Eskata Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: hydrogen peroxide topical solution
- Brand Name: Eskata
- Drug Class: Topical Skin Products
side effects drug center eskata (hydrogen peroxide topical solution) drug
Drug Description
What is Eskata and how is it used?
Eskata is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of Seborrheic Keratosis. Eskata may be used alone or with other medications.
Eskata belongs to a class of drugs called Topical Skin Products.
It is not known if Eskata is safe and effective in children.
What are the possible side effects of Eskata?
Eskata may cause serious side effects including:
- redness or blistering of the skin,
- peeling,
- burning of the skin,
- itching,
- pain,
- rash,
- stinging,
- ulcerations,
- cracking or scarring of the skin,
- thinning skin,
- swelling of the eyelid, and
- blisters on the body
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Eskata include:
- discoloration,
- dry, peeling, or crusting of the skin,
- lightening of the skin color, and
- lightening of the treated areas of dark skin
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Eskata. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
DESCRIPTION
ESKATA (hydrogen peroxide) topical solution, 40% (w/w) is a clear, colorless solution for topical administration, which contains the active ingredient, hydrogen peroxide.
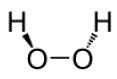
The chemical name of hydrogen peroxide is dihydrogen dioxide.
The molecular formula of hydrogen peroxide is H2O2 and the molecular weight is 34.01. Hydrogen peroxide is represented by the following structural formula:
 |
ESKATA contains 40% (w/w) hydrogen peroxide in an aqueous solution of isopropyl alcohol and water.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
ESKATA is indicated for the treatment of seborrheic keratoses that are raised.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Important Administration Information
ESKATA is to be administered by a health care provider.
For topical use only. Not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
Do not apply ESKATA topical solution to open or infected seborrheic keratoses.
Prior to application of ESKATA, ensure the surface of seborrheic keratosis lesion is clear of oil and debris (an alcohol wipe can be used).
During a single in-office treatment session, apply ESKATA to seborrheic keratosis lesions 4 times, approximately 1 minute apart. After one use, replace the cap and discard the unit dose applicator.
When treating seborrheic keratoses on the face, take appropriate actions to ensure that ESKATA will not come into contact with the eyes.
If the treated lesions have not completely cleared approximately 3 weeks after treatment, another treatment may be administered following the same procedure.
Dosage And Administration Instructions
Preparation Of The ESKATA Applicator
Wear nitrile or vinyl examination gloves during the activation of the ESKATA applicator and during the administration of the solution to the lesion(s).
The method for preparing the ESKATA applicator for use is illustrated below. While activating the applicator, hold it away from the patient. Do not remove the cap until after completion of Step 4 (below).
Step 1: Hold the ESKATA applicator so that the applicator cap is pointing up
 |
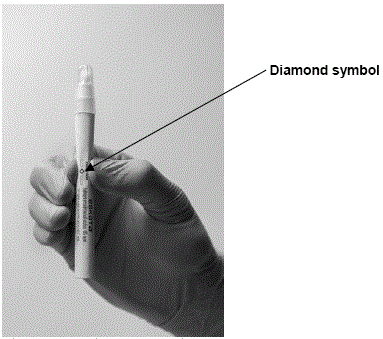
Step 2: Crush the ampule in the applicator by applying finger pressure to the diamond symbol on the applicator barrel
 |
Step 3: Remove the sleeve.
 |
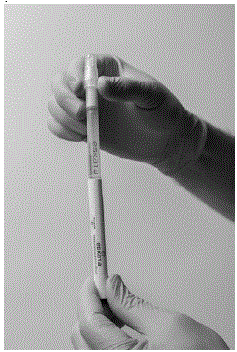
Step 4: Holding the applicator with cap pointing up, tap the bottom of the applicator to separate the solution from the crushed ampule.
 |
Application Of ESKATA Topical Solution
Following release of the solution from the ampule, remove the cap from the ESKATA applicator. Gently squeeze the applicator barrel to express the solution to the applicator tip. Using the applicator, apply the solution directly to the seborrheic keratosis in a circular motion. Apply enough solution to uniformly wet the lesion surface, including the edges without excess running or dripping.
Wait 1 minute and observe. Whitening of the lesion may occur.
Do not progress to subsequent applications if severe erythema/edema or pain occur. Apply again in the same manner 3 additional applications 1 minute apart.
Minimize the amount of drug that comes into contact with surrounding skin. If ESKATA does come into contact with surrounding skin, use an absorbent wipe to remove any excess solution (do not use paper towels or tissue).
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
ESKATA topical solution is a clear, colorless solution containing 40% (w/w) hydrogen peroxide.
Storage And Handling
ESKATA (hydrogen peroxide) topical solution, 40% (w/w) is a clear, colorless solution and is supplied in a unit dose package. The available carton packages are presented below:
| Dosage Strength | Fill Volume | Deliverable Volume | Number of unit dose packages per carton | NDC# |
| 40% (w/w) | 1.5 mL | 0.7 mL | 1 | 71180-001-01 |
| 3 | 71180-001-03 | |||
| 12 | 71180-001-12 | |||
| 2.2 mL | 1.3 mL | 1 | 71180-002-01 | |
| 3 | 71180-002-03 | |||
| 12 | 71180-002-12 |
Store ESKATA at controlled room temperature of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59° F and 86° F).
Manufactured & Packaged by: James Alexander Corp., 845 Route 94, Blairstown, NJ 07825, United States. For: Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc., 640 Lee Road, Suite 200, Wayne, PA 19087, United States. Revised: Feb 2019
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to ESKATA or vehicle in a total of 937 subjects with seborrheic keratoses that are raised. Overall, 42% of the subjects were male and 58% were female. Ninety-eight (98) percent of the subjects were Caucasian and the mean age was 68.7 years.
At each visit, local skin reactions were graded for severity to determine the maximum severity after treatment. Table 1 presents the percentage of subjects with the local adverse reactions by the most severe grade reported during the course of the trials.
Table 1: Percentage of
Subjects with Local Skin Reactions by Severity
| ESKATA N=467 |
Vehicle N=470 |
|||||||
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | Total | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Total | |
| Erythema | 13 | 67 | 19 | 99 | 29 | 5 | <1 | 34 |
| Stinging | 34 | 49 | 15 | 97 | 9 | 1 | <1 | 10 |
| Edema | 28 | 48 | 15 | 91 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| Scaling | 49 | 36 | 5 | 90 | 28 | 5 | 1 | 33 |
| Crusting | 34 | 38 | 8 | 81 | 13 | 5 | 1 | 19 |
| Pruritus | 34 | 18 | 5 | 58 | 7 | 1 | <1 | 8 |
| Hyperpigmentation | 32 | 7 | <1 | 39 | 1 | <1 | 0 | 1 |
| Vesicles | 21 | 3 | 1 | 24 | <1 | 0 | 0 | <1 |
| Hypopigmentation | 16 | 3 | <1 | 19 | 1 | <1 | 0 | 1 |
| Erosion | 12 | 2 | 1 | 15 | <1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Ulceration | 6 | 2 | <1 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Atrophy | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Scarring | 3 | <1 | <1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Common local skin reactions observed 10 minutes after treatment include: erythema (98%), stinging (93%), edema (85%), pruritus (32%), and vesiculation (18%).
Common local skin reactions observed 1 week after treatment are scaling (72%), erythema (66%), crusting (67%), pruritus (18%), erosion (9%), and ulceration (4%).
Common local skin reactions observed 15 weeks after the initial treatment are erythema (21%), hyperpigmentation (18%), scaling (16%), crusting (12%), and hypopigmentation (7%).
Less common adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 0.5% of subjects treated with ESKATA include eyelid edema (0.6%) and herpes zoster (0.6%).
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ESKATA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and subcutaneous tissues disorders: crepitus
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No Information provided
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the PRECAUTIONS section.
PRECAUTIONS
Eye Disorders
Do not apply to the eyes or mucous membranes. Avoid treating seborrheic keratoses within the orbital rim. Direct contact with the eye can cause corneal injury (erosion, ulceration, perforation, and scarring), chemical conjunctivitis, eyelid edema, severe eye pain, or permanent eye injury, including blindness.
If accidental exposure occurs, flush with water for 15 to 30 minutes and initiate monitoring, and further evaluation as appropriate.
Local Skin Reactions
Skin reactions occurred in the treatment area after application of ESKATA. Severe local skin reactions included erosion, ulceration, vesiculation and scarring. [See ADVERSE REACTIONS]. Do not initiate a second treatment course with ESKATA until the skin has recovered from any reaction caused by the previous treatment.
Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (PATIENT INFORMATION).
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
Inform patients that severe eye injury can occur with ESKATA application. Advise patients to inform the healthcare provider immediately if ESKATA runs into eyes, mouth, or nose during administration [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Local Skin Reactions
Inform patients that treatment with ESKATA may lead to local skin reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of ESKATA or hydrogen peroxide.
Hydrogen peroxide has been found to exhibit positive results in in vitro tests for genotoxicity, but has not exhibited positive results in in vivo tests for genotoxicity, presumably due to the rapid metabolism of hydrogen peroxide.
The effects of hydrogen peroxide on fertility have not been evaluated. Hydrogen peroxide has been associated with effects on sperm function and elevated testicular hydrogen peroxide concentration has been implicated in male infertility, although in vivo, no effect of hydrogen peroxide on sperm function has been demonstrated.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Hydrogen peroxide is not absorbed systemically following topical administration, and maternal use is not expected to result in fetal exposure to the drug.
Lactation
Risk Summary
Hydrogen peroxide is not absorbed systemically by the mother following topical administration, and breastfeeding is not expected to result in exposure of the child to hydrogen peroxide.
Pediatric Use
Seborrheic keratosis is not seen in the pediatric population.
Geriatric Use
Of the 841 subjects treated with ESKATA in the clinical trials, 70% were 65 years of age and older and 26% were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
Topical overdosing of ESKATA could result in an increased incidence and severity of local skin reactions.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
The mechanism of action for ESKATA for the treatment of seborrheic keratosis is unknown.
Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of ESKATA in the treatment of seborrheic keratosis are unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Following application of ESKATA in patients with seborrheic keratosis lesions, hydrogen peroxide rapidly dissociates into water and reactive oxygen species. Indirect assessment of reactive oxygen species in patients with seborrheic keratosis lesions did not demonstrate any systemic absorption of hydrogen peroxide.
Clinical Studies
In two double-blind, vehicle-controlled clinical trials, 937 subjects with 4 clinically typical seborrheic keratoses that are raised on the face, trunk, or extremities were randomized to treatment with either ESKATA or vehicle. Subjects ranged from 42 to 91 years of age (mean 68.7 years), 58% percent were female, and 98% were Caucasian. A total of 925 subjects completed the trials. Each lesion was treated with 4 applications, at baseline and again at Day 22, if needed, and subjects were followed through Day 106.
Efficacy was assessed at Day 106. Success rate was defined as the proportion of subjects achieving “clear” on the Physician's Lesion Assessment Scale for all 4 treated lesions. Efficacy was also assessed for the proportion of subjects achieving “clear” on the Physician's Lesion Assessment Scale for at least 3 of 4 lesions. Table 3 presents the efficacy results for the two clinical trials.
Table 3: Percentage of
Subjects Achieving Clearance of Target Lesions at Day 106 in Study 1 and Study 2
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
| ESKATA N=223 |
Vehicle N=227 |
ESKATA N=244 |
Vehicle N=243 |
|
| All 4 lesions “Clear” | 4% | 0% | 8% | 0% |
| At least 3 of 4 lesions “Clear” | 13% | 0% | 23% | 0% |
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
No information provided. Please refer to the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS sections.
