Lower Back Pain Symptoms
There are many causes of pain in the back. Symptoms in the low back can be a result of problems in the bony lumbar spine, discs between the vertebrae, ligaments around the spine and discs, spinal cord and nerves, muscles of the low back, internal organs of the pelvis and abdomen, and the skin covering the lumbar area. Pains in the upper back can also be a result of disorders of the aorta, chest tumors, and inflammation of spine.
Common causes of lower back pain include strain injury from athletics or overuse, disc herniation, kidney infection, pinched nerve in the spine, and pregnancy. Less common causes of back pain include infection of the spine, ankylosing spondylitis with lumbosacral and sacroiliac joint disease, compression fracture of a spinal vertebra, disc ligament tear (annular tear), and spinal tumor or cancer in the bone of the spine.
Symptoms that can be associated with low back pain include
- dull ache,
- numbness,
- tingling,
- sharp pain,
- pulsating pain,
- pain with movement of the spine,
- pins and needles sensation,
- muscle spasm,
- tenderness,
- sciatica with shooting pain down one or both lower extremities,
- rash, and
- loss of continence of bowel or bladder.
Get immediate lower back pain relief

Other causes of back pain
- Bleeding Into Pelvis
- Dissection of the Aorta
- Infection of the Spine or Pelvis
- Metastatic Cancer
- Virus Infections
Main Article on Back Pain
Causes of Back Pain
-

Kyphosis (Roundback)
Kyphosis is an outward curvature of the thoracic spine (upper back). Kyphosis results in the appearance of a hunchback, which is accompanied by back pain, stiffness, and muscle fatigue in the back. There are three types of abnormal kyphosis: postural, Scheuermann's, and congenital kyphosis.
-

Prostatitis vs. BPH (Enlarged Prostate): What Is the Difference?
Prostatitis and BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia, enlarged prostate gland) are both conditions of the prostate gland. There are four types of prostatitis that can be caused by infections (usually bacterial) or other health conditions or problems, acute bacterial prostatitis (type I), chronic bacterial prostatitis (type II), chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (type III), and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis (type IV). BPH is inflammation of the prostate gland, and most men have the condition by age 50. Doctor's don't know what causes this inflammation, but they theorize that it may be related to hormones. Both of these conditions can cause similar symptoms like low back pain, pain during urination, or difficulty or the inability to urinate. However, prostatitis has many more symptoms and signs than BPH, and they based on the type of prostatitis. Examples include low back pain and/or abdominal pain, painful urination, fever, chills, feeling tired, recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs), painful urination intermittently, intermittent obstruction urinary tract symptoms (frequent, painful, or incomplete urination), pelvic pain and/or discomfort, pain with ejaculation, and erectile dysfunction (ED). If you think you have either of these conditions contact your doctor or other health care professional. Bacterial prostatitis can be cured with antibiotics; however, there is no cure for BPH.
-
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Abdominal aortic aneurysm is a ballooning or widening of the main artery (the aorta) as it courses down through the abdomen. Most abdominal aortic aneurysms produce no symptoms. Treatment may include observation or surgical repair.
-

Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that causes chronic inflammation of the spine. The tendency to develop ankylosing spondylitis is genetically inherited. Treatment incorporates medications, physical therapy, and exercise.
-

Are You Too Sick to Work?
When you're not feeling well, it may be difficult to decide whether to stay home or go to school or work. Conditions that are very painful may prevent you from working effectively. Anyone with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, or dizziness should stay home.
-

Blood in Semen
Blood in semen is also known as hematospermia. Blood in semen can be caused by many conditions affecting the tubes that distribute semen from the testicles (seminal vesicles) or the prostate gland. Symptoms that may accompany blood in semen include blood in the urine, fever, painful urination, pain with ejaculation, tenderness, and swelling in the testes or groin area. Urinalysis, ultrasound, and MRI may be used to diagnose blood in the semen. Treatment depends upon the underlying cause of blood in the semen.
-
Bone Cancer
Bone cancer is a rare type of cancer that occurs in cells that make up the bones. Primary bone cancer that arises in bone cells is different than metastatic bone cancer, which is cancer that arises in another part of the body and then spreads to the bones. Hereditary and environmental factors likely contribute to the risk of bone cancer. Signs and symptoms of bone cancer may include pain, the presence of a mass or lump, and bone fractures. There are different types of bone cancer (osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, pleomorphic sarcoma, fibrosarcoma). Treatment for bone cancer may include surgical removal of the tumor, chemotherapy, radiation, and/or a stem cell transplant. The prognosis for bone cancer depends on the type of cancer and the extent of spread.
-

Broken Bone
A broken bone is a fracture. There are different types of fractures, such as: compressed, open, stress, greenstick, spiral, vertebral compression, compound, and comminuted. Symptoms of a broken bone include pain at the site of injury, swelling, and bruising around the area of injury. Treatment of a fracture depends on the type and location of the injury.
-

Brucellosis
The bacteria Brucella causes brucellosis, an infectious zoonotic disease in humans. Symptoms and signs include fatigue, fever, sweating, and appetite loss. The preferred treatment is doxycycline and rifampin taken for six to eight weeks.
-

Coccydynia (Tailbone Pain)
Coccydynia is an inflammation of the bony area (tailbone or coccyx) located between the buttocks. Coccydynia is associated with pain and tenderness at the tip of the tailbone between the buttocks. Pain is often worsened by sitting. There are many causes of tailbone pain that can mimic coccydynia including: fracture, pilonidal cysts, infection, and sciatica. Treatment methods include medication and rest.
-
Cold Agglutinin Disease
Cold agglutinin hemolytic anemia or cold agglutinin hemolytic disease, is rare disorder of the autoimmune system. There are two types of cold agglutinin disease, primary and secondary. Characteristics, symptoms, and signs of in cold agglutinin disease are premature destruction of red blood cells in the body’s natural defense antibodies. The lifespan of red blood cells is approximately 120 before the spleen destroys the antibodies. In cold agglutinin disease, the severity of the condition is determined by how long it takes for the red blood cells to survive, and at the rate that the bone marrow continues to produce more red cells. Immune hemolytic anemias are classified by the optimal temperature when the antibodies try to destroy red blood cells. Cold agglutinin anemia occurs at temperatures between 10 C (50 F) and 37 C (F 98.6) or above while the body warms antibody hemolytic anemia. Usually, cold agglutinin anemia becomes apparent between the ages of 50 to 60. Other symptoms of the disease include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fingers and/or toes are cold and sweat, an uneven bluish or reddish discoloration of the toes, ankles, and wrists (Raynaud's syndrome), and fingers. Usually, cold agglutinin anemia affects people that are older. The disease is diagnosed by a physical exam, and the Coomb's test. If the red blood cells destruction seem to be slowing on its own, treatment therapies, usually, isn’t needed. Other treatments for cold agglutinin anemia are corticosteroids, and splenectomy (removal of the spleen). There is no cure for cold agglutinin disease.
-

Degenerative Disc Disease and Sciatica
Degenerative disc disease makes the disc more susceptible to herniation (rupture) which can lead to localized or radiating pain. The pain from degenerative disc or joint disease of the spine is usually treated conservatively with intermittent heat, rest, rehabilitative exercises and medications to relieve pain, muscle spasm and inflammation.
-

Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is contracted from the bite of a striped Aedes aegypti mosquito. Symptoms and signs of dengue include headache, fever, exhaustion, severe joint and muscle pain, rash, and swollen glands. Since dengue is caused by a virus, there is no specific medicine to treat it. Treatment instead focuses on relieving the symptoms.
-

Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH or Forestier's disease) is a form of degenerative arthritis. It is characterized by calcification along the sides of the vertebrae of the spine. Symptoms include stiffness and pain in the upper and lower back. Anti-inflammatory medications are used to treat DISH.
-
Endometriosis
Endometriosis implants are most commonly found on the ovaries, the Fallopian tubes, outer surfaces of the uterus or intestines, and on the surface lining of the pelvic cavity. They also can be found in the vagina, cervix, and bladder. Endometriosis may not produce any symptoms, but when it does the most common symptom is pelvic pain that worsens just prior to menstruation and improves at the end of the menstrual period. Other symptoms of endometriosis include pain during sex, pain with pelvic examinations, cramping or pain during bowel movements or urination, and infertility. Treatment of endometriosis can be with medication or surgery.
-
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the esophagus. Risk factors of cancer of the esophagus include smoking, heavy alcohol use, Barrett's esophagus, being male and being over age 60. Severe weight loss, vomiting, hoarseness, coughing up blood, painful swallowing, and pain in the throat or back are symptoms. Treatment depends upon the size, location and staging of the cancer and the health of the patient.
-

Fabry Disease
Fabry disease (Fabry's disease, alpha-galactosidase-A) is a genetic disorder with symptoms such as burning sensations in the hands, small-raised reddish-purplish blemishes on the skin, fever, decreases sweating, and gastrointestinal (GI) difficulties. Fabry disease patients are at increased risk of heart attack, heart disease, kidney failure, and stroke. Symptoms of Fabry disease can be treated with medication.
-
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, sleep disturbances, and tender points. Stress reduction, exercise, and medication are the standard treatments for fibromyalgia.
-

Flatfoot (Pes Planus)
Flatfoot is a disorder in which the foot's entire sole is touching the ground while standing. Symptoms and signs of flatfoot include heel, ankle, knee, hip, and lower back pain and shin splints. Treatment depends upon the type of flatfoot, the symptoms, and the stage of the disorder.
-
Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancer is cancer of the oral cavity, salivary glands, paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, or lymph nodes in the upper part of the neck. These cancers account for 3% to 5% of cancers in the U.S. Tobacco and alcohol use are important risk factors. Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, and/or chemotherapy.
-
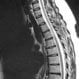
Herniated Disc
A herniated disc may be caused by injury or degeneration from age. Symptoms depend on the location of the herniation and whether nerve tissue is being irritated. An MRI or CT scan is performed to diagnose a herniated disc. Treatment may involve physical therapy, cortisone injection, pain medications, anti-inflammatory medications, muscle relaxants, and surgery.
-

How Can I Get Rid of Back Spasms?
When your back is stiff or weak, it becomes prone to injury. While most muscle spasms in your back are harmless and can be treated effectively, some indicate that there is an underlying issue that needs to be addressed. Common ways to get rid of back spasms include massage, heat and ice therapy, NSAIDs and other strategies.
-

How Do You Fix a Herniated Disc?
Learn how to tell if you have a herniated disc, and what medical treatments are available to you.
-
How Does Scoliosis Affect the Body?
What is scoliosis? Learn the causes and symptoms of scoliosis, how it affects the spine, and how it is treated.
-
Kidney Angiomyolipoma
Angiomyolipomas are noncancerous tumors that are typically found in the kidney, but may occur in the liver, ovary, colon, or Fallopian tube. Symptoms and signs include shock, chronic kidney disease, anemia, vomiting, nausea, and back or flank pain. Treatment may involve taking medication and embolization of the tumor.
-

Kidney Pain vs. Back Pain
The signs and symptoms of kidney pain and back pain depend upon the underlying cause. Doctors may use blood tests, X-rays, CT, and/or MRI to diagnose kidney pain and back pain. Treatment may include rest, ice, stretching, muscle strengthening, and pain-relieving medications.
-

Kyphosis vs Lordosis: Differences and Similarities
Any deviation in the curvature of the spine can lead to problems that may present as pain, stiffness, difficulty in balancing, and abnormal posture. Deviations in the normal curvature of the spine are called spinal deformities. They can include kyphosis (commonly known as round-back or hunchback), lordosis (also known as swayback), flatback syndrome (the spinal curvature is reduced), and scoliosis (sideways curvature of the spine).
-

Lassa Fever
Lassa fever is a viral hemorrhagic fever that causes flu-like symptoms. Ribavirin is the standard treatment for Lassa fever. Hearing loss is a common complication of Lassa fever.
-

Low Back Pain (Lumbar Spine Pain)
There are many causes of back pain. Pain in the low back can relate to the bony lumbar spine, discs between the vertebrae, ligaments around the spine and discs, spinal cord and nerves, muscles of the low back, internal organs of the pelvis and abdomen, and the skin covering the lumbar area.
-

Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Lumbar stenosis can be caused by degenerative arthritis (the most common cause), tumor, infection, or metabolic disorders (Paget's disease of the bone). Symptoms include low back pain, weakness, pain, numbness, and loss of sensation in the legs. Other conditions may cause similar symptoms of lumbar stenosis, including diabetic neuropathy, claudication, and peripheral vascular disease. Lumbar stenosis may be treated with medication or surgery.
-
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a form of cancer that develops in plasma cells, the white blood cells that make antibodies. Symptoms include bone pain, weakness, extreme thirst, nausea, frequent urination, and broken bones. Treatment of multiple myeloma depends upon the staging and symptoms of the disease.
-

Muscle Spasms
Muscle spasms are involuntary muscle contractions that come on suddenly and are usually quite painful. Dehydration, doing strenuous exercise in a hot environment, prolonged muscle use, and certain diseases of the nervous system may cause muscle spasms. Symptoms and signs of a muscle spasm include an acute onset of pain and a possible bulge seen or felt beneath the skin where the muscle is located. Gently stretching the muscle usually resolves a muscle spasm.
-

Neck Pain (Cervical Pain)
Neck pain (cervical pain) may be caused by any number of disorders and diseases. Tenderness is another symptom of neck pain. Though treatment for neck pain really depends upon the cause, treatment typically may involve heat/ice application, traction, physical therapy, cortisone injection, topical anesthetic creams, and muscle relaxants.
-

Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain is a chronic condition that leads to ongoing pain symptoms. Patients can be predisposed to developing neuropathic pain who have conditions such as diabetes, cancer, stroke, HIV, vitamin deficiencies, shingles, and multiple sclerosis. Patient history and nerve testing are used to diagnose neuropathic pain. Antidepressants, antiseizure medications, and other types of medications are used to treat neuropathic pain. Many people with neuropathic pain are able to attain some level of relief.
-

Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA)
Non-radiographic spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) is an inflammatory arthritis that mainly affects the joints of the spine. Morning stiffness and back pain are the usual symptoms of nr-axSpA. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, exercise, and biologics are treatments for nr-axSpA.
-

Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis caused by inflammation, breakdown, and eventual loss of cartilage in the joints. Also known as degenerative arthritis, osteoarthritis can be caused by aging, heredity, and injury from trauma or disease.
-

Osteopenia
Osteopenia is a bone condition characterized by bone loss that is not as severe as in osteoporosis. Bone fracture is the typical symptom of osteopenia, though the condition may be present without symptoms. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications (quitting smoking, not drinking in excess) and ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin D and calcium.
-

Osteoporosis
Learn about osteoporosis, a condition characterized by the loss of bone density, which leads to an increased risk of bone fracture. Unless one experiences a fracture, a person may have osteoporosis for decades without knowing it. Treatment for osteoporosis may involve medications that stop bone loss and increase bone strength and bone formation, as well as quitting smoking, regular exercise, cutting back on alcohol intake, and eating a calcium- and vitamin D-rich balanced diet.
-
Paget's Disease
Paget's disease, also called Paget's disease of bone, is a chronic bone disorder due to irregular breakdown and formation of bone tissue. Paget's disease symptoms include bone pain, headaches and hearing loss, pressure on nerves, increased head size, hip pain, and damage to cartilage of joints.
-
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor of the pancreas. Pancreatic cancer has been called a "silent" disease because early pancreatic cancer usually does not cause early symptoms. Typically, pancreatic cancer has metastasized (spread to adjacent organs, such as the liver) by the time most people receive a dignosis of pancreatic cancer. Symptoms and signs usually appear later in the course of the disease and include jaundice, back pain, nausea, weight loss, itching, and loss of appetite. Treatment depends upon the type of pancreatic cancer but may include surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy.
-
Pancreatic Cysts
Pancreatic cysts are collections of fluid within the pancreas. Some are benign, malignant, or pseudocysts. There are two major types of pancreatic cysts, 1) pseudocysts (inflammatory) and 2) true cysts (non-inflammatory). Symptoms of pancreatic cysts include abdominal pain, jaundice, fever, chills, and sepsis. Treatment depends on the type of cyst, and patient health.
-

Pilonidal Cyst
A pilonidal cyst is a cyst that forms near the cleft of the buttocks. The cysts are thought to be caused by the penetration of loose hairs into the skin. Symptoms and signs include pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and drainage of pus from the area of the cyst. Treatment of a pilonidal cyst involves incision and drainage.
-
Piriformis Syndrome
Piriformis syndrome may develop if the piriformis muscle spasms and compresses the sciatic nerve. This causes buttock pain that radiates down the back of the leg along the sciatic nerve. Symptoms include numbness, a pins-and-needles tingling sensation, and low back pain. Treatment of piriformis syndrome depends upon the syndrome's phase: acute, recovery, or maintenance.
-

Pregnancy (Week by Week, Trimesters)
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy vary by stage (trimester). The earliest pregnancy symptom is typically a missed period, but others include breast swelling and tenderness, nausea and sometimes vomiting, fatigue, and bloating. Second trimester symptoms include backache, weight gain, itching, and possible stretch marks. Third trimester symptoms are additional weight gain, heartburn, hemorrhoids, swelling of the ankles, fingers, and face, breast tenderness, and trouble sleeping. Eating a healthy diet, getting a moderate amount of exercise, also are recommended for a healthy pregnancy. Information about the week by week growth of your baby in the womb are provided.
-

Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a disease that causes skin and joint inflammation. Symptoms and signs include painful, stiff, and swollen joints, tendinitis, and organ inflammation. Treatment involves anti-inflammatory medications and exercise.
-

Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis is a chronic, systemic rheumatic disease characterized by three conditions, including conjunctivitis, joint inflammation, and genital, urinary, or gastrointestinal system inflammation. Inflammation leads to pain, swelling, warmth, redness, and stiffness of the affected joints. Non-joint areas may experience irritation and pain. Treatment for reactive arthritis depends on which area of the body is affected. Joint inflammation is treated with anti-inflammatory medications.
-

Sciatica Exercises
Sciatica is pain that radiates from the lower back down the leg. Nerve compression is the usual cause of sciatica. Exercises, stretching, physical therapy, heat and ice therapy, acupuncture, massage, and spinal manipulation are treatment options.
-

Sciatica Pain
Sciatica pain, caused by irritation of the sciatic nerve, typically radiates from the low back to behind the thigh to below the knee. Disc herniation is usually the cause of sciatica. Medication to alleviate pain, physical therapy, and bed rest are treatments for sciatica.
-
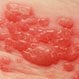
Shingles
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful rash caused by the varicella zoster virus. Other shingles symptoms include headache, fever, nausea, and body aches. Treatment focuses on pain management and shortening the duration of the illness with antiviral medications.
-

Spondylolisthesis
The five types of spondylolisthesis include dysplastic, isthmic, degenerative, traumatic, and pathologic. The most common symptom of spondylolisthesis is lower back pain. Treatment depends on the type and severity of spondylolisthesis. Surgery is required in some cases of spondylolisthesis.
-
Sprains and Strains
An injury to a ligament is called a sprain, and an injury to muscle or tendon is called a strain. Sprains and strains may be caused by repetitive movements or a single stressful incident. Symptoms and signs include pain and swelling. Though treatment depends upon the extent and location of the injury, rest, ice, compression, and elevation are key elements of treatment.
-

Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer symptoms include a painless lump or swelling in a testicle, testicle or scrotum pain, a dull ache in the abdomen, back, or groin, and a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum. Treatment for cancer of the testicles depends on the type of cancer (seminoma or nonseminoma), the stage of the cancer, and the patient's age and health.
-

The First Signs of Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis)
Kidney stones are solid masses of crystalline material that form in the kidneys. Symptoms of kidney stones can include pain, nausea, vomiting, and even fever and chills. Kidney stones are diagnosed via CT scans and specialized X-rays. Treatment of kidney stones involves drinking lots of fluids and taking over-the-counter pain medications to medical intervention including prescription medications, lithotripsy, and sometimes even surgery.
-

Typhus
Typhus is a disease caused by Rickettsia bacteria. Symptoms and signs include fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and rash. Antibiotics are recommended as the treatment for endemic and epidemic typhus infections.
-

Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE)
Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) infection is the most common type of infection acquired by patients while hospitalized. Patients at risk for VRE are those who are already ill, and hospitalized, including individuals with diabetes, elderly, ICU patients, kidney failure patients, or patients requiring catheters. Enterococci can survive for months in the digestive tract and female genital tract. Other risk factors for acquiring VRE include those how have been previously treated with vancomycin and combinations of other antibiotics. Treatment of VRE is generally with other antibiotics other than vancomycin. Prevention of VRE can be achieved by proper hand hygiene.
-

What are the Best Stretches for Back Pain Relief at Home?
Learn what stretches can help you deal with back pain and manage this condition at home.
-

What Are the Causes of Spondylosis?
What is spondylosis, and what are spondylosis symptoms? Learn the causes of spondylosis and how spondylosis is treated.
-

What Causes Back Pain in Pregnancy?
Does back pain mean miscarriage during pregnancy? Back pain in pregnancy is usually due to preexisting back pain issues, hormone changes, changes in the abdominal muscles, and posture changes. Back pain is a common issue that affects many pregnant women. Learn the signs of back pain in pregnancy, what causes it, and how you can treat it.
-

What Could Be the Cause of Upper Back Pain?
There are many potential upper back pain causes. Learn about upper back pain, why upper back pain happens, and how upper back pain is treated.
-

What Exercises Relieve Sacroiliac Pain?
Learn what causes your sacroiliac pain and three exercises to help you manage sacroiliac back pain.
-

What Is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis causes an abnormal curvature of the spine. When the cause of scoliosis is unknown the disorder is described based on the age when the scoliosis develops (infantile, juvenile, or adolescent idiopathic scoliosis). In functional scoliosis, curvature develops due to a problem somewhere else in the body. With neuromuscular scoliosis, there is a problem when the bones of the spine are formed. Treatment typically involves observation, bracing, and surgery and is dependent upon the severity of the curvature.
-

What Is the Best Exercise for Back Pain?
We are often a bit negligent toward our back while doing chores or physical exercise. While the causes for back pain may vary, regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for keeping the back healthy.
-

What Is the Best Treatment for Degenerative Disc Disease?
Learn what medical treatments can help ease your degenerative disc disease symptoms and speed up your recovery.
-

What Is the Most Common Spine Surgery?
Spine surgery is often an excellent option to provide pain relief for pain and discomfort due to a spinal condition. The most common type of spine surgery in the U.S. is spinal decompression and fusion.
-

What Is the Treatment for Sacroiliitis?
Learn what medical treatments can help treat sacroiliitis and help you manage this sacroiliitis.
-

What Lower Back Exercises Can I Do at Home?
Lower back exercises are some of the easiest to do at home. Here are some exercises to strengthen your lower back.
-

Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is an infectious disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. Side effects are rare with the yellow fever vaccine. Symptoms include fever, chills, back pain, nausea, vomiting, and headache. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms.
Examples of Medications for Back Pain
- carisoprodol (Soma)
- celecoxib (Celebrex)
- codeine (for Pain)
- cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril, Amrix, Fexmid)
- diflunisal (Dolobid)
- fenoprofen (Nalfon)
- flurbiprofen (Ansaid)
- hydrocodone and ibuprofen, Vicoprofen
- hydrocodone/acetaminophen (Vicodin, Norco)
- ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, Nuprin)
- ketoprofen
- Ketorolac vs. diclofenac
- Ketorolac vs. ibuprofen (Advil)
- Ketorolac vs. naproxen (Aleve)
- nabumetone
- Naprelan (naproxen) Side Effects, Warnings, and Interactions
- naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprelan, Naprosyn)
- Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- propoxyphene (Darvon, Dolene)
- rofecoxib, Vioxx
- tolmetin (Tolectin [Discontinued Brand])
- tramadol (Ultram)
- Ultram (tramadol) Side Effects, Warnings, and Interactions
- Kyphosis (Roundback)
- Prostatitis vs. BPH (Enlarged Prostate): What Is the Difference?
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Are You Too Sick to Work?
- Blood in Semen
- Bone Cancer
- Broken Bone
- Brucellosis
- Coccydynia (Tailbone Pain)
- Cold Agglutinin Disease
- Degenerative Disc Disease and Sciatica
- Dengue Fever
- Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
- Endometriosis
- Esophageal Cancer
- Fabry Disease
- Fibromyalgia
- Flatfoot (Pes Planus)
- Head and Neck Cancer
- Herniated Disc
- How Can I Get Rid of Back Spasms?
- How Do You Fix a Herniated Disc?
- How Does Scoliosis Affect the Body?
- Kidney Angiomyolipoma
- Kidney Pain vs. Back Pain
- Kyphosis vs Lordosis: Differences and Similarities
- Lassa Fever
- Low Back Pain (Lumbar Spine Pain)
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Multiple Myeloma
- Muscle Spasms
- Neck Pain (Cervical Pain)
- Neuropathic Pain
- Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA)
- Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Osteopenia
- Osteoporosis
- Paget's Disease
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Pancreatic Cysts
- Pilonidal Cyst
- Piriformis Syndrome
- Pregnancy (Week by Week, Trimesters)
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Reactive Arthritis
- Sciatica Exercises
- Sciatica Pain
- Shingles
- Spondylolisthesis
- Sprains and Strains
- Testicular Cancer
- The First Signs of Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis)
- Typhus
- Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE)
- What are the Best Stretches for Back Pain Relief at Home?
- What Are the Causes of Spondylosis?
- What Causes Back Pain in Pregnancy?
- What Could Be the Cause of Upper Back Pain?
- What Exercises Relieve Sacroiliac Pain?
- What Is Scoliosis?
- What Is the Best Exercise for Back Pain?
- What Is the Best Treatment for Degenerative Disc Disease?
- What Is the Most Common Spine Surgery?
- What Is the Treatment for Sacroiliitis?
- What Lower Back Exercises Can I Do at Home?
- Yellow Fever
