The principle of CT examinations
What is Computed Tomography (CT)?
Computed Tomography (CT), often called a CT scan or CAT scan, is an advanced diagnostic imaging procedure that uses specialized X-ray equipment combined with sophisticated computers to produce detailed cross-sectional images ("slices") of the body. It essentially creates a virtual model of the internal structures based on how different tissues absorb X-ray beams passed through them from multiple angles.
CT scanning provides much more detail than conventional X-rays, especially for soft tissues, blood vessels, and complex bone structures. Modern CT scanners, particularly Multislice CT (MSCT), are incredibly fast and can differentiate tissues with very subtle density differences (as small as 0.1%). The high diagnostic accuracy makes CT invaluable across many fields of medicine.
The term "computed" highlights the essential role of powerful computer processing in reconstructing the final images from the raw X-ray data collected by the scanner.
How Does CT Work? (Technique)
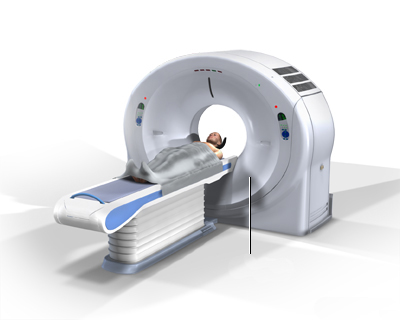
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a motorized table that moves through the center of a large, doughnut-shaped machine called the gantry. Inside the gantry, an X-ray tube rotates rapidly around the patient, emitting narrow beams of X-rays through the body section being examined.
Opposite the X-ray tube, an array of electronic detectors measures the amount of X-ray radiation that passes through different tissues. Tissues with higher density (like bone) absorb more radiation, while less dense tissues (like air or fat) allow more to pass through.
This process is repeated from many different angles as the tube rotates and the table moves. The computer then processes the vast amount of data collected by the detectors, using complex mathematical algorithms (reconstruction algorithms) to generate cross-sectional images (slices) that represent the internal anatomy. These slices can be viewed individually on a monitor, printed on film, or further processed.
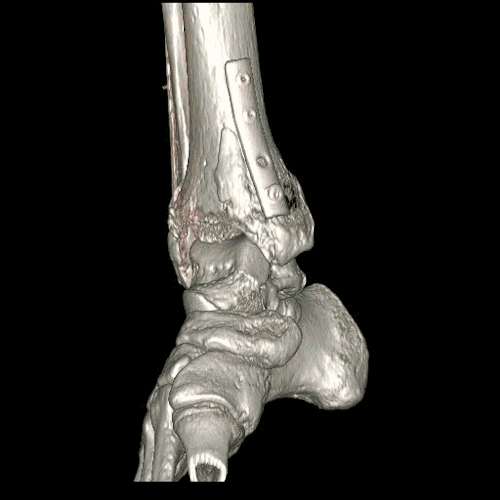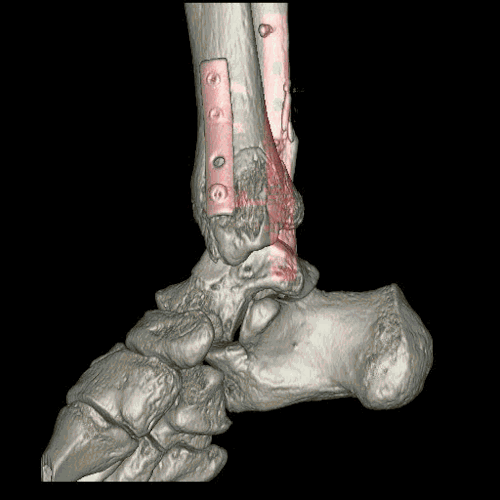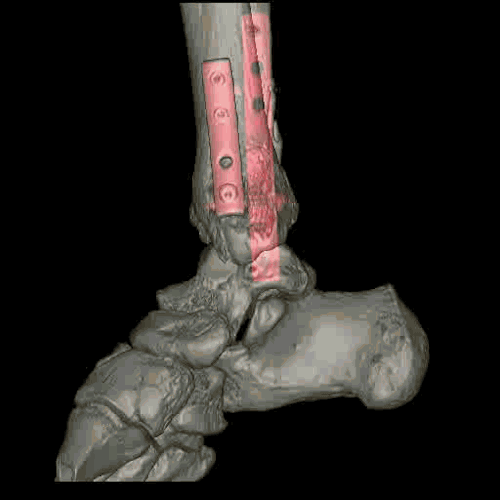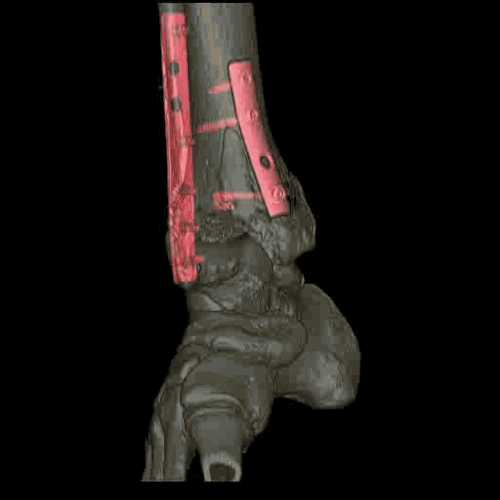
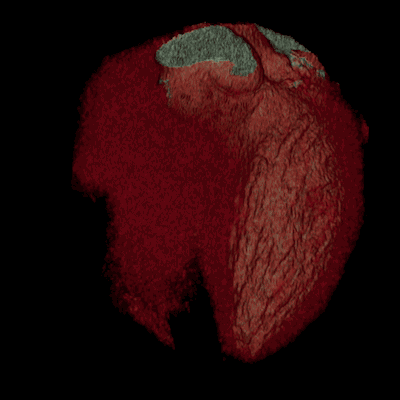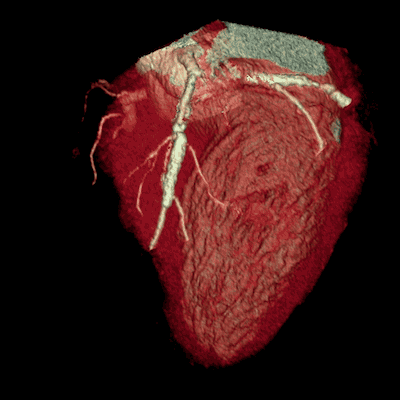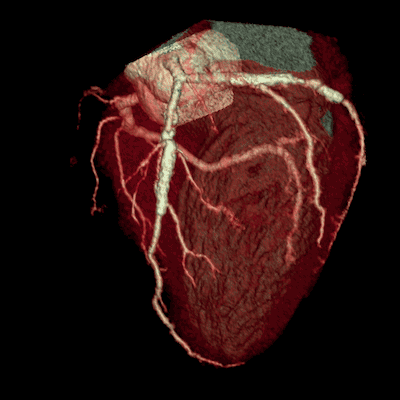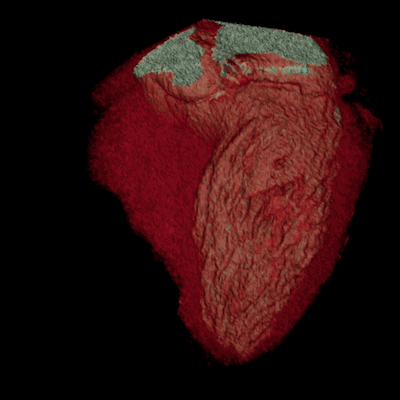
Modern helical or multislice CT (MSCT) scanners acquire data continuously as the table moves through the gantry, allowing for very rapid scanning of large body regions. This speed minimizes motion artifacts and allows for advanced applications like CT angiography. The acquired "volume" of data allows the computer to reconstruct images in any plane (axial, coronal, sagittal) or create detailed three-dimensional (3D) models of organs, bones, and blood vessels.
The entire imaging process for a specific body part typically takes only a few minutes, with the actual scanning often lasting less than a minute with modern MSCT scanners.
Use of Contrast Media
For certain CT examinations, a special dye called contrast media (or contrast agent) is used to enhance the visibility of specific tissues, organs, or blood vessels. Contrast media temporarily changes how these structures absorb X-rays, making them stand out more clearly on the final images.
Contrast media can be administered in several ways, depending on the area being studied:
- Intravenous (IV) Contrast: Injected into a vein (commonly in the arm or hand). This is frequently used to highlight blood vessels (CT angiography), assess organ perfusion, and detect inflammation or tumors which often show increased enhancement.
- Oral Contrast: Swallowed by the patient before the scan. This is used to outline the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, helping to distinguish the bowel from surrounding structures in abdominal and pelvic CT scans. Oral contrast often has a chalky or slightly sweet taste; flavorings may be added.
- Rectal Contrast: Administered via an enema. This is used specifically to visualize the rectum and distal colon.
If IV contrast is used, it's normal to experience a temporary sensation of warmth spreading through the body, a metallic taste in the mouth, or a feeling like one needs to urinate. These effects usually disappear within seconds to minutes.
Patient Preparation for CT Scan
Preparation depends on the type of CT scan being performed:
- Clothing: Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. You may be asked to change into a hospital gown.
- Metal Objects: Remove metal objects like jewelry (necklaces, earrings, piercings if in the scan area), eyeglasses, dentures, and hairpins, as metal can interfere with the images (create artifacts).
- Fasting: If IV contrast is planned, you may be asked not to eat or drink for 4-6 hours before the scan. Instructions for oral contrast involve drinking the liquid over a specific period (e.g., 1-2 hours) before the scan. For scans without contrast (like some head, spine, or extremity CTs), fasting is usually not required.
- Allergies and Medical Conditions: Inform your doctor and the CT technologist about any allergies (especially to iodine or previous contrast reactions), medications you are taking, and significant medical conditions like kidney disease, diabetes, asthma, heart disease, or thyroid problems. It is crucial to inform them if there is any possibility you are pregnant.
- Contrast Allergy Premedication: Patients with known significant allergies to IV contrast may require premedication with corticosteroids or antihistamines before the scan.
- Weight Limits: While modern scanners accommodate higher weights, extremely high body weight can sometimes exceed table limits or affect image quality. Older scanners had lower weight limits (e.g., around 130 kg / 285 lbs).
The CT Procedure Experience
The CT scan itself is generally painless. Some patients may find the scanner table slightly hard or experience mild discomfort from having to lie still in one position.
The scanner can be somewhat noisy, producing whirring or clicking sounds as it operates. You will be able to communicate with the technologist operating the scanner via an intercom system. They will provide instructions, such as when to hold your breath.
As mentioned earlier, if IV contrast is administered, the temporary sensations of warmth, metallic taste, or needing to urinate are common and not usually cause for concern.
Overall, the procedure is fast. While preparation and positioning take time, the actual scanning phase where images are acquired often lasts less than a minute for many standard examinations using modern MSCT scanners.
Risks and Benefits of CT Scans
Benefits:
- Fast, widely available, and provides detailed cross-sectional images.
- Excellent for evaluating bone, soft tissues, and blood vessels simultaneously.
- Painless and non-invasive (though IV contrast injection involves a needle).
- Crucial in emergency settings for rapid diagnosis of trauma, stroke, and acute abdominal conditions.
- Less sensitive to patient motion than MRI.
- Can guide biopsies and drainage procedures.
- Safe for patients with most implanted medical devices (unlike MRI).
Risks:
- Ionizing Radiation Exposure: CT scans use X-rays, which are a form of ionizing radiation. While the dose from a single scan is generally low and carefully controlled (using the ALARA - As Low As Reasonably Achievable - principle), there is a small, theoretical increase in lifetime cancer risk associated with cumulative radiation exposure from multiple scans. The diagnostic benefit must always be weighed against this potential risk. Repeat scans are only performed when medically necessary.
- Contrast Media Reactions:
- Allergic-like reactions: Most IV contrast agents contain iodine. Mild reactions (itching, hives, nausea) can occur. More severe, anaphylactic reactions are rare but possible. Patients with a history of allergy to contrast media or significant other allergies are at higher risk.
- Kidney Effects (Contrast-Induced Nephropathy - CIN): IV contrast can potentially strain the kidneys, especially in patients with pre-existing moderate to severe kidney disease or diabetes. Kidney function tests may be required before contrast administration in at-risk individuals, and hydration protocols may be used.
- Pregnancy: CT scans are generally avoided during pregnancy, especially abdominal/pelvic scans, due to potential radiation risk to the developing fetus. Alternative imaging like ultrasound or MRI is preferred if possible. If a CT scan is essential, measures are taken to minimize fetal dose. Women who might be pregnant must inform their doctor.
- Incidental Findings: CT scans can sometimes reveal unexpected abnormalities unrelated to the reason for the scan, which may cause anxiety and require further investigation.
It is important to discuss any concerns about the risks and benefits of a CT scan with your referring doctor or the radiology staff.
References
- National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB). (n.d.). Computed Tomography (CT). NIH - National Institutes of Health. Retrieved from https://www.nibib.nih.gov/science-education/science-topics/computed-tomography-ct
- Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) & American College of Radiology (ACR). (n.d.). Computed Tomography (CT). RadiologyInfo.org. Retrieved from https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/ct-scan
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2022). CT scan. Mayo Clinic Patient Care & Health Information. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ct-scan/about/pac-20393675
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). (2023). Computed Tomography (CT). FDA Medical Imaging and Radiation. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/radiation-emitting-products/medical-imaging/computed-tomography-ct
- American College of Radiology. (2023). ACR Manual on Contrast Media. Retrieved from https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Contrast-Manual