Bleeding Gums Symptoms
Bleeding, redness, and painful or sore gums can be a symptom of gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) that arises due to a number of different causes. Bleeding of the gums is sometimes referred to as gingival bleeding, and it may occur during brushing or flossing. The soreness can be accompanied by swelling of the gum tissues. Most commonly, gingivitis is the result of plaque buildup on the teeth around the gum line. Without adequate removal, the plaque hardens to become tartar, which worsens gingivitis and can, over time, lead to receding gums and even damage the bones of the jaws. Bleeding from the gums, particularly when accompanied by easy bruising and/or bleeding at other sites in the body, can also be caused by diseases that interfere with the normal blood-clotting process. Blood-thinner medications are another potential cause of bleeding gums. The hormonal changes during pregnancy can also increase the sensitivity of the gums, which may lead to increased bleeding in some cases. Those with chronic conditions that affect the function of the immune system, such as HIV infection or diabetes, may also have an increased tendency to develop gingivitis.
Other causes of bleeding gums
- Bacterial Infection
- Excessively Hard Toothbrushing
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
- Medications
- Other Bleeding or Blood Clotting Disorders
- Poorly Fitting Dentures
- Poor Nutrition
- Poor Oral Hygiene
- Tartar
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia Purpura (TTP)
- Trauma to the Mouth and/or Gums
- Trench Mouth
- Vitamin C Deficiency (Scurvy)
- Vitamin K Deficiency
- Von Willebrand Disease
Causes of Bleeding Gums
-
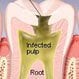
Abscessed Tooth
An abscessed tooth is an infection within a tooth that has spread to the root. Symptoms of an abscessed tooth may include pain, swelling, tenderness, redness, and the presence of a pus-filled lesion on the gum. A dental professional diagnoses an abscessed tooth and dental X-rays may be required. An abscessed tooth is treated with a root canal.
-

Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is contracted from the bite of a striped Aedes aegypti mosquito. Symptoms and signs of dengue include headache, fever, exhaustion, severe joint and muscle pain, rash, and swollen glands. Since dengue is caused by a virus, there is no specific medicine to treat it. Treatment instead focuses on relieving the symptoms.
-
Diabetes (Type 1 and Type 2)
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. The two types of diabetes are referred to as type 1 (insulin dependent) and type 2 (non-insulin dependent). Symptoms of diabetes include increased urine output, thirst, hunger, and fatigue. Treatment of diabetes depends on the type.
-
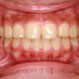
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Gum disease is caused by plaque and may result in tooth loss without proper treatment. Symptoms and signs of gum disease (gingivitis or periodontal disease) include receding gums, bad breath and pocket formation between the teeth and gums. Treatment depends upon the stage of the gum disease, how you responded to earlier treatments, and your overall health.
-
Gum Problems
Gum problems may be caused by improper brushing and flossing, gum disease, canker sores, treatments and hormonal changes. Symptoms of gum problems include red, swollen, sore and bleeding gums. These symptoms can be prevented by brushing twice a day, flossing daily, eating a well-balanced diet, drinking enough water, not smoking, and relaxing.
-
Hemophilia A and B (Bleeding Disorders)
Hemophilia is defined as one of a group of inherited bleeding disorders. Hemophilia A and hemophilia B are inherited in an X-linked recessive genetic pattern. Symptoms of hemophilia include bleeding into the: joints, muscles, GI or urinary tract, or brain or skull. Hemophilia treatment generally involves the replacement of blood clotting factors.
-

Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection left untreated causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Still incurable, AIDS describes immune system collapse that opens the way for opportunistic infections and cancers to kill the patient. Early symptoms and signs of HIV infection include flu-like symptoms and fungal infections, but some people may not show any symptoms for years. Highly active antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the standard treatment for HIV infection. These combination drug regimens have made HIV much less deadly, but a cure or vaccine for the pandemic remains out of reach. HIV is usually transmitted through sexual contact or sharing IV drug needles, but can also infect someone through contact with infected blood. Sexual abstinence, safe sex practices, quitting IV drugs (or at least using clean needles), and proper safety equipment by clinicians and first responders can drastically reduce transmission rates for HIV/AIDS.
-

Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Idiopathic means that the cause of the condition isn't known. Thrombocytopenic means there's a lower than normal number of platelets in the blood. Purpura refers to purple bruises caused by bleeding under the skin. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is a bleeding condition in which the blood doesn't clot as it should. This is due to a low number of blood cell fragments called platelets.
-
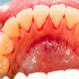
Is Gingivitis Contagious?
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. Poor dental hygiene, stress, smoking, some medications, and a poor diet can cause gingivitis. Gingivitis-causing bacteria can be passed from one individual to another.
-

Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of cancer of the blood cells in which the growth and development of the blood cells are abnormal. Strictly speaking, leukemia should refer only to cancer of the white blood cells (the leukocytes) but in practice it can apply to malignancy of any cellular element in the blood or bone marrow, as in red cell leukemia (erythroleukemia).
-

Pregnancy (Week by Week, Trimesters)
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy vary by stage (trimester). The earliest pregnancy symptom is typically a missed period, but others include breast swelling and tenderness, nausea and sometimes vomiting, fatigue, and bloating. Second trimester symptoms include backache, weight gain, itching, and possible stretch marks. Third trimester symptoms are additional weight gain, heartburn, hemorrhoids, swelling of the ankles, fingers, and face, breast tenderness, and trouble sleeping. Eating a healthy diet, getting a moderate amount of exercise, also are recommended for a healthy pregnancy. Information about the week by week growth of your baby in the womb are provided.
-

Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is an infectious disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. Side effects are rare with the yellow fever vaccine. Symptoms include fever, chills, back pain, nausea, vomiting, and headache. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms.
