Jaw Pain Symptoms
The jaw joint, medically referred to as the temporomandibular joint or TMJ, is made up of the bone below the mouth (the mandible, commonly referred to as the jawbone) and the bone just above the mouth (the maxilla). The TMJ allows the upper jaw to close on the lower jaw and is one of the most frequently used joints of the body.
The temporomandibular joints are complex structures containing muscles, tendons, and bones. Injury to or disorders of these structures can all result in pain in the jaw area. Jaw pain may occur on one side or on both sides, depending upon the cause. Jaw pain can result from trauma to the jawbone, including fractures and dislocations. Also depending upon the exact cause, the pain may occur when chewing or may occur at rest. Additionally, other medical conditions not related to the TMJ may cause perceived pain in the jaw area. One of the most characteristic of these is the pain associated with coronary artery disease (angina) or heart attack, which typically occurs in the chest but can radiate (spread) to the jaw area. Some kinds of arthritis, often osteoarthritis, can affect the TMJ and lead to pain when moving the joint. Relaxation and softening of the joints during pregnancy due to secretion of the relaxin hormone can aggravate jaw pain in pregnancy. Less common causes of jaw pain include tumors, cysts, and infection of bone (osteomyelitis). Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition of the nervous system that causes extreme facial pain that sometimes involves the jaw area. Jaw pain can be associated with other symptoms, including
- a "popping" sensation,
- tooth pain,
- difficulty chewing,
- tenderness and aching of other areas of the face or neck.
Other causes of jaw pain
- Dislocation
- Infection/Abscess
- Misalignment of Teeth
- Postural Factors (Such as Holding a Telephone Between the Ear and Shoulder)
- Trauma
Causes of Jaw Pain
-
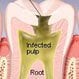
Abscessed Tooth
An abscessed tooth is an infection within a tooth that has spread to the root. Symptoms of an abscessed tooth may include pain, swelling, tenderness, redness, and the presence of a pus-filled lesion on the gum. A dental professional diagnoses an abscessed tooth and dental X-rays may be required. An abscessed tooth is treated with a root canal.
-

Angina Symptoms
Angina is chest pain due to inadequate blood supply to the heart. Angina symptoms may include chest tightness, burning, squeezing, and aching. Coronary artery disease is the main cause of angina but there are other causes. Angina is diagnosed by taking the patient's medical history and performing tests such as an electrocardiogram (EKG), blood test, stress test, echocardiogram, cardiac CT scan, and heart catheterization. Treatment of angina usually includes lifestyle modification, medication, and sometimes, surgery. The risk of angina can be reduced by following a heart healthy lifestyle.
-

Arthritis (Joint Inflammation)
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints. When joints are inflamed they can develop stiffness, warmth, swelling, redness and pain. There are over 100 types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, lupus, gout, and pseudogout.
-

Broken Bone
A broken bone is a fracture. There are different types of fractures, such as: compressed, open, stress, greenstick, spiral, vertebral compression, compound, and comminuted. Symptoms of a broken bone include pain at the site of injury, swelling, and bruising around the area of injury. Treatment of a fracture depends on the type and location of the injury.
-

Bruises
A bruise, or contusion, is caused when blood vessels are damaged or broken as the result of a blow to the skin. The raised area of a bump or bruise results from blood leaking from these injured blood vessels into the tissues as well as from the body's response to the injury. Treatments include applying an ice pack and pressure to the area by hand.
-

Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are a type of headache that recurs over a period. Episodes can last one to three times a day during this time, which may last from 2 weeks to 3 months. The three main types of treatments for cluster headaches are, 1) Abortive medications that work to stop the process in the brain that causes migraines and stops the symptoms too. 2) Preventive prescription medications, or 3) surgery which involves blocking the trigeminal nerve.
-
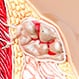
Cyst
Cysts are sac-like structures that may be filled with gas, liquid, or solid materials. Cysts may produce symptoms and signs depending on their location. Treatment of a cyst depends upon what caused the cyst in the first place.
-

Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA or Temporal Arteritis)
Giant cell arteritis, inflammation of blood vessel walls, affects 10%-15% of polymyalgia rheumatica patients. Symptoms and signs of giant cell arteritis include fatigue, weight loss, low-grade fever, jaw pain when chewing, scalp tenderness, and headaches. High doses of cortisone medications are used to treat giant cell arteritis.
-

Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
A heart attack happens when a blood clot completely obstructs a coronary artery supplying blood to the heart muscle. A heart attack can cause chest pain, heart failure, and electrical instability of the heart.
-

Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media)
Middle ear infection (otitis media) is inflammation of the middle ear. There are two forms of this type of ear infection, acute and chronic. Acute otitis media is generally short in duration, and chronic otitis media generally lasts several weeks. Babies, toddlers, and children with a middle ear infection may be irritable, pull and tug at their ears, and experience numerous other symptoms and signs. Treatment depends upon the type of ear infection.
-

Migraine Headache
Migraine headache is a type of headache associated with a sensitivity to light, smells, or sounds, eye pain, severe pounding on one side of the head, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. The exact cause of migraine headaches is not known. Triggers for migraine headaches include certain foods, stress, hormonal changes, strong stimuli (loud noises), and oversleeping. Treatment guidelines for migraines include medicine, pain management, diet changes, avoiding foods that trigger migraines, staying hydrated, getting adequate sleep, and exercising regularly. Prevention of migraine triggers include getting regular exercise, drinking water daily, reducing stress, and avoiding trigger foods.
-

Muscle Pain (Myofascial Pain Syndrome)
Muscle pain (myofascial pain syndrome) is muscle pain in the body's soft tissues due to injury or strain. Symptoms include muscle pain with tender points and fatigue. Treatment usually involves physical therapy, massage therapy, or trigger point injection.
-

Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
Sinus infection (sinusitis) is caused by allergies, infection, and chemicals or other irritants of sinuses. Signs and symptoms are headache, fever, and facial tenderness, pressure, or pain. Treatments of sinus infections are generally with antibiotics and at times, home remedies.
-

Stress
Stress occurs when forces from the outside world impinge on the individual. Stress is a normal part of life. However, over-stress, can be harmful. There is now speculation, as well as some evidence, that points to the abnormal stress responses as being involved in causing various diseases or conditions.
-
Swimmer's Ear (External Otitis)
Swimmer's ear (external otitis) is an infection of the skin that covers the outer ear canal. Causes of swimmer's ear include excessive water exposure that leads to trapped bacteria in the ear canal. Symptoms of simmer's include a feeling of fullness in the ear, itching, and ear pain. Chronic swimmer's ear may be caused by eczema, seborrhea, fungus, chronic irritation, and other conditions. Common treatment includes antibiotic ear drops.
-

Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Bruxism is the medical term for teeth grinding. Bruxism may be caused by stress or anxiety and often happens during sleep. Symptoms and signs include jaw pain, headache, and abnormalities in your teeth. Treatment may involve practicing stress-management techniques, cutting back on caffeine and alcohol, avoiding gum chewing, training oneself not to grind the teeth, and wearing a mouth guard.
-

Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ)
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) syndrome is a disorder that causes symptoms like pain, clicking, and popping of the jaw. TMJ is caused by injury to the temporomandibular joint. Stress, poor posture, jaw trauma, genetic predisposition, and inflammatory disorders are risk factors for the condition. A variety of self-care measures (application of ice, use of over-the-counter pain medication, massage, relaxation techniques) and medical treatment options (dental splint, Botox, prescription medications, surgery) are available to manage TMJ. The prognosis of TMJ is good with proper treatment.
-

Toothache
A toothache is pain on or around a tooth. It may have a variety of causes, including a cavity, abscess, or even sinusitis. Toothache symptoms include pain, headache, earache, bad taste in the mouth, and gum swelling. Dental X-rays and other tests performed by a dentist are used to diagnose the cause of a toothache. Toothache treatment depends on the underlying cause. Taking proper care of the teeth and gums can help prevent toothache.
-

Trigeminal Neuralgia
Pain that originates in the face is referred to as trigeminal neuralgia. This pain may be caused by: an injury, an infection in the face, a nerve disorder, or it can occur for no known reason. Trigeminal neuralgia can be treated with antiseizure medications. Some antidepressant drugs also have significant pain relieving effects.
-

What Are the Warning Signs of Tetanus?
Tetanus is a severe disease that affects many people. Learn the warning signs and diagnosis process for tetanus disease.
-

What Is Burkitt Lymphoma?
There are multiple types of Burkitt lymphoma. Burkitt lymphomas are types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma that affect the bone marrow and central nervous system. Symptoms of Burkitt lymphoma may include nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue, enlarged lymph nodes, and many other symptoms. Diagnosis involves lab testing, imaging studies, patient history, and cytogenic evaluation. There are multiple staging systems used to stage Burkitt lymphoma. Treatment consists of chemotherapy. The prognosis tends to be more favorable in children than in adults.
Examples of Medications for Jaw Pain
- acetaminophen (Tylenol, Tylenol Arthritis Pain, Tylenol Ext, Little Fevers Children's Fever/Pain)
- aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, Bayer, Ecotrin, and others)
- ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, Nuprin)
- Ketorolac vs. diclofenac
- Ketorolac vs. ibuprofen (Advil)
- Ketorolac vs. naproxen (Aleve)
- naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprelan, Naprosyn)
- OTC Pain Relievers and Fever Reducers
- Ultram (tramadol) Side Effects, Warnings, and Interactions
- Abscessed Tooth
- Angina Symptoms
- Arthritis (Joint Inflammation)
- Broken Bone
- Bruises
- Cluster Headaches
- Cyst
- Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA or Temporal Arteritis)
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
- Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media)
- Migraine Headache
- Muscle Pain (Myofascial Pain Syndrome)
- Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
- Stress
- Swimmer's Ear (External Otitis)
- Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
- Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ)
- Toothache
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
- What Are the Warning Signs of Tetanus?
- What Is Burkitt Lymphoma?
