Abscess
Understanding Abscesses
Definition and Formation
An abscess is a localized collection of pus (a thick fluid containing dead white blood cells, tissue debris, and microorganisms) that accumulates within a tissue, organ, or confined space in the body. It is a result of the body's inflammatory response to an infection, typically bacterial, which leads to the liquefaction and fusion of affected tissue, thereby forming a cavity filled with pus. This cavity is often surrounded by a wall of inflamed tissue (pyogenic membrane) that attempts to contain the infection.
Etiology and Pathogenesis
The primary cause of an abscess is the invasion of pyogenic (pus-forming) microbes into tissues. Common causative bacteria include *Staphylococcus aureus* (often MRSA - Methicillin-resistant *Staphylococcus aureus*), *Streptococcus pyogenes*, and various anaerobic bacteria. The routes of microbial entry include:
- Direct Inoculation: Through breaks in the skin or mucous membranes, such as abrasions, cuts, puncture wounds, or injections. Microorganisms can be introduced during accidental injuries or medical procedures (e.g., subcutaneous or intramuscular injections) if aseptic techniques are not strictly observed.
- Spread from an Existing Infection: An abscess can develop as a complication of acute purulent inflammation in any organ or tissue. Examples include:
- Skin infections like furunculosis (boils), carbuncles, or cellulitis/phlegmon.
- Inflamed lymph nodes (lymphadenitis).
- Organ-specific infections (e.g., lung abscess, liver abscess, dental abscess).
- Hematoma Suppuration: An abscess can form at the site of a pre-existing hemorrhage or hematoma (a collection of clotted blood) if it becomes secondarily infected.
- Hematogenous Metastasis: In cases of systemic bacteremia or sepsis (general purulent infection), bacteria can spread through the bloodstream and seed distant sites, leading to the formation of metastatic abscesses.
- Obstruction of Glandular Ducts: Blockage of ducts of sebaceous glands, sweat glands, or other glands can lead to retained secretions and subsequent infection and abscess formation (e.g., hidradenitis suppurativa, Bartholin's gland abscess).
Common Locations and Types
Abscesses can occur virtually anywhere in the body. Common types include:
- Skin and Soft Tissue Abscesses: The most frequent type, occurring in the skin, subcutaneous tissue, or deeper soft tissues.
- Dental Abscesses: Associated with infected teeth.
- Internal Abscesses: Occurring within organs (e.g., liver, lung, brain, kidney, spleen) or body cavities (e.g., intra-abdominal abscess, pelvic abscess).
- Breast Abscesses: Often related to mastitis.
- Perianal and Perirectal Abscesses.
Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Clinical Course of an Abscess
Abscesses, which can be caused by various types of microflora, exhibit considerable diversity in size and location. They typically develop in the center of an existing inflammatory infiltrate, except for metastatic abscesses, which are located distant from the primary inflammatory focus. The shape of the abscess cavity can range from simple and rounded to complex, with numerous pockets and blind passages (loculations).
Clinical Manifestations
The clinical presentation depends on the location, size, and depth of the abscess, as well as the virulence of the infecting organism and the host's immune response.
- Local Signs of Inflammation (Cardinal Signs):
- Swelling (Tumor): A visible or palpable lump or swelling.
- Redness (Rubor/Hyperemia): The skin overlying a superficial abscess is typically red and inflamed. This may not be visible with deep-seated abscesses.
- Warmth (Calor): The affected area often feels warm to the touch.
- Pain (Dolor): Abscesses are usually painful and tender. The pain can be throbbing in nature.
- Loss of Function (Functio Laesa): Movement or function of the affected part may be impaired due to pain and swelling.
- Fluctuation: In acute inflammation leading to a mature abscess, the symptom of fluctuation (a wave-like or boggy feeling on palpation) is very important. It indicates the presence of liquid pus trapped within a cavity with elastic walls that transmit a pressure wave. Fluctuation may be absent if the abscess wall is very thick, the abscess is small and deep, or if it is under significant tension.
- Pus Drainage: A mature abscess may point (come to a head) and spontaneously rupture, discharging pus.
- Systemic Symptoms: Fever, chills, malaise, fatigue, and loss of appetite can occur, especially with larger or deeper abscesses, or if there is associated cellulitis or bacteremia. Leukocytosis (elevated white blood cell count) and elevated inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP) are common.
In a **chronic abscess**, the classic acute signs of inflammation (redness, warmth, acute pain) may be minimal or completely absent. The abscess might present as a persistent, firm, or slightly fluctuant swelling, sometimes with a draining sinus tract.
Diagnostic Evaluation
- Physical Examination: Observation for swelling, redness, warmth, and palpation for tenderness and fluctuation.
- Test Puncture (Needle Aspiration): The diagnosis of a liquefactive abscess can often be confirmed by a diagnostic puncture of the suspected cavity with a sterile, thick needle. Aspiration of pus confirms the diagnosis. The aspirated material should be sent for Gram stain, culture (aerobic and anaerobic), and antibiotic sensitivity testing.
- Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound: Very useful for superficial abscesses to confirm the presence of a fluid collection, determine its size and extent, and guide needle aspiration or drainage.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Often used for deeper abscesses or those in complex anatomical locations (e.g., intra-abdominal, pelvic, deep neck space). CT with intravenous contrast can show a characteristic rim-enhancing fluid collection.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): May be used for better soft tissue delineation or if CT is inconclusive, especially for abscesses near critical structures or in the central nervous system.
Potential Complications of Abscesses
Untreated or inadequately treated abscesses can lead to serious complications:
- Rupture into Adjacent Cavities or Structures: A breakthrough of an abscess into a sterile body cavity (e.g., joint space leading to septic arthritis, pleural cavity causing empyema, peritoneal cavity causing peritonitis) is a serious complication.
- Spread of Infection:
- Cellulitis/Phlegmon: Diffuse spread of infection into surrounding soft tissues.
- Lymphangitis/Lymphadenitis: Spread along lymphatic channels to regional lymph nodes.
- Bacteremia/Sepsis: Entry of bacteria into the bloodstream, potentially leading to life-threatening systemic infection.
- Thrombophlebitis: If an abscess is located near large veins, inflammation can spread to the vein wall, leading to progressive thrombophlebitis (inflammation and clotting within the vein), which can result in septic emboli.
- Tissue Necrosis and Destruction: Pressure from the abscess or the destructive nature of the infection can cause necrosis of surrounding tissues.
- Fistula Formation: Development of an abnormal tract from the abscess cavity to a body surface or another organ.
- Chronic Abscess or Sinus Tract: If drainage is inadequate, the abscess may become chronic or form a persistent draining sinus.
Abscesses located in internal organs (e.g., liver, lungs, brain) are particularly dangerous due to the risk of organ dysfunction and severe systemic complications.
Treatment of Abscesses
The management of purulent-inflammatory processes, including abscesses, depends on the stage of inflammation and the characteristics of the abscess.
Conservative Management (Early Stage/Small Abscesses)
In the early stages of inflammation (e.g., cellulitis or phlegmon, before the formation of a distinct purulent cavity or liquefaction), conservative methods may be employed:
- Antibiotics: Systemic antibiotics (oral or parenteral) are prescribed to target the likely or confirmed pathogens.
- Warm Compresses: Applied locally to promote blood flow, help localize the infection, and encourage spontaneous drainage or maturation of the abscess.
- Elevation and Rest: Of the affected part, if applicable, to reduce swelling.
- Analgesics: For pain relief.
Small, superficial abscesses with low virulence flora and minimal systemic signs might sometimes be cured by repeated needle aspirations (with or without ultrasound guidance) combined with appropriate antibiotic therapy. This involves suctioning out the pus and sometimes instilling a solution of antibiotics directly into the cavity (less common now).
Incision and Drainage (I&D)
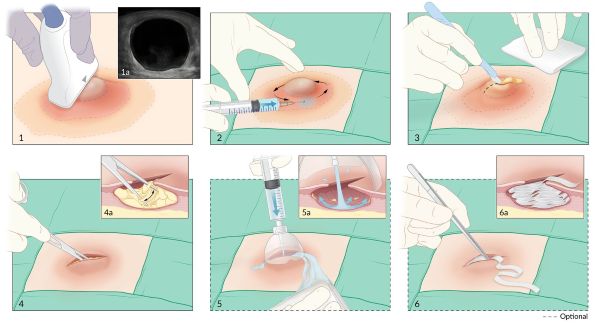
Once a collection of pus has formed (a mature abscess, often indicated by fluctuation), the cornerstone of treatment is **incision and drainage**. The indications and urgency of the operation are determined by the size and location of the abscess, the severity of local and systemic symptoms, and the degree of patient intoxication.
- Procedure:
- The area is prepared with antiseptic solution. Local anesthesia is typically used for superficial abscesses; regional or general anesthesia may be required for larger, deeper, or more complex abscesses, or in uncooperative patients (e.g., young children).
- An incision is made over the most fluctuant part of the abscess, or where it is pointing. Incisions should ideally correspond to the direction of skin tension lines (Langer's lines) to promote better cosmetic healing. On limbs, incisions should consider the lines of flexion of joints. The incision must be adequate in length and depth to ensure complete evacuation of pus and allow for thorough exploration of the cavity.
- Pus is evacuated, and samples are taken for Gram stain, culture, and antibiotic sensitivity.
- The abscess cavity is explored gently with a hemostat or finger to break down any loculations (internal pockets or septations) and ensure complete drainage.
- The cavity may be irrigated with sterile saline.
- A drain (e.g., Penrose drain, iodoform gauze wick, or specialized catheter) is often inserted into the cavity to keep the incision open and allow for continued drainage of any residual pus or serous fluid. The drain is typically removed once drainage significantly decreases (usually after 24-72 hours).
- Repeated incisions or wider debridement may be required for extensive abscesses or those with significant necrotic tissue or multiple leaks.
Antibiotic Therapy
Systemic antibiotics are an important adjunct to drainage, especially for:
- Abscesses associated with significant surrounding cellulitis.
- Patients with systemic signs of infection (fever, malaise).
- Immunocompromised patients.
- Abscesses in high-risk anatomical locations (e.g., face, hands, perineum).
- Failure of incision and drainage alone or recurrent abscesses.
The choice of antibiotic should cover likely pathogens (e.g., *S. aureus*, Streptococci) and be adjusted based on culture and sensitivity results. For simple, well-drained cutaneous abscesses in otherwise healthy individuals without significant cellulitis, antibiotics may not always be necessary after incision and drainage.
Management of Deep or Complex Abscesses
Deep abscesses (e.g., intra-abdominal, organ-specific) are often opened following a preliminary diagnostic trial puncture, frequently guided by imaging (ultrasound or CT). After pus is aspirated and its presence confirmed, the needle may be left in place as a guide, and the incision is made along or over the needle track. Patients with significant abscesses accompanied by a pronounced general systemic reaction are typically hospitalized, often in a specialized purulent surgical department, for intensive treatment and monitoring.
Differential Diagnosis of Localized Swelling and Inflammation
A localized area of swelling, redness, warmth, and pain can be caused by conditions other than an abscess. The differential diagnosis includes:
| Condition | Key Differentiating Features |
|---|---|
| Abscess | Localized collection of pus, often fluctuant when mature, surrounded by inflammation. Usually caused by bacterial infection. Aspiration yields pus. |
| Cellulitis/Phlegmon | Diffuse, spreading inflammation of skin and subcutaneous tissue without a discrete, drainable collection of pus (though cellulitis can surround an abscess or progress to one). Skin is red, warm, swollen, tender. Borders are often indistinct. |
| Hematoma | Collection of clotted blood due to trauma or bleeding disorder. Initially may be firm, later can liquefy. Skin may be bruised. Aspiration yields blood. Can become secondarily infected (forming an abscess). |
| Cyst (e.g., Sebaceous, Epidermoid) - Inflamed or Infected | Pre-existing cyst that becomes inflamed or infected. May have a central punctum. Contents may be cheesy (sebaceous) or purulent if infected. |
| Lymphadenitis | Inflammation of lymph nodes, often tender and enlarged. Usually secondary to infection elsewhere in the drainage area. Nodes are typically discrete and mobile unless matted. |
| Benign or Malignant Soft Tissue Tumor | Usually slower growing, may be firm or hard. Inflammatory signs less prominent unless secondarily infected or rapidly growing. Imaging and biopsy often needed. |
| Insect Bite or Sting with Severe Local Reaction | History of bite/sting. Intense itching, localized edema, redness. Central punctum may be visible. Less likely to be fluctuant with pus unless secondarily infected. |
| Contact Dermatitis (Severe) | Inflammation due to allergen/irritant contact. Itching, redness, vesicles, edema. History of exposure. |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) - for limb swelling | Swelling, pain, warmth, redness of an extremity. Risk factors for DVT. Ultrasound (Doppler) is diagnostic. Not typically fluctuant with pus. |
Prevention of Abscesses
Measures to prevent abscess formation include:
- Good Personal Hygiene: Regular handwashing and keeping skin clean can prevent infections.
- Proper Wound Care: Cleaning and covering any breaks in the skin (cuts, abrasions) promptly to prevent bacterial entry.
- Avoiding Squeezing or Picking Skin Lesions: Such as pimples or boils, as this can spread infection deeper.
- Aseptic Technique for Injections: Ensuring sterile procedures for any injections or medical interventions that break the skin.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Controlling conditions like diabetes or immune deficiencies that increase susceptibility to infection.
- Prompt Treatment of Localized Infections: Early antibiotic treatment for conditions like cellulitis or furunculosis can sometimes prevent progression to abscess formation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Medical attention should be sought if an individual develops signs suggestive of an abscess, particularly:
- A localized, painful, swollen, red, and warm area on the skin or deeper tissue.
- The presence of fluctuation (a boggy or wave-like feeling) on palpation of the swelling.
- Spontaneous drainage of pus from a lesion.
- Fever, chills, or feeling generally unwell associated with a localized infection.
- Red streaks extending from the infected area (lymphangitis).
- Worsening or spreading infection despite home care or initial antibiotic treatment.
- Abscesses in high-risk areas (e.g., face, hands, neck, groin, perianal region).
- Individuals with underlying health conditions (e.g., diabetes, immunodeficiency) who develop skin infections.
Prompt medical evaluation and appropriate treatment, often including incision and drainage, are crucial for resolving abscesses and preventing complications.
References
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections: 2014 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2014 Jul 15;59(2):e10-52.
- Brook I. Microbiology and management of skin and soft tissue infections. Wounds. 2005;17(1):23-35.
- Singer AJ, Talan DA. Management of skin abscesses in the era of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. N Engl J Med. 2014 Mar 13;370(11):1039-47.
- Fitch MT, Manthey DE, McGinnis HD, Nicks BA, Pformat M. Abscess incision and drainage. N Engl J Med. 2007 Nov 1;357(19):e20.
- Llach F, Aboltins CA, Kotsanas D, et al. Clinical presentation, microbiology and management of cutaneous abscesses in an Australian tertiary hospital. J Infect. 2013 Jul;67(1):24-9.
- Talan DA, Mower WR, Krishnadasan A, et al; EMERGEncy ID NET Study Group. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole versus placebo for uncomplicated skin abscess. N Engl J Med. 2016 Mar 3;374(9):823-32.
- Schwartz MN. Cellulitis and subcutaneous tissue infections. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Elsevier Saunders; 2015:chap 94.
See also
- Abscess
- Breast diseases (mastopathy, cyst, calcifications, fibroadenoma, intraductal papilloma, cancer)
- Bursitis
- Furuncle (boil)
- Ganglion cyst
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)
- Ingrown toenail
- Lipoma (fatty tumor)
- Lymphostasis
- Paronychia, panaritium (whitlow or felon)
- Sebaceous cyst (epidermoid cyst)
- Tenosynovitis (infectious, stenosing)