Pitocin Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: oxytocin injection
- Brand Name: Pitocin
side effects drug center pitocin (oxytocin injection) drug
Drug Description
What is Pitocin and how is it used?
Pitocin is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of postpartum hemorrhage, labor induction, and incomplete or inevitable abortion. Pitocin may be used alone or with other medications.
Pitocin belongs to a class of drugs called Oxytocic Agents.
It is not known if Pitocin is safe and effective in children.
What are the possible side effects of Pitocin?
Pitocin may cause serious side effects including:
- fast, slow or uneven heart rate,
- excessing bleeding long after childbirth,
- severe headache,
- blurred vision,
- pounding in your neck or ears,
- confusion,
- severe weakness, and
- feeling unsteady
Serious side effects for the baby:
- slow heartbeats or other abnormal heart rate,
- yellow appearance of the baby’s skin (jaundice),
- convulsion (seizure),
- eye problems, and
- problems with breathing, muscle tone and other signs of health
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Pitocin include:
- nausea,
- vomiting, and
- more intense or more frequent contractions (expected effect)
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Pitocin. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Pharmacy Bulk Package - Not for Direct Infusion
DESCRIPTION
Pitocin (oxytocin injection, USP) is a sterile, clear, colorless aqueous solution of synthetic oxytocin, for intravenous infusion or intramuscular injection. Pitocin is a nonapeptide found in pituitary extracts from mammals. It is standardized to contain 10 units of oxytocic hormone/mL and contains 0.5% Chlorobutanol, a chloroform derivative as a preservative, with the pH adjusted with acetic acid. Pitocin may contain up to 16% of total impurities. The hormone is prepared synthetically to avoid possible contamination with vasopressin (ADH) and other small polypeptides with biologic activity. Pitocin has the empirical formula C43H66N12O12S2 (molecular weight 1007.19). The structural formula is as follows:
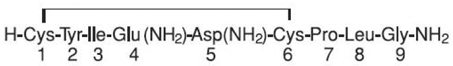 |
Indications
IMPORTANT NOTICE
Elective induction of labor is defined as the initiation of labor in a pregnant individual who has no medical indications for induction. Since the available data are inadequate to evaluate the benefitsto- risks considerations, Pitocin is not indicated for elective induction of labor.
Antepartum
Pitocin is indicated for the initiation or improvement of uterine contractions, where this is desirable and considered suitable for reasons of fetal or maternal concern, in order to achieve vaginal delivery. It is indicated for (1) induction of labor in patients with a medical indication for the initiation of labor, such as Rh problems, maternal diabetes, preeclampsia at or near term, when delivery is in the best interests of mother and fetus or when membranes are prematurely ruptured and delivery is indicated; (2) stimulation or reinforcement of labor, as in selected cases of uterine inertia; (3) as adjunctive therapy in the management of incomplete or inevitable abortion. In the first trimester, curettage is generally considered primary therapy. In second trimester abortion, oxytocin infusion will often be successful in emptying the uterus. Other means of therapy, however, may be required in such cases.
Postpartum
Pitocin is indicated to produce uterine contractions during the third stage of labor and to control postpartum bleeding or hemorrhage.
Dosage
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
The dosage of oxytocin is determined by the uterine response and must therefore be individualized and initiated at a very low level. The following dosage information is based upon various regimens and indications in general use.
Induction Or Stimulation Of Labor
Intravenous infusion (drip method) is the only acceptable method of parenteral administration of Pitocin for the induction or stimulation of labor. Accurate control of the rate of infusion is essential and is best accomplished by an infusion pump. It is convenient to piggyback the Pitocin infusion on a physiologic electrolyte solution, permitting the Pitocin infusion to be stopped abruptly without interrupting the electrolyte infusion. This is done in the following way.
Preparation
- The standard solution for infusion of Pitocin is prepared by adding 1 mL (containing 10 units of oxytocin) to 1000 mL of 0.9% aqueous sodium chloride or Ringer's lactate. The combined solution containing 10 milliunits (mU) of oxytocin/mL is rotated in the infusion bottle for thorough mixing.
- Establish the infusion with a separate bottle of physiologic electrolyte solution not containing Pitocin.
- Attach (piggyback) the Pitocin-containing bottle with the infusion pump to the infusion line as close to the infusion site as possible.
Administration
The initial dose should be 0.5–1 mU/min (equal to 3–6 mL of the dilute oxytocin solution per hour). At 30–60 minute intervals the dose should be gradually increased in increments of 1–2 mU/min until the desired contraction pattern has been established. Once the desired frequency of contractions has been reached and labor has progressed to 5–6 cm dilation, the dose may be reduced by similar increments.
Studies of the concentrations of oxytocin in the maternal plasma during Pitocin infusion have shown that infusion rates up to 6 mU/min give the same oxytocin levels that are found in spontaneous labor. At term, higher infusion rates should be given with great care, and rates exceeding 9–10 mU/min are rarely required. Before term, when the sensitivity of the uterus is lower because of a lower concentration of oxytocin receptors, a higher infusion rate may be required.
Monitoring
- Electronically monitor the uterine activity and the fetal heart rate throughout the infusion of Pitocin. Attention should be given to tonus, amplitude and frequency of contractions, and to the fetal heart rate in relation to uterine contractions. If uterine contractions become too powerful, the infusion can be abruptly stopped, and oxytocic stimulation of the uterine musculature will soon wane (see PRECAUTIONS section).
- Discontinue the infusion of Pitocin immediately in the event of uterine hyperactivity and/or fetal distress. Administer oxygen to the mother, who preferably should be put in a lateral position. The condition of mother and fetus should immediately be evaluated by the responsible physician and appropriate steps taken.
Control Of Postpartum Uterine Bleeding
- Intravenous infusion (drip method). If the patient has an intravenous infusion running, 10 to 40 units of oxytocin may be added to the bottle, depending on the amount of electrolyte or dextrose solution remaining (maximum 40 units to 1000 mL). Adjust the infusion rate to sustain uterine contraction and control uterine atony.
- Intramuscular administration. 1 mL (10 units) of Pitocin can be given after the delivery of the placenta.
Treatment Of Incomplete, Inevitable, Or Elective Abortion
Intravenous infusion of 10 units of Pitocin added to 500 mL of a physiologic saline solution or 5% dextrose-in-water solution may help the uterus contract after a suction or sharp curettage for an incomplete, inevitable, or elective abortion.
Subsequent to intra-amniotic injection of hypertonic saline, prostaglandins, urea, etc., for midtrimester elective abortion, the injection-to-abortion time may be shortened by infusion of Pitocin at the rate of 10 to 20 milliunits (20 to 40 drops) per minute. The total dose should not exceed 30 units in a 12-hour period due to the risk of water intoxication.
Directions For Dispensing
Pharmacy Bulk Package – Not for Direct Infusion: The pharmacy bulk package is for use in a pharmacy admixture service only in a suitable work area, such as a laminar flow hood. The closure should be penetrated only once utilizing an appropriate sterile transfer device, which allows measured distribution of the contents. The transfer device should be inserted into the Pharmacy Bulk Package using aseptic technique.
Contents should be used as soon as possible following initial closure puncture. Discard any unused portion within 24 hours of first entry. Following closure puncture, container should be maintained under labeled storage conditions between 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) under a laminar flow hood until contents are dispensed.
HOW SUPPLIED
Pitocin (Oxytocin Injection, USP) Synthetic is available as follows:
NDC 42023-130-06 Packages of six 50 mL Pharmacy Bulk Packages, each containing 10 units of oxytocin per mL (total = 500 units of oxytocin per vial).
Storage
Store between 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature.
REFERENCES
1. Seitchik J, Castillo M: Oxytocin augmentation of dysfunctional labor. I. Clinical data. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982; 144:899–905.
2. Seitchik J, Castillo M: Oxytocin augmentation of dysfunctional labor. II. Multiparous patients. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983; 145:777–780.
3. Fuchs A, Goeschen K, Husslein P, et al: Oxytocin and the initiation of human parturition. III. Plasma concentrations of oxytocin and 13, 14-dihydro-15-keto-prostaglandin F2a in spontaneous and oxytocin-induced labor at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983; 145:497–502.
4. Seitchik J, Amico J, et al: Oxytocin augmentation of dysfunctional labor. IV. Oxytocin pharmacokinetics. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984; 150:225–228.
5. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: ACOG Technical Bulletin Number 110— November 1987: Induction and augmentation of labor.
Distributed by: Par Pharmaceutical, Chestnut Ridge, NY 10977. Revised : Nov 2020
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
The following adverse reactions have been reported in the mother:
| Anaphylactic reaction | Premature ventricular contractions |
| Postpartum hemorrhage | Pelvic hematoma |
| Cardiac arrhythmia | Subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| Fatal afibrinogenemia | Hypertensive episodes |
| Nausea | Rupture of the uterus |
| Vomiting |
Excessive dosage or hypersensitivity to the drug may result in uterine hypertonicity, spasm, titanic contraction, or rupture of the uterus.
The possibility of increased blood loss and afibrinogenemia should be kept in mind when administering the drug.
Severe water intoxication with convulsions and coma has occurred, associated with a slow oxytocin infusion over a 24-hour period. Maternal death due to oxytocin-induced water intoxication has been reported.
The following adverse reactions have been reported in the fetus or neonate:
| Due to induced uterine motility: | Due to use of oxytocin in the mother: |
| Bradycardia | Low Apgar scores at five minutes |
| Premature ventricular contractions and other arrhythmias | Neonatal jaundice |
| Permanent CNS or brain damage | Neonatal retinal hemorrhage |
| Fetal death | |
| Neonatal seizures have been reported with the use of Pitocin. |
For medical advice about adverse reactions contact your medical professional. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Par Pharmaceutical at 1-800-828-9393 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 (1-800-332-1088) or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Severe hypertension has been reported when oxytocin was given three to four hours following prophylactic administration of a vasoconstrictor in conjunction with caudal block anesthesia. Cyclopropane anesthesia may modify oxytocin's cardiovascular effects, so as to produce unexpected results such as hypotension. Maternal sinus bradycardia with abnormal atrioventricular rhythms has also been noted when oxytocin was used concomitantly with cyclopropane anesthesia.
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Pitocin, when given for induction of labor or augmentation of uterine activity, should be administered only by the intravenous route and with adequate medical supervision in a hospital.
PRECAUTIONS
General
- All patients receiving intravenous oxytocin must be under continuous observation by trained personnel who have a thorough knowledge of the drug and are qualified to identify complications. A physician qualified to manage any complications should be immediately available. Electronic fetal monitoring provides the best means for early detection of overdosage (see OVERDOSAGE section). However, it must be borne in mind that only intrauterine pressure recording can accurately measure the intrauterine pressure during contractions. A fetal scalp electrode provides a more dependable recording of the fetal heart rate than any external monitoring system.
- When properly administered, oxytocin should stimulate uterine contractions comparable to those seen in normal labor. Overstimulation of the uterus by improper administration can be hazardous to both mother and fetus. Even with proper administration and adequate supervision, hypertonic contractions can occur in patients whose uteri are hypersensitive to oxytocin. This fact must be considered by the physician in exercising his judgment regarding patient selection.
- Except in unusual circumstances, oxytocin should not be administered in the following conditions: fetal distress, hydramnios, partial placenta previa, prematurity, borderline cephalopelvic disproportion, and any condition in which there is a predisposition for uterine rupture, such as previous major surgery on the cervix or uterus including cesarean section, overdistention of the uterus, grand multiparity, or past history of uterine sepsis or of traumatic delivery. Because of the variability of the combinations of factors which may be present in the conditions listed above, the definition of “unusual circumstances” must be left to the judgment of the physician. The decision can be made only by carefully weighing the potential benefits which oxytocin can provide in a given case against rare but definite potential for the drug to produce hypertonicity or tetanic spasm.
- Maternal deaths due to hypertensive episodes, subarachnoid hemorrhage, rupture of the uterus, and fetal deaths due to various causes have been reported associated with the use of parenteral oxytocic drugs for induction of labor or for augmentation in the first and second stages of labor.
- Oxytocin has been shown to have an intrinsic antidiuretic effect, acting to increase water reabsorption from the glomerular filtrate. Consideration should, therefore, be given to the possibility of water intoxication, particularly when oxytocin is administered continuously by infusion and the patient is receiving fluids by mouth.
- When oxytocin is used for induction or reinforcement of already existent labor, patients should be carefully selected. Pelvic adequacy must be considered and maternal and fetal conditions evaluated before use of the drug.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
There are no animal or human studies on the carcinogenicity and mutagenicity of this drug, nor is there any information on its effect on fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with oxytocin. There are no known indications for use in the first trimester of pregnancy other than in relation to spontaneous or induced abortion. Based on the wide experience with this drug and its chemical structure and pharmacological properties, it would not be expected to present a risk of fetal abnormalities when used as indicated.
Nonteratogenic Effects
See ADVERSE REACTIONS in the fetus or neonate.
Labor And Delivery
See INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
Overdosage with oxytocin depends essentially on uterine hyperactivity whether or not due to hypersensitivity to this agent. Hyperstimulation with strong (hypertonic) or prolonged (tetanic) contractions, or a resting tone of 15 to 20 mmHg or more between contractions can lead to tumultuous labor, uterine rupture, cervical and vaginal lacerations, postpartum hemorrhage, uteroplacental hypoperfusion, and variable deceleration of fetal heart, fetal hypoxia, hypercapnia, perinatal hepatic necrosis or death. Water intoxication with convulsions, which is caused by the inherent antidiuretic effect of oxytocin, is a serious complication that may occur if large doses (40 to 50 milliunits/minute) are infused for long periods. Management consists of immediate discontinuation of oxytocin and symptomatic and supportive therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Antepartum use of Pitocin is contraindicated in any of the following circumstances:
- Where there is significant cephalopelvic disproportion;
- In unfavorable fetal positions or presentations, such as transverse lies, which are undeliverable without conversion prior to delivery;
- In obstetrical emergencies where the benefit-to-risk ratio for either the fetus or the mother favors surgical intervention;
- In fetal distress where delivery is not imminent;
- Where adequate uterine activity fails to achieve satisfactory progress;
- Where the uterus is already hyperactive or hypertonic;
- In cases where vaginal delivery is contraindicated, such as invasive cervical carcinoma, active herpes genitalis, total placenta previa, vasa previa, and cord presentation or prolapse of the cord;
- In patients with hypersensitivity to the drug.
Clinical Pharmacology
Uterine motility depends on the formation of the contractile protein actomyosin under the influence of the Ca2+- dependent phosphorylating enzyme myosin light-chain kinase. Oxytocin promotes contractions by increasing the intracellular Ca2+. Oxytocin has specific receptors in the myometrium and the receptor concentration increases greatly during pregnancy, reaching a maximum in early labor at term. The response to a given dose of oxytocin is very individualized and depends on the sensitivity of the uterus, which is determined by the oxytocin receptor concentration. However, the physician should be aware of the fact that oxytocin even in its pure form has inherent pressor and antidiuretic properties which may become manifest when large doses are administered. These properties are thought to be due to the fact that oxytocin and vasopressin differ in regard to only two of the eight amino acids (see PRECAUTIONS section).
Oxytocin is distributed throughout the extracellular fluid. Small amounts of the drug probably reach the fetal circulation. Oxytocin has a plasma half-life of about 1 to 6 minutes which is decreased in late pregnancy and during lactation. Following intravenous administration of oxytocin, uterine response occurs almost immediately and subsides within 1 hour. Following intramuscular injection of the drug, uterine response occurs within 3 to 5 minutes and persists for 2 to 3 hours. Its rapid removal from plasma is accomplished largely by the kidney and the liver. Only small amounts are excreted in urine unchanged.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
No information provided. Please refer to the WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS sections.
