Spasticity Symptoms
Spasticity is a condition of increased muscle tone in which muscles acquire a state of near constant contraction, or activity. Muscle spasticity causes a loss of range of motion of the affected area and a loss of function. There is also a resistance to movement by an examiner. In the affected muscles, spasticity can also cause symptoms such as
- pain,
- stiffness, and
- tightness.
Hyperactive reflexes, sudden or involuntary movements, abnormal posture, and bone and joint deformities can result from spasticity. Spasticity occurs when there has been damage or injury to part of the spinal cord or brain. Examples of conditions that can lead to spasticity include stroke, brain or spinal cord trauma, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis.
Other causes of spasticity
- Adrenoleukodystrophy
- Friedrich's Ataxia
- Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Spinal Cord Tumor
Causes of Spasticity
-
ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) Symptoms, Causes, Life Expectancy
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, Lou Gehrig's disease) is a neurological disease that progresses rapidly. The disease attacks the nerve cells responsible for the control of voluntary muscles. Early symptoms include cramping, twitching, or stiffness of the muscles; slurred nasal speech; difficulty swallowing or chewing, and muscle weakness in an arm or leg. Currently, the cause of ALS is not known. ALS is a fatal disease. No cure has been found for ALS, however, the drug riluzole (Rilutek) is FDA approved, and this drug reduces the damage to motor neurons by decreasing the release of glutamate.
-
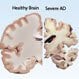
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease is a common cause of dementia. Symptoms and warning signs of Alzheimer's disease include memory loss, difficulty performing familiar tasks, disorientation to time and place, misplacing things, and more. The biggest risk factor for Alzheimer's disease is increased age. Treatment for Alzheimer's is often targeted toward decreasing the symptoms and progression of the disease.
-
Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors in Adults (Symptoms, Signs, Causes, Treatment Options, Life Expectancy)
Brain and spinal tumor are diseases in which cancer (malignant) cells begin to grow in the tissues of the brain. Tumors that start in the brain are called primary brain tumors. Tumors that start in the brain and spread to other organs are called primary brain tumors. Symptoms may include headaches, personality changes, dizziness, and trouble walking. Treatment depends upon the type and grade of tumor.
-
Brain Tumor: Warning Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatments, and Cure
A brain tumor can be either non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant), primary, or secondary. Common symptoms of a primary brain tumor are headaches, seizures, memory problems, personality changes, and nausea and vomiting. Causes and risk factors include age, gender, family history, and exposure to chemicals. Treatment is depends upon the tumor type, grade, and location.
-
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is an abnormality of motor function and postural tone acquired at an early age (even before birth). Cerebral palsy is generally caused by brain trauma. Types of cerebral palsy include: spastic, dyskinetic (dystonic or choreoathetoid), hypotonic, and mixed types. There is no cure for cerebral palsy, and treatment is generally managing the symptoms of the condition.
-

Head Injury (Brain Injury)
In the United States, head injuries are one of the most common causes of death and disability. Head injuries due to bleeding are generally classified by the location of the blood within the skull, these include epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid bleed, intracranial bleed, sheer injury, edema, and skull fracture. Some common symptoms of a head injury include vomiting, bleeding from the ear, speech difficulties, paralysis, difficulty swallowing, and body numbness. Treatment of a head injury depends on the type and severity of the injury.
-
Huntington's Disease
Huntington's disease is the result of degeneration of neurons in areas of the brain. Huntington's disease is an inherited disorder. Early symptoms include mood swings, apathy, depression, and anger uncharacteristic of the individual. Judgement, memory, and other cognitive functions may become impaired. Presymptomatic testing is available for individuals who have a family history of Huntington's disease. Treatment includes medication and therapy for symptoms.
-
Lewy Body Dementia (Dementia with Lewy Bodies)
Lewy body dementia (LBD or dementia with Lewy bodies) is one the most common causes of dementia. There are two types of LBD: 1) dementia with Lewy bodies, and 2) Parkinson's disease dementia. Symptoms of LBD are changes in a person's ability to think, movement problems, and sleep disorders. Treatment of LBD includes lifestyle changes, management of symptoms, palliative care, and medications to manage symptoms.
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis or MS is an autoimmune disorder in which brain and spinal cord nerve cells become demyelinated. This damage results in symptoms that may include numbness, weakness, vertigo, paralysis, and involuntary muscle contractions. Different forms of MS can follow variable courses from relatively benign to life-threatening. MS is treated with disease-modifying therapies. Some MS symptoms can be treated with medications.
-

Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is a slowly progressive neurological disease characterized by a fixed inexpressive face, a tremor at rest, slowing of voluntary movements, a gait with short accelerating steps, peculiar posture and muscle weakness, caused by degeneration of an area of the brain called the basal ganglia, and by low production of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Most patients are over 50, but at least 10 percent are under 40.
-

Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disorder that is inherited. PKU disorder increases the levels of phenylalanine in the blood. Phenylalanine is an amino acid that is obtained through diet, and is found in some artificial sweeteners. Signs and symptoms of PKU may vary from mild to severe, and may include: Behavioral problems Developmental delays Autism Seizures PKU has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
-
Stroke
A stroke is an interruption of the blood supply to part of the brain caused by either a blood clot (ischemic) or bleeding (hemorrhagic). Symptoms of a stroke may include weakness, numbness, double vision or vision loss, confusion, vertigo, difficulty speaking or understanding speech. A physical exam, imaging tests, neurological exam, and blood tests may be used to diagnose a stroke. Treatment may include administration of clot-busting drugs, supportive care, and in some instances, neurosurgery. The risk of stroke can be reduced by controlling high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and stopping smoking.
Examples of Medications for Spasticity
- baclofen (Gablofen, Lioresal)
- clonazepam (Klonopin)
- dantrolene - oral, Dantrium
- diazepam (Valium, Diastat, Acudial, Diastat Pediatric, Diazepam Intensol)
- onabotulinumtoxinA, Botox, Botox Cosmetic
- tizanidine (Zanaflex)
- ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) Symptoms, Causes, Life Expectancy
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors in Adults (Symptoms, Signs, Causes, Treatment Options, Life Expectancy)
- Brain Tumor: Warning Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatments, and Cure
- Cerebral Palsy
- Head Injury (Brain Injury)
- Huntington's Disease
- Lewy Body Dementia (Dementia with Lewy Bodies)
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Parkinson's Disease
- Phenylketonuria
- Stroke
