Bumps on Skin
People often describe localized swollen areas on, or under, the skin as lumps or bumps. While bumps on, or under, the skin may result from conditions that give rise to a skin rash, many other conditions can result in solitary raised lumps on the skin. Infections, tumors, and the body's response to trauma or injury can all lead to lumps or bumps that appear to be located on or underneath the skin.
Depending upon the cause, skin lumps or bumps may vary in size and be firm or soft to the touch. The overlying skin may be reddened or ulcerated. Skin bumps may or may not be painful or tender, depending upon the cause of the lesions.
Other causes of bumps on skin
- Dermatofibroma
- Granuloma Annulare
- Hemangioma
- Hyperplasia
- Infections/Abscesses
- Intradermal Cyst
- Keratoacanthoma
- Lipoma
- Metastatic Carcinoma
- Neurofibromatosis
- Polymorphic Light Eruption
- Pyogenic Granuloma
- Rheumatoid Nodules
- Sebaceous (Epidermoid) Cysts
- Sebaceous Gland
- Seborrheic Keratosis
- Soft Tissue Sarcomas
- Splinters or Other Foreign Bodies
- Xanthomas
Causes of Bumps on Skin
-

Acne (Pimples)
Acne is a localized skin inflammation as a result of overactivity of oil glands at the base of hair follicles. This inflammation, depending on its location, can take the form of a superficial pustule (contains pus), a pimple, a deeper cyst, congested pores, whiteheads, or blackheads. Treatments vary depending on the severity of the acne.
-
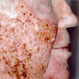
Actinic Keratosis
Actinic keratoses are rough, scaly patches of skin that are considered precancerous and are due to sun exposure. Prevention is to cut sun exposure and wear sunscreen.
-

Anthrax
Anthrax is a deadly infectious disease that may be transmitted to humans by infected animals or by biological warfare. There are three types of anthrax: cutaneous, inhalation, and gastrointestinal. Symptoms of cutaneous anthrax include a swollen glands, muscle ache, headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, and a red-brown raised spot that enlarges, blisters, and hardens, forming an ulcer crater with black crust. Symptoms of inhalation anthrax are flu-like and may progress to respiratory distress, shock, coma, and death. Symptoms of gastrointestinal anthrax include loss of appetite, bloody diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Treatment for cutaneous anthrax involves penicillin, tetracycline, erythromycin, and ciprofloxin. Inhalation anthrax necessitates treatment with IV therapy with antibiotics.
-
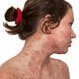
Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema is a general term for many types dermatitis (skin inflammation). Atopic dermatitis is the most common of the many types of eczema. Other types of eczema include: contact eczema, allergic contact eczema, seborrheic eczema, nummular eczema, stasis dermatitis, and dyshidrotic eczema.
-

Bed Bugs Bites
Bed bugs (from the insect family Cimicidae) are small, reddish-brown tick-like insects that feed by sucking the blood of mammals. They are often found in poorly sanitized areas or in crowded living quarters.
-

Birthmark
A birthmark is any abnormal mark, spot, or bump that is present in or around the time of birth on the skin of an infant. Types of birthmarks include cafe au lait marks, Mongolian spots, strawberry marks, and others. Depending on the birthmark type, birthmarks can be removed by scalpel surgery, lasers, and rarely radiation.
-

Bug Bites and Stings
Bug bites and stings have been known to transmit insect-borne illnesses such as West Nile virus, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and Lyme disease. Though most reactions to insect bites and stings are mild, some reactions may be life-threatening. Preventing bug bites and stings with insect repellant, wearing the proper protective attire, and not wearing heavily scented perfumes when in grassy, wooded, and brushy areas is key.
-
Can You Get Rid of Cellulite?
Learn what treatments can help you reduce cellulite or get rid of it for good.
-
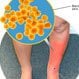
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is an acute spreading bacterial infection below the surface of the skin characterized by redness, warmth, inflammation, and pain. The most common cause of cellulitis is the bacteria staph (Staphylococcus aureus).
-

Chickenpox (Varicella)
Chickenpox (chicken pox) is a contagious childhood disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Symptoms have an incubation period of 14 to 16 days and include a couple days of mild fever, weakness, and red, raised rash that progresses to blisters that eventually burst and crust over. Complications include bacterial infection of the open sores, scarring, encephalitis, nerve palsies, and Reye's syndrome.
-

Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a rash that occurs after exposure to an irritant. Symptoms of contact dermatitis include a red, elevated rash at the site of contact with the irritating substance. Contact dermatitis treatment may involve creams, application of cool water compresses, and applying topical steroids.
-
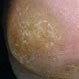
Corns and Calluses
Corns and calluses are sometimes painful areas of thickened skin that appear between the toes and fingers or on the soles of the feet. Abnormal foot anatomy, ill-fitting footwear, and unusual gait can put increased pressure in specific areas, causing corns and calluses. Treatment may involve using over-the-counter salicylic-acid products, visiting a podiatrist to be fitted with an orthotic device, or surgical removal.
-
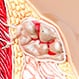
Cyst
Cysts are sac-like structures that may be filled with gas, liquid, or solid materials. Cysts may produce symptoms and signs depending on their location. Treatment of a cyst depends upon what caused the cyst in the first place.
-
Erythema Nodosum
Erythema nodosum is a skin inflammation that results in reddish, painful, tender lumps most commonly located in the front of the legs below the knees. Erythema nodosum can resolve on its own in three to six weeks, leaving a bruised area. Treatments include anti-inflammatory medications and cortisone by mouth or injection.
-

Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a skin condition that causes small red bumps to form around the hair follicles. Skin bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas may infect the follicles. Treatment involves over-the-counter bacterial washes, topical antibiotics, and/or topical steroids.
-
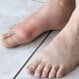
Gout
Buildup of uric acid crystals in a joint causes gouty arthritis. Symptoms and signs include joint pain, swelling, heat, and redness, typically of a single joint. Gout may be treated with diet and lifestyle changes, as well as medication.
-
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (Acne Inversa)
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS or acne inversa) is a chronic skin condition that causes painful red abscesses in the groin and armpits that may drain foul-smelling pus. Treatment options include weight loss, smoking cessation, topical antibiotics, and avoidance of tight-fitting underwear. Finasteride and adalimumab may be helpful for those with resistant cases of HS.
-
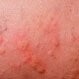
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives, also called urticaria, is a raised, itchy area of skin. Most often the cause of hives is unknown. Sometimes it is a sign of an allergic reaction to food or medications, but the cause of the allergy (the allergen) is unknown. Dermatographism and swelling (angioedema) may accompany hives. Treatment to get rid of hives and alleviate symptoms typically includes antihistamines.
-

How Do I Get Rid of Intertrigo?
Intertrigo is painful and itchy skin inflammation that occurs between skin folds, such as in the groin, buttocks, or between fat folds. Sometimes, bacteria can infect this red skin, worsening inflammation. Losing weight and various topical remedies – especially before workouts or jogging, etc. – can reduce the effects of intertrigo.
-

Impetigo: Treatment, Symptoms, and Complications
Impetigo is a contagious skin infection caused by staph and strep bacteria. There are two types of impetigo: nonbullous and bullous. Symptoms of nonbullous impetigo include small blisters on the nose, face, arms, or legs and possibly swollen glands. Bullous impetigo signs include blisters in various areas, particularly in the buttocks area. Treatment involves gentle cleansing, removing the crusts of popped blisters, and the application of prescription-strength mupirocin antibiotic ointment.
-
Ingrown Hair
Ingrown hairs may be caused by improper shaving, waxing, or blockage of the hair follicle. Symptoms and signs of ingrown hairs include itching, tenderness, and small red pus bumps. Ingrown hairs usually heal on their own, but topical antibiotics, chemical depilatories, and hair-removal laser may be used in the treatment of ingrown hairs.
-

Insect Sting Allergies
The majority of stinging insects in the United States are from bees, yellow jackets, hornets, wasps, and fire ants. Severity of reactions to stings varies greatly. Avoidance and prompt treatment are essential. In selected cases, allergy injection therapy is highly effective.
-

Jock Itch
Jock itch is an itchy red rash that appears in the groin area. The rash may be caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. People with diabetes and those who are obese are more susceptible to developing jock itch. Antifungal shampoos, creams, and pills may be needed to treat fungal jock itch. Bacterial jock itch may be treated with antibacterial soaps and topical and oral antibiotics.
-
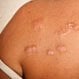
Keloid Scar
A keloid is a scar that doesn't know when to stop. When the cells keep on reproducing, the result is an overgrown (hypertrophic) scar or a keloid. A keloid looks shiny and is often dome-shaped, ranging in color from slightly pink to red. It feels hard and thick and is always raised above the surrounding skin.
-

Keratosis Pilaris (KP)
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is a common skin disorder in which small white or red bumps appear around hair follicles on the upper arms, thighs, buttocks, and cheeks. The cause of KP is unknown. There is no cure for keratosis pilaris, and the condition may resolve on its own. Gentle exfoliation, professional manual extraction, chemical peels, and microdermabrasion, along with topical products, are the best treatments for this condition.
-
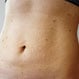
Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is a common skin disease that features small, itchy pink or purple spots on the arms or legs. The abnormal areas on the skin in lichen planus are typically flat-topped (hence the term planus), itchy, and frequently have a polygonal or angular shape.
-
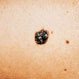
Melanoma
Second Source article from Government
-

Melanoma (Skin Cancer)
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer which begins in skin cells called melanocytes and affects more than 53,600 people in the United States each year. These melanocytes can grow together to form benign moles which, after a change in size, shape, or color can be a sign of melanoma. Caused by sun exposure, early detection becomes extremely important to avoid a spread to other areas of the body. Diagnosis is confirmed through a biopsy of the abnormal skin and treatment depends on the extent and characteristics of the patient. Metastatic melanoma is melanoma that has spread to various organs.
-
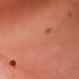
Moles
Moles are small skin growths that may appear flat or raised and are often tan, brown, black, reddish brown, or skin colored. They are typically about the size of a pencil eraser. There are three types of moles. Monthly skin self-exams are essential in the early detection of abnormal moles and melanomas.
-
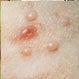
Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin disease that causes pink painless bumps on the skin. It typically resolves in 6 to 12 months. Cryotherapy, laser therapy, and curettage may also treat the nodules of molluscum contagiosum.
-
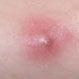
MRSA
MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) bacteria causes skin infections with the following signs and symptoms: cellulitis, abscesses, carbuncles, impetigo, styes, and boils. Normal skin tissue doesn't usually allow MRSA infection to develop. Individuals with depressed immune systems and people with cuts, abrasions, or chronic skin disease are more susceptible to MRSA infection.
-

Mycobacterium Marinum
Mycobacterium marinum (M. marinum) is bacteria found in fresh and saltwater that can infect the skin through cuts or scrapes, causing granulomas to appear on the skin near the site of infection. This infection may be treated with a long course of oral antibiotics.
-

Onchocerciasis
Onchocerciasis, or river blindness, is a parasitic disease that may cause blindness. It is transmitted by the bite of a female blackfly. Symptoms include skin depigmentation, vision loss, and itch. Ivermectin is used to treat the disease.
-

Pimple vs. Cold Sore
Pimples are areas of skin inflammation with pus in the center. Cold sores are fluid-filled blisters. Pimples are caused by bacterial overgrowth and inflammation. Cold sores are caused by infection with herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1 and HSV-2). Benzoyl peroxide and sometimes antibiotics treat acne. Antiviral medications accelerate the healing process of oral herpes.
-

Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-term skin condition that may cause large plaques of red, raised skin, flakes of dry skin, and skin scales. There are several types of psoriasis, including psoriasis vulgaris, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, and pustular psoriasis. Symptoms vary depending on the type of psoriasis the patient has. Treatment of psoriasis may include creams, lotions, oral medications, injections and infusions of biologics, and light therapy. There is no cure for psoriasis.
-
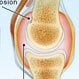
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease resulting in chronic inflammation of the joints, the tissue around the joints, as well as other organs in the body. Early RA signs and symptoms include anemia, both sides of the body affected (symmetric), depression, fatigue, fever, joint deformity, joint pain, joint redness, joint stiffness, joint swelling, joint tenderness, joint warmth, limping, loss of joint function, loss of joint range of motion, and polyarthritis.
-
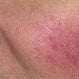
Rosacea
Rosacea is a skin disease that causes redness of the forehead, chin, and lower half of the nose. In addition to inflammation of the facial skin, symptoms include dilation of the blood vessels and pimples (acne rosacea) in the middle third of the face. Oral and topical antibiotics are treatments for rosacea. If left untreated, rhinophyma (a disfiguring nose condition) may result.
-
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis, a disease resulting from chronic inflammation, causes small lumps (granulomas) to develop in a great range of body tissues and can appear in almost any body organ. However, sarcoidosis most often starts in the lungs or lymph nodes.
-
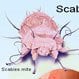
Scabies
Scabies are itch mites that burrow under the skin and produce intense itching that's usually worse at night. Symptoms of scabies are small bumps and blisters on the wrists, knees, between the fingers, on the back of the elbows, in the groin and on the buttocks. Treatment involves applying a mite-killing cream, antihistamines for itch relief, washing bedclothes and linens.
-

Scarlet Fever (Scarlatina)
Scarlet fever, a bacterial infection caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria, causes symptoms and signs such as fever, rash with a sandpaper-like texture, and sore throat. Oral penicillin is the standard treatment for scarlet fever, or scarlatina.
-
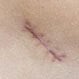
Scars
Scar formation is a natural part of the healing process after injury. The depth and size of the wound incision and the location of the injury impact the scar's characteristics, but your age, heredity and even sex or ethnicity will affect how your skin reacts.
-
Skin Cancer
Skin cancers occur when skin cells undergo malignant transformations and grow into tumors. The most common types of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, are highly curable when they are diagnosed and treated early. Sun exposure, tanning beds, depressed immune system, radiation exposure, and certain viral infections are risk factors for skin cancer. Skin cancers are treated with surgery or radiation. The prognosis of nonmelanoma skin cancers is generally very good.
-

Skin Rash
The word "rash" means an outbreak of red bumps on the body. The way people use this term, "a rash" can refer to many different skin conditions. The most common of these are scaly patches of skin and red, itchy bumps or patches all over the place.
-
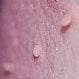
Skin Tag Removal
A skin tag is a small benign growth of skin that projects from the surrounding skin. Skin tags can vary in appearance (smooth, irregular, flesh colored, dark pigment, raised). Skin tags generally do not cause symptoms unless repeatedly irritated. Treatment for skin tag varies depending on the location on the body.
-
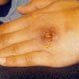
Sporotrichosis
Sporotrichosis is a skin infection caused by a fungus called Sporothrix schenckii. The fungus, which may be present in sphagnum moss, thorny plants, or baled hay, enters the skin through punctures and small cuts. Symptoms include painless bumps on the skin near the site of infection. The nodules may open and look like boils. The infection is treated with potassium iodide or itraconazole (Sporanox).
-
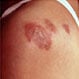
Sweet Syndrome (Acute Febrile Neutrophilic Dermatosis)
Sweet syndrome (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a skin condition that sometimes occurs due to an immune system response to RA, pregnancy, certain cancers, inflammatory bowel diseases, blood disorders, respiratory tract infections, and particular medications. Symptoms and signs include characteristic skin lesions that grow and spread into clusters. Sore eyes, high fever, mouth ulcers, headache, and aching joints may accompany the lesions. Though Sweet syndrome may resolve on its own, more severe cases may require medications like corticosteroids.
-

Swollen Lymph Nodes (Glands)
Lymph nodes help the body's immune system fight infections. Causes of swollen lymph nodes (glands) may include infection (viral, bacterial, fungal, parasites). Symptoms of swollen lymph nodes vary greatly, but may include fever, night sweats, toothache, sore throat, or weight loss. Causes of swollen lymph nodes also vary, but may include cancer, the common cold, mono, chickenox, HIV, and herpes. The treatment of swollen lymph nodes depends upon the cause.
-
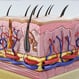
The Skin (Human Anatomy): Picture, Definition, Function and Skin Conditions
The skin is the largest organ in the body that covers the entire external surface. It protects the internal organs from germs and thus helps prevent infections. The skin is made up of three main layers.
-

The Skin: 7 Most Important Layers and Functions
The skin is the largest organ in the body and it covers the body's entire external surface. It is made up of seven layers. The first five layers form the epidermis, which is the outermost, thick layer of the skin. The hypodermis is the deepest layer of skin situated below the dermis.
-

Ticks vs. Bedbugs
Bedbugs are parasites. Ticks are arthropods. Tick and bedbug bites are typically painless. Calamine lotion can be helpful with both bedbug and tick bites. Bedbugs typically do not spread disease, while tick bites may often transmit disease.
-

Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare genetic disease caused by defects on two genes. The signs and symptoms of TSC vary depending on which organs and systems are involved. Common symptoms include benign tumors, seizures, behavior problems, skin abnormalities, and cognitive impairment. TSC treatment focuses on alleviating the symptoms with medications, special schooling, surgery, supplemental oxygen therapy, lung transplantation, and occupational therapy.
-
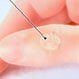
Warts (Common Warts)
Common warts are skin growths causes by the human papillomavirus. There are many types of warts, including plantar warts, common hand warts, warts under the nails, mosaic wars, and flat warts. Over-the-counter treatments typically involve the use of salicylic acid products.
-

What Are Boils (Skin Abscesses)?
A boil is a skin abscess, a collection of pus localized deep in the skin. There are several different types of boils. Among them are the following: furuncle or carbuncle, cystic acne, hidradenitis suppurativa, and pilonidal cyst.
-

What Is Eosinophilic Fasciitis (Shulman's Syndrome)?
Eosinophilic fasciitis is a skin disease that causes thickening and inflammation of the skin and fascia. Symptoms include redness, warmth, and hardening of the skin, as well as occasional tissue and joint pain. Treatment for eosinophilic fasciitis aims to eliminate inflammation through the use of aspirin, NSAIDs, and cortisone.
-

What Is Weber-Christian Disease?
Weber-Christian disease is a rare inflammatory disease that affects the body's fat tissues. The disorder appears on the skin as red or purple tender, raised lumps usually on the thighs and lower legs. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, weight loss, joint pain, and abdominal pain. There is no cure for the disease, but anti-inflammatory medications may help with inflammation.
-
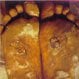
What Is Yaws?
Yaws is an infectious disease that mainly occurs in the tropical areas of South and Central America, Asia, Africa, and the Pacific Islands. The disease is caused by a bacterium called Treponema pertenue, which causes lesions that look like bumps on the skin of the feet, hands, face, and genital area. Yaws is treated with penicillin or another antibiotic.

