Blisters
Blisters are small raised areas that are filled with fluid and located in the superficial layer of the skin. They look like bubbles on the surface of the skin. Although they are often caused by irritation or friction (such as with a poorly fitting shoe), blisters can also represent disease processes. Blisters can accompany some types of skin rashes and inflammatory conditions, including certain autoimmune diseases. Depending upon the cause of the blisters, blisters may occur singly or in groups. In contrast to abscesses and boils, which are collections of inflammatory fluid found deep in the tissues, blisters are found in the most superficial layer of skin.
Small fluid-filled blisters are medically known as vesicles. Bullae (singular = bulla) are blisters that are larger than 1 cm across.
Other causes of blisters
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis
- Freezing/Cold Injury
- Friction or Trauma
- Pemphigus
- Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
- Radiation Injury
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Causes of Blisters
-

30 Sunburn Natural and Home Remedies for Severe Sunburns
There are many natural and home remedies that are thought to relieve the symptoms ofa sunburn. Check out our top 30 tips to cool that sunburn, for example drink lots of water, juice, or sports drinks; apply a cool compress containing Burow's solution; coconut oil can be used as a moisturizer after sunburn pain has stopped; apply topical over-the-counter (OTC) 1% hydrocortisone cream; and take OTC pain relievers like NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve).
-

Allergy (Allergies)
An allergy refers to a misguided reaction by our immune system in response to bodily contact with certain foreign substances. When these allergens come in contact with the body, it causes the immune system to develop an allergic reaction in people who are allergic to it. It is estimated that 50 million North Americans are affected by allergic conditions. The parts of the body that are prone to react to allergies include the eyes, nose, lungs, skin, and stomach. Common allergic disorders include hay fever, asthma, allergic eyes, allergic eczema, hives, and allergic shock.
-

Anthrax
Anthrax is a deadly infectious disease that may be transmitted to humans by infected animals or by biological warfare. There are three types of anthrax: cutaneous, inhalation, and gastrointestinal. Symptoms of cutaneous anthrax include a swollen glands, muscle ache, headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, and a red-brown raised spot that enlarges, blisters, and hardens, forming an ulcer crater with black crust. Symptoms of inhalation anthrax are flu-like and may progress to respiratory distress, shock, coma, and death. Symptoms of gastrointestinal anthrax include loss of appetite, bloody diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Treatment for cutaneous anthrax involves penicillin, tetracycline, erythromycin, and ciprofloxin. Inhalation anthrax necessitates treatment with IV therapy with antibiotics.
-

Are Cold Sores (Fever Blisters) Contagious?
About 20% of cases of cold sores are caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), and approximately 80% of cold sores are caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Cold sores are transmitted by sharing utensils and razors, kissing, and oral sex. There is no cure for cold sores.
-

Bed Bugs Bites
Bed bugs (from the insect family Cimicidae) are small, reddish-brown tick-like insects that feed by sucking the blood of mammals. They are often found in poorly sanitized areas or in crowded living quarters.
-

Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid is a skin disease that causes blistering eruptions on the skin's surface and sometimes affects the inner lining of the mouth. Symptoms include severe itching and burning sensations. Treatment involves topical cortisone and sometimes high doses of cortisone. Severe cases may require immune-suppression drugs such as azathioprine.
-
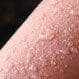
Burns (First Aid)
Burn types are based on their severity: first-degree burns, second-degree burns, and third-degree burns. First-degree burns are similar to a painful sunburn. The damage is more severe with second-degree burns, leading to blistering and more intense pain. The skin turns white and loses sensation with third-degree burns. Burn treatment depends upon the burn location, total burn area, and intensity of the burn.
-

Capnocytophaga canimorsus
The bacteria Capnocytophaga canimorsus is common in the mouths of cats, people, and dogs. People with weak immune systems are at risk for contracting Capnocytophaga infections. Antibiotics can kill this bacteria.
-

Chickenpox (Varicella)
Chickenpox (chicken pox) is a contagious childhood disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Symptoms have an incubation period of 14 to 16 days and include a couple days of mild fever, weakness, and red, raised rash that progresses to blisters that eventually burst and crust over. Complications include bacterial infection of the open sores, scarring, encephalitis, nerve palsies, and Reye's syndrome.
-

Cold Sores (Oral Herpes, Herpes Labialis)
Herpes simplex infections are common and when they appear around the mouth and lips, people often refer to them as "cold sores" and "fever blisters." Canker sores are different than cold sores. Air droplets can spread the virus, as can direct contact with the fluid from the blisters. Cold sore treatment include over-the-counter medication, as well as prescription medications.
-

Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a rash that occurs after exposure to an irritant. Symptoms of contact dermatitis include a red, elevated rash at the site of contact with the irritating substance. Contact dermatitis treatment may involve creams, application of cool water compresses, and applying topical steroids.
-

Cuts, Scrapes, and Puncture Wounds
Cuts, scrapes, and puncture wounds are common, and most people will experience one of these in their lifetime. Evaluating the injury, and thoroughly cleaning the injury is important. Some injuries should be evaluated by a doctor, and a tetanus shot may be necessary. Treatment will depend upon the severity of the injury.
-

Diaper Rash
A diaper rash is a skin irritation that develops in the diaper-covered region. Most diaper rashes are caused by bacterial or yeast infections, though some may be caused by contact dermatitis or allergic reactions to the diapers and wipes. Cleansing with water and soft cloths, followed by application of petroleum jelly or zinc oxide and frequent diaper changes is the best treatment for a diaper rash.
-
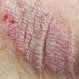
Eczema
Eczema refers to skin inflammation. There are many different types of eczema that produce symptoms and signs that range from oozing blisters to crusty plaques of skin. Treatment varies depending upon the type of eczema the person has.
-

Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB)
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of inherited diseases characterized by skin blistering, erosion, and fragility. EB affects eight of 1 million Americans. There is no cure for EB, and the only treatment is supportive care.
-
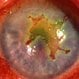
Eye Herpes
Herpes of the eye occurs due to herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1). Symptoms of herpes of the eye include pain in and around the eye, rash or sores on the eyelids, redness, swelling, and cloudiness of the cornea.
-

Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a skin condition that causes small red bumps to form around the hair follicles. Skin bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas may infect the follicles. Treatment involves over-the-counter bacterial washes, topical antibiotics, and/or topical steroids.
-

Frostbite (Frostnip)
There are two categories of cold weather-related injuries. 1) no freezing of body tissue (trench foot and chilblains), and 2) freezing of body tissues (frostbite). Chilblains in general, will not need medical attention (unless there is infection). Trench foot and frostbite, however, require medical attention. Symptoms of frostbite include pain, burning, numbness, and eventually a complete loss of sensation in the affected body part. The young, elderly, and patients with certain medical conditions (diabetes, hypothyroidism, circulatory problems, and psychiatric illnesses), are more susceptible to cold weather-related injuries. People who abuse alcohol and illicit drug user are also at risk for cold weather-related injuries.
-
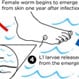
Guinea Worm Disease
Guinea worm disease (GWD or dracunculiasis) is an infection caused by the parasite Dracunculus medinensis. After a person drinks water contaminated by water fleas that harbor Guinea worm larvae, the larvae grow into adult worms (2-3 feet) in the small intestine and then migrate and emerge from the skin. Symptoms and signs include fever, swelling, and pain near the blister on the skin where the worm will emerge. As there is no medication to treat GWD and no vaccine to prevent infection, treatment focuses on minimizing pain and swelling (with the use of ibuprofen or aspirin) as the worms are slowly pulled from the wound over the course of a few days to a few months.
-
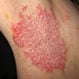
Hailey-Hailey Disease (Familial Benign Pemphigus)
Hailey-Hailey disease (familial benign pemphigus) is a hereditary skin disease that causes painful blistering the skin folds. There is no specific treatment for this disease, and treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms and signs.
-
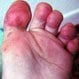
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth syndrome is clinical pattern consisting of a rash on the hands and feet, and in the mouth. Hand, foot, and mouth syndrome is caused by various viruses, including several types of Coxsackieviruses. Other symptoms include sore throat, decreased appetite, irritability, and (or) fever.
-

Impetigo: Treatment, Symptoms, and Complications
Impetigo is a contagious skin infection caused by staph and strep bacteria. There are two types of impetigo: nonbullous and bullous. Symptoms of nonbullous impetigo include small blisters on the nose, face, arms, or legs and possibly swollen glands. Bullous impetigo signs include blisters in various areas, particularly in the buttocks area. Treatment involves gentle cleansing, removing the crusts of popped blisters, and the application of prescription-strength mupirocin antibiotic ointment.
-

Is Chickenpox Contagious?
Chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by the varicella zoster virus. Chickenpox symptoms and signs include a blistering, itchy rash, fatigue, fever, and tiredness. Chickenpox is transmitted via contaminated droplets produced during sneezing or coughing and by coming in contact with blister fluid.
-
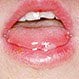
Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) Contagious?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a highly contagious disease caused by several enteroviruses. These viruses are transmitted via nasal secretions, kissing, and saliva. HFMD causes the following symptoms and signs: decreased appetite, sore throat, fever, weakness, and painful sores on the hands, feet, and in the mouth.
-

Is Impetigo Contagious?
Impetigo is a contagious bacterial infection that usually occurs in children ages 2-5. There are two types of impetigo: bullous and nonbullous. With nonbullous impetigo, pus-filled blisters develop, ooze, and crust over on the patient's torso, in contrast with bullous impetigo, which is typically confined to the extremities and the face near the mouth.
-

Is Poison Ivy Contagious?
Poison ivy produces urushiol, an oily chemical that causes an itchy, painful reddish rash in people who come in contact with the plant. The rash lasts for one to three weeks. People should seek medical care for poison ivy exposure if the resulting rash covers a large portion of the body, if the rash develops on the genitalia or face, or if there is swelling around the eyes or of the throat.
-

Is Shingles Contagious?
Shingles is an infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Shingles symptoms and signs include skin burning, numbness, and tingling along with a painful red, blistering rash. Shingles is contagious until all of the blisters have crusted over.
-

Jock Itch
Jock itch is an itchy red rash that appears in the groin area. The rash may be caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. People with diabetes and those who are obese are more susceptible to developing jock itch. Antifungal shampoos, creams, and pills may be needed to treat fungal jock itch. Bacterial jock itch may be treated with antibacterial soaps and topical and oral antibiotics.
-

Lichen Sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus is a skin disease that causes white spots to form on the skin, which later grow into large, thin, and crinkled patches of skin that tear easily. Symptoms include itching, pain, blisters, and bleeding. Patches on the upper body usually go away over time, but patches in the genital region may scar if left untreated, causing problems with urination or sex. Treatment may involve surgery or the use of a very strong cortisone cream.
-

Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis is also known as a flesh-eating bacterial infection, Fournier's gangrene, suppurative fasciitis, and necrotizing cellulitis. The disease is occasionally caused by fungi, but most cases are caused by bacteria that enter the skin through insect bites, cuts, puncture wounds, or surgical incisions. Signs and symptoms include pain, redness, swelling, fever, chills, skin ulceration, bullae formation, black scabs, gas formation, and fluid draining from the site of infection. Treatment involves hospitalization, the use of intravenous antibiotics, and debridement of the necrotic tissue.
-

Pimple vs. Cold Sore
Pimples are areas of skin inflammation with pus in the center. Cold sores are fluid-filled blisters. Pimples are caused by bacterial overgrowth and inflammation. Cold sores are caused by infection with herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1 and HSV-2). Benzoyl peroxide and sometimes antibiotics treat acne. Antiviral medications accelerate the healing process of oral herpes.
-

Poison Ivy, Oak, and Sumac
Poison ivy, oak, and sumac contain a substance called urushiol, which causes a rash on people who come in contact with them. Symptoms and signs include a red, swollen, itchy, blistering, bumpy rash. Treatment involves rinsing the exposed area with water, taking antihistamines and over-the-counter pain medications, using topical treatments such as calamine lotion, and applying cool compresses.
-
Scabies
Scabies are itch mites that burrow under the skin and produce intense itching that's usually worse at night. Symptoms of scabies are small bumps and blisters on the wrists, knees, between the fingers, on the back of the elbows, in the groin and on the buttocks. Treatment involves applying a mite-killing cream, antihistamines for itch relief, washing bedclothes and linens.
-
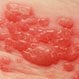
Shingles
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful rash caused by the varicella zoster virus. Other shingles symptoms include headache, fever, nausea, and body aches. Treatment focuses on pain management and shortening the duration of the illness with antiviral medications.
-

Skin Rash
The word "rash" means an outbreak of red bumps on the body. The way people use this term, "a rash" can refer to many different skin conditions. The most common of these are scaly patches of skin and red, itchy bumps or patches all over the place.
-

Smallpox
Smallpox is a disease caused by the variola virus. Symptoms and signs include: a characteristic rash and high fever. Treatment focuses on supporting the patient. Smallpox may be prevented with the ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine.
-

Spider Bites (Black Widow and Brown Recluse)
Most spiders in the United States are harmless; however, black widow and brown recluse spider bites may need medical treatment. Symptoms of a harmless spider bite generally include pain, redness, and irritation. Signs and symptoms of black widow spider bite include pain immediately, redness, burning, and swelling at the site of the bite. Sometimes the person will feel a pinprick or double fang marks. Brown recluse spider bite symptoms and signs are a mild sting, followed by severe pain and local redness. These symptoms usually develop within eight hours or more after the bite. Black widow and brown recluse spider bites have similar symptoms, for example, nausea, vomiting, fever, headache, and abdominal or joint pain. Generally, brown recluse and black widow spider bites need immediate medical treatment. If you think that you or someone you know has been bitten by a brown recluse or black widow spider, go to your nearest Urgent Care or Emergency Department for medical treatment.
-

STDs in Men
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections transmitted during sexual contact. They may be caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. STDs in men cause no symptoms or symptoms like genital burning, itching, sores, rashes, or discharge. Common infections that are sexually transmitted in men include gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, hepatitis C and B, genital warts, human papillomavirus (HPV), and genital herpes. Some STDs in men are treatable while others are not. STDs are diagnosed with tests that identify proteins or genetic material of the organisms causing the infection. The prognosis of an STD depends on whether the infection is treatable or not. Use of latex condoms can help reduce the risk of contracting an STD but it does not eliminate the risk entirely.
-

Sunburn (Sun Poisoning)
Sunburn is caused by overexposure to UV radiation from the sun. UV rays can also damage the eyes. Repeated overexposure to UV rays also increases the risk for scarring, freckles, wrinkles, and dry skin. Symptoms of sunburn include painful, red, tender, and hot skin.The skin may blister, swell, and peel. Sun poisoning (severe sunburn) include nausea, fever, chills, rapid pulse, dizziness and more. Home remedies can help relieve sunburn pain, blisters, and peeling. Severe sunburns may need medical treatment. Sun protection and sunscreen for an person's skin type is recommended to decrease the chance of a severe sunburn and sun poisoning.
-
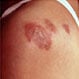
Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
Sweet syndrome (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a skin condition that sometimes occurs due to an immune system response to RA, pregnancy, certain cancers, inflammatory bowel diseases, blood disorders, respiratory tract infections, and particular medications. Symptoms and signs include characteristic skin lesions that grow and spread into clusters. Sore eyes, high fever, mouth ulcers, headache, and aching joints may accompany the lesions. Though Sweet syndrome may resolve on its own, more severe cases may require medications like corticosteroids.
-

Ticks vs. Bedbugs
Bedbugs are parasites. Ticks are arthropods. Tick and bedbug bites are typically painless. Calamine lotion can be helpful with both bedbug and tick bites. Bedbugs typically do not spread disease, while tick bites may often transmit disease.
-

What Are Boils (Skin Abscesses)?
A boil is a skin abscess, a collection of pus localized deep in the skin. There are several different types of boils. Among them are the following: furuncle or carbuncle, cystic acne, hidradenitis suppurativa, and pilonidal cyst.
-

What Are the Causes of Blisters on the Hands?
Hand blisters are a common sight in everyday life. Learn what causes hand blisters, when to see a doctor, and how to treat hand blisters.
-

What Causes Blisters on Lips?
What are blisters on lips and what causes blisters on lips? Learn about these mouth sores, what causes blisters on lips, and how to treat blisters on lips.
-

What Causes Blisters on Your Feet?
What are foot blisters and what causes them? Learn about the types of foot blisters, what causes them, and how to treat them.
-

What Is Genital Herpes in Women?
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). Symptoms of genital herpes include painful blisters and often fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes for the first outbreak. Genital herpes is diagnosed with lab tests to test for the presence of the virus. Treatment for genital herpes includes antiviral medications to shorten the duration of the outbreak or reduce the risk of future outbreaks. There is no cure for genital herpes. Condoms may help prevent the spread of genital herpes.

