Vaginal Bleeding Symptoms
Normal vaginal bleeding is the periodic blood that flows as a discharge from the woman's uterus as a result of normal cyclic hormonal changes each month. Normal vaginal bleeding is also called menorrhea. The process by which menorrhea occurs is called menstruation.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding is a flow of blood from the vagina that occurs either at an unusual time during the month or in inappropriate amounts.
Other causes of vaginal bleeding
- Cervix-Related (Cervicitis, Cervical Polyp)
- Medical Illnesses (Clotting Disorders, Hyperprolactinemia, Kidney Disease, Liver Disease, Thyroid or Adrenal Dysfunction)
- Medications (Both Prescription and Nonprescription)
- Ovary or Fallopian Tube-Related (Ovarian Tumors, Salpingo-oophoritis)
- Uterus-Related (Adenomyosis, Endometrial Hyperplasia, Endometrial Polyp, Endometritis, Fibroids, Intrauterine Device/IUD)
- Vulvar or Vaginal-Related (Coitus, Foreign Body in Vagina, Vaginal Tumor, Vulvitis)
Causes of Vaginal Bleeding
-

Birth Control Options
Birth control is available in a variety of methods and types. The method of birth control varies from person to person, and their preferences to either become pregnant or not. Examples of barrier methods include barrier methods (sponge, spermicides, condoms), hormonal methods (pill, patch), surgical sterilization (tubal ligation, vasectomy), natural methods, and the morning after pill. Side effects and risks of each birth control option should be reviewed prior to using any birth control method.
-

Bleeding During Pregnancy (First Trimester)
Bleeding during pregnancy is never normal. Causes of bleeding during the first trimester of a pregnancy may be caused by implantation bleeding, ectopic or tubal pregnancy, subchorionic hemorrhaging, infections, and miscarriage. Bleeding during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy can be caused by a variety of factors.
-

Can Vaginal Atrophy Be Reversed?
Learn what medical treatments can ease your vaginal atrophy symptoms and help you manage this condition.
-

Cancer
Cancer is a disease caused by an abnormal growth of cells, also called malignancy. It is a group of 100 different diseases, and is not contagious. Cancer can be treated through chemotherapy, a treatment of drugs that destroy cancer cells.
-
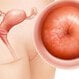
Cervical Cancer (Cancer of the Cervix)
Cervical cancer is cancer of the entrance to the womb (uterus) caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Regular pelvic exams, Pap testing and screening can detect precancerous changes in the cervix. Cervical cancer can be prevented by a vaccine. The most common signs and symptoms are an increase in vaginal discharge, painful sex, and postmenopausal bleeding. The prognosis and survival rate depends upon the stage at which the cancer was diagnosed.
-
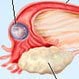
Ectopic Pregnancy (Tubal Pregnancy)
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy located outside the inner lining of the uterus. The majority of ectopic pregnancies occur in the Fallopian tube. Signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may include abdominal pain, lack of menstrual period (amenorrhea), vaginal bleeding, fainting, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Treatment options for an ectopic pregnancy include observation, medication, or surgery.
-
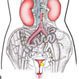
Endometrial Cancer Prevention
Endometrial cancer, or uterine cancer, affects the endometrium of the uterus. It's the most common invasive cancer of the female reproductive system. Risk factors include smoking, obesity, lack of exercise, taking estrogen-only hormone therapy, early menstruation, late menopause, and never being pregnant.
-
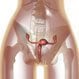
Endometriosis
Endometriosis implants are most commonly found on the ovaries, the Fallopian tubes, outer surfaces of the uterus or intestines, and on the surface lining of the pelvic cavity. They also can be found in the vagina, cervix, and bladder. Endometriosis may not produce any symptoms, but when it does the most common symptom is pelvic pain that worsens just prior to menstruation and improves at the end of the menstrual period. Other symptoms of endometriosis include pain during sex, pain with pelvic examinations, cramping or pain during bowel movements or urination, and infertility. Treatment of endometriosis can be with medication or surgery.
-
How Long Is a Bakri Balloon Left In?
The Bakri balloon is indicated to manage postpartum hemorrhage occurring within 24 hours of delivery. The balloon is inflated with about 500 ml of sterile liquid, such as sterile water, saline or Ringer's lactate solution. The Bakri balloon is left in the uterus for a maximum of 24 hours.
-
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is any state in which thyroid hormone production is below normal. Normally, the rate of thyroid hormone production is controlled by the brain by the pituitary gland. Hypothyroidism is a very common condition and the symptoms of hypothyroidism are often subtle, but may include, constipation, memory loss, hair loss, and depression. There are a variety of causes of hypothyroidism, and treatment depends on the cause.
-

Is It My Period or Implantation Bleeding?
What is the difference between implantation bleeding and your period? Learn the symptoms and treatments for each.
-

Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of cancer of the blood cells in which the growth and development of the blood cells are abnormal. Strictly speaking, leukemia should refer only to cancer of the white blood cells (the leukocytes) but in practice it can apply to malignancy of any cellular element in the blood or bone marrow, as in red cell leukemia (erythroleukemia).
-
Menstruation (Menstrual Cycle)
Menstruation (menstrual cycle) is also referred to as a "period." When a woman menstruates, the lining of the uterus is shed. This shedding of the uterine linking is the menstrual blood flow. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days. There can be problems with a woman's period, including heavy bleeding, pain, or skipped periods. Causes of these problems may be amenorrhea (lack of a period), menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea), or abnormal vaginal or uterine bleeding. There are a variety of situations in which a girl or woman should see a doctor about her menstrual cycle.
-
Ovarian Cancer
There are many types of ovarian cancer, epithelial carcinoma is the most common. Women with a family history of ovarian cancer have an increased risk of developing the disease. Some ovarian cancer symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and abnormal vaginal bleeding, however, they usually do not present until the disease has progressed. Early diagnosis is important for successful treatment.
-
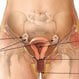
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is the most common and serious complication of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), aside from AIDS, among women. The signs and symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease include: fever, vaginal discharge with a foul odor, abdominal pain, including pain during intercourse, and irregular vaginal bleeding. Pelvic inflammatory disease can scar the Fallopian tubes, ovaries, and related structures and lead to ectopic pregnancies, infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and other serious consequences. Pelvic inflammatory disease treatment includes several types of antibiotics.
-

Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the time in a woman's life when she is approaching menopause. During this time a woman starts to develop symptoms of declining estrogen levels that may include mood swings, painful sex, night sweats, hot flashes, and weight gain. Every adult woman eventually will experience perimenopause.
-

Pregnancy (Week by Week, Trimesters)
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy vary by stage (trimester). The earliest pregnancy symptom is typically a missed period, but others include breast swelling and tenderness, nausea and sometimes vomiting, fatigue, and bloating. Second trimester symptoms include backache, weight gain, itching, and possible stretch marks. Third trimester symptoms are additional weight gain, heartburn, hemorrhoids, swelling of the ankles, fingers, and face, breast tenderness, and trouble sleeping. Eating a healthy diet, getting a moderate amount of exercise, also are recommended for a healthy pregnancy. Information about the week by week growth of your baby in the womb are provided.
-

Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are among the most common infectious diseases in the United States. STDs can be spread through any type of sexual activity involving the sex organs, the anus or mouth, or through contact with blood during sexual activity. Examples of STDs include, chancroid, chlamydia, gonorrhea, granuloma inguinale, lymphogranuloma venereum, syphilis, genital herpes, genital warts, trichomoniasis, pubic lice (crabs), and scabies. Treatment is generally with antibiotics; however, some STDs that go untreated can lead to death.
-
Spotting vs. Period
Menstruation (a female's "period") occurs due to the shedding of the lining of the uterus. Menstrual bleeding lasts about three to five days, and the bleeding is heavy the first couple of days and then it lessens. Spotting is vaginal bleeding between periods.
-
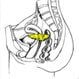
Uterine Cancer
Though uterine cancer's cause is unknown, there are many factors that will put a woman at risk, including being over age 50, having endometrial hyperplasia, using hormone replacement therapy, obesity, using tamoxifen, being Caucasian, and/or having colorectal cancer. Symptoms and signs of cancer of the uterus (endometrial cancer) include abnormal vaginal bleeding, painful urination, painful intercourse, and pelvic pain. Treatment depends on staging and may include radiation therapy or hormone therapy.
-
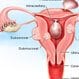
Uterine Fibroids (Benign Tumors of the Uterus)
Uterine fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) tumors in the womb (uterus). Most uterine fibroids do not cause symptoms; however, if the fibroid is large enough and in the right location, it may cause symptoms of pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding, and pressure on the bladder or rectum. Uterine fibroids that remain small and do not grow usually do not need treatment; however, surgery to remove the fibroid may be necessary. Uterine fibroids do not cause cancer; however, there is a rare, fast-growing cancerous called leiomyosarcoma.
-
Uterine Growths
Benign uterine growths are tissue enlargements of the female womb (uterus). Three types of benign uterine growths are uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, and uterine polyps. Symptoms include abdominal pressure and pain, pelvic pain, pain during intercourse, and pain during bowel movements. Diagnosis and treatment of benign uterine growths depends upon the type of growth.
-

Vaginal Cancer
Vaginal cancer is fairly uncommon. There are two types of vaginal cancer: squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Risk factors include being 60 or older, exposure to DES while in the womb, HPV infection, and having a history of abnormal cervical cells. Painful intercourse, pelvic pain, vaginal lumps, and abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge are all symptoms of vaginal cancer. Treatment depends upon the stage of the vaginal cancer and may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and the use of radiosensitizers.
-

Vaginitis (Inflammation of the Vagina)
Vaginitis refers to inflammation of the vagina. Vaginitis can be caused by infections, menopause, or poor hygiene. Symptoms of vaginitis include vaginal itching, discharge, odor, pain, or discomfort. Treatment for vaginitis depends on the cause. Antibiotics may be necessary for some forms of vaginitis.
Examples of Medications for Vaginal Bleeding
- Vaginal Bleeding
- Birth Control Options
- Bleeding During Pregnancy (First Trimester)
- Can Vaginal Atrophy Be Reversed?
- Cancer
- Cervical Cancer (Cancer of the Cervix)
- Ectopic Pregnancy (Tubal Pregnancy)
- Endometrial Cancer Prevention
- Endometriosis
- How Long Is a Bakri Balloon Left In?
- Hypothyroidism
- Is It My Period or Implantation Bleeding?
- Leukemia
- Menstruation (Menstrual Cycle)
- Ovarian Cancer
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Perimenopause
- Pregnancy (Week by Week, Trimesters)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
- Spotting vs. Period
- Uterine Cancer
- Uterine Fibroids (Benign Tumors of the Uterus)
- Uterine Growths
- Vaginal Cancer
- Vaginitis (Inflammation of the Vagina)
