Acute ethmoiditis (ethmoid sinus inflammation)
- Understanding Acute Ethmoiditis (Ethmoid Sinus Inflammation)
- Symptoms of Acute Ethmoiditis
- Diagnosis of Acute Ethmoiditis
- Treatment of Acute Ethmoiditis
- Differential Diagnosis of Acute Ethmoiditis
- Potential Complications of Acute Ethmoiditis
- Prevention Strategies
- When to Seek Urgent Medical Attention
- References
Understanding Acute Ethmoiditis (Ethmoid Sinus Inflammation)
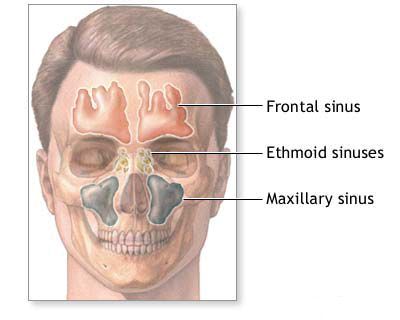
Acute ethmoiditis refers to an acute inflammation of the mucosal lining of the ethmoid sinuses. The ethmoid sinuses are a complex labyrinth of numerous small, interconnected air-filled cells located between the eyes and deep within the nose, at the roof of the nasal cavity. In childhood, ethmoiditis is often considered the most frequently involved sinus in cases of acute rhinosinusitis, partly because the ethmoid sinuses are relatively well-developed at birth compared to other paranasal sinuses like the frontal or sphenoid sinuses.
Prevalence and Pathophysiology
Acute ethmoiditis can develop at any age, from very early infancy to adulthood, though it is particularly common in children. The inflammation typically results from an obstruction of the narrow drainage pathways (ostia) of the ethmoid air cells, which open into the middle and superior meatus of the nasal cavity. This obstruction leads to an accumulation of mucus within the sinus cells, creating a favorable environment for viral or bacterial proliferation and subsequent infection.
Causes and Predisposing Factors
The primary causes of acute ethmoiditis are infections, with predisposing factors that compromise sinus ventilation and drainage:
- Viral Upper Respiratory Infections (URIs): Most cases of acute ethmoiditis begin as a common cold or other viral infection (e.g., influenza, adenovirus, rhinovirus). Viral inflammation causes swelling of the nasal and sinus mucosa, obstructing the ethmoid ostia.
- Bacterial Infections: Secondary bacterial infection often follows viral URIs if sinus obstruction persists. Common bacterial pathogens include *Streptococcus pneumoniae*, *Haemophilus influenzae*, and *Moraxella catarrhalis*.
- Allergic Rhinitis: Allergic inflammation can cause chronic mucosal swelling and predispose to sinus blockage.
- Anatomical Factors:
- Narrowness of the middle nasal meatus or natural ethmoid outflow tracts.
- Anomalies of the middle turbinate (e.g., concha bullosa - an aerated middle turbinate, paradoxical middle turbinate).
- Deviated nasal septum impinging on the middle meatus.
- Nasal polyps.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to cold air or irritants can exacerbate mucosal swelling.
- Impaired Mucociliary Clearance: Conditions that affect the normal cleansing mechanism of the sinuses, such as cystic fibrosis or primary ciliary dyskinesia.
- Immunodeficiency: Compromised immune status increases susceptibility to infections.
The ease with which nasal mucosal swelling occurs in children, coupled with their relatively smaller nasal passages, contributes to obstructed outflow of discharge and the development of ethmoiditis.
Symptoms of Acute Ethmoiditis (Ethmoid Sinus Inflammation)
The clinical presentation of acute ethmoiditis can vary with age.
Symptoms in Young Children (Under 2 Years)
In children under the age of 2 years, subjective symptoms of ethmoiditis are often difficult to elicit or are non-specific. Therefore, objective signs and findings from clinical examination become critically important for diagnosis. Common manifestations include:
- Systemic Symptoms:
- Increase in body temperature (fever), which may be high.
- Decreased appetite, poor feeding.
- Irritability, lethargy.
- Indigestion or gastrointestinal upset.
- Nasal Symptoms:
- Profuse nasal discharge, which can be watery, mucoid, or mucopurulent (thick, yellowish-green).
- Difficulty with nasal breathing, leading to mouth breathing, snoring, and feeding difficulties (as infants are obligate nasal breathers).
- Periorbital/Orbital Signs (due to proximity of ethmoids to the orbit):
- Swelling and edema (puffiness) at the medial (inner) edge of the orbit, near the root of the nose.
- Swelling of the upper eyelid, sometimes the lower eyelid as well.
- Skin hyperemia (redness) around the affected eye.
- Narrowing of the palpebral fissure (eye opening).
- In severe cases, proptosis (bulging of the eye) or limited eye movements may occur, indicating spread of infection into the orbit (orbital cellulitis or abscess), which is a serious complication.
Symptoms in Older Children and Adults
In older children and adults, symptoms are often more localized and specific:
- Facial Pain or Pressure: Pain or a feeling of pressure localized between the eyes, at the root of the nose, or radiating to the medial canthal area. The pain may worsen when bending forward or with eye movement.
- Headache: Often frontal or retro-orbital (behind the eyes).
- Nasal Congestion or Obstruction.
- Nasal Discharge: Purulent or mucopurulent, often with post-nasal drip.
- Reduced or Lost Sense of Smell (Hyposmia/Anosmia).
- Fever and Malaise.
- Tenderness: Tenderness to palpation over the ethmoid sinus area (medial to the eyes).
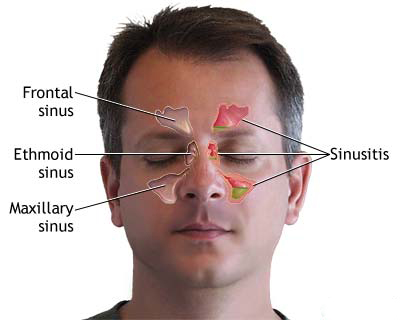
Diagnosis of Acute Ethmoiditis
The diagnosis of acute ethmoiditis is primarily clinical, based on history and physical examination. Imaging is not routinely required for uncomplicated cases but may be used if complications are suspected or the diagnosis is unclear.
- Clinical Examination:
- Anterior Rhinoscopy: Reveals sharply edematous (swollen) and hyperemic (red) nasal mucosa. After application of a topical decongestant (anemization) to the middle nasal meatus, abundant mucopurulent discharge can often be seen draining from the ethmoid region.
- Nasal Endoscopy: Provides a more detailed view of the middle and superior meatus, allowing direct visualization of pus draining from the ethmoid ostia and assessment for polyps or anatomical abnormalities.
- Assessment for periorbital/orbital signs (swelling, redness, proptosis, ophthalmoplegia).
- Imaging Studies:
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT of the paranasal sinuses is the preferred imaging modality if complications (e.g., orbital or intracranial extension) are suspected, if symptoms are severe or persistent despite treatment, or in recurrent cases. It will show opacification or inflammatory fluid within the ethmoid air cells and any associated bony changes or complications.
- Plain X-rays: Radiographs of the sinuses (e.g., Waters, Caldwell views) may show clouding or opacification of the ethmoid sinuses but have limited sensitivity and specificity compared to CT and are less commonly used.
- Laboratory Tests: Generally not required for uncomplicated acute ethmoiditis. A complete blood count might show leukocytosis in bacterial infections. Cultures of nasal discharge are not routinely recommended for acute sinusitis unless infection is severe, recurrent, or unresponsive to initial therapy.
Acute ethmoiditis in young children, particularly with orbital signs, must be differentiated from **acute osteomyelitis of the upper jaw (maxilla)**. Maxillary osteomyelitis typically proceeds more violently, with a more pronounced increase in body temperature and more abundant purulent discharge often from only one half of the nose. On the first day of maxillary osteomyelitis, sharp swelling of the corresponding cheek and edema of the eyelids often appear. The nasolabial fold may be smoothed out, the angle of the mouth lowered, and the mobility of the upper lip limited. Intraorally, small infiltrates covered with hyperemic mucous membrane may appear on the alveolar process (from the vestibule of the mouth) and on the hard palate. These infiltrates can then progress to abscesses, which may open spontaneously, leaving fistulas with purulent discharge in the alveolar ridge, hard palate, or near the medial corner of the eye. Other conditions to differentiate include dacryocystitis (infection of the tear sac), preseptal or orbital cellulitis from other causes, and dental abscesses.
Treatment of Acute Ethmoiditis (Ethmoid Sinus Inflammation)
The primary goals of treating acute ethmoiditis are to relieve symptoms, promote drainage from the affected ethmoid sinuses, eradicate infection (if bacterial), restore normal nasal breathing, and prevent complications.
Medical Management
- Nasal Decongestion (Anemization): Actively and systematically promoting decongestion of the nasal mucosa is crucial to open the ethmoid drainage pathways.
- Topical decongestant nasal sprays or drops (e.g., oxymetazoline, xylometazoline, phenylephrine) are used for a short duration (typically 3-5 days) to reduce mucosal swelling.
- In a clinical setting, tampons or cotton pledgets moistened with a 0.1% adrenaline (epinephrine) solution may be carefully placed in the area of the middle nasal meatus for 5-10 minutes to achieve rapid and effective decongestion.
- Nasal Saline Irrigation: Regular rinsing of the nasal passages with isotonic or hypertonic saline solution helps to clear mucus, pus, and irritants, and improves mucociliary function.
- Analgesics and Antipyretics: Medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen are used to control pain and fever.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is suspected (e.g., symptoms persisting or worsening after 7-10 days, severe onset with high fever and purulent discharge, or "double sickening" - initial improvement followed by worsening), antibiotics are prescribed. Common choices include amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, or alternatives like cephalosporins or macrolides based on local resistance patterns and patient allergies. The duration is typically 7-14 days.
- Intranasal Corticosteroids: These can be helpful in reducing inflammation, especially if there is an underlying allergic component or significant mucosal edema.
- Mucus Aspiration and Instillation: With abundant discharge, the pathological contents from the inflamed ethmoid sinus area can be gently aspirated (suctioned) by a physician, followed by instillation of medications like 1% protargol solution (a mild silver proteinate antiseptic, historically used) into the nasal cavity.
- Supportive Care: Adequate hydration, rest, and use of a humidifier can help alleviate symptoms.
- Physiotherapy: Certain physical therapy modalities, such as local heat or shortwave diathermy, may be considered in some settings to promote resolution of inflammation, but their role is generally adjunctive.
Surgical Intervention (Rare in Uncomplicated Acute Cases)
Surgical intervention for uncomplicated acute ethmoiditis is rarely necessary. However, surgery (typically Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery - FESS) may be indicated in cases of:
- Failure of maximal medical therapy.
- Recurrent acute ethmoiditis.
- Development of orbital or intracranial complications (which require urgent surgical drainage and management).
- Presence of underlying anatomical abnormalities significantly predisposing to infection (e.g., extensive polyposis, severe concha bullosa obstructing drainage).
Differential Diagnosis of Acute Ethmoiditis
It's important to differentiate acute ethmoiditis from other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, especially in children:
| Condition | Key Differentiating Features |
|---|---|
| Acute Ethmoiditis | Pain/pressure between eyes/root of nose, nasal congestion, purulent discharge, fever. Periorbital swelling common in children. Endoscopy shows pus from middle/superior meatus. CT confirms ethmoid opacification. |
| Acute Maxillary Sinusitis | Cheek pain/pressure, dental pain, purulent discharge often from middle meatus. May coexist with ethmoiditis. |
| Acute Frontal Sinusitis | Severe forehead headache, tenderness over frontal sinus, fever. Often coexists with anterior ethmoiditis. |
| Acute Dacryocystitis | Inflammation/infection of the lacrimal sac; swelling, redness, tenderness at medial canthus; tearing; pus may be expressed from puncta. Usually no significant nasal discharge unless secondary. |
| Orbital/Preseptal Cellulitis (non-sinus origin) | Eyelid swelling, redness, warmth. May arise from skin infection or trauma. If orbital, proptosis and ophthalmoplegia may occur. Sinuses may be clear on imaging. |
| Infantile Maxillary Osteomyelitis | Severe facial/cheek swelling, systemic toxicity, dental involvement (loose teeth), fistulae. More severe bone involvement on imaging. (See specific section if detailed) |
| Nasal Furunculosis with Cellulitis | Localized boil/infection in nasal vestibule, can cause significant surrounding facial/periorbital swelling and redness. |
| Allergic Rhinitis (acute flare) | Nasal itching, sneezing, watery rhinorrhea, pale/boggy mucosa. Usually no fever or purulent discharge unless secondarily infected. |
Potential Complications of Acute Ethmoiditis
Due to the proximity of the ethmoid sinuses to the orbit and intracranial cavity, separated by thin bony walls (lamina papyracea medially from the orbit), acute ethmoiditis can lead to serious complications, especially in children:
- Orbital Complications (most common):
- Preseptal (Periorbital) Cellulitis: Inflammation and infection of the tissues anterior to the orbital septum. Eyelid swelling and redness, but usually normal vision and eye movements.
- Orbital Cellulitis: Infection spreads posterior to the orbital septum into the orbit. Causes proptosis (bulging eye), ophthalmoplegia (restricted or painful eye movements), chemosis (conjunctival swelling), and potentially decreased vision. This is an emergency.
- Subperiosteal Abscess: Collection of pus between the lamina papyracea and the periorbita (lining of the orbit). Causes significant proptosis and displacement of the eyeball.
- Orbital Abscess: Collection of pus within the orbital fat and tissues. Severe proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, and vision loss are common.
- Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis: Rare but life-threatening spread of infection to the cavernous sinus at the base of the brain.
- Intracranial Complications (rare):
- Meningitis
- Epidural abscess
- Subdural empyema
- Brain abscess
- Bony Complications: Osteitis or osteomyelitis of the ethmoid bones (rare).
- Spread to Other Sinuses: Development of pansinusitis.
- Chronic Ethmoiditis: Acute episodes can transition to chronic inflammation if not fully resolved.
Prompt recognition and treatment of acute ethmoiditis are crucial to prevent these potentially severe complications.
Prevention Strategies
While not all cases can be prevented, measures to reduce the risk of acute ethmoiditis include:
- Prompt Treatment of URIs: Managing common colds effectively.
- Good Hygiene: Frequent handwashing to reduce viral spread.
- Allergy Management: Effective control of allergic rhinitis to prevent chronic nasal inflammation.
- Avoidance of Nasal Irritants.
- Humidification: Especially in dry environments.
- Vaccinations: Routine childhood immunizations (e.g., against *Haemophilus influenzae* type b, *Streptococcus pneumoniae*) and annual influenza vaccination can prevent some primary infections that lead to sinusitis.
- Addressing Anatomical Predispositions: In cases of recurrent sinusitis due to significant anatomical issues, surgical correction may be considered.
When to Seek Urgent Medical Attention
Urgent medical evaluation is necessary if an individual (especially a child) with suspected acute ethmoiditis develops:
- Swelling or redness around the eye(s).
- Proptosis (bulging of the eye).
- Pain with eye movements or restricted eye movements.
- Changes in vision (double vision, decreased vision).
- Severe headache, especially if accompanied by neck stiffness or altered mental status.
- High fever unresponsive to antipyretics.
- Persistent vomiting or lethargy.
- Symptoms that worsen rapidly despite initial treatment.
These can be signs of orbital or intracranial complications requiring immediate, often hospital-based, management including imaging and potentially surgical intervention.
References
- Wald ER, Applegate KE, Bordley C, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of acute bacterial sinusitis in children aged 1 to 18 years. Pediatrics. 2013 Jul;132(1):e262-80.
- Chow AW, Benninger MS, Brook I, et al. IDSA clinical practice guideline for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in children and adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Apr;54(8):e72-e112.
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020 (EPOS 2020). Rhinology. 2020 Feb 20;58(Suppl S29):1-464.
- Chandler JR, Langenbrunner DJ, Stevens ER. The pathogenesis of orbital complications in acute sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1970 Sep;80(9):1414-28.
- Hartley BE, Shankar L, Muzzi E, et al. Paediatric acute rhinosinusitis: when is a CT scan necessary? Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1998 Nov 15;46(1-2):31-6.
- Sobol SE, Samadi DS, Kazahaya K, Tom LW. Orbital complications of sinusitis in children. J Otolaryngol. 2002 Feb;31(1):12-7.
- Brook I. Microbiology and antimicrobial treatment of orbital and intracranial complications of sinusitis in children and their management. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009 Jul;73(7):1183-6.
See also
Nasal cavity diseases:
- Runny nose, acute rhinitis, rhinopharyngitis
- Allergic rhinitis and sinusitis, vasomotor rhinitis
- Chlamydial and Trichomonas rhinitis
- Chronic rhinitis: catarrhal, hypertrophic, atrophic
- Deviated nasal septum (DNS) and nasal bones deformation
- Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
- External nose diseases: furunculosis, eczema, sycosis, erysipelas, frostbite
- Gonococcal rhinitis
- Changes of the nasal mucosa in influenza, diphtheria, measles and scarlet fever
- Nasal foreign bodies (NFBs)
- Nasal septal cartilage perichondritis
- Nasal septal hematoma, nasal septal abscess
- Nose injuries
- Ozena (atrophic rhinitis)
- Post-traumatic nasal cavity synechiae and choanal atresia
- Nasal scabs removing
- Rhinitis-like conditions (runny nose) in adolescents and adults
- Rhinogenous neuroses in adolescents and adults
- Smell (olfaction) disorders
- Subatrophic, trophic rhinitis and related pathologies
- Nasal breathing and olfaction (sense of smell) disorders in young children
Paranasal sinuses diseases:
- Acute and chronic frontal sinusitis (frontitis)
- Acute and chronic sphenoid sinusitis (sphenoiditis)
- Acute ethmoiditis (ethmoid sinus inflammation)
- Acute maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Chronic ethmoid sinusitis (ethmoiditis)
- Chronic maxillary sinusitis (rhinosinusitis)
- Infantile maxillary sinus osteomyelitis
- Nasal polyps
- Paranasal sinuses traumatic injuries
- Rhinogenic orbital and intracranial complications
- Tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses, sarcoidosis