Acute maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Understanding Acute Maxillary Sinusitis (Rhinosinusitis)
- Symptoms of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis
- Diagnosis of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis
- Treatment of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis
- Differential Diagnosis of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis
- Potential Complications
- Prevention Strategies
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- References
Understanding Acute Maxillary Sinusitis (Rhinosinusitis)
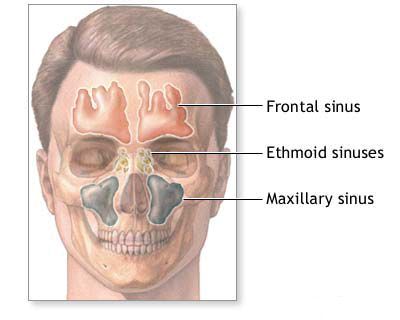
Acute maxillary sinusitis, a common form of acute rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucosal lining of the maxillary sinuses (the air-filled cavities located within the cheekbones, on either side of the nose). This condition typically has a duration of less than four weeks. It often arises as a complication of a viral upper respiratory infection (URI) but can also have bacterial or, rarely, fungal origins.
Pathophysiology and Common Causes
The maxillary sinuses drain into the nasal cavity through a small opening called the maxillary ostium, located in the middle meatus. Acute maxillary sinusitis develops when this ostium becomes blocked, leading to impaired ventilation and drainage of mucus from the sinus. This stasis of secretions creates an environment conducive to viral replication and/or secondary bacterial overgrowth.
Common causes and predisposing factors include:
- Viral Upper Respiratory Infections (URIs): The most common cause, with viruses like rhinovirus, influenza virus, and parainfluenza virus leading to mucosal inflammation and ostial obstruction.
- Bacterial Infections: Often secondary to a viral URI. Common bacterial pathogens include *Streptococcus pneumoniae*, *Haemophilus influenzae*, and *Moraxella catarrhalis*.
- Allergic Rhinitis: Allergic inflammation can cause chronic mucosal swelling, predisposing to sinus blockage.
- Anatomical Obstructions: Deviated nasal septum, nasal polyps, concha bullosa (aerated middle turbinate), or hypertrophied turbinates can impair sinus drainage.
- Odontogenic (Dental) Infections: Infections originating from the roots of the upper teeth (premolars and molars), whose apices are close to the maxillary sinus floor, can spread directly into the sinus. This often leads to unilateral maxillary sinusitis with foul-smelling discharge.
- Barotrauma: Changes in atmospheric pressure (e.g., during flying or scuba diving) can sometimes cause sinus ostial blockage.
- Impaired Mucociliary Clearance: Conditions like cystic fibrosis or primary ciliary dyskinesia.
- Immunocompromised States.
Clinical Course Variations
The clinical presentation of acute maxillary sinusitis can vary. While classic symptoms include nasal congestion, facial pain/pressure, and purulent discharge, subjective symptoms can sometimes be mild. In early childhood, the disease may even be relatively asymptomatic or present with non-specific signs, making diagnosis more challenging.
In cases of acute sinusitis with severe symptoms, individuals may experience a significant increase in body temperature, signs of systemic intoxication (malaise, fatigue), swelling of the cheek and periorbital area (around the eye) on the affected side, profuse purulent nasal discharge, and intense pain in the sinus area. Sometimes, acute sinusitis manifests initially with symptoms of a preceding pathology, such as influenza or other acute respiratory diseases. Prolonged forms of acute inflammation of the maxillary sinus with a sluggish or indolent course can also occur, potentially bridging into subacute or chronic sinusitis if not adequately resolved.
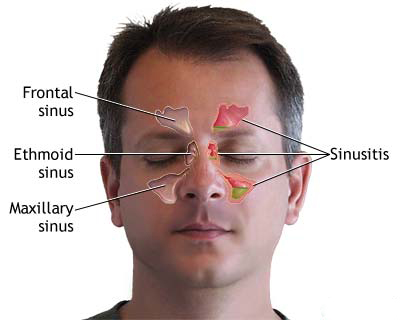
Symptoms of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis (Rhinosinusitis)
The hallmark symptoms of acute maxillary sinusitis include a combination of local nasal and facial symptoms, and sometimes systemic manifestations:
- Facial Pain or Pressure: Typically localized over the affected maxillary sinus (cheek area). The pain may be described as dull, aching, or a feeling of fullness or heaviness. It often worsens when bending forward or lying down. Tenderness may be elicited on palpation over the cheek.
- Nasal Congestion or Obstruction: Difficulty breathing through the nose on one or both sides.
- Nasal Discharge:
- Anterior Rhinorrhea: Runny nose with discharge that is often initially clear or watery (in viral cases) but frequently becomes thick, opaque, and purulent (yellowish or greenish) if a bacterial infection develops.
- Posterior Nasal Drip: Sensation of mucus dripping down the back of the throat.
- Reduced or Lost Sense of Smell (Hyposmia/Anosmia).
- Fever: May be present, especially in bacterial sinusitis, along with malaise and fatigue.
- Headache: Often frontal or generalized.
- Dental Pain: Pain in the upper teeth (premolars/molars) on the affected side, as their roots are close to the sinus floor.
- Cough: Often worse at night, due to post-nasal drip.
- Ear Fullness or Pain: Due to associated Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Halitosis (Bad Breath).
In severe cases, as mentioned, swelling of the cheek and periorbital tissues on the affected side can occur, along with more pronounced systemic signs of intoxication.
Rhinoscopic Findings
Rhinoscopic examination (anterior rhinoscopy or nasal endoscopy) of a patient with acute maxillary sinusitis may reveal:
- Inflammatory changes in the nasal mucosa, such as redness (hyperemia) and swelling (edema), especially in the region of the middle nasal meatus.
- Purulent or mucopurulent discharge draining from the maxillary sinus ostium in the middle meatus. However, inflammatory signs may sometimes be absent or minimal, especially if the ostium is completely blocked.
- The patency and condition of the natural sinus openings significantly influence the course of acute sinusitis and the consistency of pathological contents within the sinuses.
It's noteworthy that prior treatment with antibiotics for a preceding illness (e.g., a viral URI) can sometimes mask or alter the typical clinical course of acute maxillary sinusitis, potentially making the diagnosis less straightforward if a full picture is not obtained.
Diagnosis of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis
The diagnosis of acute maxillary sinusitis is primarily clinical, based on the presence of characteristic symptoms and signs. According to guidelines like EPOS (European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps) and IDSA (Infectious Diseases Society of America), acute rhinosinusitis is defined by the sudden onset of two or more symptoms, one of which should be either nasal blockage/congestion/obstruction or nasal discharge (anterior/posterior rhinorrhea), ± facial pain/pressure, ± reduction/loss of smell, lasting <12 weeks.
- Clinical Criteria for Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis (ABRS): A bacterial cause is more likely if:
- Symptoms persist without improvement for ≥10 days.
- Severe symptoms occur at onset (e.g., high fever ≥39°C or 102°F and purulent nasal discharge or facial pain for at least 3-4 consecutive days).
- "Double sickening" or worsening of symptoms after initial improvement of a typical viral URI.
- Physical Examination: As described above (anterior rhinoscopy/nasal endoscopy) looking for mucosal inflammation and purulent discharge from the middle meatus. Facial tenderness over the maxillary sinus may be present.
- Imaging Studies:
- Routine imaging (X-rays or CT scans) is **not recommended** for uncomplicated acute maxillary sinusitis that meets clinical diagnostic criteria.
- Imaging (preferably a CT scan of the paranasal sinuses) is indicated if:
- Complications are suspected (e.g., orbital, intracranial).
- The diagnosis is uncertain.
- The patient is immunocompromised.
- Symptoms are severe or persistent despite appropriate medical therapy.
- Recurrent acute sinusitis occurs, to evaluate for underlying anatomical issues.
- Microbiological Cultures: Not routinely performed for uncomplicated acute sinusitis. Endoscopically guided cultures from the middle meatus may be considered in patients who fail initial therapy, in severe infections, or in immunocompromised individuals to guide targeted antibiotic therapy.
Treatment of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis (Rhinosinusitis)
The goals of treatment are to relieve symptoms, promote sinus drainage, eradicate infection if bacterial, and prevent complications or progression to chronic sinusitis.
Medical Management
- Symptomatic Relief (for Viral or Mild Bacterial Sinusitis):
- Analgesics and Antipyretics: Acetaminophen or NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) for pain and fever.
- Nasal Saline Irrigation: Helps to clear nasal passages, remove secretions, and improve mucociliary function.
- Topical Nasal Decongestants: Sprays or drops containing agents like oxymetazoline or phenylephrine (e.g., ephedrine, naphthyzine were historical mentions) can provide temporary relief from nasal congestion. Use should be limited to 3-5 days to avoid rebound congestion (rhinitis medicamentosa).
- Oral Decongestants: Pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine may offer some benefit for congestion but should be used with caution in patients with hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions.
- Intranasal Corticosteroids: Can help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms, particularly nasal congestion. They may be used as monotherapy for mild symptoms or as an adjunct to antibiotics in ABRS.
- Mucolytics (e.g., guaifenesin): May help thin mucus, although evidence for their efficacy in acute sinusitis is limited.
- Antihistamines: Generally not recommended unless there is a clear coexisting allergic rhinitis, as they can thicken secretions.
- Antibiotics (for suspected Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis - ABRS):
- Indicated based on clinical criteria suggesting a bacterial infection (see Diagnosis section).
- Initial empiric therapy often involves amoxicillin or amoxicillin-clavulanate. Alternatives for penicillin-allergic patients include doxycycline (not for young children), levofloxacin/moxifloxacin (for adults), or clindamycin plus a cephalosporin.
- Duration of therapy is typically 5-10 days for uncomplicated ABRS in adults, and 10-14 days in children.
- Physiotherapy Procedures (Historical/Adjunctive): Modalities like UHF currents, microwave therapy, or Sollux lamp (infrared heat) have been used in some settings with the aim of reducing inflammation, but their role in modern evidence-based guidelines is minimal for acute sinusitis.
Interventional Procedures (Sinus Puncture/Lavage)
Maxillary sinus puncture (antral lavage or washout) is an invasive procedure that involves inserting a trocar or needle into the maxillary sinus (usually through the inferior meatus or canine fossa) to aspirate its contents and irrigate the sinus cavity. It is **not routinely indicated** for uncomplicated acute maxillary sinusitis.
It may be considered in specific situations, such as:
- Severe pain unresponsive to analgesics.
- Failure to respond to appropriate antibiotic therapy.
- Suspected or confirmed suppurative complications.
- Immunocompromised patients where microbiological diagnosis is critical.
- To obtain material for culture in refractory cases.
This procedure provides immediate relief of pressure and allows for direct sampling but carries risks (pain, bleeding, infection, damage to adjacent structures) and is generally reserved for select cases by experienced practitioners.
Surgical Treatment for Complications
Surgical intervention is primarily reserved for the management of orbital or intracranial complications of acute maxillary sinusitis. This typically involves endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) to drain infected sinuses and any associated abscesses (e.g., orbital subperiosteal abscess). Urgent surgical drainage is often necessary for these severe complications.
Differential Diagnosis of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis
It's important to differentiate acute maxillary sinusitis from other conditions presenting with similar facial pain or nasal symptoms:
| Condition | Key Differentiating Features |
|---|---|
| Acute Maxillary Sinusitis | Facial pain/pressure over cheek, nasal congestion, purulent discharge (often unilateral initially), fever, dental pain. Positive findings on endoscopy. Responds to sinusitis treatment. |
| Viral Upper Respiratory Infection (Common Cold) | More diffuse symptoms: sore throat, cough, sneezing, watery/mucoid rhinorrhea. Facial pain less prominent. Usually self-limiting within 7-10 days. |
| Allergic Rhinitis | Itching (nose, eyes, palate), sneezing, clear watery rhinorrhea, nasal congestion. Often seasonal or related to specific allergen exposure. Usually no fever or purulent discharge unless secondarily infected. |
| Odontogenic Infection (Dental Abscess) | Pain localized to a specific upper tooth, gum swelling, sensitivity to percussion on the tooth. May cause secondary maxillary sinusitis, often unilateral and foul-smelling. Dental X-rays are key. |
| Migraine or Tension-Type Headache | Headache is primary symptom. Migraine often unilateral, throbbing, with nausea/photophobia. Tension headache often bilateral, band-like. "Sinus headache" can be a migraine variant; purulent discharge usually absent. |
| Trigeminal Neuralgia | Paroxysmal, severe, electric shock-like facial pain in trigeminal nerve distribution (V2 for maxillary). Triggered by light touch. No nasal discharge/congestion. |
| Acute Ethmoiditis/Frontal Sinusitis | Pain localized more between eyes/root of nose (ethmoiditis) or forehead (frontal sinusitis). Often coexist with maxillary sinusitis. |
Potential Complications
While uncommon with appropriate treatment, acute maxillary sinusitis can lead to complications, particularly if severe or untreated:
- Orbital Complications: Preseptal cellulitis, orbital cellulitis, subperiosteal abscess, orbital abscess (less common from isolated maxillary sinusitis compared to ethmoiditis, but possible).
- Intracranial Complications: Extremely rare from isolated maxillary sinusitis, but include meningitis, epidural/subdural abscess, brain abscess, cavernous sinus thrombosis.
- Osteomyelitis: Infection of the maxillary bone (especially in infants or immunocompromised individuals).
- Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis: Acute infection may fail to resolve and transition into a chronic state.
- Mucocele/Pyocele Formation: Due to chronic ostial blockage.
Prevention Strategies
Measures to reduce the risk of developing acute maxillary sinusitis include:
- Prompt Management of URIs: Rest, hydration, symptomatic relief for common colds.
- Good Hygiene: Frequent handwashing to prevent viral spread.
- Allergy Control: Effective management of allergic rhinitis.
- Avoidance of Nasal Irritants: Such as cigarette smoke and pollutants.
- Humidification: Using a humidifier in dry environments.
- Dental Health: Regular dental check-ups and prompt treatment of dental infections.
- Vaccinations: Annual influenza vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine (for high-risk individuals) can prevent some primary infections that predispose to sinusitis.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Medical evaluation is recommended if an individual experiences:
- Symptoms of sinusitis lasting longer than 10 days without improvement.
- Severe symptoms from the outset (high fever, intense facial pain, purulent discharge for 3-4 days).
- "Double sickening": initial improvement of cold symptoms followed by sudden worsening.
- Signs of potential complications: swelling or redness around the eye, vision changes, severe headache, stiff neck, altered mental status.
- Recurrent episodes of acute sinusitis.
- Symptoms in an immunocompromised individual.
Early and appropriate management can lead to faster recovery and reduce the risk of complications or chronic disease.
References
- Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS, et al. Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015 Apr;152(2 Suppl):S1-S39.
- Chow AW, Benninger MS, Brook I, et al. IDSA clinical practice guideline for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in children and adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Apr;54(8):e72-e112.
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020 (EPOS 2020). Rhinology. 2020 Feb 20;58(Suppl S29):1-464.
- Wald ER, Applegate KE, Bordley C, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of acute bacterial sinusitis in children aged 1 to 18 years. Pediatrics. 2013 Jul;132(1):e262-80.
- Ah-See KW, Evans AS. Sinusitis and its complications in the pediatric patient. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2007 Feb;54(1):117-32, viii.
- Brook I. Acute sinusitis in children. Pediatr Ann. 2007 Oct;36(10):630-5.
- Slavin RG, Spector SL, Bernstein IL, et al. The diagnosis and management of sinusitis: a practice parameter update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005 Dec;116(6 Suppl):S13-47.
See also
Nasal cavity diseases:
- Runny nose, acute rhinitis, rhinopharyngitis
- Allergic rhinitis and sinusitis, vasomotor rhinitis
- Chlamydial and Trichomonas rhinitis
- Chronic rhinitis: catarrhal, hypertrophic, atrophic
- Deviated nasal septum (DNS) and nasal bones deformation
- Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
- External nose diseases: furunculosis, eczema, sycosis, erysipelas, frostbite
- Gonococcal rhinitis
- Changes of the nasal mucosa in influenza, diphtheria, measles and scarlet fever
- Nasal foreign bodies (NFBs)
- Nasal septal cartilage perichondritis
- Nasal septal hematoma, nasal septal abscess
- Nose injuries
- Ozena (atrophic rhinitis)
- Post-traumatic nasal cavity synechiae and choanal atresia
- Nasal scabs removing
- Rhinitis-like conditions (runny nose) in adolescents and adults
- Rhinogenous neuroses in adolescents and adults
- Smell (olfaction) disorders
- Subatrophic, trophic rhinitis and related pathologies
- Nasal breathing and olfaction (sense of smell) disorders in young children
Paranasal sinuses diseases:
- Acute and chronic frontal sinusitis (frontitis)
- Acute and chronic sphenoid sinusitis (sphenoiditis)
- Acute ethmoiditis (ethmoid sinus inflammation)
- Acute maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Chronic ethmoid sinusitis (ethmoiditis)
- Chronic maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Infantile maxillary sinus osteomyelitis
- Nasal polyps
- Paranasal sinuses traumatic injuries
- Rhinogenic orbital and intracranial complications
- Tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses, sarcoidosis