Pale Skin Symptoms
Paleness of the skin refers to an abnormal lightening of the skin or mucous membranes. Pale skin may be generalized (occurring all over the body) or localized to one area. It is often accompanied by paleness or pallor in the linings of the eyes, inside of the mouth, and on the surface of the tongue. True paleness of the skin is related to the thickness and density of blood vessels beneath the skin and not to the amount of melanin (skin pigment) that is present. However, some people may confuse loss of skin pigmentation (as with albinism) with paleness. In dark-skinned people, paleness may only be apparent when examining the mucous membranes. Pale skin generally results from a decrease in blood flow, as with fainting or shock. It may also result from a reduction in the number of red blood cells (anemia).
Other causes of pale skin
- Albinism
- Aplastic Anemia
- Arterial Occlusion
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
- Bleeding
- Chemical Poisoning
- Diamond-Blackfan Syndrome
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
- Fair Complexion
- Fanconi Anemia
- Fear or Panic Reaction
- Folic Acid Deficiency
- Lack of Sun Exposure
- Low Environmental Temperature
- Malnutrition
- Medication Side Effects
- Respiratory Failure
- Severe Trauma
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
- Transient Erythroblastopenia of Childhood (TEC)
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Causes of Pale Skin
-

Alpha Thalassemia
Alpha thalassemia is a disorder in which the alpha globin protein is underproduced. There are two pairs of genes that carry the code for the alpha chains of hemoglobin. When one gene is impaired, that person is in a carrier state and suffers no medical problems. When four genes are impaired, the production of fetal and adult hemoglobin is prevented, resulting in hydrops fetalis and leading to death before birth.
-

Anemia: Symptoms, Treatment and Causes
Anemia is the condition of having less than the normal number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. The oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is, therefore, decreased. There are several types of anemia such as iron deficiency anemia (the most common type), sickle cell anemia, vitamin B12 anemia, pernicious anemia, and aplastic anemia. Symptoms of anemia may include fatigue, malaise, hair loss, palpitations, menstruation, and medications. Treatment for anemia includes treating the underlying cause for the condition. Iron supplements, vitamin B12 injections, and certain medications may also be necessary.
-

Beta Thalassemia
Beta Thalassemia is the most familiar type of thalassemia. Thalassemia is not just one disease but rather a complex series of genetic (inherited) disorders all of which involve underproduction of hemoglobin. Beta thalassemia major symptoms include pale skin, irritability, growth retardation, swelling of the abdomen, and jaundice. Beta thalassemia treatments include directly relieving the symptoms of the illness.
-
Cold Agglutinin Disease
Cold agglutinin hemolytic anemia or cold agglutinin hemolytic disease, is rare disorder of the autoimmune system. There are two types of cold agglutinin disease, primary and secondary. Characteristics, symptoms, and signs of in cold agglutinin disease are premature destruction of red blood cells in the body’s natural defense antibodies. The lifespan of red blood cells is approximately 120 before the spleen destroys the antibodies. In cold agglutinin disease, the severity of the condition is determined by how long it takes for the red blood cells to survive, and at the rate that the bone marrow continues to produce more red cells. Immune hemolytic anemias are classified by the optimal temperature when the antibodies try to destroy red blood cells. Cold agglutinin anemia occurs at temperatures between 10 C (50 F) and 37 C (F 98.6) or above while the body warms antibody hemolytic anemia. Usually, cold agglutinin anemia becomes apparent between the ages of 50 to 60. Other symptoms of the disease include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fingers and/or toes are cold and sweat, an uneven bluish or reddish discoloration of the toes, ankles, and wrists (Raynaud's syndrome), and fingers. Usually, cold agglutinin anemia affects people that are older. The disease is diagnosed by a physical exam, and the Coomb's test. If the red blood cells destruction seem to be slowing on its own, treatment therapies, usually, isn’t needed. Other treatments for cold agglutinin anemia are corticosteroids, and splenectomy (removal of the spleen). There is no cure for cold agglutinin disease.
-

Congenital Heart Defects
Congenital heart defects are heart problems that are present at birth. Genetics may play a role in some heart defects. Symptoms can range from nonexistent to severe and life-threatening. Fatigue, rapid breathing, and decreased blood circulation are a few possible symptoms of congenital heart defects. Many cases do not require any treatment. Procedures using catheters and surgery may be used to repair severe heart defects.
-
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a disease of the mucus and sweat glands. Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease. The outcome of the disease leaves the body malnourished, with bulky and fouls smelling stools, vitamin insufficiency, gas, painful or swollen abdomen, infertility, susceptible to heat emergencies, and respiratory failure. There is no cure for cystic fibrosis, treatment of symptoms is used to manage the disease.
-
Drug Abuse
Drug addiction is a chronic disease that causes drug-seeking behavior and drug use despite negative consequences to the user and those around him. Though the initial decision to use drugs is voluntary, changes in the brain caused by repeated drug abuse can affect a person's self-control and ability to make the right decisions and increase the urge to take drugs. Drug abuse and addiction are preventable.
-

Frostbite (Frostnip)
There are two categories of cold weather-related injuries. 1) no freezing of body tissue (trench foot and chilblains), and 2) freezing of body tissues (frostbite). Chilblains in general, will not need medical attention (unless there is infection). Trench foot and frostbite, however, require medical attention. Symptoms of frostbite include pain, burning, numbness, and eventually a complete loss of sensation in the affected body part. The young, elderly, and patients with certain medical conditions (diabetes, hypothyroidism, circulatory problems, and psychiatric illnesses), are more susceptible to cold weather-related injuries. People who abuse alcohol and illicit drug user are also at risk for cold weather-related injuries.
-
G6PD Deficiency
G6PD deficiency (Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase) leads to a condition called hemolytic anemia. Causes of G6PD deficiency is an abnormal gene located in the X-chromosome, therefore, it is more common in males. Hemolytic anemia caused by G6PD deficiency generally occurs after exposure to malaria medications, antiitching drugs, and fava beans. Pneumonia and other infections can also precipitate hemolytic anemia in individuals with G6PD deficiency. Treatment is generally discontinuing the drug or compound treating infection. Blood transfusions are necessary in some individuals.
-

Heat Stroke (A Very Serious Condition)
Heat stroke (heatstroke or sun stroke) is a form of hyperthermia. Heat stroke is a true medical emergency that can be fatal if not promptly and properly treated. Symptoms of heat stroke include high body temperature, absence of sweating, hot red or flushed dry skin, rapid pulse, difficulty breathing, strange behavior, hallucinations, confusion, agitation, disorientation, seizure, and coma. A victim of heat stroke must receive immediate treatment to avoid permanent organ damage.
-
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a diseases in which blood clots within the capillaries. Causes associated with HUS include: E. coli, birth control pills, pneumonia, medications such as chemotherapy, Ticlid, and quinine. Symptoms of HUS include: gastroenteritis, abdominal cramping, vomiting, and bloody diarrhea. Diagnosis of HUS includes: medical history, physical examination, and medical tests. Treatment includes: rest, fluids, possible hospitalization for blood transfusion or complications due to kidney failure.
-
Iron Deficiency
Iron is a mineral our bodies need. Iron deficiency is a condition resulting from not enough iron in the body. It is the most common nutritional deficiency and the leading cause in the US. Iron deficiency is caused due to increased iron deficiency from diseases, nutritional deficiency, or blood loss and the body's inability to intake or absorb iron. Children, teen girls, pregnant women, and babies are at most risk for developing iron deficiency. Symptoms of iron deficiency include feeling weak and tired, decreased work or school performance, slow social development, difficulty maintaining body temperature, decreased immune function, and an inflamed tongue. Blood tests can confirm an iron deficiency in an individual. Treatment depends on the cause of the deficiency. Proper diet that includes recommended daily allowances of iron may prevent some cases of iron deficiency.
-

Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of cancer of the blood cells in which the growth and development of the blood cells are abnormal. Strictly speaking, leukemia should refer only to cancer of the white blood cells (the leukocytes) but in practice it can apply to malignancy of any cellular element in the blood or bone marrow, as in red cell leukemia (erythroleukemia).
-

Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
Low blood pressure, also referred to as hypotension, is blood pressure that is so low that it causes symptoms or signs due to the low flow of blood through the arteries and veins. Some of the symptoms of low blood pressure include light-headedness, dizziness, and fainting if not enough blood is getting to the brain. Diseases and medications can also cause low blood pressure. When the flow of blood is too low to deliver enough oxygen and nutrients to vital organs such as the brain, heart, and kidneys; the organs do not function normally and may be permanently damaged.
-

Migraine Headache
Migraine headache is a type of headache associated with a sensitivity to light, smells, or sounds, eye pain, severe pounding on one side of the head, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. The exact cause of migraine headaches is not known. Triggers for migraine headaches include certain foods, stress, hormonal changes, strong stimuli (loud noises), and oversleeping. Treatment guidelines for migraines include medicine, pain management, diet changes, avoiding foods that trigger migraines, staying hydrated, getting adequate sleep, and exercising regularly. Prevention of migraine triggers include getting regular exercise, drinking water daily, reducing stress, and avoiding trigger foods.
-

Raynaud's Phenomenon
Raynaud's phenomenon is characterized by a pale-blue-red sequence of color changes of the digits, most commonly after exposure to cold. Occurring as a result of spasm of blood vessels, the cause is unknown. Symptoms and signs of Raynaud's phenomenon depend on the severity, frequency, and duration of the blood vessel spasm. Treatments include protection of the digits, medications, and avoiding emotional stresses, smoking, cold temperature, and tools that vibrate the hands.
-

Sepsis
Sepsis (blood poisoning) is a potentially deadly infection with signs and symptoms that include elevated heart rate, low or high temperature, rapid breathing and/or a white blood cell count that is too high or too low and has more than 10% band cells. Most cases of sepsis are caused by bacterial infections, and some cases are caused by fungal infections. Treatment requires hospitalization, IV antibiotics, and therapy to treat any organ dysfunction.
-

Shock (Medical)
Medical shock is a life-threatening medical condition. There are several types of medical shock, including: septic shock, anaphylactic shock, cardiogenic shock, hypovolemic shock, and neurogenic shock. Causes of shock include: heart attack, heart failure, heavy bleeding (internal and external), infection, anaphylaxis, spinal cord injury, severe burns, chronic vomiting or diarrhea. Low blood pressure is the key sign of sock. Treatment is dependant upon the type of shock.
-

Sickle Cell Disease (Anemia)
Sickle cell anemia (sickle cell disease), a blood disease which shortens life expectancy, is caused by an inherited abnormal hemoglobin. Symptoms of sickle cell anemia may include bacterial infections, painful swelling of the hands and feet, fever, leg ulcers, fatigue, anemia, eye damage, and lung and heart injury. Treatment for sickle cell anemia aims to manage and prevent the worst manifestations of the disease and focuses on therapies that block red blood cells from stacking together, which can lead to tissue and organ damage and pain.
-
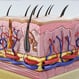
The Skin (Human Anatomy): Picture, Definition, Function and Skin Conditions
The skin is the largest organ in the body that covers the entire external surface. It protects the internal organs from germs and thus helps prevent infections. The skin is made up of three main layers.
-

The Skin: 7 Most Important Layers and Functions
The skin is the largest organ in the body and it covers the body's entire external surface. It is made up of seven layers. The first five layers form the epidermis, which is the outermost, thick layer of the skin. The hypodermis is the deepest layer of skin situated below the dermis.
-
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a condition in which the skin turns white due to the loss of pigment from the melanocytes, cells that produce the pigment melanin that gives the skin color.
-

What Is Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) is cancer of the lymphatic system, a vital part of the body's immune system. Symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, coughing, weakness, chest pain, unexplained weight loss, and abdominal pain.
- Alpha Thalassemia
- Anemia: Symptoms, Treatment and Causes
- Beta Thalassemia
- Cold Agglutinin Disease
- Congenital Heart Defects
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Drug Abuse
- Frostbite (Frostnip)
- G6PD Deficiency
- Heat Stroke (A Very Serious Condition)
- Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Iron Deficiency
- Leukemia
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
- Migraine Headache
- Raynaud's Phenomenon
- Sepsis
- Shock (Medical)
- Sickle Cell Disease (Anemia)
- The Skin (Human Anatomy): Picture, Definition, Function and Skin Conditions
- The Skin: 7 Most Important Layers and Functions
- Vitiligo
- What Is Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma?
