Acute and chronic frontal sinusitis (frontitis)
- Understanding Acute Frontal Sinusitis (Frontitis)
- Causes and Risk Factors for Acute Frontal Sinusitis
- Symptoms of Acute Frontal Sinusitis
- Understanding Chronic Frontal Sinusitis
- Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Frontal Sinusitis
- Differential Diagnosis of Forehead Pain and Pressure
- Treatment of Acute and Chronic Frontal Sinusitis
- Potential Complications of Frontal Sinusitis
- Prevention Strategies
- References
Understanding Acute Frontal Sinusitis (Frontitis)
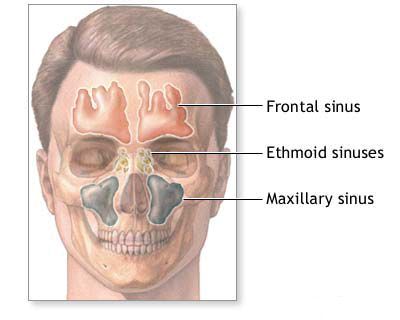
Acute frontal sinusitis, also known as frontitis, refers to an inflammation of the mucosal lining of the frontal sinuses, which are air-filled cavities located in the frontal bone above the eyes (forehead region). This condition is often more severe and can lead to more significant discomfort and potential complications compared to acute inflammation of other paranasal sinuses, such as the maxillary or sphenoid sinuses. This increased severity, particularly in children, is partly due to the anatomical location of the frontal sinuses and their drainage pathways.
Pathophysiology and Severity
The frontal sinuses drain into the nasal cavity via a narrow and often complex passage called the frontonasal duct (or frontal recess), which opens into the middle meatus. Obstruction of this duct due to mucosal swelling (from infection, allergy, or anatomical variations) prevents proper ventilation and mucus drainage. This stasis of secretions creates a favorable environment for pathogens (viruses, bacteria, or rarely fungi) to proliferate, leading to infection and inflammation.
Acute frontal sinusitis almost invariably occurs in conjunction with inflammation of the ethmoid sinuses (ethmoiditis) because the frontal sinus drainage pathway is intimately related to the anterior ethmoid cells. It may also, though less commonly, be associated with maxillary sinusitis as part of a broader pansinusitis (inflammation of multiple or all paranasal sinuses). The confined space of the frontal sinus and its proximity to critical structures like the orbit (eye socket) and the anterior cranial fossa (containing the brain) contribute to the potential for more serious symptoms and complications if the infection is not adequately managed.
Causes and Risk Factors for Acute Frontal Sinusitis
The development of acute frontal sinusitis is typically preceded by factors that disrupt normal sinus ventilation and drainage. Key causes and contributing risk factors include:
- Viral Upper Respiratory Infections (URIs): The common cold or influenza is the most frequent precursor. Viral infections cause inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa, including the lining of the frontonasal duct, leading to obstruction.
- Bacterial Infections: While often initiated by viruses, secondary bacterial infection can occur if sinus obstruction persists. Common bacterial pathogens include *Streptococcus pneumoniae*, *Haemophilus influenzae*, and *Moraxella catarrhalis*.
- Allergic Rhinitis: Allergic reactions cause chronic inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa, predisposing individuals to sinus blockage.
- Anatomical Abnormalities:
- A narrow or congenitally deviated frontonasal duct.
- Deviated nasal septum that obstructs the middle meatus region.
- Nasal polyps or hypertrophied (enlarged) turbinates that block sinus drainage pathways.
- Concha bullosa (aerated middle turbinate) that may narrow the outflow tract.
- Facial Trauma: Injuries to the facial skeleton, particularly involving the frontal bone or supraorbital region, can damage or obstruct the frontal sinus drainage pathways.
- Foreign Bodies in the Nose: Prolonged presence of foreign objects, especially in children, can cause localized inflammation and obstruction.
- Changes in Atmospheric Pressure: Activities like flying or scuba diving can sometimes precipitate sinus issues (barotrauma) if there is pre-existing mild obstruction.
- Dental Infections: Though more commonly associated with maxillary sinusitis, severe dental abscesses in the upper teeth can rarely spread to affect other sinuses.
- Immunocompromised States: Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infections, including sinusitis.
- Cystic Fibrosis: A genetic condition leading to thick mucus production, which predisposes to sinus blockage and infection.
Understanding these underlying factors is crucial for both treatment and prevention of recurrent episodes.
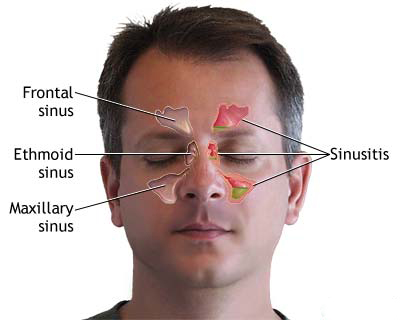
Symptoms of Acute Frontal Sinusitis
Acute frontal sinusitis typically presents with a distinct set of symptoms, often more intense than those of other sinus infections:
- Severe Frontal Headache: This is the hallmark symptom. The headache is usually localized over the forehead, above the eyebrows, and can be throbbing or feel like intense pressure. It characteristically worsens when bending forward, lying down, or upon percussion (tapping) over the affected frontal sinus. The headache may have a diurnal pattern, often starting or worsening at a certain time of day (e.g., morning). It is frequently so severe that it is not adequately relieved by common analgesics.
- Facial Pain/Pressure: Tenderness, pain, or a feeling of fullness over the forehead and sometimes radiating to the orbits (behind the eyes) or temporal area.
- Nasal Congestion or Obstruction: Difficulty breathing through the nose, often on one or both sides.
- Nasal Discharge: May be thick, purulent (yellow or green), or blood-tinged. Post-nasal drip (sensation of mucus dripping down the throat) is common.
- Fever: High body temperature (fever) is often present, especially in acute bacterial infections. Chills may also occur.
- Reduced or Lost Sense of Smell (Hyposmia/Anosmia): Due to mucosal swelling and obstruction.
- Malaise and Fatigue: A general feeling of unwellness, tiredness, and lack of energy.
- Swelling and Redness: Soft tissue swelling may occur over the forehead or around the inner corner of the eye on the affected side. Swelling and redness of the eyelids (periorbital edema) can also be observed.
- Eye Symptoms: Tearing (lacrimation) and photophobia (sensitivity to light) may be present if there is orbital involvement or severe inflammation.
- Cough: Often worse at night, due to post-nasal drip.
- Ear Pressure or Fullness: Due to Eustachian tube dysfunction secondary to nasal inflammation.
The sudden onset and intensity of the headache in acute frontal sinusitis can significantly impact a patient's daily life, often disrupting sleep, appetite, and overall activity levels.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe headache or facial pain not relieved by over-the-counter pain medication.
- Symptoms that persist for more than 7-10 days or worsen after initial improvement.
- High fever (above 101.5°F or 38.6°C).
- Swelling or redness around the eyes, forehead, or cheek.
- Changes in vision (double vision, decreased vision).
- Stiff neck or severe light sensitivity.
- Confusion or altered mental status.
- Symptoms of a sinus infection if you have a weakened immune system or other chronic health conditions.
Understanding Chronic Frontal Sinusitis
Chronic frontal sinusitis is defined as inflammation of the frontal sinus mucosa lasting for 12 weeks or longer, despite attempts at medical treatment. It often develops as a consequence of inadequately treated or recurrent acute frontal sinusitis episodes.
Transition from Acute to Chronic
The transition from acute to chronic sinusitis involves persistent inflammation, impaired mucociliary clearance (the self-cleaning mechanism of the sinuses), and often long-term changes in the sinus lining. Factors contributing to chronicity include:
- Persistent obstruction of the frontonasal duct.
- Formation of bacterial biofilms, which are resistant to antibiotics.
- Underlying conditions like allergies, nasal polyps, or immune deficiencies.
- Repeated irritant exposure.
Symptoms of Chronic Frontal Sinusitis
Symptoms of chronic frontal sinusitis can be more persistent but sometimes less intense than acute episodes, or they may involve periods of exacerbation (flare-ups) with more severe symptoms. Common signs include:
- Persistent Dull Headache or Forehead Pressure: Often a constant, nagging ache or pressure in the forehead, which may be less severe than in acute attacks but more continuous.
- Chronic Nasal Congestion or Blockage.
- Persistent Nasal Discharge: May be thick, discolored, or clear; post-nasal drip is common.
- Reduced Sense of Smell (Hyposmia) or Complete Loss of Smell (Anosmia).
- Facial Fullness or Tenderness over the Frontal Sinuses.
- Chronic Cough: Especially at night.
- Fatigue and General Malaise.
- Bad Breath (Halitosis).
- The vasomotor form of allergic inflammation of the frontal sinuses can be characterized by paroxysmal headaches in the forehead, sneezing, profuse watery nasal discharge, impaired nasal breathing and olfaction, watery eyes, and a sensation of tickling in the nose.
In some cases, chronic frontal sinusitis can progress rapidly, spreading to involve the periosteum (bone lining) and bone itself (osteomyelitis), potentially leading to subperiosteal abscesses or more severe orbital and intracranial complications.
Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Frontal Sinusitis
Diagnosing frontal sinusitis involves a combination of clinical assessment and, in some cases, imaging studies:
- Medical History and Symptom Review: The doctor will ask about the nature, duration, and severity of symptoms, previous sinus infections, allergies, and any underlying health conditions.
- Physical Examination:
- Anterior Rhinoscopy: Visual examination of the front part of the nasal cavities using a nasal speculum to look for swelling, redness, and purulent discharge, especially in the middle meatus region where the frontal sinus drains.
- Nasal Endoscopy: A thin, lighted tube (endoscope) is inserted into the nasal passages for a more detailed view of the nasal cavity, sinus openings, and any anatomical abnormalities or polyps. This is particularly useful in diagnosing chronic sinusitis.
- Palpation and percussion over the frontal sinuses to elicit tenderness.
- Imaging Studies:
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scan of the paranasal sinuses is the gold standard for imaging sinusitis, especially chronic or complicated cases. It provides detailed images of the sinus anatomy, mucosal thickening, fluid levels, and any bony abnormalities. It's often performed if symptoms are persistent, severe, or if surgery is being considered.
- X-rays: Plain sinus X-rays are less commonly used now due to their limited detail compared to CT scans but may occasionally be used for initial assessment in acute, uncomplicated cases.
- Nasal Cultures: If purulent discharge is present and accessible, a sample might be taken for culture and sensitivity testing to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and guide antibiotic therapy, especially in chronic or recurrent cases.
Differential Diagnosis of Forehead Pain and Pressure
Forehead pain and pressure are common symptoms that can arise from various conditions. It's important to differentiate frontal sinusitis from other potential causes:
| Condition | Key Differentiating Features |
|---|---|
| Frontal Sinusitis | Localized pain/pressure over forehead, worse on bending forward, often with nasal congestion, purulent discharge, fever, and tenderness over sinuses. CT scan shows sinus inflammation. |
| Tension-Type Headache | Bilateral, band-like pressure or tightness around the head, often related to stress or muscle tension. Usually not associated with fever or nasal symptoms. |
| Migraine Headache | Often unilateral, throbbing pain, may be preceded by aura, associated with nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia. Can sometimes have nasal symptoms (migrainous rhinitis). |
| Cluster Headache | Severe, excruciating, unilateral pain around the eye or temple, occurring in clusters. Associated with autonomic symptoms like tearing, nasal congestion, eyelid drooping on the affected side. |
| Trigeminal Neuralgia | Sudden, severe, electric shock-like facial pain along the trigeminal nerve distribution (often V1 branch for forehead). Triggered by light touch, chewing, talking. |
| Temporal Arteritis (Giant Cell Arteritis) | Typically in older adults (>50 years). New-onset headache, scalp tenderness (especially temporal arteries), jaw claudication, visual disturbances. Elevated ESR/CRP. Requires urgent diagnosis and treatment. |
| Eye Strain / Refractive Errors | Frontal headache often related to prolonged visual tasks, reading. Relieved by rest or vision correction. |
Treatment of Acute and Chronic Frontal Sinusitis
The primary goals of treating frontal sinusitis are to relieve symptoms, eradicate infection (if present), reduce inflammation, promote sinus drainage, and prevent complications or recurrence.
Medical Management of Acute Frontal Sinusitis
Treatment focuses on promoting drainage and resolving inflammation. Measures include:
- Nasal Decongestants: To improve sinus emptying and ventilation, anemization (shrinking) of the nasal mucosa, particularly in the middle nasal passage where the frontal sinus ostium is located, is crucial.
- Topical vasoconstrictors like 0.05% naphazoline (Naphthyzin) solution (2-4 drops, 3-4 times daily) or Sanorin (solution or emulsion, 2-4 drops, 3-4 times daily) can be used. Similar effects are seen with xylometazoline (Galazolin) or oxymetazoline. These should be used for a limited period (typically 3-5 days) to avoid rebound congestion.
- Intranasal epinephrine solution (1:1000; 1-2 drops, 2-3 times daily) may be used for rapid effect under medical supervision. Cotton pledgets soaked in these solutions can be inserted into the nasal cavity, ensuring they are secured to prevent aspiration in children.
- Analgesics and Antipyretics: For pain and fever relief, medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen are recommended. Amidopyrine was historically used but is less common now due to potential side effects.
- Nasal Saline Irrigation: Regular rinsing with saline solution helps to clear nasal passages and remove secretions.
- Intranasal Corticosteroids: Sprays containing corticosteroids can help reduce mucosal inflammation, especially if an allergic component is present or inflammation is significant.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is suspected (e.g., symptoms lasting >10 days, severe symptoms, purulent discharge, "double sickening"), antibiotics are prescribed. Choices may include amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, or alternatives like doxycycline or fluoroquinolones for adults, and age-appropriate doses of tetracycline, erythromycin (historically oletetrin, vitacycline), or penicillin (intramuscularly) were used. Combination with sulfonamides (e.g., sulfadimezin, norsulfazol, etazol) or long-acting sulfonamides (sulfadimethoxine) was also a practice. Current guidelines emphasize judicious antibiotic use.
- Calcium Gluconate: Historically used, with less evidence supporting its routine use now.
- Hydration and Humidification: Drinking plenty of fluids and using a humidifier can help thin mucus.
It is important to note that prolonged use (beyond 6-7 days) of topical vasoconstrictor drugs like Sanorin or naphazoline can lead to persistent atony (loss of tone) of the nasal mucosa, chronic swelling, and even sensitization or the development of edematous polyps. Therefore, their use should be short-term, followed by a break or change in medication if needed.
Medical Management of Chronic Frontal Sinusitis
Management of chronic frontal sinusitis aims to control inflammation, maintain sinus patency, and manage underlying contributing factors:
- Long-term Intranasal Corticosteroids: This is often a cornerstone of treatment to control chronic inflammation.
- Regular Nasal Saline Irrigation.
- Antibiotics: May be used for longer courses (e.g., 3-6 weeks) in some cases or for acute exacerbations. Culture-directed therapy is ideal.
- Oral Corticosteroids: Short courses may be prescribed for severe inflammation or nasal polyps to reduce swelling and improve symptoms temporarily.
- Leukotriene Modifiers: Can be beneficial if allergies or asthma coexist.
- Treatment of Underlying Conditions: Managing allergies (e.g., with antihistamines, immunotherapy), addressing structural issues, or treating immune deficiencies is crucial. For allergic components, hyposensitization therapy and antihistamines are indicated. In life-threatening allergic events (e.g., laryngeal edema), intravenous prednisolone (1-3 ml over 3 minutes) may be used. If allergic frontal sinusitis is accompanied by asthma or asthmatic bronchitis, intravenous aminophylline or diaphylline (2.4% solution, 10 ml slowly) may be administered during an attack.
- Physical Therapy: Local thermal procedures like hot compresses or Solux lamp application to the forehead and nose (8-10 sessions) may be used. UHF therapy (10-12 sessions) is thought to penetrate deeper, affecting vascular innervation and promoting absorption of inflammatory substances. Intranasal blue light therapy (8-10 sessions) or a combination of UHF and blue light can also be employed. For allergic forms, intranasal electrophoresis with 5-10% calcium chloride solution or 1% diphenhydramine solution (8-12 sessions) has been described.
Surgical Interventions for Frontal Sinusitis
Surgical intervention is considered if medical management fails, if there are significant anatomical obstructions, or if complications arise.
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS): This is the most common surgical approach. Using an endoscope, the surgeon enlarges the natural drainage pathway of the frontal sinus (frontonasal duct) by removing obstructing tissue, polyps, or diseased bone. The goal is to restore normal ventilation and drainage. Endonasal probing and irrigation of the frontal sinus with subsequent introduction of medications can sometimes be effective. Probing in children can be challenging but is possible. If probing is difficult, trepanation of anterior ethmoid cells and resection of an excessively developed uncinate process may be needed.
- Frontal Sinus Trephination/Trepanopuncture: In cases of acute, severe frontal sinusitis with retained pus and intense pain not responding to medical therapy, a small hole can be drilled through the anterior wall or floor (orbital wall) of the frontal sinus to allow for drainage and irrigation. This is less common now with advances in FESS but can be a temporizing or diagnostic measure. Special devices with automatic tripping mechanisms have been developed to enhance safety during trepanopuncture by stopping the drill once the bony wall is passed, signaled audibly and visually. After creating the channel, a cannula can be inserted for further sinus study and treatment.
- External Frontal Sinus Procedures (e.g., Lynch or Riedel procedures): These are more invasive external approaches, typically reserved for very severe, complicated, or recurrent chronic frontal sinusitis where FESS has failed or is not feasible. They involve an external incision (e.g., along the eyebrow) to directly access and clean out the frontal sinus, often creating a wider drainage pathway. These procedures carry more risk and potential for cosmetic changes. Variations include leaving a bone bridge to support soft tissues or combining endonasal and extranasal approaches.
Endonasal approaches to the frontal sinus in children without surgical optics (microscope or endoscope) are generally not successful due to the technical difficulty and risk of operating "blindly." Modern procedures emphasize microscopic or endoscopic control for precise removal of anterior ethmoid cells and creation of a large frontonasal communication. Postoperatively, drainage tubes (e.g., from PTFE or heterogeneous peritoneum, considered less traumatic than rubber) may be placed, and the sinus can be washed with antibiotics or other medications. Such tubes are typically removed after about 3 weeks.
Prior to any major frontal sinus surgery, thorough radiological assessment (X-rays in 2 planes, CT scan of paranasal sinuses) is crucial to define sinus size, wall integrity, and relationship to critical structures.
Adjunctive and Home Care Measures
- Rest: Adequate rest helps the body fight infection.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus.
- Humidification: Using a humidifier or inhaling steam can soothe nasal passages and loosen secretions.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the forehead can help relieve pain.
- Elevating the Head: Sleeping with the head elevated can promote sinus drainage.
- For allergic attacks, hot foot baths (1 tablespoon dry mustard in 6 liters hot water) or mustard plasters on the calves have been traditionally used for reflex reduction of nasal hyperemia and edema. Intranasal novocaine blockade (1 ml of 0.5-1% novocaine solution into the mucosa of lower or middle turbinates) has also been described. Sedatives like Belladonna tincture with Valerian (up to 10 drops 3 times a day) or 0.1% aqueous atropine solution (up to 6 drops 2 times a day orally for profuse watery secretions) were historical remedies.
Potential Complications of Frontal Sinusitis
Due to its location, untreated or inadequately treated frontal sinusitis can lead to serious, even life-threatening, complications:
- Orbital Complications:
- Preseptal (Periorbital) Cellulitis: Inflammation and infection of the tissues in front of the orbital septum.
- Orbital Cellulitis: Infection spreads behind the orbital septum into the orbit itself, causing eyelid swelling, redness, pain with eye movements, proptosis (bulging eye), and potentially vision loss.
- Subperiosteal Abscess: Collection of pus between the bone of the orbit and the periosteum.
- Orbital Abscess: Pus collection within the orbital tissues.
- Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis: A rare but very serious condition involving a blood clot in the cavernous sinus at the base of the brain, often leading to severe neurological deficits.
- Intracranial Complications:
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- Epidural Abscess: Pus collection between the dura mater (outer brain lining) and the skull.
- Subdural Abscess/Empyema: Pus collection beneath the dura mater.
- Brain Abscess: Localized collection of pus within the brain tissue.
- Bony Complications:
- Osteomyelitis of the Frontal Bone (Pott's Puffy Tumor): Infection of the frontal bone, leading to a soft, boggy swelling on the forehead.
- Mucocele or Pyocele: A mucocele is a mucus-filled, expansile cyst that forms due to chronic obstruction of the sinus ostium. If it becomes infected, it is called a pyocele. These can gradually expand and erode surrounding bone.
- Chronic Sinusitis: Acute episodes can transition into chronic inflammation if not fully resolved.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent these severe outcomes.
Prevention Strategies
While not all cases of frontal sinusitis can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Prompt Treatment of URIs: Manage colds and flu effectively to prevent them from progressing to sinus infections.
- Good Hygiene: Frequent handwashing can reduce the spread of viruses and bacteria.
- Manage Allergies: Effective control of allergic rhinitis can prevent chronic nasal inflammation and obstruction.
- Avoid Nasal Irritants: Minimize exposure to cigarette smoke, pollution, and strong chemical fumes.
- Use a Humidifier: Especially in dry environments, to keep nasal passages moist.
- Nasal Saline Irrigation: Regular use can help keep nasal passages clear, especially for those prone to sinus issues or with allergies.
- Stay Hydrated: Helps to keep mucus thin.
- Address Anatomical Issues: If significant structural abnormalities (e.g., deviated septum, polyps) contribute to recurrent sinusitis, surgical correction may be considered.
- Influenza Vaccination: Annual flu shots can help prevent influenza, a common precursor to sinusitis.
References
- Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS, et al. Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015 Apr;152(2 Suppl):S1-S39.
- Chow AW, Benninger MS, Brook I, et al. IDSA clinical practice guideline for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in children and adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Apr;54(8):e72-e112.
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020 (EPOS 2020). Rhinology. 2020 Feb 20;58(Suppl S29):1-464.
- Benninger MS, Ferguson BJ, Hadley JA, et al. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003 Sep;129(3 Suppl):S1-S32.
- Hwang PH, Getz A. Complications of rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2006 Feb;39(1):167-81, vii.
- Lund VJ. Diagnosis and treatment of nasal polyps. BMJ. 1995 Nov 18;311(7016):1411-4.
- Anand VK. Epidemiology and economic impact of rhinosinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 2004 May;193:3-5.
See also
Nasal cavity diseases:
- Runny nose, acute rhinitis, rhinopharyngitis
- Allergic rhinitis and sinusitis, vasomotor rhinitis
- Chlamydial and Trichomonas rhinitis
- Chronic rhinitis: catarrhal, hypertrophic, atrophic
- Deviated nasal septum (DNS) and nasal bones deformation
- Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
- External nose diseases: furunculosis, eczema, sycosis, erysipelas, frostbite
- Gonococcal rhinitis
- Changes of the nasal mucosa in influenza, diphtheria, measles and scarlet fever
- Nasal foreign bodies (NFBs)
- Nasal septal cartilage perichondritis
- Nasal septal hematoma, nasal septal abscess
- Nose injuries
- Ozena (atrophic rhinitis)
- Post-traumatic nasal cavity synechiae and choanal atresia
- Nasal scabs removing
- Rhinitis-like conditions (runny nose) in adolescents and adults
- Rhinogenous neuroses in adolescents and adults
- Smell (olfaction) disorders
- Subatrophic, trophic rhinitis and related pathologies
- Nasal breathing and olfaction (sense of smell) disorders in young children
Paranasal sinuses diseases:
- Acute and chronic frontal sinusitis (frontitis)
- Acute and chronic sphenoid sinusitis (sphenoiditis)
- Acute ethmoiditis (ethmoid sinus inflammation)
- Acute maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Chronic ethmoid sinusitis (ethmoiditis)
- Chronic maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Infantile maxillary sinus osteomyelitis
- Nasal polyps
- Paranasal sinuses traumatic injuries
- Rhinogenic orbital and intracranial complications
- Tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses, sarcoidosis