Nasal septal cartilage perichondritis
- Understanding Nasal Septal Cartilage Perichondritis
- Symptoms and Clinical Presentation of Septal Perichondritis
- Diagnosis of Nasal Septal Perichondritis
- Treatment of Nasal Septal Cartilage Perichondritis
- Potential Complications
- Differential Diagnosis of Septal Swelling and Pain
- Prevention and When to Seek Urgent Care
- References
Understanding Nasal Septal Cartilage Perichondritis
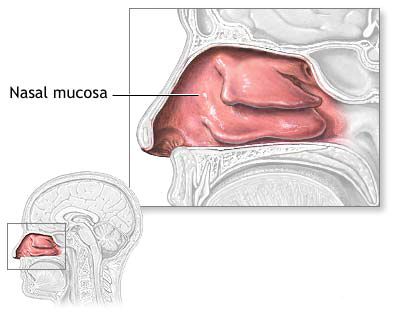
Nasal septal perichondritis is an inflammation of the perichondrium, which is the connective tissue membrane covering the nasal septal cartilage (specifically the quadrangular cartilage). This condition can lead to serious consequences, including necrosis (death) of the underlying cartilage and subsequent nasal deformities if not treated promptly and effectively.
Pathophysiology and Common Causes
The most common cause of perichondritis of the nasal septum in children, as well as adults, is **nasal trauma**. Trauma can lead to the formation of a nasal septal hematoma (a collection of blood between the perichondrium and the cartilage) or a nasal septal abscess (an infected hematoma or pus collection in the same plane). Both hematoma and abscess disrupt the blood supply from the perichondrium to the avascular septal cartilage. This impaired blood supply, combined with the inflammatory process of perichondritis itself (often caused by bacterial infection spreading from the hematoma/abscess or introduced at the time of trauma), can lead to necrosis of the quadrangular cartilage.
Other causes and predisposing factors include:
- Complication of Infections: Nasal septal perichondritis can arise as a complication of severe nasal infections, sinusitis, or even systemic infections that spread to the nasal septum.
- Extension from Osteomyelitis: Osteomyelitis (bone infection) of the upper jaw (maxilla) can rarely extend to involve the nasal septum.
- Chronic Specific Granulomatous Diseases: Conditions like tuberculosis, syphilis, or leprosy can involve the nasal septum and lead to chronic inflammation and perichondritis, though these are less common in many regions today.
- Post-Surgical Complication: Following nasal septal surgery (e.g., septoplasty), if infection or hematoma occurs.
- Nasal Piercings: Improperly performed or infected nasal piercings involving the septum.
- Systemic Inflammatory Conditions: Rarely, conditions like relapsing polychondritis can affect cartilage throughout the body, including the nasal septum.
Associated Conditions
As noted, nasal septal perichondritis is frequently linked with:
- Nasal Septal Hematoma: Often the precursor, providing a medium for bacterial growth.
- Nasal Septal Abscess: Represents an established infection within the subperichondrial space, directly causing perichondritis.
The inflammation of the perichondrium itself further compromises the cartilage, creating a vicious cycle that can rapidly lead to cartilage destruction.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation of Nasal Septal Cartilage Perichondritis
Nasal septal perichondritis is characterized by a combination of local and sometimes systemic symptoms:
- Severe Nasal Pain: Often intense and localized to the nose, particularly the septum. The pain may be throbbing in nature if an abscess is present.
- Nasal Obstruction: Significant difficulty breathing through one or both nostrils due to swelling of the nasal septum. This can be bilateral if both sides of the perichondrium are involved.
- Fever: Body temperature is often elevated, especially if there is an underlying abscess or significant infection.
- Swelling of the Nasal Septum: On examination (rhinoscopy), the cartilaginous part of the nasal septum appears diffusely swollen, erythematous (red), and exquisitely tender. The swelling is typically firm or indurated, distinguishing it from the fluctuant swelling of an uncomplicated hematoma (though perichondritis often coexists with an abscess, which would be fluctuant).
- External Nasal Swelling and Redness: The external nose, particularly the tip and columella, may become swollen, red, and tender.
- Nasal Discharge: May be present, ranging from serosanguineous to frankly purulent if an abscess is draining or associated with sinusitis.
- Headache and Malaise: General systemic symptoms can accompany the local inflammation.
- Tenderness of Regional Lymph Nodes: Submandibular lymph nodes may be enlarged and tender.
If perichondritis leads to cartilage necrosis, a saddle nose deformity (collapse of the nasal bridge) can develop over time as the structural support of the septum is lost.
Diagnosis of Nasal Septal Perichondritis
The diagnosis of nasal septal perichondritis is primarily clinical, based on the patient's history and physical examination findings. Key diagnostic elements include:
- History: A history of recent nasal trauma, previous septal hematoma or abscess, nasal surgery, or underlying systemic conditions is important.
- Physical Examination (Anterior Rhinoscopy/Nasal Endoscopy): Reveals diffuse, erythematous, tender swelling of the nasal septum, typically involving the cartilaginous portion. The mucosa may appear thickened and inflamed. If an abscess is present, fluctuance may be detected on palpation with a cotton-tipped applicator.
- Needle Aspiration: If an abscess is suspected beneath the inflamed perichondrium, diagnostic needle aspiration can be attempted. However, in established perichondritis without a large liquid collection, aspiration may not yield fluid. If pus is obtained, it should be sent for Gram stain, culture, and antibiotic sensitivity.
- Imaging Studies:
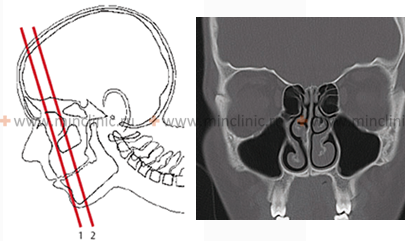
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: While not always necessary for uncomplicated perichondritis, a CT scan of the nose and paranasal sinuses can be useful to assess the extent of inflammation, identify an underlying septal abscess or hematoma, evaluate for associated sinusitis, detect cartilage destruction or sequestra, and rule out other pathologies. It can help diagnose the source of perichondritis if it's related to osteomyelitis or sinus disease.
- MRI: May be more sensitive for detecting early cartilage changes or soft tissue inflammation.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may show an elevated white blood cell count (leukocytosis) and inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP) if significant infection is present.
Treatment of Nasal Septal Cartilage Perichondritis
Nasal septal perichondritis requires prompt and aggressive treatment to prevent cartilage necrosis and subsequent nasal deformity. Management typically involves a combination of medical and, if necessary, surgical approaches.
Conservative Management (Primarily for early/mild cases or adjunctive)
- Systemic Antibiotics: Broad-spectrum antibiotics that cover common pathogens (especially *Staphylococcus aureus*, including MRSA if prevalent, and Streptococci) should be started immediately. Intravenous administration may be necessary for severe infections. Antibiotic choice can be tailored once culture and sensitivity results are available (if pus was obtained).
- Analgesics: For pain relief (e.g., NSAIDs, acetaminophen).
- Warm Compresses: May provide some symptomatic relief and promote local blood flow.
- Nasal Decongestants: Topical or oral decongestants may be used cautiously for a short period to improve nasal breathing if significant mucosal edema is present, but their role in primary perichondritis is limited.
Surgical Intervention
If conservative treatment fails to resolve the inflammation quickly, if there is evidence of an underlying septal abscess, or if cartilage necrosis is suspected, surgical intervention is often necessary. The primary goals of surgery are to:
- Drain Purulent Collections: If a septal abscess is present, it must be incised and drained urgently.
- Debride Necrotic Tissue: Remove any devitalized or necrotic cartilage and infected perichondrium to control the infection and promote healing. The excision of the affected cartilaginous septum should extend into healthy cartilage tissue.
- Address Underlying Causes: If the perichondritis is secondary to osteomyelitis of adjacent nasal bones, debridement of necrotic bone (sequestrectomy, often using a bone spoon or curette) is also performed.
- Ensure Adequate Drainage: Placement of small drains or packing may be necessary to prevent re-accumulation of fluid or pus.
Surgery is typically performed under local or general anesthesia. The aim is to remove all infected and non-viable tissue while preserving as much healthy structural support as possible.
Potential Complications
Untreated or inadequately treated nasal septal perichondritis can lead to severe and often irreversible complications:
- Nasal Septal Cartilage Necrosis: Destruction of the quadrangular cartilage.
- Saddle Nose Deformity: Collapse of the cartilaginous nasal dorsum due to loss of septal support, resulting in a characteristic depression of the nasal bridge. This is a significant cosmetic and sometimes functional deformity.
- Septal Perforation: A hole develops in the nasal septum, which can cause crusting, whistling, and recurrent epistaxis.
- Spread of Infection: Rarely, infection can spread to adjacent structures, potentially causing:
- Orbital complications (e.g., cellulitis).
- Intracranial complications (e.g., cavernous sinus thrombosis, meningitis - though very rare from isolated septal perichondritis).
- Chronic Nasal Obstruction: Due to scarring, persistent swelling, or septal deformity.
- Cosmetic Deformity of the External Nose.
Prompt and aggressive treatment is essential to minimize these risks.
Differential Diagnosis of Septal Swelling and Pain
When a patient presents with painful swelling of the nasal septum, several conditions should be considered:
| Condition | Key Differentiating Features |
|---|---|
| Nasal Septal Perichondritis | Diffuse, erythematous, tender, often firm swelling of septal cartilage; fever, nasal obstruction, severe pain. Often follows trauma, hematoma, or abscess. |
| Nasal Septal Hematoma | History of trauma; bilateral, smooth, fluctuant, reddish/bluish septal swelling; severe obstruction; pain. Aspiration yields blood. Can lead to perichondritis if untreated or infected. |
| Nasal Septal Abscess | Often follows hematoma; similar swelling but more intensely erythematous, exquisitely tender, fluctuant; high fever, severe pain. Aspiration yields pus. Always associated with perichondritis. |
| Severe Acute Rhinitis with Septal Mucositis | Diffuse nasal mucosal inflammation, discharge, congestion. Septal mucosa may be swollen and tender, but distinct perichondrial involvement/cartilage focus is less likely unless complicated. |
| Nasal Furunculosis (if involving septal vestibule) | Localized, painful, erythematous nodule/pustule at a hair follicle on the anterior septum or vestibule. More superficial. |
| Deviated Nasal Septum (Acute Trauma) | History of trauma; septal deviation is firm, not fluctuant, unless a hematoma is also present. |
| Relapsing Polychondritis | Rare systemic autoimmune disease causing inflammation of cartilage throughout the body (ears, nose, joints, respiratory tract). Nasal involvement causes pain, swelling, potential for saddle nose. Often recurrent episodes. |
| Granulomatous Diseases (e.g., GPA/Wegener's, Sarcoidosis, Tuberculosis) | Chronic inflammation, crusting, ulceration, potential for septal perforation or saddle nose. Systemic symptoms may be present. Biopsy is key. |
Prevention and When to Seek Urgent Care
Prevention primarily involves:
- Prompt and adequate drainage of any nasal septal hematoma to prevent it from becoming infected and leading to perichondritis/abscess.
- Careful management of nasal trauma to identify and treat septal injuries early.
- Aseptic technique during nasal surgeries or procedures.
It is crucial to seek **urgent medical attention (preferably from an ENT specialist or in an emergency department)** if you suspect nasal septal perichondritis, particularly if experiencing:
- Severe, worsening nasal pain.
- Progressive bilateral nasal obstruction.
- Fever associated with nasal pain and swelling.
- Redness and swelling of the external nose, especially the tip or bridge, following trauma or nasal infection.
- Any signs of a septal hematoma or abscess.
Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are paramount to prevent cartilage destruction and long-term deformities like saddle nose.
References
- Ginsburg CM. Nasal septal hematoma. Pediatr Rev. 1998 Apr;19(4):142-3. (Context for precursor condition)
- Alshaikh N, Lo S. Nasal septal abscess in children: from diagnosis to management and prevention. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011 May;75(5):737-44. (Closely related condition often involving perichondritis)
- Dawood M, Elsherif M, Elsherif S. Nasal Septal Perichondritis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-.
- Cantrell RW, Gussen R. Perichondritis. Its Eetioogy, pathology, and treatment. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1978 Feb;11(1):27-37. (General perichondritis context)
- Ambrus PS, Eavey RD, Pizzuto MP, et al. Management of nasal septal hematoma and abscess. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991 Jun;117(6):681-3.
- Kao CH. Nasal septal abscess: a review of 11 cases. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2000 Aug;16(8):410-4.
- Pasha R, Zulqarnain. Nasal Septal Abscess Complicating Perichondritis: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Cureus. 2018 Jan 24;10(1):e2105.
See also
Nasal cavity diseases:
- Runny nose, acute rhinitis, rhinopharyngitis
- Allergic rhinitis and sinusitis, vasomotor rhinitis
- Chlamydial and Trichomonas rhinitis
- Chronic rhinitis: catarrhal, hypertrophic, atrophic
- Deviated nasal septum (DNS) and nasal bones deformation
- Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
- External nose diseases: furunculosis, eczema, sycosis, erysipelas, frostbite
- Gonococcal rhinitis
- Changes of the nasal mucosa in influenza, diphtheria, measles and scarlet fever
- Nasal foreign bodies (NFBs)
- Nasal septal cartilage perichondritis
- Nasal septal hematoma, nasal septal abscess
- Nose injuries
- Ozena (atrophic rhinitis)
- Post-traumatic nasal cavity synechiae and choanal atresia
- Nasal scabs removing
- Rhinitis-like conditions (runny nose) in adolescents and adults
- Rhinogenous neuroses in adolescents and adults
- Smell (olfaction) disorders
- Subatrophic, trophic rhinitis and related pathologies
- Nasal breathing and olfaction (sense of smell) disorders in young children
Paranasal sinuses diseases:
- Acute and chronic frontal sinusitis (frontitis)
- Acute and chronic sphenoid sinusitis (sphenoiditis)
- Acute ethmoiditis (ethmoid sinus inflammation)
- Acute maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Chronic ethmoid sinusitis (ethmoiditis)
- Chronic maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Infantile maxillary sinus osteomyelitis
- Nasal polyps
- Paranasal sinuses traumatic injuries
- Rhinogenic orbital and intracranial complications
- Tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses, sarcoidosis