Fever Symptoms
Fever is considered a temperature above 100.4 degrees F (38 degrees C). A feverish sensation, however, may occur when the body temperature is above the average normal of 98.6 degrees F. (37 degrees C).
Fever is part of the body's own disease-fighting arsenal. Rising body temperatures apparently are capable of killing off many disease-producing organisms. For that reason, low fevers should normally go untreated. Although, if the fever is accompanied by any other troubling symptoms, you may need to see your doctor to be certain. As fevers range to 104 F and above, however, there can be unwanted consequences, particularly for children. These can include delirium and convulsions. A fever of this sort demands immediate home treatment and then medical attention. Home treatment possibilities include the use of aspirin or, in children, nonaspirin painkillers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), cool baths, or sponging to reduce the fever while seeking medical help. Fever may occur with almost any type of infection of illness. The temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Fever is also called pyrexia.
Other causes of fever
- Abscess
- Bacterial Infection
- Medications (Both Prescription and Nonprescription)
- Parasite Infection
- Virus Infection
Main Article on Fever
Causes of Fever
-

Prostatitis vs. BPH (Enlarged Prostate): What Is the Difference?
Prostatitis and BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia, enlarged prostate gland) are both conditions of the prostate gland. There are four types of prostatitis that can be caused by infections (usually bacterial) or other health conditions or problems, acute bacterial prostatitis (type I), chronic bacterial prostatitis (type II), chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (type III), and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis (type IV). BPH is inflammation of the prostate gland, and most men have the condition by age 50. Doctor's don't know what causes this inflammation, but they theorize that it may be related to hormones. Both of these conditions can cause similar symptoms like low back pain, pain during urination, or difficulty or the inability to urinate. However, prostatitis has many more symptoms and signs than BPH, and they based on the type of prostatitis. Examples include low back pain and/or abdominal pain, painful urination, fever, chills, feeling tired, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs), painful urination intermittently, intermittent obstruction urinary tract symptoms (frequent, painful, or incomplete urination), pelvic pain and/or discomfort, pain with ejaculation, and erectile dysfunction (ED). If you think you have either of these conditions contact your doctor or other health care professional. Bacterial prostatitis can be cured with antibiotics; however, there is no cure for BPH.
-

Listeria (Listeriosis)
Listeria is a type of bacteria that can cause food poisoning. Listeriosis symptoms include diarrhea, nausea, and fever. Pregnant women are 20 times more likely than other healthy adults to get listeriosis. Listeria infection is treated with antibiotics.
-

16 Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Signs & Symptoms
Early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) symptoms and signs vary differently from person to person. The most common body parts that are initially affected by RA include the small joints of the hands, wrists, and feet, and the knees and hip joints. Joint inflammation causes stiffness. Warmth, redness, and pain may vary in degree.
-
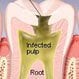
Abscessed Tooth
An abscessed tooth is an infection within a tooth that has spread to the root. Symptoms of an abscessed tooth may include pain, swelling, tenderness, redness, and the presence of a pus-filled lesion on the gum. A dental professional diagnoses an abscessed tooth and dental X-rays may be required. An abscessed tooth is treated with a root canal.
-

Adenovirus 14 (Killer Cold Virus)
Adenovirus infection, particularly Ad14, or the "killer cold virus" has been on the increase in the past two years. Symptoms range from those experienced with colds, sore throat, bronchitis, pneumonia, diarrhea, pinkeye, fever, bladder infection, and neurological conditions. Diagnosis and treatment options need to be discussed with your physician.
-

Anencephaly
Anencephaly is a neural tube defect that prevents abnormal development of the brain and bones of the skull, and are missing large areas of the brain; some may have and incomplete skull. Ancecephaly affects the thinking, hearing, vision, emotion, and coordination areas of the brain. A combination of genetic and environmental factors are believed to to cause this condition. There is no treatment for anencephaly.
-

Anthrax
Anthrax is a deadly infectious disease that may be transmitted to humans by infected animals or by biological warfare. There are three types of anthrax: cutaneous, inhalation, and gastrointestinal. Symptoms of cutaneous anthrax include a swollen glands, muscle ache, headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, and a red-brown raised spot that enlarges, blisters, and hardens, forming an ulcer crater with black crust. Symptoms of inhalation anthrax are flu-like and may progress to respiratory distress, shock, coma, and death. Symptoms of gastrointestinal anthrax include loss of appetite, bloody diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Treatment for cutaneous anthrax involves penicillin, tetracycline, erythromycin, and ciprofloxin. Inhalation anthrax necessitates treatment with IV therapy with antibiotics.
-
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix. Appendicitis often causes sings and symptoms such as abdominal pain in the lower right quadrant, nausea, vomiting, abdominal tenderness, fever, and loss of appetite. Delay in surgery can result in appendix rupture with potentially serious complications.
-

Are You Too Sick to Work?
When you're not feeling well, it may be difficult to decide whether to stay home or go to school or work. Conditions that are very painful may prevent you from working effectively. Anyone with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, or dizziness should stay home.
-

Arthritis (Joint Inflammation)
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints. When joints are inflamed they can develop stiffness, warmth, swelling, redness and pain. There are over 100 types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, lupus, gout, and pseudogout.
-

Ascariasis Disease
A parasite names Ascaris lumbricoides causes ascariasis. Symptoms and signs include abdominal pain, abdominal swelling, nausea, vomiting, fever, and passage of parasites and eggs in stool. Treatment involves taking oral medications for one to three days.
-

Aspergillus Infection (Aspergillosis)
An Aspergillus infection is a fungal infection. Signs and symptoms can include cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, bloody sputum, difficulty breathing, and chest and/or joint pain. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the disease.
-
Balamuthia
Balamuthia mandrillarisis is an ameba that lives in dust and soil. Signs and symptoms of Balamuthia include fever, nausea and vomiting, light sensitivity, headache, stiff neck, and headaches. There are various diagnostic tests and medications that treat Balamuthia infection.
-

Bath Salts
Ingredients of the drug bath salts include mephedrone, methylone, MDPV, or MDPK. Feeling high and sexually stimulated are symptoms of bath salt abuse. The primary goals for the treatment of addiction symptoms are abstinence, relapse prevention, and rehabilitation.
-
Bile Duct Cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma)
Bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) is a rare type of cancer that arises from cells that line the drainage system from the liver and gallbladder to the intestine. Symptoms of bile duct cancer include jaundice, itching, weight loss, and abdominal pain. Physical examination, specialized blood tests, and imaging tests may be used to diagnose bile duct cancer. Treatment for bile duct cancer may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and photodynamic therapy. Bile duct cancer typically has a poor prognosis. Preventing liver damage may decrease the risk of developing bile duct cancer.
-
Bird Flu (Avian Influenza, Avian Flu)
Bird flu (avian flu, avian influenza) infection in humans may result from contact with infected poultry. There is a vaccine to prevent human infection with the H5N1 strain of the avian flu virus.
-
Bladder Infection (Cystitis)
Bladder infection is an infection of the bladder, usually caused by bacteria or, rarely, by Candida. Certain people, including females, the elderly, men with enlarged prostates, and those with chronic medical conditions are at increased risk for bladder infection. Bladder infections are treated with antibiotics, but cranberry products and adequate hydration may help prevent bladder infections.
-

Blood in Semen
Blood in semen is also known as hematospermia. Blood in semen can be caused by many conditions affecting the tubes that distribute semen from the testicles (seminal vesicles) or the prostate gland. Symptoms that may accompany blood in semen include blood in the urine, fever, painful urination, pain with ejaculation, tenderness, and swelling in the testes or groin area. Urinalysis, ultrasound, and MRI may be used to diagnose blood in the semen. Treatment depends upon the underlying cause of blood in the semen.
-

Bocavirus
Bocavirus infection is usually only found in those with lower respiratory infections or diarrhea. Symptoms include cyanosis, cough, wheezing, runny nose, vomiting, and fever. There is no treatment that effectively targets the bocavirus strain.
-
Bone Cancer
Bone cancer is a rare type of cancer that occurs in cells that make up the bones. Primary bone cancer that arises in bone cells is different than metastatic bone cancer, which is cancer that arises in another part of the body and then spreads to the bones. Hereditary and environmental factors likely contribute to the risk of bone cancer. Signs and symptoms of bone cancer may include pain, the presence of a mass or lump, and bone fractures. There are different types of bone cancer (osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, pleomorphic sarcoma, fibrosarcoma). Treatment for bone cancer may include surgical removal of the tumor, chemotherapy, radiation, and/or a stem cell transplant. The prognosis for bone cancer depends on the type of cancer and the extent of spread.
-

Brain Eating Amoeba (Naegleria fowleri)
Naegleria fowleri is an amoeba found in freshwater and soil. Infection results when the amoeba enters the nose and travels to the brain and spinal cord, causing primary amebic meningoencephalitis, which destroys brain tissue.
-
Brain Lesions (Lesions on the Brain)
A brain lesion is defined as an area of damaged brain. Brain lesions (lesions on the brain) are caused by trauma, inflammation, autoimmune diseases, cancers, other diseases, stroke, bleeding, pituitary adenomas, and cerebral palsy. Symptoms of brain lesions include headache, nausea, fever, neck pain and stiffness, affected vision and speech, and weakness or paralysis to one side of the body. Diagnosis of brain lesions is generally accomplished with imaging studies like CT or MRI scans. Treatment and prognosis of brain lesions depends on the cause of the lesion.
-

Brucellosis
The bacteria Brucella causes brucellosis, an infectious zoonotic disease in humans. Symptoms and signs include fatigue, fever, sweating, and appetite loss. The preferred treatment is doxycycline and rifampin taken for six to eight weeks.
-

Can a Liver Hemangioma Go Away on Its Own?
No, liver hemangioma doesn’t go away without treatment. People who have liver hemangioma rarely experience signs and symptoms and typically don't need treatment. They are generally small and even if they become large they may not carry significant risk.
-

Cancer
Cancer is a disease caused by an abnormal growth of cells, also called malignancy. It is a group of 100 different diseases, and is not contagious. Cancer can be treated through chemotherapy, a treatment of drugs that destroy cancer cells.
-

Capnocytophaga canimorsus
The bacteria Capnocytophaga canimorsus is common in the mouths of cats, people, and dogs. People with weak immune systems are at risk for contracting Capnocytophaga infections. Antibiotics can kill this bacteria.
-

Cat Scratch Disease
Cat scratch disease (CSD or cat scratch fever), a bacterial disease caused by Bartonella henselae, is characterized by fever, headache, fatigue, poor appetite, swelling of the lymph nodes, and mild infection at the site of the bite or scratch. Cats that carry B. henselae don't show signs of illness. Approximately 40% of cats carry the bacteria at some point in their lives.
-
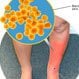
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is an acute spreading bacterial infection below the surface of the skin characterized by redness, warmth, inflammation, and pain. The most common cause of cellulitis is the bacteria staph (Staphylococcus aureus).
-

Chagas Disease
Chagas disease is an infection caused by the T. cruzi parasite. Symptoms of Chagas disease include rash, swollen lymph nodes, fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and the Romaña sign. An ELISA test is used to diagnose Chagas disease. Treatment depends upon the phase of the disease and the patient's age.
-

Chest Pain
Chest pain is a common complaint by a patient in the ER. Causes of chest pain include broken or bruised ribs, pleurisy, pneumothorax, shingles, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, angina, heart attack, costochondritis, pericarditis, aorta or aortic dissection, and reflux esophagitis. Diagnosis and treatment of chest pain depends upon the cause and clinical presentation of the patient's chest pain.
-

Chickenpox (Varicella)
Chickenpox (chicken pox) is a contagious childhood disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Symptoms have an incubation period of 14 to 16 days and include a couple days of mild fever, weakness, and red, raised rash that progresses to blisters that eventually burst and crust over. Complications include bacterial infection of the open sores, scarring, encephalitis, nerve palsies, and Reye's syndrome.
-
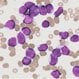
Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia is the most common type of cancer in children. Symptoms and signs include fever, easy bruising, bone or joint pain, weakness, loss of appetite, and painless lumps in the neck, underarm, stomach, or groin. Treatment depends upon staging and may include chemotherapy, radiation, or stem cell transplant.
-

Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS or SEID)
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) or systemic exertion intolerance disease (SEID) is a debilitating and complex disorder characterized by profound fatigue that lasts 6 months or longer, is not improved by bed rest, and may be worsened by physical or mental activity.
-

Cold vs. Flu
Though the common cold and flu share many signs and symptoms, they are caused by different viruses. Signs and symptoms include sneezing, sore throat, runny nose, fatigue, and cough. Treatment options for the cold and flu are similar and focus on reducing symptoms. Doctors may prescribe antivirals/neuraminidase inhibitors for the flu.
-

Cold, Flu, Allergy Treatments
Before treating a cold, the flu, or allergies with over-the-counter (OTC) medications, it's important to know what's causing the symptoms, which symptoms one wishes to relieve, and the active ingredients in the OTC product. Taking products that only contain the medications needed for relieving your symptoms prevents ingestion of unnecessary medications and reduces the chances of side effects.
-
Colitis
Colitis refers to inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. Symptoms of the inflammation of the colon lining include diarrhea, pain, and blood in the stool. There are several causes of colitis, including infection, ischemia of the colon, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, infectious colitis like C. difficile, or microscopic colitis). Treatment depends on the cause of the colitis.
-

Common Cold
The common cold (viral upper respiratory tract infection) is a contagious illness that may be caused by various viruses. Symptoms include a stuffy nose, headache, cough, sore throat, and maybe a fever. Antibiotics have no effect upon the common cold, and there is no evidence that zinc and vitamin C are effective treatments.
-
Connective Tissue (CT) Disease
Connective tissue disease is when the body's connective tissues come under attack, possibly becoming injured by inflammation. Inherited connective tissue diseases include Marfan syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, polymositis, and dermatomyositis are examples of connective tissue diseases that have no known cause.
-
COVID-19 (Coronavirus) Prevention Tips
COVID-19 is a novel coronavirus that spreads from person to person via infected respiratory droplets. The main symptoms of COVID-19 infection include cough, fever, and shortness of breath. Occasionally, people infected with COVID-19 may experience diarrhea, a sore throat, a runny or stuffy nose, or aches and pains. Avoiding contact with infected people, social distancing, not touching your face, frequent hand washing, cleaning, and disinfecting of frequently touched surfaces can help to reduce your risk of contracting the 2019 novel coronavirus.
-
COVID-19 (Coronavirus, 2019-nCoV)
Infection with COVID-19 (2019 novel coronavirus, 2019-nCoV) causes respiratory problems in humans. Transmission of COVID-19 occurs mainly through contact with respiratory sections from an infected person, however, fecal contamination may also spread the virus. Symptoms start off flu-like and progress to coughing, fever, shortness of breath, shaking chills, headache, loss of sense of taste and/or smell, muscle pain, and sore throat. Treatment focuses on supportive care and symptom relief. COVID-19 vaccines are available.
-
Coxsackievirus
Coxsackieviruses may be divided into two groups. Type A causes hand, foot, and mouth disease and conjunctivitis, while type B causes pleurodynia. Both types sometimes cause meningitis, myocarditis, and pericarditis. There is no specific treatment for this disease.
-

CRE Bacteria Infection
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) is a type of bacteria that is highly resistant to antibiotics. Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Klebsiella are common types of Enterobacteriaceae that can be found in the human intestines. However, these bacteria can cause infections if they escape the intestines. Carbapenems are broad-spectrum antibiotics that treat infections caused by bacteria that are highly resistant to other types of antibiotics.
-

Croup
Croup is a contagious viral infection that affects children's respiratory systems. Symptoms include a barking cough, stridor, fever, and difficulty breathing. Treatment may incorporate the use of a humidifier, saline nasal spray, and pain relievers such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
-

Cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis is an intestinal disease caused by the Cryptosporidium parasite. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea and vomiting, fever, weight loss, dehydration, and weight loss. Antibiotics are used in the treatment of cyptosporidiosis.
-
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a disease of the mucus and sweat glands. Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease. The outcome of the disease leaves the body malnourished, with bulky and fouls smelling stools, vitamin insufficiency, gas, painful or swollen abdomen, infertility, susceptible to heat emergencies, and respiratory failure. There is no cure for cystic fibrosis, treatment of symptoms is used to manage the disease.
-
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a virus that is spread from person to person via spit, semen, vaginal secretions, urine, blood, sexual contact, breastfeeding, blood transfusions, organ transplants, and breast milk. Symptoms of CMV include fatigue, swollen glands, fever, and sore throat. You can take precautions to prevent CMV such as washing hands frequently and thoroughly and using condoms. If you work in a day care center, wash your hands thoroughly after contact with body secretions, and avoid oral contact with objects covered in saliva. Individuals with HIV infection are at most risk of contracting CMV.
-

Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is contracted from the bite of a striped Aedes aegypti mosquito. Symptoms and signs of dengue include headache, fever, exhaustion, severe joint and muscle pain, rash, and swollen glands. Since dengue is caused by a virus, there is no specific medicine to treat it. Treatment instead focuses on relieving the symptoms.
-

Diverticulitis (Diverticulosis, Diverticular Disease)
Most people with diverticulosis have few if any symptoms at all. When people do experience signs and symptoms of diverticulosis (diverticular disease) they may include abdominal pain, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, constipation, and bloating. Diverticulitis is a condition in which diverticuli in the colon rupture. The rupture results in infection in the tissues that surround the colon. Treatment methods for diverticulitis includes prescription medications, and in some cases, diverticulitis surgery.
-

E. coli (0157:H7) Infection
There are many types of E. coli (Escherichia coli). E. coli can cause urinary tract and bladder infections, or lead to sepsis. E coli O157:H7 (EHEC) causes bloody diarrhea and colitis. Complications of E. coli infection include hemorrhagic diarrhea, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. E coli O157:H7 commonly is due to eating raw or undercooked hamburger or raw milk or dairy products.
-

Ebola (Ebola Virus Disease or Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever)
Ebola hemorrhagic fever (HF) is an often-fatal disease that causes fever, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, sore throat, stomach pain, rash, and red eyes. There is no standard treatment for Ebola HF.
-

Encephalitis
Encephalitis is a brain inflammation that causes sudden fever, vomiting, headache, light sensitivity, stiff neck and back, drowsiness, and irritability. Treatment may incorporate anticonvulsants and antiviral medications.
-
Endocarditis
Endocarditis, a serious infection of one of the four heart valves is caused by growth of bacteria on one of the heart valves; leading to an infected massed called a "vegetation." The infection can be caused by having bacteria in the bloodstream after dental work, colonoscopy, or other similar procedures. Endocarditis symptoms include fever, fatigue, weakness, chills, aching muscles and joints, night sweats, edema in the legs, feet, or abdomen, malaise, shortness of breath and small skin lesions. Treatment for endocarditis is generally aggressive antibiotic treatment.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a common cause of mononucleosis (viral pharyngitis). Symptoms and signs of an EBV infection include swollen lymph nodes, fever, rash, sore throat, malaise, and a swollen liver and/or spleen. Treatment focuses on reducing the severity of the symptoms and signs. There is no vaccine to prevent EBV infections.
-

Factitious Disorders
Factitious disorders are conditions in which people pretend to have physical or mental illnesses when they aren't sick. These people may lie about or fake symptoms to obtain the sympathy and attention given to people who are genuinely ill. Symptoms of factitious disorders include dramatic, inconsistent medical history, the presence of many surgical scars, and a history of seeking treatment at many different hospitals.
-

Fever and Headache
Illnesses, diseases, conditions, and infections like cancer, RA, bacterial and fungal infections, encephalitis, meningitis, flu, and colds can cause a headache and fever. Associated symptoms and signs include rash, nausea and vomiting, cough, sweating, neck stiffness, seizure, decreased appetite, and joint pain and swelling. Treatment depends upon the cause but may include antibiotics, antifungal or antiviral drugs, pain-control drugs, decongestants, and cough suppressants.
-

Fever in Adults and Children
Although a fever technically is any body temperature above the normal of 98.6 F (37 C), in practice, a person is usually not considered to have a significant fever until the temperature is above 100.4 F (38 C). Fever is part of the body's own disease-fighting arsenal; rising body temperatures apparently are capable of killing off many disease-producing organisms.
-
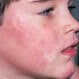
Fifth Disease (Parvovirus, Erythema Infectiosum)
Fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) is caused by a virus known as parvovirus B 19. Symptoms include low-grade fever, fatigue, a "rash," and a rash over the whole body. The name fifth disease reflects the historical belief that it was one of the five diseases that produced a rash in children.
-

Flu (Influenza)
Influenza (flu) is a respiratory illness caused by a virus. Flu symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches. The flu may be prevented with an annual influenza vaccination.
-

Fungal Arthritis
Fungal arthritis is inflammation of a joint by a fungus that has invaded the body and is growing in the normally sterile joint. Fungal arthritis symptoms and signs include pain, redness, loss of range of motion, and swelling. Fungal arthritis treatment includes antibiotics, adequate drainage of the joint, and sometimes surgery.
-

Fungal Meningitis
Fungal meningitis is a rare disease that is not contagious. Symptoms include fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea, and vomiting. Treatment involves administering high doses of antifungal medications.
-

Gangrene
Gangrene may result when blood flow to a tissue is lost or not adequate to keep the tissue alive. There are two types of gangrene: wet and dry. All cases of wet gangrene are infected by bacteria. Most cases of dry gangrene are not infected. If wet gangrene goes untreated, the patient may die of sepsis within hours or days. Dry gangrene usually doesn't cause the patient to die. Symptoms of dry gangrene include numbness, discoloration, and mummification of the affected tissue. Wet gangrene symptoms include swelling, pain, pus, bad smell, and black appearance of the affected tissue. Treatment depends upon the type of gangrene and how much tissue is compromised by the gangrene.
-

German Measles (Rubella)
German measles is a disease that's caused by a virus. Symptoms include rash and fever for two to three days. The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine prevents this disease.
-
Giardia Lamblia
Giardiasis (Giardia lamblia) is a parasite responsible for a common form of infectious diarrhea. The parasite lives in two stages: trophozoites and cysts. People at risk for giardiasis are those that live in areas where there is inadequate sanitation or treatment of drinking water. Giardiasis also is a common cause of outbreaks of diarrhea in day-care centers. Symptoms and signs of giardiasis include abdominal pain, stomach cramping, bloating, nausea, and fatigue. Treatment for giardiasis is with antibiotic medication.
-

Group B Strep
Group B strep are bacteria called Streptococcus agalactiae that may sometimes cause infections both in a pregnant woman and her baby. Symptoms include fever, seizures, heart rate abnormalities, breathing problems, and fussiness. Intravenous antibiotics are used to treat group B strep infections.
-
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth syndrome is clinical pattern consisting of a rash on the hands and feet, and in the mouth. Hand, foot, and mouth syndrome is caused by various viruses, including several types of Coxsackieviruses. Other symptoms include sore throat, decreased appetite, irritability, and (or) fever.
-

Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) is a disease transmitted by rodents. Symptoms include fever and muscle pain. HPS can be prevented by sealing up rodent entry holes, trapping rats and mice with an appropriate snap trap, and cleaning up rodent food sources.
-
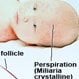
Heat Rash: Pictures, Symptoms, and Treatment
Heat rash is a skin irritation caused by excessive sweating. It can occur at any age and it appears as a rash that itches or feels prickly, and looks like a red cluster of pimples or small blisters. Heat rash remedies include OTC creams and sprays. Usually heat rash resolves when the skin is cooled sufficiently. Medical treatment may be necessary if the sweat glands become infected.
-

Hepatitis (Viral Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, G)
Hepatitis is most often viral, due to infection with one of the hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, E, F (not confirmed), and G) or another virus (such as those that cause infectious mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus disease). The main nonviral causes of hepatitis are alcohol and drugs. Many patients infected with hepatitis A, B, and C have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fever, weakness, tiredness, and aching in the abdomen. Treatment of viral hepatitis is dependent on the type of hepatitis.
-

Hepatitis E Viral Infection
Hepatitis E (hep E) is a type of hepatitis viral infection that includes hepatitis A, B, C, D, F, which is caused by the hepatitis E virus. Usually, you get (transmitted) hepatitis E from eating or drinking dirty or contaminated water. Hepatitis E can be very serious, especially if a woman is pregnant. Up to ¼ of women who are pregnant with the hep E virus can die from the infection. The signs and symptoms of hepatitis E infection are nausea and vomiting, brown or dark urine, stool changes jaundice (yellow eyes and skin), pain in the right side of the abdomen, dark or brown urine, and light-colored stool. Some people with hep E don’t have any symptoms so they don’t know that they are contagious. It takes about 6 weeks to recover from hep E. A person who has any type of hepatitis, including hepatitis E, should not drink any alcohol. Hep E complications are rare, but when they do occur they include severe (“fulminant”) hepatitis, liver failure, and death. Currently, no specific drugs or treatments are available for hepatitis E. Moreover, the only hepatitis E vaccine currently is available in China. Avoid alcohol, keep hydrated, and getting rest are home remedies for hepatitis E. Talk to your doctor before taking any over-the-counter (medications), especially those containing acetaminophen (Tylenol and others). Usually, the prognosis and life expectancy for hepatitis E after recovery is good. Most people do not have long term liver problems from the infection.
-
Herpangina
Herpangina is a contagious illness often seen in children. It is caused by a Coxsackievirus or an enterovirus. Symptoms and signs include mouth sores, fever, and sore throat. Treatment focuses on alleviating fever and pain with acetaminophen and ibuprofen. It is important for children to stay well hydrated, as children may be resistant to eating or drinking.
-

HIV vs. AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus causes HIV infection. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a condition that results after HIV has extensively damaged a person's immune system. Risk factors for HIV and AIDS include use of contaminated needles or syringes, unprotected sex, STDs, receiving a blood transfusion prior to 1985 in the United States, having many sex partners, and transmission from a mother to her child.
-

Hodgkin's Disease
Hodgkin's disease is a cancer of the lymphatic system with symptoms that include unexplained, recurring fevers, unexplained weight loss, itchy skin, and painless swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, underarm, and groin. Treatment for adult Hodgkin's disease depends on the staging of the disease, the size of the lymph nodes, and the health of the patient.
-

Hodgkin's vs. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Both Hodgkin's disease (sometimes referred to as Hodgkin's lymphoma) and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma are cancers that originate in a type of white blood cell known as a lymphocyte, an important component of the body's immune system.
-

How Do I Bring My Baby's Fever Down?
A baby with a fever always makes parents anxious, but fever is actually a defense mechanism of the body. It prepares the body to fight infection. Most fevers do not need antibiotic therapy and may resolve on their own in five to seven days. There are a few things a parent may try to manage the child’s fever and make them feel more comfortable.
-

How Long Is a Cold or Flu Contagious?
Viruses cause the common cold and the flu. Early symptoms and signs for a cold and the flu are similar, however, flu symptoms are typically more severe than cold symptoms. Cold and flu viruses are transmitted typically via coughing or sneezing.
-

Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection left untreated causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Still incurable, AIDS describes immune system collapse that opens the way for opportunistic infections and cancers to kill the patient. Early symptoms and signs of HIV infection include flu-like symptoms and fungal infections, but some people may not show any symptoms for years. Highly active antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the standard treatment for HIV infection. These combination drug regimens have made HIV much less deadly, but a cure or vaccine for the pandemic remains out of reach. HIV is usually transmitted through sexual contact or sharing IV drug needles, but can also infect someone through contact with infected blood. Sexual abstinence, safe sex practices, quitting IV drugs (or at least using clean needles), and proper safety equipment by clinicians and first responders can drastically reduce transmission rates for HIV/AIDS.
-
Infectious Mononucleosis (Mono)
Infectious mononucleosis is a virus infection in which there is an increase of white blood cells that are mononuclear (with a single nucleus) "Mono" and "kissing disease" are popular terms for this very common illness caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
-

Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
The inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). The intestinal complications of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis differ because of the characteristically dissimilar behaviors of the intestinal inflammation in these two diseases.
-
Is C. diff (Clostridium difficile) Contagious?
C. diff, or Clostridium difficile, is a bacteria that infects the colon. C. diff bacteria can be found on furniture, bathroom floors, telephones, fingernails, jewelry, toilet seats, and other places. Symptoms of C. diff infection are fever, abdominal pain, and cramps; however, not all people infected with C. diff have symptoms. Treatments for C. diff are antibiotics and surgery in some cases.
-
Is E. coli Contagious? (Symptoms and Cure)
E. coli is an infection found worldwide. There are several subtypes of the E. coli species. E. coli spreads from person to person via contaminated food or water. Symptoms and signs of E. coli infection include diarrhea, stomach cramps, and sometimes fever. Antibiotics treat E. coli infection.
-

Is a Staph Infection Contagious?
A staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. Staph can cause boils, food poisoning, cellulitis, toxic shock syndrome, MRSA, and various other illnesses and infections. Most staph infections are transmitted from person to person.
-

Is Chickenpox Contagious?
Chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by the varicella zoster virus. Chickenpox symptoms and signs include a blistering, itchy rash, fatigue, fever, and tiredness. Chickenpox is transmitted via contaminated droplets produced during sneezing or coughing and by coming in contact with blister fluid.
-
Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) Contagious?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a highly contagious disease caused by several enteroviruses. These viruses are transmitted via nasal secretions, kissing, and saliva. HFMD causes the following symptoms and signs: decreased appetite, sore throat, fever, weakness, and painful sores on the hands, feet, and in the mouth.
-

Is Hepatitis A Contagious?
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis A is one type of hepatitis. Hepatitis is transmitted through person to person contact, contaminated ice, vegetables, fruits, and untreated water. Hepatitis A can be prevented by the hepatitis A vaccine. Symptoms of hepatitis A may include nausea and/or vomiting, fever, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (yellowish color to skin and/or eyes, or joint pain.
-

Is Lupus Contagious?
Systemic lupus erythematosus in an inflammatory disease. Symptoms and signs include joint pain, fever, and rash. Though lupus is incurable, early medical intervention can help to reduce inflammation and protect the affected individual's organs.
-

Is Malaria Contagious?
Malaria is transmitted via the bite of an infected mosquito. The incubation period for malaria depends upon the species of Plasmodium that the infected mosquito transmits to the individual. Symptoms include high fever, chills, sweating, headaches, vomiting, and nausea.
-
Is Meningitis Contagious?
Meningitis, inflammation of the meninges, symptoms and signs include neck stiffness, headache, and fever. There are five types of meningitis: viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic, and noninfectious.
-

Is Mononucleosis (Mono) Contagious?
Mononucleosis (mono) is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and can be transmitted by an infected person's saliva. Mono symptoms and signs include rash, enlarged spleen, swollen lymph nodes, fever, sore throat, and fatigue.
-

Is MRSA Contagious?
MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA typically spreads through person-to-person contact, but it can also spread via aerosolized droplets. A MRSA skin infection will rapidly become painful, swollen, drain pus, and be warm to the touch.
-

Is Pneumonia Contagious?
Pneumonia is inflammation of the lung usually caused by bacterial or viral infection (rarely, also by fungi) that causes the air sacs to fill with pus. If inflammation affects both lungs, the infection is termed double pneumonia. If it affects one lung, it is termed single pneumonia. If it affects only a certain lobe of a lung it's termed lobar pneumonia. Most pneumonias are caused by bacteria and viruses, but some pneumonias are caused by inhaling toxic chemicals that damage lung tissue.
-

Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Contagious?
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a contagious viral infection that causes symptoms such as decreased appetite, runny nose, sneezing, coughing, and mild fever. The incubation period is 4-6 days, and the contagious period ends after the symptoms disappear.
-

Is Salmonella Contagious?
Salmonella is a bacteria that can cause a variety of diseases. Salmonella can be transmitted via direct and indirect contact. Salmonellosis typically lasts for 3-5 days and resolves on its own. Supportive care to prevent dehydration due to nausea and vomiting is usually the only treatment.
-

Is Scarlet Fever Contagious?
Scarlet fever is contagious when caused by a certain Group A strep bacteria strain. Scarlet fever can be transmitted via person-to-person contact and by coming in contact with contaminated objects. Treatment includes antibiotics. Scarlet fever symptoms include a red rash, fever, a red, sore throat, strawberry tongue, and others.
-

Is Sepsis Contagious?
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening infection that may be caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites. Sepsis spreads within the body from the infection site. Treatment of sepsis typically involves the administration of intravenous medications.
-

Is Swine Flu (H1N1) Contagious?
Swine flu (H1N1) is a contagious virus that spreads when an infected individual expels virus-containing droplets into the air during coughing or sneezing. Symptoms include sore throat, runny nose, fever, cough, chills, headache, fatigue, and possible vomiting and/or diarrhea. An H1N1 infection typically lasts for about a week.
-

Is the Ebola Virus Contagious?
Ebola hemorrhagic fever is a highly contagious disease that is transmitted through direct contact. Ebola's incubation period ranges from two to 21 days, and it's considered contagious for a period of 21 days after successful treatment/hospitalization. Ebola symptoms and signs include headache, fever, diarrhea, vomiting, and hemorrhaging.
-
Is Thrush Contagious?
Thrush is a fungal infection caused by Candida albicans. An infant with thrush can infect his/her mother with thrush during breastfeeding. Treatment typically involves using antifungal lozenges or mouthwash.
-
Is Tuberculosis (TB) Contagious?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes tuberculosis (TB). TB may be transmitted when an infected person sings, sneezes, coughs, or talks. TB symptoms and signs include coughing bloody sputum, night sweats, severe cough, fever, chills, fatigue, and weight loss.
-

Is Whooping Cough (Pertussis) Contagious?
Whooping cough (pertussis) is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis. Whooping cough symptoms include severe coughing fits and whooping sound produced during inhalation. The bacteria spreads via airborne droplets produced during sneezing or coughing. There is a whooping cough vaccine that is typically administered during childhood vaccinations.
-

Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA)
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) annually affects one child in every thousand. There are six types of JRA. Treatment of juvenile arthritis depends upon the type the child has and should focus on treating the symptoms that manifest.
-

Kidney Cancer
There are several types of kidney cancer, including renal cell cancer (renal adenocarcinoma or hypernephroma), transitional cell carcinoma, and Wilms tumor. Symptoms of kidney cancer include blood in the urine, an abdominal lump or mass, chronic pain in the side, and tiredness. Treatment of kidney cancer -- which may include surgery, arterial embolization, radiation therapy, biological therapy or chemotherapy -- depends upon the stage of the disease and the patient's overall health.
-

Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis)
Kidney infection (pyelonephritis) usually is caused by E. coli and other bacteria that have spread from the bladder from a UTI (urinary tract infection), poor hygiene, sexual intercourse, pregnancy, catheter, cystoscope exam, surgery, kidney stones, or prostate enlargement. Symptoms of kidney infection include back pain, frequent urination, pain during urination, fever, and or pus or blood in the urine. Kidney infection can be cured with antibiotic treatment. Cranberry juice may prevent UTIs, but that hasn’t been proven in all research studies.
-
Kidney Pain: Symptoms, Treatment, and Causes
Kidney pain has a variety of causes and symptoms. Infection, injury, trauma, bleeding disorders, kidney stones, and less common conditions may lead to kidney pain. Symptoms associated with kidney pain may include fever, vomiting, nausea, flank pain, and painful urination. Treatment of kidney pain depends on the cause of the pain.
-
Legionnaires' Disease
Legionellosis is an infection caused by the Legionella pneumophila bacterium. There are two forms of legionellosis: Pontiac fever and Legionnaires' disease, which is the more severe of the two infections. Symptoms of Pontiac fever include fever, headache, muscle aches, and chills. Symptoms of Legionnaires' disease include cough, chills, fever and sometimes muscle aches, headaches, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and severe pneumonia. While Pontiac fever resolves on its own, Legionnaires' disease must be treated with antibiotics.
-
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by the bite of an infected sand fly. The most common types of leishmania infection are cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis. Leishmaniasis is found mainly in the subtropics and tropics. Symptoms and signs of cutaneous leishmaniasis include skin sores with a raised edge and central crater, while those with visceral leishmaniasis usually have fever, weight loss, and an enlarged liver and spleen.
-

Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is an infectious disease that causes symptoms such as fever, headache, and chills. Treatment for leptospirosis requires antibiotics.
-

Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of cancer of the blood cells in which the growth and development of the blood cells are abnormal. Strictly speaking, leukemia should refer only to cancer of the white blood cells (the leukocytes) but in practice it can apply to malignancy of any cellular element in the blood or bone marrow, as in red cell leukemia (erythroleukemia).
-

Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
Low blood pressure, also referred to as hypotension, is blood pressure that is so low that it causes symptoms or signs due to the low flow of blood through the arteries and veins. Some of the symptoms of low blood pressure include light-headedness, dizziness, and fainting if not enough blood is getting to the brain. Diseases and medications can also cause low blood pressure. When the flow of blood is too low to deliver enough oxygen and nutrients to vital organs such as the brain, heart, and kidneys; the organs do not function normally and may be permanently damaged.
-

Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus or SLE)
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a condition characterized by chronic inflammation of body tissues caused by autoimmune disease. Lupus can cause disease of the skin, heart, lungs, kidneys, joints, and nervous system. When only the skin is involved, the condition is called discoid lupus. When internal organs are involved, the condition is called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
-

Malaria
Malaria is a disease that is spread by the bite of an infected Anopheles mosquito. Malaria symptoms include fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and body aches. Treatment involves supportive care and antibiotics.
-
Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a rare form of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is not known what causes MCL. MCL signs and symptoms include fever, enlarged spleen and liver, fatigue, and weight loss. Treatment of MCL incorporates radiotherapy and chemotherapy. MCL has a poor prognosis as it typically is diagnosed in a late stage.
-
Marburg Virus Disease
Marburg virus disease is a zoonotic infection that produces symptoms such as chills, headaches, fever, and muscle aches. The treatment for Marburg virus disease involves supportive care. Barrier and isolation techniques are the best preventive measures for Marburg infections.
-
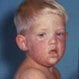
Measles
Measles (rubeola) is a highly contagious disease that's caused by a virus. Symptoms include a rash, high fever, cough, runny nose, and red eyes. Treatment focuses on symptom relief. The disease can be prevented with the measles, mumps, rubella, and chickenpox (varicella) vaccine (MMRV).
-

Melioidosis
Melioidosis (Whitmore's disease) is an infectious disease caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei bacteria. Symptoms include bronchitis, pneumonia, fever, headache, loss of appetite, cough, and chest pain. Treatment involves antibiotics or surgical removal of the lung abscess in severe cases.
-

Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the membranes that cover the spinal cord and brain. Symptoms include fever, headache, and a stiff neck. Treatment of meningitis depends upon the cause of the infection and may include antibiotics or antiviral medications.
-
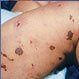
Meningococcemia (Meningococcal Disease)
Meningococcemia is a bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria meningitides. Meningococcemia symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, and body aches. Meningococcemia is treated with intravenous antibiotics. There is an effective and safe vaccine to protect against most serogroups of meningococcus that cause meningococcemia.
-
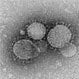
MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome)
MERS-CoV (Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus) infection can be spread through respiratory secretions. Symptoms include fever, dry cough, and severe shortness of breath. Treatment focuses on supportive care.
-

Mold Exposure: Symptoms, Removal, and Remediation
Mold exposure may cause symptoms in people who are sensitive to molds. Symptoms of mold allergy include sneezing, runny nose, wheezing, coughing, redness of the eyes, and rash. Prevent mold growth by keeping indoor humidity low, between 30%-50%, using bathroom fans when showering, repairing plumbing leaks quickly, and using an air conditioner during humid seasons.
-

Monkeypox
Monkeypox is a viral disease that causes symptoms such as fever, sweating, and a rash with papules and pustules on the face and chest. PCR, ELISA, or Western blot tests are used to diagnose monkeypox. Treatment usually involves administering a smallpox vaccination, cidofovir, and possibly vaccinia immune globulin.
-
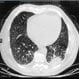
Mucormycosis
Mucormycosis (zygomycosis) is a fungal infection caused by Zygomycetes. Symptoms and signs include fever, headache, coughing, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, bloody vomit, and possible altered mental status. Treatment usually involves debridement of infected tissue and antifungal drugs.
-
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a form of cancer that develops in plasma cells, the white blood cells that make antibodies. Symptoms include bone pain, weakness, extreme thirst, nausea, frequent urination, and broken bones. Treatment of multiple myeloma depends upon the staging and symptoms of the disease.
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis or MS is an autoimmune disorder in which brain and spinal cord nerve cells become demyelinated. This damage results in symptoms that may include numbness, weakness, vertigo, paralysis, and involuntary muscle contractions. Different forms of MS can follow variable courses from relatively benign to life-threatening. MS is treated with disease-modifying therapies. Some MS symptoms can be treated with medications.
-

Mumps
Mumps is an acute viral illness caused by the mumps virus. Symptoms and signs of mumps include fever, headache, muscle aches, tiredness, and loss of appetite, followed by swelling of the salivary glands.
-
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis, a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disease. Varying degrees of weakness of the voluntary muscles of the body are the main characteristics. A defect in the transmission of nerve impulses of the muscles is the cause of myasthenia gravis. Myasthenic crisis is when the muscles that control breathing weaken, which requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include weakness of the eye muscles, facial expression, and difficulty swallowing. Treatment of myasthenia gravis includes medical therapies to control the symptoms of the disease.
-

NDM-1
NDM-1 (New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase) is an enzyme produced by certain strains of bacteria that have recently acquired the genetic ability to make this compound. Bacteria that produce NDM-1 are resistant to all commonly used beta-lactam antibiotics. Klebsiella, Escherichia and Acinetobacter are known to possess the gene for NDM-1, which can turn these bacteria into superbugs. Symptoms and signs of NDM-1 infection include fever, fatigue, and shock. Treatment depends upon the NDM-1 strain.
-

Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis is also known as a flesh-eating bacterial infection, Fournier's gangrene, suppurative fasciitis, and necrotizing cellulitis. The disease is occasionally caused by fungi, but most cases are caused by bacteria that enter the skin through insect bites, cuts, puncture wounds, or surgical incisions. Signs and symptoms include pain, redness, swelling, fever, chills, skin ulceration, bullae formation, black scabs, gas formation, and fluid draining from the site of infection. Treatment involves hospitalization, the use of intravenous antibiotics, and debridement of the necrotic tissue.
-

Nipah Virus Infection
Nipah virus infection is a zoonotic infection that fruit bats and pigs can transmit to humans. NiV signs and symptoms include headache, fever, myalgia, atypical pneumonia, and encephalitis. Treatment focuses on supportive care.
-
Norovirus Infection
Norovirus infection causes stomach flu, or gastroenteritis. It's a very contagious illness with symptoms that include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, fever, headache, chills, and muscle aches. Norovirus infection cannot be treated with antibiotics, so treatment focuses on maintaining proper hydration.
-
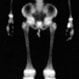
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone. Potential causes include injections around the bone, fractures that puncture the skin, recent surgeries, and bacterial infections that travel from other areas of the body, spreading through the blood to the bone. Symptoms include pain, fever, chills, stiffness, and nausea. Treatment involves antibiotics and pain medications. Surgery is sometimes necessary.
-

Palpitations
Palpitations are uncomfortable sensations of the heart beating hard, rapidly, or irregularly. Some types of palpitations are benign, while others are more serious. Palpitations are diagnosed by taking the patient history and by performing an EKG or heart monitoring along with blood tests. An electrophysiology study may also be performed. Treatment of palpitations may include lifestyle changes, medication, ablation, or implantation of a pacemaker. The prognosis if palpitations depends on the underlying cause.
-

Pericoronitis
Pericoronitis is inflammation of the gum tissue around the molars. Pericoronitis commonly occurs in teens or young people when the wisdom teeth erupt. Symptoms include pain, swelling, swollen lymph nodes, and difficulty opening the mouth. Pericoronitis can be diagnosed by a dentist and is treated with pain medication. Severe cases may be treated with surgery.
-

Peritonitis
Peritonitis is a bacterial infection inside of the abdomen. Some doctors choose to group the causes of peritonitis into five categories; 1) primary peritonitis, 2) secondary peritonitis, 3) tertiary peritonitis, 4) chemical (sterile) peritonitis, and 5) peritoneal abscess. Others do not categorize peritonitis, they use a term to describe the disease in front or behind the word peritonitis. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Treatment is generally with antibiotics.
-

Pilonidal Cyst
A pilonidal cyst is a cyst that forms near the cleft of the buttocks. The cysts are thought to be caused by the penetration of loose hairs into the skin. Symptoms and signs include pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and drainage of pus from the area of the cyst. Treatment of a pilonidal cyst involves incision and drainage.
-

Plague (Black Death)
Plague is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria Yersinia pestis. Transmission to humans occurs via fleas that have bitten infected rodents. There are three forms of plague that infect humans: bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic. Antibiotics are the standard treatment for plague.
-

Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflammation of the lungs caused by fungi, bacteria, or viruses. Symptoms and signs include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chills. Antibiotics treat pneumonia, and the choice of the antibiotic depends upon the cause of the infection.
-

Powassan Virus Disease
Powassan (POW) virus disease is a rare tick-borne disease that causes symptoms such as confusion, memory problems, fever, headache, vomiting, and seizures. POW virus treatment focuses on supportive care that aims to reduce symptoms. There is no medication or cure for POW virus disease.
-

Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that is transmitted via the bite of an infected animal. Symptoms include fever, headaches, and weakness. Treatment involves a series of injections: rabies immune globulin and four rabies vaccines administered over 2 weeks.
-

Rat Lungworm (Angiostrongylus cantonensis)
Rat lungworm (Angiostrongylus cantonensis) is a parasite that infects rats. The parasite can infect people if ingested by eating undercooked or raw infected snails or slugs. Though rat lungworm often causes no signs and symptoms, the parasite can cause eosinophlic meningitis in some. Stiff neck, headach, vomiting, nausea, and fever are symptoms of eosinophilic meningitis. Treatment is usually unnecessary. For more severe infections, treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms.
-
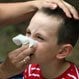
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a highly contagious viral infection. Symptoms and signs include fever and nasal congestion and discharge. Treatment focuses on supportive care. This disease has a good prognosis in babies and infants.
-

Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever is a disease that sometimes occurs after a group A streptococcal infection of the throat. Symptoms and signs include carditis, polyarthritis, Aschoff bodies, rash, Sydenham's chorea, and fever. Treatment for rheumatic fever involves eliminating the bacteria with penicillin, erythromycin, or azithromycin. Further treatment focuses on alleviating the symptoms brought on by the body's immunologic response to the bacteria.
-
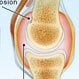
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease resulting in chronic inflammation of the joints, the tissue around the joints, as well as other organs in the body. Early RA signs and symptoms include anemia, both sides of the body affected (symmetric), depression, fatigue, fever, joint deformity, joint pain, joint redness, joint stiffness, joint swelling, joint tenderness, joint warmth, limping, loss of joint function, loss of joint range of motion, and polyarthritis.
-

Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
Rocky Mountain spotted fever is a tick-borne disease that causes symptoms and signs such as fever, rash, headache, and muscle aches. The antibiotic doxycycline is the standard treatment for Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
-

Roseola
Roseola is a viral illness that most commonly affects young children. Symptoms and signs include a sudden high fever that lasts for three to five days, swollen neck glands, runny nose, puffy eyelids, diarrhea, irritability, and a bulging soft spot on the head.
-

Rotavirus
Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe diarrhea among infants and children throughout the world. Almost all children have become infected with rotavirus by their third birthday. Repeat infections with different viral strains are possible, and most children have several episodes of rotavirus infection in the first years of life. Children between the ages of six and 24 months are at greatest risk for developing severe disease from rotavirus infection. Rotavirus symptoms include: fever, vomiting, watery diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Rotavirus infection can be associated with severe dehydration in infants and children.
-

Salmonella
Salmonella infection (salmonellosis) is typically caused by the consumption of contaminated foods. Symptoms of salmonellosis include fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Salmonellosis typically resolves on its own in four to seven days. It's important to increase one's fluid intake to compensate for the fluid lost by vomiting and/or diarrhea.
-
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis, a disease resulting from chronic inflammation, causes small lumps (granulomas) to develop in a great range of body tissues and can appear in almost any body organ. However, sarcoidosis most often starts in the lungs or lymph nodes.
-

SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a respiratory disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV. Symptoms include fever and shortness of breath. Patients with SARS often require oxygen and severe cases require mechanical ventilation.
-

Scarlet Fever (Scarlatina)
Scarlet fever, a bacterial infection caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria, causes symptoms and signs such as fever, rash with a sandpaper-like texture, and sore throat. Oral penicillin is the standard treatment for scarlet fever, or scarlatina.
-

Sepsis
Sepsis (blood poisoning) is a potentially deadly infection with signs and symptoms that include elevated heart rate, low or high temperature, rapid breathing and/or a white blood cell count that is too high or too low and has more than 10% band cells. Most cases of sepsis are caused by bacterial infections, and some cases are caused by fungal infections. Treatment requires hospitalization, IV antibiotics, and therapy to treat any organ dysfunction.
-

Septic Shock
Septic shock is a system-wide infection that causes low blood pressure and organ failure. Symptoms and signs include vomiting, nausea, anxiety, confusion, fever, shakes, chills, rapid heart rate, and increased breathing rate. Treatment may incorporate intravenous fluids and antibiotics and possible intubation.
-

Shigella Infection
Shigellosis is a disease caused by the Shigella bacteria. Bloody diarrhea, stomach cramps, and fever are common symptoms. Mild infections usually resolve on their own. Antibiotics are used to treat more severe cases.
-
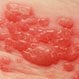
Shingles
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful rash caused by the varicella zoster virus. Other shingles symptoms include headache, fever, nausea, and body aches. Treatment focuses on pain management and shortening the duration of the illness with antiviral medications.
-

Smallpox
Smallpox is a disease caused by the variola virus. Symptoms and signs include: a characteristic rash and high fever. Treatment focuses on supporting the patient. Smallpox may be prevented with the ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine.
-

Sore Throat
Sore throat (throat pain) usually is described as pain or discomfort in the throat area. A sore throat may be caused by bacterial infections, viral infections, toxins, irritants, trauma, or injury to the throat area. Common symptoms of a sore throat include a fever, cough, runny nose, hoarseness, earaches, sneezing, and body aches. Home remedies for a sore throat include warm soothing liquids and throat lozenges. OTC remedies for a sore throat include OTC pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Antibiotics may be necessary for some cases of sore throat.
-
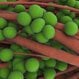
Staph (Staphylococcus) Infection
Staphylococcus or staph is a group of bacteria that can cause a multitude of diseases. Staph infections can cause illness directly by infection or indirectly by the toxins they produce. Symptoms and signs of a staph infection include redness, swelling, pain, and drainage of pus. Minor skin infections are treated with an antibiotic ointment, while more serious infections are treated with intravenous antibiotics.
-

STDs in Men
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections transmitted during sexual contact. They may be caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. STDs in men cause no symptoms or symptoms like genital burning, itching, sores, rashes, or discharge. Common infections that are sexually transmitted in men include gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, hepatitis C and B, genital warts, human papillomavirus (HPV), and genital herpes. Some STDs in men are treatable while others are not. STDs are diagnosed with tests that identify proteins or genetic material of the organisms causing the infection. The prognosis of an STD depends on whether the infection is treatable or not. Use of latex condoms can help reduce the risk of contracting an STD but it does not eliminate the risk entirely.
-
Still's Disease
Still's disease (systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis) is a disorder characterized by inflammation with high fever spikes, fatigue, salmon-colored rash, and/or arthritis. Though there have been several theories regarding the cause(s) of Still's disease, the cause is not yet known. Many symptoms of Still's disease are often treatable with anti-inflammatory drugs.
-
Stomach Flu (Gastroenteritis) Symptoms Signs, Treatment Remedies, Diet
Stomach flu (gastroenteritis) is a term referred used to describe a variety of gastrointestinal problems. The most common signs and symptoms of gastroenteritis are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. The most common cause of gastroenteritis in the United States is Norovirus. Other causes of gastroenteritis include Rotavirus, Astrovirus, Adenovirus, and Sapovirus. There are bacterial causes of gastroenteritis such as Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter Aeromonas, E. coli, Clostridium, Vibrio, Campylobacter, and Yersinia spp. Parasites that cause gastroenteritis include Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora, and Entamoeba. Treatment for gastroenteritis is generally home remedies such as keeping hydrated to prevent dehydration. At times, hospitalization may be necessary if dehydration occurs.
-
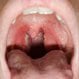
Strep Throat
Strep throat is a bacterial infection of the throat. Signs and symptoms of strep throat include headache, nausea, vomiting, sore throat, and fever. Strep throat symptoms in infants and children are different than in adults. Strep throat is contagious and is generally passed from person-to-person. Treatment for strep throat symptoms include home remedies and OTC medication; however, the only cure for strep throat are antibiotics.
-

Streptococcal Infections
Group A streptococcal infections are caused by group A Streptococcus, a bacteria that causes a variety of health problems, including strep throat, impetigo, cellulitis, erysipelas, and scarlet fever. There are more than 10 million group A strep infections each year.
-
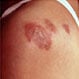
Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
Sweet syndrome (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a skin condition that sometimes occurs due to an immune system response to RA, pregnancy, certain cancers, inflammatory bowel diseases, blood disorders, respiratory tract infections, and particular medications. Symptoms and signs include characteristic skin lesions that grow and spread into clusters. Sore eyes, high fever, mouth ulcers, headache, and aching joints may accompany the lesions. Though Sweet syndrome may resolve on its own, more severe cases may require medications like corticosteroids.
-
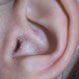
Swimmer's Ear (External Otitis)
Swimmer's ear (external otitis) is an infection of the skin that covers the outer ear canal. Causes of swimmer's ear include excessive water exposure that leads to trapped bacteria in the ear canal. Symptoms of simmer's include a feeling of fullness in the ear, itching, and ear pain. Chronic swimmer's ear may be caused by eczema, seborrhea, fungus, chronic irritation, and other conditions. Common treatment includes antibiotic ear drops.
-

Swine Flu
Novel H1N1 influenza A virus infection (swine flu) is an infection that generally is transferred from an infected pig to a human, however there have been reported cases where infection has occured with no contact with infected pigs. Symptoms of swine flu are "flu-like" and include fever, cough, and sore throat. Treatment is generally with the antibiotics oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza).
-

Swollen Lymph Nodes (Glands)
Lymph nodes help the body's immune system fight infections. Causes of swollen lymph nodes (glands) may include infection (viral, bacterial, fungal, parasites). Symptoms of swollen lymph nodes vary greatly, but may include fever, night sweats, toothache, sore throat, or weight loss. Causes of swollen lymph nodes also vary, but may include cancer, the common cold, mono, chickenox, HIV, and herpes. The treatment of swollen lymph nodes depends upon the cause.
-
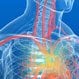
Takayasu Disease
Takayasu disease (also referred to as Takayasu arteritis) is a chronic inflammation of the aorta and its branch arteries. Takayasu disease is most common of Women of Asian descent and usually begins between 10 and 30 years of age. Symptoms include painful extremities, dizziness, headaches, chest and abdominal pain, and a low-grade fever. Treatment for Takayasu disease includes cortisone medication to suppress the inflammation.
-

The First Signs of Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis)
Kidney stones are solid masses of crystalline material that form in the kidneys. Symptoms of kidney stones can include pain, nausea, vomiting, and even fever and chills. Kidney stones are diagnosed via CT scans and specialized X-rays. Treatment of kidney stones involves drinking lots of fluids and taking over-the-counter pain medications to medical intervention including prescription medications, lithotripsy, and sometimes even surgery.
-

Thymoma
Thymoma is an uncommon cancer of the thymus gland. Many thymomas are asymptomatic. When symptoms do occur, they include chest pain, shortness of breath, and cough. Treatment of thymomas includes surgery, and sometimes, radiation and chemotherapy. The prognosis for thymoma is excellent when it is found in the early stages.
-

Ticks
Ticks are known transmitters of disease to humans and animals. Tick-borne diseases include Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Q fever, tularemia, babesiosis, and Southern tick-associated rash illness. Infected ticks spread disease once they've bitten a host, allowing the pathogens in their saliva and mouth get into the host's skin and blood. Tick bites are typically painless, but the site of the bite may later itch, burn, turn red, and feel painful. Individuals allergic to tick bites may develop a rash, swelling, shortness of breath, numbness, or paralysis. Tick bite treatment involves cleaning and applying antibiotic cream.
-
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is an infection caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus. Toxic shock syndrome symptoms include low blood pressure, fever, and a rash with peeling skin. Treatment involves IV fluids to treat the shock, IV antibiotics, cleaning infected wounds, and hospitalization in the intensive care for other assorted treatments.
-
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis (toxo) is a parasitic infection that causes flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes, and muscle aches and pains that may last from a few days to several weeks. Toxoplasmosis can be contracted by touching the hands to the mouth after gardening, cleaning a cat's litter box, or anything that came into contact with cat feces. Toxoplasmosis can also be contracted by eating raw or partly cooked meat, especially pork or lamb, or touching the hands to the mouth after contact with raw or undercooked meat
-

Travel Medicine
Travelers should prepare for their trip by visiting their physician to get the proper vaccinations and obtain the necessary medication if they have a medical condition or chronic disease. Diseases that travelers may pick up from contaminated water or food, insect or animal bites, or from other people include: malaria, meningococcal meningitis, yellow fever, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, polio, and cholera.
-

Tuberculosis (TB)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that causes tuberculosis (TB). Symptoms and signs of TB include bloody sputum, fever, cough, weight loss, and chest pain. Treatment depends upon the type of TB infection.
-
Tularemia
Tularemia (rabbit fever) is an infection caused by the Francisella tularensis bacteria. People can become infected with tularemia by coming into contact with infected animals or via a tick bite. Symptoms and signs include fever, headache and rash. Tularemia is treated with streptomycin or gentamicin.
-
Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever is an illness caused by the Salmonella typhi bacteria. The illness is contracted by ingesting the bacteria in contaminated water or food. Symptoms include headaches, fever, diarrhea, lethargy, aches and pains, and poor appetite. Treatment focuses on killing the Salmonella bacteria with antibiotics.
-

Typhus
Typhus is a disease caused by Rickettsia bacteria. Symptoms and signs include fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and rash. Antibiotics are recommended as the treatment for endemic and epidemic typhus infections.
-

Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the bladder, kidneys, ureters, or urethra. E. coli, a type of bacteria that lives in the bowel and near the anus, causes most UTIs. UTI symptoms include pain, abdominal pain, mild fever, urinary urgency, and frequency. Treatment involves a course of antibiotics.
-

Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE)
Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) infection is the most common type of infection acquired by patients while hospitalized. Patients at risk for VRE are those who are already ill, and hospitalized, including individuals with diabetes, elderly, ICU patients, kidney failure patients, or patients requiring catheters. Enterococci can survive for months in the digestive tract and female genital tract. Other risk factors for acquiring VRE include those how have been previously treated with vancomycin and combinations of other antibiotics. Treatment of VRE is generally with other antibiotics other than vancomycin. Prevention of VRE can be achieved by proper hand hygiene.
-

Vibrio Infection (Vibriosis)
Vibrio bacteria thrive in warm coastal waters and cause illness when people eat undercooked shellfish or when brackish or saltwater comes in contact with an open wound. Treatment involves drinking plenty of liquid.
-

Viral Hemorrhagic Fever
Viral hemorrhagic fever(s), or VHFs are a group of illnesses caused by distinct families of viruses. Many of these viruses are life-threatening, and classified as biosafety level four (BSL-4) pathogens. Viral hemorrhagic fever viruses are caused arenaviruses, filoviruses, bunyaviruses, and flaviviruses. The viruses are carried in rodents and transmitted through urine, fecal, saliva, or other body excretions from the infected rodents. Symptoms of viral hemorrhagic fever include marked fatigue, dizziness, muscle aches, loss of strength, fever, and exhaustion. Severely ill patients may also suffer shock coma, seizures, delirium, kidney failure, or nervous system malfunction. There is no established cure for viral hemorrhagic fever.
-

West Nile Virus
West Nile virus (West Nile encephalitis) is a brain infection caused by a virus. People become infected with the virus after they're bitten by a mosquito that has fed off of a bird that's infected with the West Nile virus. Symptoms in humans include fever, headache, rash, body ache, and swollen lymph nodes. Treatment for a West Nile virus infection involves supportive care.
-

What Are the 5 Types of Fever?
Fever is a sign that your body is fighting an infection or illness. Learn the signs of fever, what causes fever, how doctors diagnose fever, and what you can do to treat fever.
-
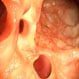
What Are the Symptoms of a Diverticulitis Flare-Up?
Diverticula are small, bulging pouches that form in the lining of the digestive system in some people. They are usually formed in the lower part of the large intestine. The presence of diverticula is known as diverticulosis. They are usually seen in people over the age of 40 and rarely cause issues. When one diverticulum or diverticula becomes inflamed or infected due to the accumulation of waste products and bacteria, the condition is called diverticulitis.
-
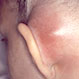
What Are the Symptoms of a Mastoid Infection?
What is a mastoid infection, and what causes it? Learn the signs of mastoiditis and how it is diagnosed and treated.
-

What Body Temperature Is Considered a Fever?
A fever is defined as a body temperature that is higher than normal. The normal body temperature, however, varies slightly among different individuals. For adults, a fever is when the body temperature is higher than 100.4°F. For children, a fever is when their body temperature is more than 100.4°F (measured rectally), 99.5°F (measured orally) or 99°F (measured under the arm).
-

What Is Chikungunya Virus?
Chikungunya virus is an infection spread (transmitted) through a bite from an infected mosquito. Common symptoms of Chikungunya virus infection include joint pain, headache, rash, and fever. There is no drug or vaccine available to treat or prevent Chikungunya virus infections. Some medicines and home remedies may help relieve symptoms of Chikungunya virus infection.
-

What Is Enterovirus (Non-Polio Enterovirus Infection)?
Non-polio enteroviruses cause a variety of infections, including aseptic meningitis, hand, foot, and mouth disease, herpangina, and the common cold. Symptoms and signs of enterovirus infection include hypoxia, eye pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fever. Treatment involves supportive care to reduce symptoms.
-
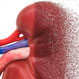
What Is IgA Nephropathy (Berger's Disease)?
Berger's disease or immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy is a kidney disorder that presents with the passing of blood in the urine. This happens due to swelling of the glomeruli (filtering units of the kidney that produce urine). The swelling is usually caused due to a buildup of a substance called IgA in the kidneys.
-

What Is Kawasaki Disease?
Kawasaki disease is a rare children's disease characterized by a fever that lasts more than five days and at least four of the following five symptoms are present: rash, swollen neck lymph gland, red tongue, swelling or redness of the hands or feet, and conjunctivitis. High doses of aspirin are used to treat Kawasaki disease. Cortisone and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be used during treatment.
-

What Is Lyme Disease in Humans?
Lyme disease is a bacterial illness, which is spread by ticks when they bite the skin. Initially the disease affects the skin causing a reddish rash associated with flu-like symptoms. It takes weeks to months after the initial redness of the skin for its effects to spread throughout the body. Lyme disease can be treated with antibiotics. Lyme disease can be prevented by using tick avoidance techniques.
-

What Is Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) is cancer of the lymphatic system, a vital part of the body's immune system. Symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, coughing, weakness, chest pain, unexplained weight loss, and abdominal pain.
-

What Is Valley Fever (Coccidioidomycosis)?
Valley fever (coccidioidomycosis) is a disease caused by the inhalation of the Coccidioides immitis or C. posadasii fungus. Symptoms are flu-like and resolve over two to six weeks. Infection typically requires no treatment, though there are many antifungal drugs to treat valley fever.
-

Whooping Cough (Pertussis)
Whooping cough (pertussis) is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. There are an estimated 300,000 plus deaths annually from whooping cough (pertussis). Whooping cough commonly affects infants and young children but can be prevented with immunization with the vaccine. First stage whooping cough symptoms are a runny nose, sneezing, low-grade fever, a mild cough with the cough gradually becoming more severe. After one to two weeks, the second stage of whooping cough begins.
-

Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is an infectious disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. Side effects are rare with the yellow fever vaccine. Symptoms include fever, chills, back pain, nausea, vomiting, and headache. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms.
-

Zika Virus (Zika Fever)
The Zika virus is transmitted by the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito. Symptoms and signs of a Zika virus infection include conjunctivitis, headache, joint pain, fever, rash, and muscle aches. Treatment for Zika virus infections aims to alleviate symptoms.
Examples of Medications for Fever
- acetaminophen (Tylenol, Tylenol Arthritis Pain, Tylenol Ext, Little Fevers Children's Fever/Pain)
- aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, Bayer, Ecotrin, and others)
- ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, Nuprin)
- naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprelan, Naprosyn)
- OTC Pain Relievers and Fever Reducers
- tacrolimus (Prograf, Astagraf XL, Envarsus XR)
- Prostatitis vs. BPH (Enlarged Prostate): What Is the Difference?
- Listeria(Listeriosis)
- 16 Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Signs & Symptoms
- Abscessed Tooth
- Adenovirus 14 (Killer Cold Virus)
- Anencephaly
- Anthrax
- Appendicitis
- Are You Too Sick to Work?
- Arthritis (Joint Inflammation)
- Ascariasis Disease
- Aspergillus Infection (Aspergillosis)
- Balamuthia
- Bath Salts
- Bile Duct Cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma)
- Bird Flu (Avian Influenza, Avian Flu)
- Bladder Infection (Cystitis)
- Blood in Semen
- Bocavirus
- Bone Cancer
- Brain Eating Amoeba (Naegleria fowleri)
- Brain Lesions (Lesions on the Brain)
- Brucellosis
- Can a Liver Hemangioma Go Away on Its Own?
- Cancer
- Capnocytophaga canimorsus
- Cat Scratch Disease
- Cellulitis
- Chagas Disease
- Chest Pain
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS or SEID)
- Cold vs. Flu
- Cold, Flu, Allergy Treatments
- Colitis
- Common Cold
- Connective Tissue (CT) Disease
- COVID-19 (Coronavirus) Prevention Tips
- COVID-19 (Coronavirus, 2019-nCoV)
- Coxsackievirus
- CRE Bacteria Infection
- Croup
- Cryptosporidiosis
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Dengue Fever
- Diverticulitis (Diverticulosis, Diverticular Disease)
- E. coli (0157:H7) Infection
- Ebola (Ebola Virus Disease or Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever)
- Encephalitis
- Endocarditis
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
- Factitious Disorders
- Fever and Headache
- Fever in Adults and Children
- Fifth Disease (Parvovirus, Erythema Infectiosum)
- Flu (Influenza)
- Fungal Arthritis
- Fungal Meningitis
- Gangrene
- German Measles (Rubella)
- Giardia Lamblia
- Group B Strep
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
- Heat Rash: Pictures, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Hepatitis (Viral Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, G)
- Hepatitis E Viral Infection
- Herpangina
- HIV vs. AIDS
- Hodgkin's Disease
- Hodgkin's vs. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- How Do I Bring My Baby's Fever Down?
- How Long Is a Cold or Flu Contagious?
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- Infectious Mononucleosis (Mono)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- IsC. diff(Clostridium difficile) Contagious?
- IsE. coliContagious? (Symptoms and Cure)
- Is a Staph Infection Contagious?
- Is Chickenpox Contagious?
- Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) Contagious?
- Is Hepatitis A Contagious?
- Is Lupus Contagious?
- Is Malaria Contagious?
- Is Meningitis Contagious?
- Is Mononucleosis (Mono) Contagious?
- Is MRSA Contagious?
- Is Pneumonia Contagious?
- Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Contagious?
- Is Salmonella Contagious?
- Is Scarlet Fever Contagious?
- Is Sepsis Contagious?
- Is Swine Flu (H1N1) Contagious?
- Is the Ebola Virus Contagious?
- Is Thrush Contagious?
- Is Tuberculosis (TB) Contagious?
- Is Whooping Cough (Pertussis) Contagious?
- Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA)
- Kidney Cancer
- Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis)
- Kidney Pain: Symptoms, Treatment, and Causes
- Legionnaires' Disease
- Leishmaniasis
- Leptospirosis
- Leukemia
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
- Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus or SLE)
- Malaria
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
- Marburg Virus Disease
- Measles
- Melioidosis
- Meningitis
- Meningococcemia (Meningococcal Disease)
- MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome)
- Mold Exposure: Symptoms, Removal, and Remediation
- Monkeypox
- Mucormycosis
- Multiple Myeloma
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Mumps
- Myasthenia Gravis
- NDM-1
- Necrotizing Fasciitis
- Nipah Virus Infection
- Norovirus Infection
- Osteomyelitis
- Palpitations
- Pericoronitis
- Peritonitis
- Pilonidal Cyst
- Plague (Black Death)
- Pneumonia
- Powassan Virus Disease
- Rabies
- Rat Lungworm (Angiostrongylus cantonensis)
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- Rheumatic Fever
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
- Roseola
- Rotavirus
- Salmonella
- Sarcoidosis
- SARS
- Scarlet Fever (Scarlatina)
- Sepsis
- Septic Shock
- Shigella Infection
- Shingles
- Smallpox
- Sore Throat
- Staph (Staphylococcus) Infection
- STDs in Men
- Still's Disease
- Stomach Flu (Gastroenteritis) Symptoms Signs, Treatment Remedies, Diet
- Strep Throat
- Streptococcal Infections
- Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
- Swimmer's Ear (External Otitis)
- Swine Flu
- Swollen Lymph Nodes (Glands)
- Takayasu Disease
- The First Signs of Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis)
- Thymoma
- Ticks
- Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
- Toxoplasmosis
- Travel Medicine
- Tuberculosis (TB)
- Tularemia
- Typhoid Fever
- Typhus
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE)
- Vibrio Infection (Vibriosis)
- Viral Hemorrhagic Fever
- West Nile Virus
- What Are the 5 Types of Fever?
- What Are the Symptoms of a Diverticulitis Flare-Up?
- What Are the Symptoms of a Mastoid Infection?
- What Body Temperature Is Considered a Fever?
- What Is Chikungunya Virus?
- What Is Enterovirus (Non-Polio Enterovirus Infection)?
- What Is IgA Nephropathy (Berger's Disease)?
- What Is Kawasaki Disease?
- What Is Lyme Disease in Humans?
- What Is Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma?
- What Is Valley Fever (Coccidioidomycosis)?
- Whooping Cough (Pertussis)
- Yellow Fever
- Zika Virus (Zika Fever)
