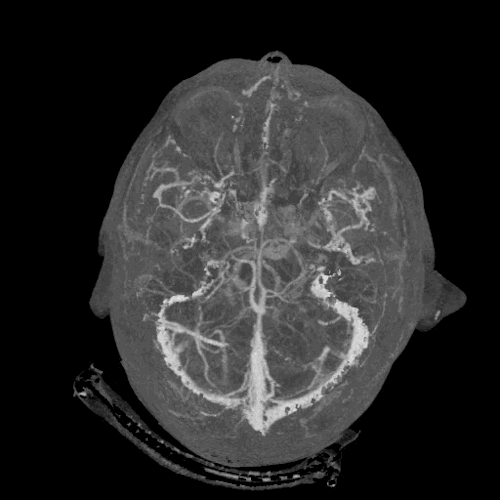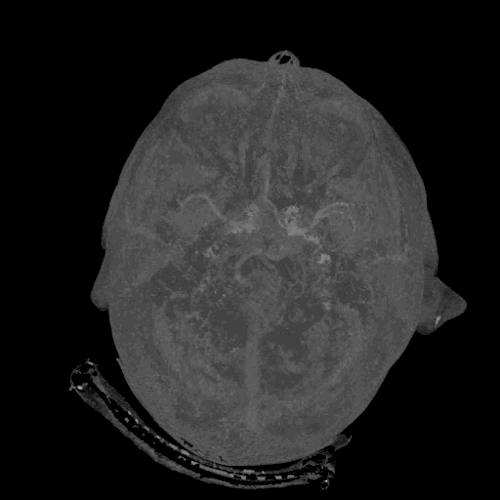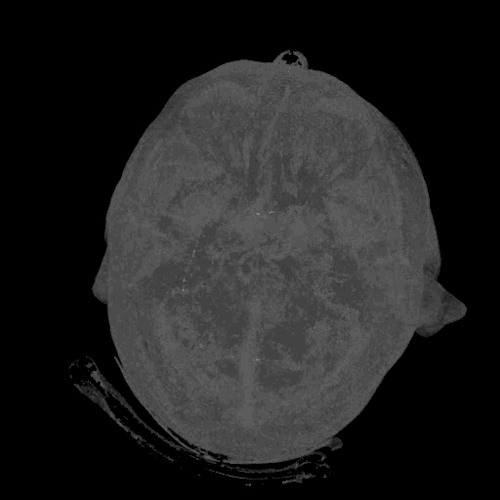
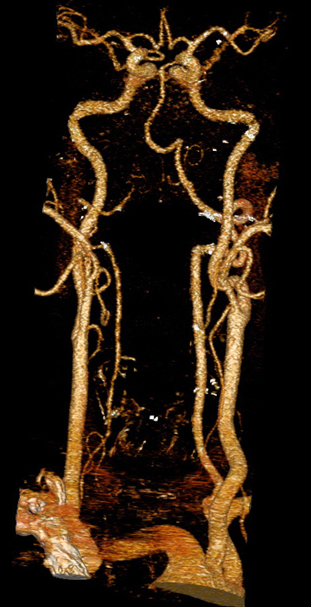
Cerebrovascular CT-angiography
Cerebral CT Angiography (CTA)
Cerebral CT Angiography (often abbreviated as CTA or CT-Angio) is a specialized, non-invasive imaging technique used to visualize blood vessels (arteries and veins) within the brain and neck. By using computed tomography combined with an intravenous contrast agent, CTA provides detailed images that allow clinicians to identify and study important signs of various cerebrovascular diseases.
CTA of the cerebral and neck arteries helps clarify morphological (structural) and functional changes in these vessels, such as blockages (stenosis or occlusion), outpouchings (aneurysms), or abnormal connections (arteriovenous malformations - AVMs).
Angiographic Signs Detected by CTA
The signs detected by cerebral CTA that indicate organic brain or vessel disease can be grouped for practical reasons:
- Changes in Vessel Position: Displacement or shifting of arteries or veins, often due to a nearby mass (like a tumor or hematoma).
- Changes in Vessel Number or Presence: Absence of expected vessels (occlusion), or the presence of abnormal vessel networks (like in AVMs or some tumors).
- Changes in Vessel Shape and Lumen Width: Narrowing (stenosis), widening (ectasia or aneurysm), irregularity of the vessel wall (atherosclerosis, vasculitis), or complete blockage (occlusion).
- Changes in Contrast Flow Dynamics: Altered speed or pattern of blood flow, such as delayed filling or early venous drainage, which can indicate ischemia or abnormal shunting.
- Contrast Extravasation: Leakage of the contrast agent outside the vessel wall, indicating active bleeding or rupture (e.g., ruptured aneurysm).
In various brain diseases, Cerebral CTA might primarily highlight one specific sign (like vessel displacement near a lesion). However, often a combination of these angiographic signs is present, providing a more complete picture of the underlying pathology.
The diagnostic significance varies among these groups of signs. Some findings on CTA, such as the characteristic appearance of an aneurysm, the abnormal tangle of vessels in an AVM, or a complete vessel blockage (thrombosis), are highly specific and can directly indicate the nature and location of the pathology.
Indications for Cerebral CT Angiography
Cerebral CT Angiography (CTA) is indicated for patients suspected of having various cerebrovascular conditions, including:
- Acute Stroke Symptoms: To rapidly identify large vessel occlusion (LVO) treatable with thrombectomy, or to rule out hemorrhage. (Ischemic stroke, cerebral ischemia)
- Suspected Brain Aneurysm: Especially in cases of sudden, severe headache ("thunderclap headache") suggestive of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), or for screening in high-risk individuals.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) and other Vascular Malformations: To diagnose and characterize these abnormal connections between arteries and veins. (AVMs of the brain)
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): To identify underlying causes like carotid artery stenosis or intracranial stenosis. (Transient ischemic attack (TIA), Cerebrovascular diseases)
- Carotid or Vertebral Artery Stenosis/Occlusion: Evaluation of narrowing or blockage in the neck arteries supplying the brain. (Atherothrombotic occlusion of internal carotid artery, Asymptomatic carotid stenosis)
- Intracranial Stenosis: Evaluation of narrowing within the arteries inside the skull.
- Vasculitis: Assessment of inflammation of the blood vessel walls. (Cerebral arteries inflammatory diseases)
- Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency (VBI): Symptoms like vertigo, dizziness, or drop attacks potentially related to poor blood flow in the posterior circulation. (VBI with vertigo, Dizziness, tinnitus)
- Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: To diagnose blood clots in the large veins draining the brain. (Sigmoid sinus thrombosis)
- Evaluation Before Neurosurgery or Endovascular Procedures: To map vascular anatomy.
- Follow-up of Treated Vascular Lesions: Monitoring aneurysms after coiling/clipping, or stenosis after stenting.
- Investigation of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: To identify an underlying vascular cause like an aneurysm or AVM, especially in non-hypertensive patients or unusual locations. (Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage)
Preparation for the Scan
Preparation for a Cerebral CT Angiogram typically involves:
- Fasting: You may be asked not to eat or drink for a few hours before the scan, particularly since intravenous (IV) contrast material is used. This minimizes the risk of nausea or aspiration.
- Clothing and Jewelry: Wear comfortable clothing. You will likely need to remove any metal objects from your head and neck area, including jewelry (earrings, necklaces), hairpins, eyeglasses, and dentures, as these can interfere with the CT images. You might be asked to change into a hospital gown.
- Medications: Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking and if you have any allergies, especially to iodine or previous contrast reactions. Patients taking metformin may need specific instructions regarding pausing the medication around the time of the scan due to the contrast agent.
- Medical History: Notify your doctor and the CT technologist about any significant medical conditions, especially kidney problems (renal insufficiency), diabetes, asthma, heart disease, or thyroid disorders. It's crucial to inform them if there is any possibility you could be pregnant.
The CTA Procedure
During the Cerebral CTA scan:
- You will lie down on the CT scanner table, usually flat on your back. A head holder or cradle might be used to help keep your head still during the scan, as movement can blur the images.
- An intravenous (IV) line will be inserted into a vein in your arm or hand. This is used to inject the contrast material during the scan.
- The table will slide into the center of the large, doughnut-shaped CT scanner. The scanner will rotate around your head and neck area to acquire the images.
- The technologist will operate the scanner from an adjacent control room but will be able to see, hear, and speak with you throughout the procedure.
- When the contrast material is injected via the IV, you might feel a temporary warm sensation spreading through your body or a metallic taste in your mouth. These sensations are normal and usually pass quickly.
- You will need to remain very still during the image acquisition, which typically takes only a few minutes, although the entire process including setup might take 15-30 minutes. You might be asked to hold your breath briefly for scans involving the lower neck.
Use of Contrast Material
Intravenous (IV) contrast material is essential for Cerebral CT Angiography. This iodine-based liquid is injected into your bloodstream through the IV line.
- The contrast makes the blood flowing within your arteries and veins appear bright white on the CT images.
- This enhancement allows for clear visualization of the vessel anatomy, including the vessel walls and the flow channel (lumen).
- It is crucial for detecting abnormalities like aneurysms, stenosis (narrowing), occlusions (blockages), AVMs, and active bleeding.
- The timing of the scan relative to the contrast injection is precisely controlled to capture the optimal phase of vessel enhancement (usually the arterial phase).
Risks and Benefits
Benefits:
- CTA is a fast, non-invasive, and widely available method for detailed visualization of the brain and neck blood vessels.
- It is excellent for diagnosing potentially life-threatening conditions like aneurysms and acute stroke due to large vessel occlusion, allowing for prompt treatment.
- Provides detailed anatomical information useful for planning surgery or endovascular procedures.
- Less invasive and generally faster than traditional catheter angiography.
Risks:
- Radiation Exposure: Like all CT scans, CTA uses ionizing radiation. While the dose is optimized to be as low as possible (ALARA principle), there is a small theoretical long-term risk associated with cumulative radiation exposure. The diagnostic benefit usually far outweighs this risk.
- Contrast Reaction: Allergic-like reactions to the iodine-based contrast material can occur, ranging from mild (itching, hives) to rare, severe reactions (anaphylaxis). Patients with prior reactions or allergies are at higher risk. Informing the medical team of any allergies is crucial.
- Kidney Issues (Contrast-Induced Nephropathy): The contrast material can potentially affect kidney function, especially in patients with pre-existing moderate to severe kidney disease or diabetes. Kidney function is often checked before administering contrast in at-risk patients.
- Contrast Extravasation: Rarely, the contrast material may leak from the vein at the injection site, causing local pain or swelling.
- Pregnancy: CT scans are generally avoided during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary due to potential radiation risk to the fetus.
References
- Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) & American College of Radiology (ACR). (2022). Head CT Angiography (CTA). RadiologyInfo.org. Retrieved from https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/ctangiog-head
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2022). CT angiogram. Mayo Clinic Patient Care & Health Information. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ct-angiogram/about/pac-20385174
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). (n.d.). Cerebral Angiography. NIH - National Institutes of Health. Retrieved from https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/diagnostic-tests/cerebral-angiography [Note: This link covers conventional angiography but principles overlap with CTA]
- American College of Radiology. (2023). ACR Manual on Contrast Media. Retrieved from https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Contrast-Manual
- Lehman, V. T., & Huston, J. (2017). Intracranial CT Angiography. In *Practical Neuroimaging*. Springer. [Note: Example of textbook-level resource]