Intestinal Gas Symptoms
Gas or "intestinal gas" means different things to different people. Everyone has gas and eliminates it by belching or passing it through the rectum, medically referred to as flatulence (slang, farting).
The ability to belch is almost universal. Belching, also known as burping, is the act of expelling gas from the stomach out through the mouth. The usual cause of belching is a distended (inflated) stomach caused by swallowed air. The distention of the stomach causes abdominal discomfort, and the belching expels the air and relieves the discomfort. The common reasons for swallowing large amounts of air (aerophagia) are gulping food or drink too rapidly, anxiety, and carbonated beverages.
Excessive air in the stomach is not the only cause of belching. For some people, belching becomes a habit and does not reflect the amount of air in their stomachs. For others, belching is a response to any type of abdominal discomfort and not just to discomfort due to increased gas.
Most people produce 1 to 3 pints of intestinal gas in their large intestines (colons) every 24 hours and pass gas an average of 14 times a day. The gas is made up primarily of carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and in some families, methane, that is mixed with nitrogen and oxygen from room air that is inhaled or swallowed. The carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and methane are produced by bacteria in the large intestine while they digest undigested food that reaches the large intestine. Although these gases are odorless, the bacteria also may produce small amounts of sulfur-containing gases that are foul-smelling. It is important to distinguish between increased flatulence (farting) and foul-smelling flatulence.
Bloating is the subjective sensation (feeling) that the abdomen is larger than normal. Thus, bloating is a symptom akin to the symptom of discomfort. In contrast, distention is the objective determination (physical finding) that the abdomen is actually larger than normal. Bloating and distention may be due to increased amounts of gas in the abdomen, but there also are other causes. Sometimes intestinal gas that is associated with bloating can be accompanied by
- abdominal pain,
- stomach cramps,
- swelling of the abdomen, and/or
- a feeling of knots in the stomach.
Other causes of gas
- Dietary Fat, Starchy Grains
- Digestive Disease
- Intestinal Blockage
- Pancreatic Insufficiency
Causes of Gas
-

Abdominal Adhesions (Scar Tissue)
Abdominal adhesions (scar tissue) bands of scar tissue that form between abdominal organs and tissues. Symptoms of abdominal adhesions are pelvic or abdominal pain. Abdominal adhesions on the intestines can cause bowel obstruction, which is a medical emergency. Treatment for abdominal adhesions is generally surgery to cut the adhesions away from the internal tissues and organs. There is no way to prevent abdominal adhesions.
-

Amebiasis (Entamoeba Histolytica Infection)
Amebiasis is an infection caused by an amoeba. Signs and symptoms include bloody stools, abdominal pain, weight loss, fever, and gas. Treatment may involve taking luminal agents or antibiotics. Surgery may be indicated for various reasons.
-
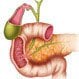
Bile Duct Cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma)
Bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) is a rare type of cancer that arises from cells that line the drainage system from the liver and gallbladder to the intestine. Symptoms of bile duct cancer include jaundice, itching, weight loss, and abdominal pain. Physical examination, specialized blood tests, and imaging tests may be used to diagnose bile duct cancer. Treatment for bile duct cancer may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and photodynamic therapy. Bile duct cancer typically has a poor prognosis. Preventing liver damage may decrease the risk of developing bile duct cancer.
-
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a condition in which a person has inflammation of the small intestinal mucosa when exposed to gluten in the diet. Symptoms of celiac disease include bloating, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Treatment is a gluten free diet. Some individuals may have refractory celiac disease in which they do not respond to a gluten free diet.
-
Cyclospora Infection (Cyclosporiasis)
Cyclospora cayetanensis is a parasite that causes infection when humans ingest food contaminated with feces from an infected individual. Symptoms include profuse diarrhea, abdominal pain, gas, cramping, and fatigue. A 7-day course of Bactrim or Septra is the standard treatment for cyclosporiasis.
-
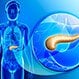
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency or EPI is a condition in which a person's pancreas can't produce or secrete certain enzymes into the gastrointestinal tract, which results in the inability to digest and absorb some minerals, vitamins, and fats from food. Symptoms of EPI include diarrhea, bloating, excessive gas, bone pain, and foul smelling bowel movements. Treatment for EPI is PERT therapy.
-
Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis is a medical condition in which the muscle of the stomach is paralyzed by a disease of either the stomach muscle itself or the nerves controlling the muscle. As a consequence, food and secretions do not empty normally from the stomach. Gastroparesis symptoms are nausea and vomiting; abdominal bloating, and pain can result.
-

Heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation experienced from acid reflux (GERD). Symptoms of heartburn include chest pain, burning in the throat, difficulty swallowing, the feeling of food sticking in the throat, and a burning feeling in the chest. Causes of heartburn include dietary habits, lifestyle habits, and medical causes. Treatments for heartburn include lifestyle changes, OTC medication,prescription medication, and surgery.
-

How Do I Get Rid of Gas Pains During My Period?
Gas pain during your period can be debilitating. Learn what causes gas pain during your period and how you can get rid of it or lower the chances of developing gas pain during your period.
-
IBS Triggers (Prevention)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional disease that can affect the quality of those who suffer from this condition. People with IBS can make lifestyle changes that may modify or control the number and severity of episodes. Certain foods, medications, and hormone levels may trigger IBS episodes, for example fatty foods, dairy products, eating foods in large quantities, foods that contain high levels of sorbitol, foods that produce intestinal gas (broccoli, onions, cabbage, and beans), chocolate, caffeine, physiological stress, some antibiotics, some antidepressants, medicine with sorbitol, and menstrual pain. Exercise, diet, and other lifestyle changes can decrease IBS flares, and prevent the number and severity of IBS episodes of diarrhea and constipation.
-
Indigestion (Dyspepsia, Upset Stomach Pain)
Indigestion (dyspepsia) can be caused by diseases or conditions that involve the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and also by some diseases and conditions that do not involve the GI tract. Indigestion can be a chronic condition in which the symptoms fluctuate in frequency and intensity. Signs and symptoms that accompany indigestion include pain in the chest, upper abdominal pain, belching, nausea, bloating, abdominal distention, feeling full after eating only a small portion of food, and rarely, vomiting.
-

Intestinal Gas and Gas Pain
Gas (intestinal gas) means different things to different people. Everyone has gas and eliminates it by belching, burping, or farting (flatulence). Bloating or abdominal distension is a subjective feeling that the stomach is larger or fuller than normal. Belching or burping occurs when gas is expelled from the stomach out through the mouth. Flatulence or farting occurs when intestinal gas is passed from the anus. Causes of belching or burping include drinking too rapidly, anxiety, carbonated drinks, habit, and swallowing air. Learn about causes of intestinal gas, foods that cause gas and bloating, treatments that reduce excessive gas and soothe gas pain, and much more.
-

Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a GI (gastrointestinal) disorder with signs and symptoms that include abdominal pain, bloating, increased gas (flatulence), abdominal cramping, diarrhea, constipation, and food intolerance.Two new tests are now available that may help diagnose irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea and constipation (IBS-M) irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D), and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C). Treatment for IBS includes diet changes, medications, and other lifestyle changes to manage symptoms.
-
Is EPI Reversible?
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is a long-lasting medical condition that affects the pancreas. It usually upsets the way the body breaks down (digests) food and can cause gastrointestinal problems. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) may be managed, but it cannot be cured.
-

Is it Normal to Bloat Every Day?
What is bloating in the stomach is it normal to have it daily? Learn the signs and causes of stomach bloating and what to do if your abdomen is distended.
-

Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common problem where a person's digestive system cannot digest lactose. Signs and symptoms include: Diarrhea Gas Abdominal pain Abdominal bloating Abdominal distention (swelling) Nausea There are several tests to diagnose lactose intolerance. Treatment is generally made with dietary changes, supplements, and adaptation to small amounts of milk.
-

Peritonitis
Peritonitis is a bacterial infection inside of the abdomen. Some doctors choose to group the causes of peritonitis into five categories; 1) primary peritonitis, 2) secondary peritonitis, 3) tertiary peritonitis, 4) chemical (sterile) peritonitis, and 5) peritoneal abscess. Others do not categorize peritonitis, they use a term to describe the disease in front or behind the word peritonitis. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Treatment is generally with antibiotics.
-

Sick Building Syndrome
Multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) or also referred to as sick building syndrome or environmental illness is the name given by some to a condition in which various symptoms reportedly appear after a person has been exposed to any of a wide range of chemicals. The exposure may occur as a major event, such as a chemical spill, or from long-term contact with low-levels of chemicals, such as in an office with poor ventilation. As a result of exposure, people with MCS (sick building syndrome) develop sensitivity and have reactions to the chemicals even at levels most people can tolerate.
-

What Is Excessive Gas a Sign of?
Gas is a normal, healthy feature of the digestive process. Excessive gas may be a sign of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), lactose intolerance, GI issues, problems digesting carbohydrates, celiac disease, GERD, and other potential problems.
-

What Relieves Bloating Fast?
Bloating is an uncomfortable belly feeling of being too full from food or air. Learn why you feel bloated and how to relieve bloating fast.
-

Why Am I So Gassy and Bloated?
Bloating is a feeling that your abdomen is distended or larger than normal, but it does not necessarily mean that it is. Gas (flatulence) also can be a problem if you are bloated. Common, less serious causes of bloating are eating too fast, too much, or too many fatty foods; swallowing air; pregnancy; and menstruation. Cancer and IBD (ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease) are examples the more serious causes of bloating. Examples of foods and drinks that cause bloating are high fiber foods if you don't eat them regularly; eventually the bloating and gassiness will resolve if you eat them on a regular basis; fatty greasy foods, dairy products (for example, cheese, ice cream, milk, and yogurt); foods high in salt (for example, processed, frozen, and canned foods), and artificial sweeteners. Some doctors and other health care professionals recommend natural remedies like chamomile or peppermint tea, or pumpkin to relieve bloating. Examples of OTC medicine (medicine available without a prescription) and other products that may relieve bloating and gassiness are, Gas-X, Beano, Pepto Bismol, Metamucil, probiotics, and Ex-Lax for constipation associated with bloating. If you have persistent or severe gas and bloating, and if you have any of these symptoms see a doctor or other healthcare professional, shortness of breath, heart palpitations, chest pain, bloody diarrhea, fever, or if you think you are or may be pregnant.
-

Why Would I Have Mucus in My Stool?
Why do you have mucus in your stool? Learn what causes mucus in stool, when to see the doctor about it, and how to get treated.
Examples of Medications for Gas
- metoclopramide, Reglan, Metozolv ODT, (Reglan ODT, Octamide, and Maxolon
- simethicone, Phazyme, Mi-Acid, Gas Relief, Mytab Gas, Gas-X, Gas-X Extra Strength
- Abdominal Adhesions (Scar Tissue)
- Amebiasis (Entamoeba Histolytica Infection)
- Bile Duct Cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma)
- Celiac Disease
- Cyclospora Infection (Cyclosporiasis)
- Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)
- Gastroparesis
- Heartburn
- How Do I Get Rid of Gas Pains During My Period?
- IBS Triggers (Prevention)
- Indigestion (Dyspepsia, Upset Stomach Pain)
- Intestinal Gas and Gas Pain
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Is EPI Reversible?
- Is it Normal to Bloat Every Day?
- Lactose Intolerance
- Peritonitis
- Sick Building Syndrome
- What Is Excessive Gas a Sign of?
- What Relieves Bloating Fast?
- Why Am I So Gassy and Bloated?
- Why Would I Have Mucus in My Stool?
