Runny Nose Symptoms
Stuffy nose is a term often used to refer to obstruction to the flow of air in and out of the nose, while runny nose refers to a discharge (fluid) coming from the nasal passages. This is often a watery, clear liquid but may be thicker and viscous. Both stuffy and runny nose are associated with inflammation and swelling (congestion) of the inner lining of the nasal passages and sinuses. Rhinitis is a term that refers to inflammation of the nasal passages, and rhinorrhea is the medical term for runny nose. A viral infection (the common cold) is the most common cause of a stuffy and/or runny nose, but allergies, influenza, other viral infections like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and sinus infections also may cause these symptoms and signs. Postnasal drip may be an associated symptom. This occurs when there is excess production of mucus by the lining cells of the nose, which accumulates in the back of the nose or in the throat.
Less commonly, anatomical obstructions (for example, a deviated nasal septum or foreign bodies) may lead to nasal congestion. Other causes of a stuffy or runny nose include environmental factors, like consumption of spicy foods or smoke exposure, hormonal changes, and some medications. Rarely, tumors of the nasal passages or chronic medical conditions may be the cause of a stuffy or runny nose.
Other causes of runny nose
- Cold Weather or Sudden Temperature Changes
- Consumption of Spicy Foods
- Enlarged Adenoids
- Environmental Irritants
- Foreign Bodies in the Nose
- Hormonal Changes
- Injury/Trauma to the Nose
- Kartagener Syndrome
- Medications
- Nasal Polyps
- Structural Abnormalities
- Tumors of the Nasal Passages
- Vasomotor Rhinitis
- Viral Infection
Causes of Runny Nose
-

Adenovirus
Adenovirus infections are common and often have no symptoms. Adenoviruses cause illnesses like bladder infections, diarrhea, pneumonia, bronchitis, pinkeye, colds, encephalitis, sore throat, and meningitis. Signs and symptoms of an adenovirus infection depend on the type of virus causing the infection. Treatment focuses on supportive care. A vaccine against adenovirus type 4 and 7 is available only to U.S. military personnel.
-

Adenovirus 14 (Killer Cold Virus)
Adenovirus infection, particularly Ad14, or the "killer cold virus" has been on the increase in the past two years. Symptoms range from those experienced with colds, sore throat, bronchitis, pneumonia, diarrhea, pinkeye, fever, bladder infection, and neurological conditions. Diagnosis and treatment options need to be discussed with your physician.
-

Allergy (Allergies)
An allergy refers to a misguided reaction by our immune system in response to bodily contact with certain foreign substances. When these allergens come in contact with the body, it causes the immune system to develop an allergic reaction in people who are allergic to it. It is estimated that 50 million North Americans are affected by allergic conditions. The parts of the body that are prone to react to allergies include the eyes, nose, lungs, skin, and stomach. Common allergic disorders include hay fever, asthma, allergic eyes, allergic eczema, hives, and allergic shock.
-

Are You Too Sick to Work?
When you're not feeling well, it may be difficult to decide whether to stay home or go to school or work. Conditions that are very painful may prevent you from working effectively. Anyone with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, or dizziness should stay home.
-

Aspergillus Infection (Aspergillosis)
An Aspergillus infection is a fungal infection. Signs and symptoms can include cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, bloody sputum, difficulty breathing, and chest and/or joint pain. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the disease.
-

Bocavirus
Bocavirus infection is usually only found in those with lower respiratory infections or diarrhea. Symptoms include cyanosis, cough, wheezing, runny nose, vomiting, and fever. There is no treatment that effectively targets the bocavirus strain.
-

Chronic Rhinitis and Post-Nasal Drip
Chronic rhinitis and post-nasal drip symptoms include an itchy, runny nose, sneezing, itchy ears, eyes, and throat. Seasonal allergic rhinitis (also called hay fever) usually is caused by pollen in the air. Perennial allergic rhinitis is a type of chronic rhinitis and is a year-round problem, often caused by indoor allergens, such as dust, animal dander, and pollens that may exist at the time. Treatment of chronic rhinitis and post nasal drip are dependent upon the type of rhinitis condition.
-

Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are a type of headache that recurs over a period. Episodes can last one to three times a day during this time, which may last from 2 weeks to 3 months. The three main types of treatments for cluster headaches are, 1) Abortive medications that work to stop the process in the brain that causes migraines and stops the symptoms too. 2) Preventive prescription medications, or 3) surgery which involves blocking the trigeminal nerve.
-

Cold vs. Flu
Though the common cold and flu share many signs and symptoms, they are caused by different viruses. Signs and symptoms include sneezing, sore throat, runny nose, fatigue, and cough. Treatment options for the cold and flu are similar and focus on reducing symptoms. Doctors may prescribe antivirals/neuraminidase inhibitors for the flu.
-

Cold, Flu, Allergy Treatments
Before treating a cold, the flu, or allergies with over-the-counter (OTC) medications, it's important to know what's causing the symptoms, which symptoms one wishes to relieve, and the active ingredients in the OTC product. Taking products that only contain the medications needed for relieving your symptoms prevents ingestion of unnecessary medications and reduces the chances of side effects.
-

Common Cold
The common cold (viral upper respiratory tract infection) is a contagious illness that may be caused by various viruses. Symptoms include a stuffy nose, headache, cough, sore throat, and maybe a fever. Antibiotics have no effect upon the common cold, and there is no evidence that zinc and vitamin C are effective treatments.
-
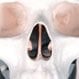
Deviated Septum
A deviate septum is a condition that may require surgery. With a deviated septum, the bone and cartilage that divide the nasal cavity of the nose in half (nasal septum) is significantly off-center or crooked. The causes of a deviated septum can be congenital, or develop after a trauma or injury to the nose. Symptoms of a deviated septum include: nasal congestion, recurrent sinus infections, nosebleeds, headache, facial pain, postnasal drip, snoring, and loud breathing. A deviated septum can be relieved with medications and, if necessary, a surgery called septoplasty.
-

Flu (Influenza)
Influenza (flu) is a respiratory illness caused by a virus. Flu symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches. The flu may be prevented with an annual influenza vaccination.
-

Food Allergy
The most common food allergies are to eggs, nuts, milk, peanuts, fish, shellfish, strawberries and tomatoes. Symptoms and signs of a food allergy reaction include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, itching, hives, eczema, asthma, lightheadedness, and anaphylaxis. Allergy skin tests, RAST, and ELISA tests may be used to diagnose a food allergy. Though dietary avoidance may be sufficient treatment for mild allergies, the use of an Epipen may be necessary for severe food allergies.
-

Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis is a condition that usually affects young or middle-aged adults, is an inflammation of the arteries supplying blood to the sinuses, lungs, and kidneys. Symptoms of granulomatosis with polyangiitis include bloody sputum, fatigue, weight loss, joint pain, sinusitis, shortness of breath, and fever. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis may be fatal within months without treatment. Treatment aims to stop inflammation with high doses of prednisone and cyclophosphamide.
-

Hay Fever (Allergic Rhinitis)
Hay fever (allergic rhinitis) is an irritation of the nose caused by pollen and is associated with the following allergic symptoms: nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, eye and nose itching, and tearing eyes. Avoidance of known allergens is the recommended treatment, but if this is not possible, antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal sprays may help alleviate symptoms.
-

How Can I Help My Baby With a Stuffy Nose?
It is distressing to all mothers to see their little ones with a stuffy nose and a cold. When your baby is irritable and does not eat, it makes you and your whole family anxious. Fortunately, there are various ways to help your baby with a stuffy nose including steam inhalation, hydration, using tissues and other strategies.
-

How Long Is a Cold or Flu Contagious?
Viruses cause the common cold and the flu. Early symptoms and signs for a cold and the flu are similar, however, flu symptoms are typically more severe than cold symptoms. Cold and flu viruses are transmitted typically via coughing or sneezing.
-

Indoor Allergens
Indoor allergens are substances that can cause an allergic reaction in some people. Common sources of indoor allergens include dust mites, cockroaches, molds, pets, and plants. Avoiding indoor allergens is one way to reduce allergy and asthma symptoms.
-

Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Contagious?
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a contagious viral infection that causes symptoms such as decreased appetite, runny nose, sneezing, coughing, and mild fever. The incubation period is 4-6 days, and the contagious period ends after the symptoms disappear.
-

Is Swine Flu (H1N1) Contagious?
Swine flu (H1N1) is a contagious virus that spreads when an infected individual expels virus-containing droplets into the air during coughing or sneezing. Symptoms include sore throat, runny nose, fever, cough, chills, headache, fatigue, and possible vomiting and/or diarrhea. An H1N1 infection typically lasts for about a week.
-
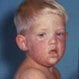
Measles
Measles (rubeola) is a highly contagious disease that's caused by a virus. Symptoms include a rash, high fever, cough, runny nose, and red eyes. Treatment focuses on symptom relief. The disease can be prevented with the measles, mumps, rubella, and chickenpox (varicella) vaccine (MMRV).
-

Mold Exposure: Symptoms, Removal, and Remediation
Mold exposure may cause symptoms in people who are sensitive to molds. Symptoms of mold allergy include sneezing, runny nose, wheezing, coughing, redness of the eyes, and rash. Prevent mold growth by keeping indoor humidity low, between 30%-50%, using bathroom fans when showering, repairing plumbing leaks quickly, and using an air conditioner during humid seasons.
-

Occupational Asthma
Occupational asthma is a type of asthma caused by exposure to a substance in the workplace. Symptoms and signs include wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. The usual treatment for occupational asthma involves removal from exposure and the use of bronchodilators and inhaled anti-inflammatory medicines.
-
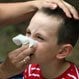
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a highly contagious viral infection. Symptoms and signs include fever and nasal congestion and discharge. Treatment focuses on supportive care. This disease has a good prognosis in babies and infants.
-

Roseola
Roseola is a viral illness that most commonly affects young children. Symptoms and signs include a sudden high fever that lasts for three to five days, swollen neck glands, runny nose, puffy eyelids, diarrhea, irritability, and a bulging soft spot on the head.
-

Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
Sinus infection (sinusitis) is caused by allergies, infection, and chemicals or other irritants of sinuses. Signs and symptoms are headache, fever, and facial tenderness, pressure, or pain. Treatments of sinus infections are generally with antibiotics and at times, home remedies.
-

Sinus Infection vs. Cold
Viruses cause the common cold and most sinus infections. Bacterial and fungal infections may also cause a sinus infection. Signs and symptoms of colds and sinus infections include nasal irritation or dryness, sore throat, stuffy nose, nasal discharge/congestion, sneezing, and cough. Additional symptoms of sinus infections include sinus pressure behind the cheeks or eyes, facial pain when pressure is applied, bad breath, and thick yellow or green mucus. Treatment focuses on symptom relief.
-
Smoking (How to Quit Smoking)
Smoking is an addiction. More than 430,000 deaths occur each year in the U.S. from smoking related illnesses. Secondhand smoke or "passive smoke" also harm family members, coworkers, and others around smokers. There are a number of techniques available to assist people who want to quit smoking.
-

Swine Flu
Novel H1N1 influenza A virus infection (swine flu) is an infection that generally is transferred from an infected pig to a human, however there have been reported cases where infection has occured with no contact with infected pigs. Symptoms of swine flu are "flu-like" and include fever, cough, and sore throat. Treatment is generally with the antibiotics oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza).
-

Teen Drug Abuse
Drugs commonly abused by teens include tobacco products, marijuana, cold medications, inhalants, depressants, stimulants, narcotics, hallucinogens, PCP, ketamine, Ecstasy, and anabolic steroids. Some of the symptoms and warning signs of teen drug abuse include reddened whites of eyes, paranoia, sleepiness, excessive happiness, seizures, memory loss, increased appetite, discolored fingertips, lips or teeth, and irritability. Treatment of drug addiction may involve a combination of medication, individual, and familial interventions.
-
What Is Mucus?
Mucus is a normal substance produced by lining tissues in the body. Excess mucus or mucus that is yellow, green, brown, or bloody may indicate a problem. Mucus production may increase when allergies, a cold, flu, cough, or sore throat are present. Antihistamines and cold and flu medications may help alleviate excess mucus. A neti pot may be used to decrease nasal congestion and clear mucus.
-

Whooping Cough (Pertussis)
Whooping cough (pertussis) is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. There are an estimated 300,000 plus deaths annually from whooping cough (pertussis). Whooping cough commonly affects infants and young children but can be prevented with immunization with the vaccine. First stage whooping cough symptoms are a runny nose, sneezing, low-grade fever, a mild cough with the cough gradually becoming more severe. After one to two weeks, the second stage of whooping cough begins.
Examples of Medications for Runny Nose
- beclomethasone dipropionate inhaler (Beconase AQ, QNASL)
- cetirizine (Zyrtec, Zyrtec Allergy, Zyrtec Hives)
- chlorpheniramine, pseudoephedrine
- diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- fexofenadine (Allegra, Mucinex Allergy)
- fexofenadine and pseudoephedrine (Allegra-D)
- loratadine and pseudoephedrine (Alavert Allergy & Sinus, Claritin-D, Claritin-D 24 hour)
- loratadine, Claritin, Claritin RediTabs, Alavert, Claritin Hives Relief, Children's Claritin
- pseudoephedrine (Oral, Afrinol, Sudafed)
- Adenovirus
- Adenovirus 14 (Killer Cold Virus)
- Allergy (Allergies)
- Are You Too Sick to Work?
- Aspergillus Infection (Aspergillosis)
- Bocavirus
- Chronic Rhinitis and Post-Nasal Drip
- Cluster Headaches
- Cold vs. Flu
- Cold, Flu, Allergy Treatments
- Common Cold
- Deviated Septum
- Flu (Influenza)
- Food Allergy
- Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
- Hay Fever (Allergic Rhinitis)
- How Can I Help My Baby With a Stuffy Nose?
- How Long Is a Cold or Flu Contagious?
- Indoor Allergens
- Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Contagious?
- Is Swine Flu (H1N1) Contagious?
- Measles
- Mold Exposure: Symptoms, Removal, and Remediation
- Occupational Asthma
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- Roseola
- Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
- Sinus Infection vs. Cold
- Smoking (How to Quit Smoking)
- Swine Flu
- Teen Drug Abuse
- What Is Mucus?
- Whooping Cough (Pertussis)
