Mouth Sores Symptoms
Sores or localized abnormalities inside the mouth can arise from a number of causes. Mouth sores can occur on the tongue, gums, lips, or inside the cheeks. They may appear as ulcers or red or white patches in the mouth. Bleeding may sometimes occur if ulceration is severe. Bite injuries to the tongue or inside of the cheek are a common cause of mouth sores. Also commonly, mouth sores represent aphthous ulcers, also known as canker sores or aphthous stomatitis. These shallow, painful mouth ulcers often occur in susceptible individuals during times of stress, infection, or changes in immune status. Certain medications (for example, methotrexate [Trexall]) can cause canker sores as well as deficiencies in some B vitamins (1, 2, 6, and 12), iron, folic acid, and zinc. However, irritation, injury, burns, or infection of any of the tissues in the oral cavity can also lead to mouth sores. Sores in the mouth can occur with certain systemic (affecting multiple locations within the body) diseases such as Crohn's disease, BehÇet's syndrome, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Rarely, mouth sores are among the initial signs of oral cancers. Herpes simplex virus infection causes so-called cold sores, which are typically located on the lips, but they can also occur on the gums. Among the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), the chancres of syphilis can occur as mouth sores.
Other causes of mouth sores
- Angular Cheilitis
- Bites
- Dental Injury
- Erythema Multiforme/Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- Medications
- Mucocele
- Pemphigus Vulgaris
- Poorly Fitting Braces or Dentures
- Ulcer
- Vitamin or Mineral Deficiency
Causes of Mouth Sores
-
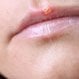
Behcet's Syndrome
BehÇet's syndrome is a disease characterized by three symptoms: genital ulcers, recurring mouth ulcers, and inflammation around the pupil of the eye. Symptoms of Behcet's syndrome may also include inflammation of other areas of the body, such as the: brain, joints, skin, retina, and bowels. Oral steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, and steroid gels, pastes, and creams may be used to treat BehÇet's syndrome.
-

Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid is a skin disease that causes blistering eruptions on the skin's surface and sometimes affects the inner lining of the mouth. Symptoms include severe itching and burning sensations. Treatment involves topical cortisone and sometimes high doses of cortisone. Severe cases may require immune-suppression drugs such as azathioprine.
-
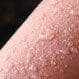
Burns (First Aid)
Burn types are based on their severity: first-degree burns, second-degree burns, and third-degree burns. First-degree burns are similar to a painful sunburn. The damage is more severe with second-degree burns, leading to blistering and more intense pain. The skin turns white and loses sensation with third-degree burns. Burn treatment depends upon the burn location, total burn area, and intensity of the burn.
-

Chickenpox (Varicella)
Chickenpox (chicken pox) is a contagious childhood disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Symptoms have an incubation period of 14 to 16 days and include a couple days of mild fever, weakness, and red, raised rash that progresses to blisters that eventually burst and crust over. Complications include bacterial infection of the open sores, scarring, encephalitis, nerve palsies, and Reye's syndrome.
-

Cocaine and Crack Addiction
Cocaine is an addictive stimulant that is smoked, snorted, and injected. Crack is cocaine that comes in a rock crystal that is heated to form vapors, which are then smoked. Cocaine has various effects on the body, including dilating pupils, constricting blood vessels, increasing body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure.
-

Cold Sores (Oral Herpes, Herpes Labialis)
Herpes simplex infections are common and when they appear around the mouth and lips, people often refer to them as "cold sores" and "fever blisters." Canker sores are different than cold sores. Air droplets can spread the virus, as can direct contact with the fluid from the blisters. Cold sore treatment include over-the-counter medication, as well as prescription medications.
-
Coxsackievirus
Coxsackieviruses may be divided into two groups. Type A causes hand, foot, and mouth disease and conjunctivitis, while type B causes pleurodynia. Both types sometimes cause meningitis, myocarditis, and pericarditis. There is no specific treatment for this disease.
-

Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Dry mouth is a common side effect of many prescription and non-prescription drugs and certain medical conditions. Symptoms of dry mouth include a sticky, dry feeling in the mouth, frequent thirst, sores in the mouth; sores or split skin at the corners of the mouth, cracked lips, a dry feeling in the throat, a burning or tingling sensation in the mouth, and a dry, red, raw tongue.
-

Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD)
Graft versus host disease (GVHD) is a condition that happens when immune cells from transplanted donor tissue attack the recipient's tissues. Signs and symptoms of acute GVHD include enteritis, hepatitis, and dermatitis. Chronic GVHD symptoms and signs include rash, skin discoloration, dry mouth or eyes, jaundice, fatigue, and wheezing, among others. The standard of GVHD treatment is immunosuppressant medications.
-
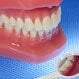
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Gum disease is caused by plaque and may result in tooth loss without proper treatment. Symptoms and signs of gum disease (gingivitis or periodontal disease) include receding gums, bad breath and pocket formation between the teeth and gums. Treatment depends upon the stage of the gum disease, how you responded to earlier treatments, and your overall health.
-
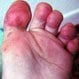
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth syndrome is clinical pattern consisting of a rash on the hands and feet, and in the mouth. Hand, foot, and mouth syndrome is caused by various viruses, including several types of Coxsackieviruses. Other symptoms include sore throat, decreased appetite, irritability, and (or) fever.
-
Herpangina
Herpangina is a contagious illness often seen in children. It is caused by a Coxsackievirus or an enterovirus. Symptoms and signs include mouth sores, fever, and sore throat. Treatment focuses on alleviating fever and pain with acetaminophen and ibuprofen. It is important for children to stay well hydrated, as children may be resistant to eating or drinking.
-

Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection left untreated causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Still incurable, AIDS describes immune system collapse that opens the way for opportunistic infections and cancers to kill the patient. Early symptoms and signs of HIV infection include flu-like symptoms and fungal infections, but some people may not show any symptoms for years. Highly active antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the standard treatment for HIV infection. These combination drug regimens have made HIV much less deadly, but a cure or vaccine for the pandemic remains out of reach. HIV is usually transmitted through sexual contact or sharing IV drug needles, but can also infect someone through contact with infected blood. Sexual abstinence, safe sex practices, quitting IV drugs (or at least using clean needles), and proper safety equipment by clinicians and first responders can drastically reduce transmission rates for HIV/AIDS.
-
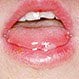
Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) Contagious?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a highly contagious disease caused by several enteroviruses. These viruses are transmitted via nasal secretions, kissing, and saliva. HFMD causes the following symptoms and signs: decreased appetite, sore throat, fever, weakness, and painful sores on the hands, feet, and in the mouth.
-
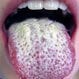
Is Thrush Contagious?
Thrush is a fungal infection caused by Candida albicans. An infant with thrush can infect his/her mother with thrush during breastfeeding. Treatment typically involves using antifungal lozenges or mouthwash.
-
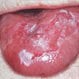
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is a white or gray patch that develops on the tongue or inside the cheek. Causes of Leukoplakia may include irritation from rough teeth fillings or crowns, chronic smoking, sun exposure to the lips, or HIV or AIDS.
-
Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is a common skin disease that features small, itchy pink or purple spots on the arms or legs. The abnormal areas on the skin in lichen planus are typically flat-topped (hence the term planus), itchy, and frequently have a polygonal or angular shape.
-

Lichen Sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus is a skin disease that causes white spots to form on the skin, which later grow into large, thin, and crinkled patches of skin that tear easily. Symptoms include itching, pain, blisters, and bleeding. Patches on the upper body usually go away over time, but patches in the genital region may scar if left untreated, causing problems with urination or sex. Treatment may involve surgery or the use of a very strong cortisone cream.
-

Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus or SLE)
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a condition characterized by chronic inflammation of body tissues caused by autoimmune disease. Lupus can cause disease of the skin, heart, lungs, kidneys, joints, and nervous system. When only the skin is involved, the condition is called discoid lupus. When internal organs are involved, the condition is called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
-

Melanoma (Skin Cancer)
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer which begins in skin cells called melanocytes and affects more than 53,600 people in the United States each year. These melanocytes can grow together to form benign moles which, after a change in size, shape, or color can be a sign of melanoma. Caused by sun exposure, early detection becomes extremely important to avoid a spread to other areas of the body. Diagnosis is confirmed through a biopsy of the abnormal skin and treatment depends on the extent and characteristics of the patient. Metastatic melanoma is melanoma that has spread to various organs.
-
Oral Cancer
The term oral cancer includes cancer of the mouth (oral cavity) and the back of the mouth (oropharynx). Red and white patches inside the mouth, bleeding, loose teeth, pain upon swallowing, a lump in the neck, earache, and a sore on your lip or in your mouth that won't heal are all symptoms of oral cancer. Treatment for oral cancer depends upon the staging of the disease and usually involves surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
-

Sjogren's Syndrome
Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disease involving the abnormal production of extra antibodies that attack the glands and connective tissue. Sjögren's syndrome with gland inflammation (resulting dry eyes and mouth, etc.) that is not associated with another connective tissue disease is referred to as primary Sjögren's syndrome. Sjögren's syndrome that is also associated with a connective tissue disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, or scleroderma, is referred to as secondary Sjögren's syndrome. Though there is no cure for Sjögren's syndrome, the symptoms may be treated by using lubricating eye ointments, drinking plenty of water, humidifying the air, and using glycerin swabs. Medications are also available to treat dry eye and dry mouth.
-
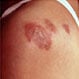
Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
Sweet syndrome (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a skin condition that sometimes occurs due to an immune system response to RA, pregnancy, certain cancers, inflammatory bowel diseases, blood disorders, respiratory tract infections, and particular medications. Symptoms and signs include characteristic skin lesions that grow and spread into clusters. Sore eyes, high fever, mouth ulcers, headache, and aching joints may accompany the lesions. Though Sweet syndrome may resolve on its own, more severe cases may require medications like corticosteroids.
-

Syphilis in Women
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a spiral-shaped type of bacteria known as a spirochete. There are three stages of syphilis with distinct symptoms. During first stage of syphilis, a painless ulcer known as a chancre forms. Irreversible organ damage can occur during the late stage of syphilis. Special blood tests are used to diagnose syphilis. Syphilis infection is treated with penicillin. Condom use can often prevent syphilis.
-
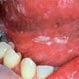
Thrush (Oral Candidiasis)
Thrush is an infection of the mouth caused by the Candida fungus. Symptoms of thrush include pain or difficulty swallowing, a feeling that food gets stuck in the throat, and fever.
-

What Are Causes of Blisters in the Mouth?
What causes blisters inside the mouth? Learn why they appear and what to do if you have mouth blisters.
-
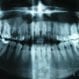
What Are Common Causes of Dental Injuries?
Dental injuries range from a chipped or fractured tooth to a knocked-out tooth. Treatment depends upon the severity of the dental injury. Dental injuries may be prevented by aligning protruding front teeth with braces and using face masks and mouthguards while playing sports.
-
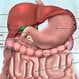
What Is Crohn's Disease?
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disease, primarily involving the small and large intestine, but which can affect other parts of the digestive system as well. Abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and weight loss are common symptoms.
Examples of Medications for Mouth Sores
- Behcet's Syndrome
- Bullous Pemphigoid
- Burns (First Aid)
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Cocaine and Crack Addiction
- Cold Sores (Oral Herpes, Herpes Labialis)
- Coxsackievirus
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
- Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD)
- Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- Herpangina
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) Contagious?
- Is Thrush Contagious?
- Leukoplakia
- Lichen Planus
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus or SLE)
- Melanoma (Skin Cancer)
- Oral Cancer
- Sjogren's Syndrome
- Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
- Syphilis in Women
- Thrush (Oral Candidiasis)
- What Are Causes of Blisters in the Mouth?
- What Are Common Causes of Dental Injuries?
- What Is Crohn's Disease?
