Aggression Symptoms
Aggression refers to hostile, angry, or violent behavior or thoughts. Aggression is potentially dangerous when directed at oneself or others. Sometimes, people feel experience aggression when provoked, but exaggerated or persistent aggression can be a feature of underlying emotional or medical conditions. People with dementia or brain injury due to various causes may display aggression.
Depending upon the cause of aggression, it can be associated with other symptoms, including
- depression,
- anger,
- tension,
- grief,
- irritability, or
- nervousness.
Aggression may take the form of
- threatening behavior,
- physical attack,
- self-harm,
- destruction of property,
- verbal threats, or
- disruptive behavior.
Aggression can also be seen in some psychiatric conditions that involve disordered thinking, such as schizophrenia.
Other causes of aggression
- Alcohol or Drug Intoxication
- Conduct Disorder
- Delirium
- Delusional Disorder
- Drug or Alcohol Withdrawal
- Intermittent Explosive Disorder (IED)
- Intoxication
- Mania
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder
- Paraphrenia
- Postpartum Psychosis
- Psychosis
- Schizophreniform Disorder
- Wilson Disease
Causes of Aggression
-

Adult ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
About 2%-6% of adults have ADHD, a common behavioral problem. Symptoms include impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention. Treatment may involve ADHD education, attending a support group, skills training, and medication.
-
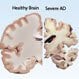
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease is a common cause of dementia. Symptoms and warning signs of Alzheimer's disease include memory loss, difficulty performing familiar tasks, disorientation to time and place, misplacing things, and more. The biggest risk factor for Alzheimer's disease is increased age. Treatment for Alzheimer's is often targeted toward decreasing the symptoms and progression of the disease.
-

Antisocial Personality Disorder
Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD) has many symptoms, signs, and causes. Therapy is one treatment option for antisocial personality disorder. It is closely related to other personality disorders (PD), such as borderline personality disorder and narcissistic personality disorder.
-

Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Teens
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in teens is a disruption of neurocognitive functioning. Genetics contribute to ADHD. Symptoms of ADHD in teens include inattention, hyperactivity/impulsivity, or a combination of these. Treatment may include cognitive behavioral therapy, behavior therapy, medication, or alternative therapies.
-

Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism in children and adults is a developmental disorder, characterized by impaired development in communication, social interaction, and behavior. Autism is classified as a pervasive developmental disorder (PDD), which is part of a broad spectrum of developmental disorders affecting young children and adults. There are numerous theories and studies about the cause of autism. The treatment model for autism is an educational program that is suitable to an individual's developmental level of performance. There is no "cure" for autism.
-

Bipolar Disorder in Children, Teen, and Adults
Bipolar disorder (or manic depression) is a mental illness characterized by depression, mania, and severe mood swings. Treatment may incorporate mood-stabilizer medications, antidepressants, and psychotherapy.
-

Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
Borderline personality disorder is a serious mental illness characterized by pervasive instability in moods, interpersonal relationships, self-image, and behavior. This instability often disrupts family and work life, long-term planning, and the individual's sense of self-identity. Originally thought to be at the "borderline" of psychosis, people with borderline personality disorder (BPD) suffer from a disorder of emotion regulation.
-
Brain Tumor: Warning Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatments, and Cure
A brain tumor can be either non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant), primary, or secondary. Common symptoms of a primary brain tumor are headaches, seizures, memory problems, personality changes, and nausea and vomiting. Causes and risk factors include age, gender, family history, and exposure to chemicals. Treatment is depends upon the tumor type, grade, and location.
-

Brief Psychotic Disorder
Brief psychotic disorder is a short-term mental illness that features psychotic symptoms. There are three forms of brief psychotic disorder. The first occurs shortly after a major stress, the second has no apparent trauma that triggers the illness, and the third is associated with postpartum onset. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, unusual behavior, disorientation, changes in eating and sleeping, and speech that doesn't make sense. Treatment typically involves medication and psychotherapy.
-

Dementia
Dementia is defined as a significant loss of intellectual abilities such as memory capacity, severe enough to interfere with social or occupational functioning. There are several different types of dementia, including cortical, subcortical, progressive, primary, and secondary dementias. Other conditions and medication reactions can also cause dementia. Dementia is diagnosed based on a certain set of criteria. Treatment for dementia is generally focused on the symptoms of the disease.
-

Depression
Depression is an illness that involves the body, mood, and thoughts and affects the way a person eats and sleeps, the way one feels about oneself, and the way one thinks about things. The principal types of depression are major depression, dysthymia, and bipolar disease (also called manic-depressive disease).
-
Drug Abuse
Drug addiction is a chronic disease that causes drug-seeking behavior and drug use despite negative consequences to the user and those around him. Though the initial decision to use drugs is voluntary, changes in the brain caused by repeated drug abuse can affect a person's self-control and ability to make the right decisions and increase the urge to take drugs. Drug abuse and addiction are preventable.
-

Encephalitis
Encephalitis is a brain inflammation that causes sudden fever, vomiting, headache, light sensitivity, stiff neck and back, drowsiness, and irritability. Treatment may incorporate anticonvulsants and antiviral medications.
-

Head Injury (Brain Injury)
In the United States, head injuries are one of the most common causes of death and disability. Head injuries due to bleeding are generally classified by the location of the blood within the skull, these include epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid bleed, intracranial bleed, sheer injury, edema, and skull fracture. Some common symptoms of a head injury include vomiting, bleeding from the ear, speech difficulties, paralysis, difficulty swallowing, and body numbness. Treatment of a head injury depends on the type and severity of the injury.
-
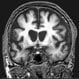
Huntington's Disease
Huntington's disease is the result of degeneration of neurons in areas of the brain. Huntington's disease is an inherited disorder. Early symptoms include mood swings, apathy, depression, and anger uncharacteristic of the individual. Judgement, memory, and other cognitive functions may become impaired. Presymptomatic testing is available for individuals who have a family history of Huntington's disease. Treatment includes medication and therapy for symptoms.
-
Lewy Body Dementia (Dementia with Lewy Bodies)
Lewy body dementia (LBD or dementia with Lewy bodies) is one the most common causes of dementia. There are two types of LBD: 1) dementia with Lewy bodies, and 2) Parkinson's disease dementia. Symptoms of LBD are changes in a person's ability to think, movement problems, and sleep disorders. Treatment of LBD includes lifestyle changes, management of symptoms, palliative care, and medications to manage symptoms.
-

Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) is a dramatic personality disorder that is characterized by a distorted self-image, preoccupation with success and power, and an abnormal love of self, which mask insecurity and a fragile self-esteem. Other symptoms include constantly seeking attention and admiration, setting unrealistic goals, exaggerating talents, self-centeredness, arrogant behavior, and an inability to recognize others' feelings. Though there is no known treatment for NPD, psychotherapy may be of some help.
-

Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is a slowly progressive neurological disease characterized by a fixed inexpressive face, a tremor at rest, slowing of voluntary movements, a gait with short accelerating steps, peculiar posture and muscle weakness, caused by degeneration of an area of the brain called the basal ganglia, and by low production of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Most patients are over 50, but at least 10 percent are under 40.
-

Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a psychiatric condition, can develop after any catastrophic life event. Symptoms include nightmares, flashbacks, sweating, rapid heart rate, detachment, amnesia, sleep problems, irritability, and exaggerated startle response. Treatment may involve psychotherapy, group support, and medication.
-

Schizoaffective Disorder
Schizoaffective disorder is a mental illness that features schizophrenia and a mood disorder, either major depression or bipolar disorder. Symptoms include agitation, suicidal thoughts, little need for sleep, delusions, hallucinations, and poor motivation. Treatment may involve psychotherapy, medication, skills training, or hospitalization.
-

Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a disabling brain disorder that may cause hallucinations and delusions and affect a person's ability to communicate and pay attention. Symptoms of psychosis appear in men in their late teens and early 20s and in women in their mid-20s to early 30s. With treatment involving the use of antipsychotic medications and psychosocial treatment, schizophrenia patients can lead rewarding and meaningful lives.
-

Steroid Drug Withdrawal (Symptoms)
Corticosteroid drugs such as prednisone and prednisolone are commonly used to treat asthma, allergic reactions, RA, and IBD. Steroids such as these do have serious drawbacks such as steroid withdrawal symptoms such as: fatigue, weakness, decreased appetite, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Speak with your health care provider prior to tapering off steroid medications.
-
Stroke
A stroke is an interruption of the blood supply to part of the brain caused by either a blood clot (ischemic) or bleeding (hemorrhagic). Symptoms of a stroke may include weakness, numbness, double vision or vision loss, confusion, vertigo, difficulty speaking or understanding speech. A physical exam, imaging tests, neurological exam, and blood tests may be used to diagnose a stroke. Treatment may include administration of clot-busting drugs, supportive care, and in some instances, neurosurgery. The risk of stroke can be reduced by controlling high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and stopping smoking.
-

What Is ADHD in Children?
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) causes the following symptoms in children: excessive activity, problems concentrating, and difficulty controlling impulses. Stimulant medications are the most common medication used to treat ADHD.
-

What Is Schizotypal Personality Disorder?
Schizotypal personality disorder is characterized by odd behaviors, feelings, perceptions, and ways of relating to others that interfere with one's ability to function. Medication and psychotherapy can help the sufferer to manage their symptoms.
Examples of Medications for Aggression
- alprazolam (Xanax)
- aripiprazole (Abilify)
- chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
- chlordiazepoxide-injection, Librium
- chlorpromazine - oral, Thorazine
- chlorpromazine-injection, Thorazine
- clonazepam (Klonopin)
- clozapine (Clozaril, Fazacio ODT, Versacloz)
- diazepam (Valium, Diastat, Acudial, Diastat Pediatric, Diazepam Intensol)
- fluphenazine (Permitil, Prolixin)
- fluphenazine concentrate - oral, Prolixin
- fluphenazine liquid - oral, Prolixin
- haloperidol (Haldol)
- lorazepam (Ativan)
- olanzapine (Zyprexa, Zydis)
- quetiapine (Seroquel)
- risperidone, Risperdal; Risperdal Consta, Risperdal M-TAB
- temazepam (Restoril)
- thiothixene - oral, Navane
- triazolam (Halcion)
- ziprasidone (Geodon)
- Adult ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Antisocial Personality Disorder
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Teens
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Bipolar Disorder in Children, Teen, and Adults
- Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
- Brain Tumor: Warning Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatments, and Cure
- Brief Psychotic Disorder
- Dementia
- Depression
- Drug Abuse
- Encephalitis
- Head Injury (Brain Injury)
- Huntington's Disease
- Lewy Body Dementia (Dementia with Lewy Bodies)
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder
- Parkinson's Disease
- Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
- Schizoaffective Disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Steroid Drug Withdrawal (Symptoms)
- Stroke
- What Is ADHD in Children?
- What Is Schizotypal Personality Disorder?
