Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis)
- Kidney Function
- Kidneys Location
- vs. UTI
- Symptoms/Signs
- Causes
- Diagnosis
- Types
- E. coli/Bacteria
- Treatment
- Food for/Cranberry Juice
Kidney infection definition and facts
- Kidney infection is one of a number of infections that can involve the urinary tract.
- Infection of the kidney is very common, especially in young females.
- Causes of kidney infection are bacteria that have gained entry to the urinary tract, usually via the anus or vagina.
- Risk factors for kidney infection are pregnancy, sexual intercourse, a history of urinary tract infection, spermicide use, kidney stones, use of urinary catheters, diabetes, and surgery or instrumentation of the urinary tract.
- Kidney infections are not contagious.
- Symptoms of kidney infection are
- fever,
- chills,
- abdominal pain,
- nausea,
- vomiting,
- painful urination, and
- a need to urinate frequently.
- Treatment of kidney infection involves oral or intravenous antibiotics.
- Kidney infections can sometimes be prevented by drinking plenty of fluids, changing urinary catheters frequently, good hygiene practices, and taking preventive antibiotics in certain people at high risk.
- If treated early and adequately, kidney infection generally has a good outcome.

What is the function of the kidneys?
The kidneys have a variety of important functions in the body. These functions include filtering and excreting the waste products from the blood as it circulates through capillaries within the kidneys, regulating blood pressure, maintaining steady levels of electrolytes (for example, calcium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, and chloride), and contributing to the production of red blood cells.
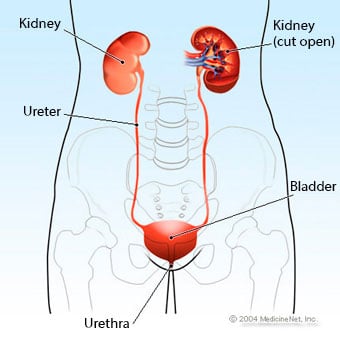
Where are the kidneys located?
The kidneys are located on either side of the body underneath the diaphragm near the lower back. Each kidney is connected to the bladder in the pelvis by ureters (long tube-like structures) that drain the urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Urine stored in the bladder is excreted from the body through the urethra. Collectively, these structures make up what is called the urinary tract.

What is a kidney infection? Is it the same as a urinary tract infection?
The main components of the urinary tract system are kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Any part of the urinary system may become infected and this is generally referred to as urinary tract infection (UTI). When a kidney becomes infected, the condition is medically referred to as pyelonephritis. Thus, kidney infection is only one of several types of infections encompassed by the term UTI. The spectrum of UTIs includes:
- Acute uncomplicated cystitis (bladder infection)
- Recurrent cystitis
- Complicated UTI
- Prostatitis (prostate infection)
- Kidney infection (pyelonephritis)
- Catheter-associated UTI (in individuals with indwelling urinary catheters)
A more general classification of urinary tract infection includes:
- Lower urinary tract infection involves the urethra, the bladder, and, in men, the prostate gland.
- Upper urinary tract infection refers to infection of the kidneys.

What are the signs and symptoms of kidney infection?
Some of the common symptoms of a kidney infection include:
- fever,
- nausea,
- vomiting,
- abdominal pain,
- shivering,
- shaking -- chills,
- painful urination (dysuria),
- frequent urination (urinary frequency),
- urge to urinate (urinary urgency),
- flank and low and mid back pain (dull kidney pain), and
- generalized malaise.
Signs of kidney infection on the exam may include:
- fever,
- tenderness on the flanks (costovertebral angle tenderness, referring to tenderness upon tapping gently on the mid-back on the sides), and
- clinical evidence of infection in the urinalysis (laboratory analysis of urine).
In elderly patients and those with weak immune systems, kidney infection may be more severe with these conditions:
- confusion,
- lethargy,
- rapid heart rate,
- low blood pressure, and
- dehydration.

What are the causes of kidney infection?
Urine, similar to other fluids in the body, is normally sterile without any bacterial infection. Therefore, the presence of bacteria in the urine is considered abnormal and may lead to urinary tract infection. Typically, bacteria gain access to the urinary system from outside through the urethra (the drainage tube for urine from the bladder). The bacteria may then ascend in the urinary system and cause kidney infections. Kidney infection (upper UTI) is typically more severe than lower UTI because bacteria may also infect the bloodstream (bacteremia) from the kidneys resulting in a more severe illness.
Bacteria may travel from the rectum or the vagina towards the urethra to gain entry into the urinary system. Other bacteria may enter from the skin. Women are more susceptible to urinary tract infections due to the shorter length of their urethras in comparison to those of men.
Is a kidney infection contagious?
Since kidney infection occurs when bacteria from the genital or anal areas enter the urinary tract, it is typically not contagious.

What are risk factors for kidney and urinary tract infection (UTI)?
There are many factors that may increase the chances of infection of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Premenopausal women are at higher risk for developing UTI and kidney infections. Risk factors within this population include:
- Sexual intercourse (for women -- may increase the risk of urinary tract infection because of the possible introduction of the bacteria around the urethra into the urinary system [a condition sometimes referred to as "honeymoon cystitis"])
- Previous urinary tract infection
- Use of spermicides
- History of a mother with recurrent UTIs (which suggests a possible genetic component to susceptibility)
- Pregnancy
In fact, some pregnant women may have urinary infections during their pregnancy. This may occur because of the slower transit of urine in the ureters during pregnancy from the pressure applied by the enlarging uterus.
In post-menopausal women, physiological factors (vaginal dryness, urinary incontinence, urinary retention, and prolapse of the pelvic organs) seem to add potential risk to develop UTIs and kidney infections.
In men, prostate enlargement is the main risk factor for UTI and kidney infections.
Urinary catheters (Foley catheters) also increase the risk of developing urinary and kidney infections. These catheters are used in settings where an individual may not be able to urinate due to paralysis (neurogenic bladder), prostate enlargement (BPH), prostate cancer, severe illness, bed-bound state, incontinence of urine (inability to hold their urine), or bladder dysfunction. Urinary catheters simply provide a physical vehicle for the bacteria from outside to be directly transported into the bladder and the urinary system.
Kidney stones and structural abnormalities of the urinary system may also cause a kidney infection. Impaired draining and blockage of urine (urinary retention) may cause bacteria to ascend to the kidney without being washed back down with the urine. Any obstruction to the flow of urine can serve as a focus of infection that can spread to other parts of the urinary tract.
Urinary stents placed in ureters to relieve obstruction due to stones or tumors are also a potential risk for kidney infection. As matter of fact, any instrumentation or procedure of the urinary system (stenting, cystoscopy, biopsy, and transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) can pose a risk for infection of the urinary tract.
Diabetes may also increase the risk of kidney infection in both men and women. Other conditions or medications that suppress immune function increase the risk of kidney infection.
In children, risk factors for kidney infection include female gender, uncircumcised male, structural abnormalities of the urinary tract, and Caucasian race (four times higher than African American).

Is screening recommended for UTI or kidney infection?
In general, screening is not recommended for urinary tract infections and kidney infections in men and nonpregnant women.
While pregnant, screening may be recommended for women because bacteria in the urine without symptoms of infection are associated with a higher rate of progression to an overt urinary tract infection and pyelonephritis. These infections can potentially compromise fetal growth and health.
Screening for bacteria in the urine without any symptoms is also recommended for any individual prior to undergoing instrumentation of the urinary tract or in men undergoing prostate procedures. The presence of bacteria in the urine with or without infection can possibly lead to an increased chance of developing urinary tract infection. Treating these bacteria can substantially reduce the infectious complications of such procedures.

How is kidney infection diagnosed?
Kidney infection may be diagnosed by a physician by performing a complete physical examination and taking a detailed medical history. The evaluation includes checking the vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and respiratory rate), assessing for signs of dehydration, and checking for tenderness on the mid and lower back. In young, female patients a pelvic exam may also be necessary to evaluate for pelvic infection (pelvic inflammatory disease or PID). A pregnancy test may also be performed.
Urinalysis test is essential for the diagnosis of kidney infection. The urine sample must be properly collected. The urethra needs to be wiped clean properly before the sample is collected in order to avoid contamination of urine by the bacteria on the skin around the urethra. The initial stream of urine is preferably voided in the toilet before the collecting urine in the provided container. This is called the mid-stream, clean-catch urine. After an appropriate amount of urine is collected (about 10 milliliters or cc's) in the container, the remaining urine may also be voided in toilet.
A urinalysis suggestive of an infection in the urine (presence of white blood cells or bacteria in the urine) in general, is highly suggestive and supportive of the diagnosis of kidney infection or urinary tract infection. A urine sample without evidence of urine infection makes kidney infection unlikely and another diagnosis may be considered.
Once white blood cells and other indications of urine infection (such as, leukocyte esterase [produced by white blood cells in urine] or nitrites [produced by bacteria in urine]) are noted on the urinalysis, it is important to determine the amount and the type of bacteria in the urine sample. Generally, a urine sample that has greater than 100,000 bacteria in one cc of urine is considered diagnostic of urinary tract infection. In some clinical settings, counts of less than 100,000 bacteria in one cc of urine may also indicate kidney infection in a clinical setting supportive of this diagnosis.

What are different types of kidney infection?
Kidney infection, or pyelonephritis, may be classified as uncomplicated, complicated, or chronic kidney infection (long-term).
A complicated kidney infection refers to a kidney infection in which there is an accompanying condition that increases the risk of severe infection and ineffective treatment, such as abnormalities of the urinary tract, urinary obstruction, or diabetes. It can also mean there is severe involvement of the kidney, for example, abscess formation, obstruction, or enlarged kidney, or gas is seen in the kidney by an imaging study, such as a CT scan. In these situations, the symptoms may be more severe and less responsive to usual treatments.
A chronic kidney infection may refer to a recurring kidney infection that could be a result of a kidney stone obstructing the ureter or other structural abnormalities in the ureters (for example, vesicoureteral reflux, a condition in which urine is forced back up toward the kidneys). These conditions are usually associated with milder symptoms, but they may last longer.
The evaluation of complicated kidney infection and chronic kidney infection typically requires a more thorough evaluation and more extensive testing such as CT scans and X-rays.
What are the common bacteria that cause kidney infections?
The most common bacteria responsible for kidney infection are Escherichia coli (E. coli), which accounts for close to 80% of cases of kidney and urinary tract infections. Other common bacteria are Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
What is the treatment for kidney infection?
The most important component of treating kidney infection (as with any bacterial infection) is the timely initiation of antibiotics under the directions of a health care professional. If a kidney infection is diagnosed, then an empiric antibiotic (an antibiotic that would cover all likely causative bacterial organisms) is usually prescribed. A urine and blood sample will be taken and sent to a laboratory for analysis of any bacterial growth (urine culture and blood culture).
When a specific type of bacteria is isolated, antibiotics may then be changed to those that are more active against that particular bacterial type. If the bacteria shows resistance (unresponsive) to the antibiotic that was initially prescribed, then the antibiotic is changed promptly to one that the organism is susceptible to in order to cure the kidney infection.
Home treatment with oral antibiotics and adequate water and fluid intake is usually sufficient for curing uncomplicated kidney infection and urinary tract infection. Nondrug home treatment with fluid intake, cranberry products, or acupuncture without antibiotics is not advisable for kidney infections.
However, if symptoms are severe (uncontrolled nausea and vomiting resulting in an inability to take medications) or the infection is difficult to control with the routine oral medications for kidney infection, then hospitalization may be required to receive intravenous antibiotics, intravenous hydration, and aggressive management of symptoms. In cases of complicated kidney, infection hospitalization may also be necessary.
Self-medication for kidney infection is considered only in patients with mild, recurrent urinary infections. In individuals who are reliable and familiar with the symptoms of kidney infection, appropriate antibiotics prescribed to them in advance by their treating physicians may be started at the onset of their symptoms.

Are there foods I should avoid if I have a kidney infection?
There is no scientific data to suggest that avoiding any type of food while suffering from a kidney infection is harmful or beneficial. However, it is important to note that severe nausea and vomiting as well as poor appetite can occur with kidney infection. Therefore, it may be difficult to maintain adequate food and liquid requirements for patients with kidney infection, as this may lead to dehydration and worsening weakness. The treating physician may prescribe medications to treat these symptoms.
Some natural remedies for kidney and urinary tract infection, cranberry and cranberry juice, may have a role in reducing the risk of future kidney infections. This approach seems to be more useful as a preventative measure than actual treatment.
Can kidney infection be prevented?
Hygiene: The main approach to the prevention of kidney infection is proper hygiene. Because the majority of infections tend to happen due to the presence of bacteria entering the urinary tract from the urethra, proper personal hygiene plays theoretical importance in preventing urinary infections. For example, in women, wiping the genital area from front to back after going to the bathroom may significantly prevent bacteria around the anus or vagina to gain access to the urethra. Hygienic use of bathtubs and douching may also have a preventive role, but is not universally supported by clinical experts.
Sex: Because sexual intercourse is another risk factor for kidney infection, it is advised to empty the bladder (urinate) after sexual activity to drain bacteria that may have entered the bladder. This practice, however, is not overwhelmingly proven by available clinical data and not recommended by some experts.
Antibiotics: Preventive antibiotic therapy can sometimes be helpful in women who have recurrent UTIs (more than 3 to 4 times per year). This could be guided by the presence of symptoms suggestive of an infection or after sexual intercourse if infections are temporally associated with sexual intercourse. Preventive (prophylactic) antibiotics are also recommended for patients undergoing invasive urologic procedures when bacteria are detected in screening urine culture.
Hormonal therapy: Daily application of topical intravaginal (inside the vagina) estriol cream may reduce episodes of symptomatic UTI and kidney infection in postmenopausal women. On the contrary, oral estrogen did not significantly reduce episodes of UTI in these women.
Foods/supplements: Cranberry and cranberry juice or other cranberry products may have benefits in preventing urinary infections as demonstrated in some, but not all, research studies.
Catheters: Other important measures may apply to special situations. For example, in individuals with indwelling bladder catheters, it is important that the catheter is changed routinely under the guidance of a physician. The area around the catheter, especially where it enters the urethra, should be monitored and cleaned routinely.
Kidney stones: In patients with kidney infection who also have kidney stones, the stone may serve as a potential focus of infection that can spread to the rest of the urinary system. Therefore, these patients may be referred to a specialist (urologist) for evaluation and possible removal of the stone(s) to prevent future urinary infections.