Optiray Injection Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: ioversol injection
- Brand Name: Optiray Injection
side effects drug center optiray injection (ioversol injection) drug
Drug Description
What is Optiray and how is it used?
Optiray (ioversol) is a radiopaque contrast agent that contains iodine, a substance that absorbs x-rays, and is used to help diagnose certain disorders of the heart.
What are side effects of Optiray?
Common side effects of Optiray include
Some side effects of Optiray can occur up to 24 hours after receiving the medication.
Optiray™ 350
[Ioversol Injection 74%]
Optiray™ 320
[Ioversol Injection 68%]
Optiray™ 300
[Ioversol Injection 64%]
Optiray™ 240
[Ioversol Injection 51%]
WARNING
NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE
DESCRIPTION
Optiray (ioversol injection) formulations are sterile, nonpyrogenic, aqueous solutions intended for intravascular administration as diagnostic radiopaque media. Ioversol is designated chemically as N,N'-Bis (2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5-[N-(2-hydroxyethyl) glycolamido] -2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide and has the following structural formula:
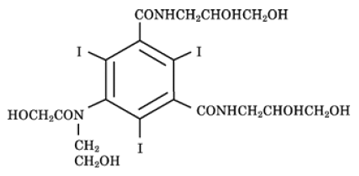 |
The molecular weight of ioversol is 807.11 and the organically bound iodine content is 47.2%. Ioversol is nonionic and does not dissociate in solution.
Each milliliter of Optiray 350 (ioversol injection 74%) contains 741 mg of ioversol with 3.6 mg of tromethamine as a buffer and 0.2 mg of edetate calcium disodium as a stabilizer. Optiray 350 provides 35% (350 mg/mL) organically bound iodine.
Each milliliter of Optiray 320 (ioversol injection 68%) contains 678 mg of ioversol with 3.6 mg of tromethamine as a buffer and 0.2 mg of edetate calcium disodium as a stabilizer. Optiray 320 provides 32% (320 mg/mL) organically bound iodine.
Each milliliter of Optiray 300 (ioversol injection 64%) contains 636 mg of ioversol with 3.6 mg of tromethamine as a buffer and 0.2 mg of edetate calcium disodium as a stabilizer. Optiray 300 provides 30% (300 mg/mL) organically bound iodine.
Each milliliter of Optiray 240 (ioversol injection 51%) contains 509 mg of ioversol with 3.6 mg of tromethamine as a buffer and 0.2 mg of edetate calcium disodium as a stabilizer. Optiray 240 provides 24% (240 mg/mL) organically bound iodine.
The pH of the Optiray formulations has been adjusted to 6.0 to 7.4 with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide. All solutions are sterilized by autoclaving and contain no preservatives. Unused portions should be discarded. Optiray solutions are sensitive to light and therefore should be protected from exposure.
Some physical and chemical properties of these formulations are listed below:
| Optiray 240 | Optiray 300 | Optiray 320 | Optiray 350 | |
| Ioversol content(mg/mL) | 509 | 636 | 678 | 741 |
| Iodine content(mg I/mL) | 240 | 300 | 320 | 350 |
| Osmolality (mOsm/kg water) | 502 | 651 | 702 | 792 |
| Viscosity (cps) | ||||
| at 25°C | 4.6 | 8.2 | 9.9 | 14.3 |
| at 37°C | 3.0 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 9.0 |
| Specific Gravity at 37°C | 1.281 | 1.352 | 1.371 | 1.405 |
The Optiray formulations are clear, colorless to pale yellow solutions containing no undissolved solids. Crystallization does not occur at room temperature. The products are supplied in containers from which the air has been displaced by nitrogen. Optiray solutions have osmolalities 1.8 to 2.8 times that of plasma (285 mOsm/kg water) as shown in the above table and are hypertonic under conditions of use.
Indications
Optiray is indicated for:
Intra-arterial
In Adults
- Optiray 300: cerebral arteriography, and peripheral arteriography.
- Optiray 320: cerebral arteriography, peripheral arteriography, visceral and renal arteriography, aortography, coronary arteriography, and left ventriculography.
- Optiray 350: peripheral arteriography, coronary arteriography, and left ventriculography.
In Pediatric Patients
- Optiray 320 and Optiray 350: angiocardiography.
Intra-Venous
In Adults
- Optiray 300: CT imaging of the head and body, venography, and intravenous excretory urography.
- Optiray 320: CT imaging of the head and body, venography, and intravenous excretory urography.
- Optiray 350: CT imaging of the head and body, venography, intravenous excretory urography, and intravenous digital subtraction angiography (IV-DSA).
In Pediatric Patients
- Optiray 320: CT imaging of the head and body, and intravenous excretory urography.
Dosage
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Important Dosage And Administration Instructions
- Optiray is for intravascular use only [see BOXED WARNING, CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
- Use sterile technique for all handling and administration of Optiray.
- Inspect glass container prior to use for breakage or other damage and do not use damaged containers.
- Warm Optiray and administer at body or room temperature.
- Inspect Optiray for particulate matter or discoloration before administration. Do not administer if Optiray contains particulate matter or is discolored.
- Do not mix Optiray with other drugs, solutions or total parenteral nutrition mixtures.
- Use the lowest dose necessary to obtain adequate visualization.
- Adjust the volume and concentration of Optiray. Modify the dose accounting for factors such as age, body weight, vessel size, blood flow rate within the vessel, Â anticipated pathology, degree and extent of opacification required, structure(s) or area to be examined, disease processes affecting the patient, and equipment and technique to be employed.
- Avoid extravasation when injecting Optiray; especially in patients with severe arterial or venous disease [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
- Hydrate patients before and after Optiray administration [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Directions For Proper Use Of Optiray Pharmacy Bulk Package
- The Pharmacy Bulk Package is not for direct infusion.
- Penetrate the container closure only one time, utilizing a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set which allows measured distribution of the contents.
- Transfer Optiray from the Pharmacy Bulk Package only in a suitable work area, such as a laminar flow hood, utilizing aseptic technique.
- Withdraw container contents immediately. However, should this not be possible, a maximum time of 4 hours from initial closure entry is permitted to complete fluid transfer operations.
- Temperature of container after the closure has been entered should not exceed 25°C (77°F).
Intra-arterial Procedures In Adults
Cerebral Arteriography
Use Optiray 300 or Optiray 320. The recommended dose for visualization of cerebral arteries is shown below (may repeat as necessary):
| Diagnostic area | Dose | Maximum Cumulative Dose |
| carotid or vertebral arteries | 2 to 12 mL | 200 mL |
| aortic arch injection (four vessel study) | 20 to 50 mL | 200 mL |
Peripheral Arteriography
Use Optiray 300, Optiray 320 or Optiray 350. The recommended dose for visualization of peripheral arteries is shown below (may repeat as necessary):
| Diagnostic area | Dose | Maximum Cumulative Dose |
| aorta-iliac runoff | 60 mL (range 20 to 90 mL) | 250 mL |
| common iliac, femoral | 40 mL (range 10 to 50 mL) | 250 mL |
| subclavian, brachial | 20 mL (range 15 to 30 mL) | 250 mL |
Visceral And Renal Arteriography And Aortography
Use Optiray 320. The recommended dose for visualization for the aorta and visceral arteries is shown below (may repeat as necessary):
| Diagnostic area | Dose | Maximum Cumulative Dose |
| aorta | 45 mL (range 10 to 80 mL) | 250 mL |
| celiac | 45 mL (range 12 to 60 mL) | 250 mL |
| superior mesenteric | 45 mL (range 15 to 60 mL) | 250 mL |
| renal or inferior mesenteric | 9 mL (range 6 to 15 mL) | 250 mL |
Coronary Arteriography And Left Ventriculography
Use Optiray 320 or Optiray 350. The recommended dose for visualization of the coronary arteries and left ventricle is shown below (may repeat as necessary):
| Diagnostic area | Dose | Maximum Cumulative Dose |
| left coronary | 8 mL (range 2 to 10 mL) | 250 mL |
| right coronary | 6 mL (range 1 to 10 mL) | 250 mL |
| left ventricle | 40 mL (range 30 to 50 mL) | 250 mL |
Intravenous Procedures In Adults
Computed Tomography
Use Optiray 300, Optiray 320 or Optiray 350 for head and body imaging.
Head Imaging
The recommended dosing is shown below:
- Scan immediately after completion of the intravenous administration.
| Infusion | |
| Optiray 300 | 50 to 150 mL |
| Optiray 320 | 50 to 150 mL |
| Optiray 350 | 50 to 150 mL |
Body Imaging
Optiray may be administered by bolus injection, by rapid infusion, or by a combination of both. The recommended dosing is shown below:
- Scanning interval will vary with indication and target organ
| Bolus Injection | Infusion | |
| Optiray 300 | 25 to 75 mL | 50 to 150 mL |
| Optiray 320 | 25 to 75 mL | 50 to 150 mL |
| Optiray 350 | 25 to 75 mL | 50 to 150 mL |
Venography
Use Optiray 300, Optiray 320 or Optiray 350. The recommended dose is 50 to 100 mL per extremity; with a maximum cumulative dose of 250 mL.
Intravenous Urography
Use Optiray 350, Optiray 320, or Optiray 300. The recommended dose is shown below:
| Usual Dose | High Dose Urography | Maximum Dose | |
| Optiray 300 | 50 to 75 mL | 1.6 mL/kg | 150 mL |
| Optiray 320 | 50 to 75 mL | 1.5 to 2 mL/kg | 150 mL |
| Optiray 350 | 50 to 75 mL | 1.4 mL/kg | 140 mL |
Intravenous Digital Subtraction Angiography (IV-DSA)
Use Optiray 350. The recommended dose range per injection is 30 to 50 mL; may repeat as necessary with a maximum cumulative dose of 250mL.
Injection rates will vary depending on the site of catheter placement and vessel size.
- Central catheter injections are usually made at a rate of between 10 and 30 mL/second.
- Peripheral injections are usually made at a rate of between 12 and 20 mL/second.
Pediatric Dosing
Intra-arterial Procedures
Angiocardiography
Use Optiray 350 or Optiray 320. The recommended single ventricular dose is 1.25 mL/kg (range 1 mL/kg to 1.5 mL/kg). The maximum cumulative dose is 5 mL/kg up to a maximum total volume of 250 mL.
Intravenous Procedures
Computed Tomography
Use Optiray 320.
Head And Body Imaging
The recommended dose in pediatric patients is 1.5 mL/kg to 2 mL/kg (range 1 mL/kg to 3 mL/kg).
Intravenous Urography
Use Optiray 320. The recommended dose for pediatric patients is 1 mL/kg to 1.5 mL/kg (range 0.5 mL/kg to 3 mL/kg); with a maximum cumulative dose not exceeding 3 mL/kg.
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
Injection: clear, colorless to pale yellow solutions containing no undissolved solids, available in a pharmacy bulk package multiple-dose container in the following strengths:
- OPTIRAY 300 (Ioversol 64%): 300 mg of organically bound iodine per mL (636 mg of ioversol per mL)
- OPTIRAY 320 (Ioversol 68%): 320 mg of organically bound iodine per mL (678 mg of ioversol per mL)
- OPTIRAY 350 (Ioversol 74%): 350 mg of organically bound iodine per mL (741 mg of ioversol per mL)
Storage And Handling
Optiray is a clear, colorless to pale yellow, sterile, pyrogen-free, aqueous solution available in three strengths in a Pharmacy Bulk Package. The products are supplied in 500 mL glass containers from which the air has been displaced by nitrogen. Optiray is supplied in the following configurations:
| NDC Number | |
| Optiray Pharmacy Bulk Package - 350 6 x 500 mL Pharmacy Bulk Packages | 0019-1333-61 |
| Optiray Pharmacy Bulk Package - 320 6 x 500 mL Pharmacy Bulk Packages | 0019-1323-61 |
| Optiray Pharmacy Bulk Package - 300 6 x 500 mL Pharmacy Bulk Packages | 0019-1332-61 |
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
Protect from strong daylight or direct exposure to the sun.
Discard Optiray containers, and their contents, if they are frozen or if crystallization occurs.
Manufactured by: Liebel-Flarsheim Company LLC Raleigh, NC 27616. Revised: Nov 2020
Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Risks Associated with Inadvertent Intrathecal Administration [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Contrast Induced Acute Kidney Injury [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Thromboembolic Events [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Clinical Studies Experience
Adult Patients
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following table shows reactions based upon clinical trials with Optiray (ioversol) in 4,187 patients. Adverse reactions are listed by organ system according to clinical importance. More severe reactions are listed before others in a system regardless of incidence. The most common reaction is nausea, occurring at a rate of 1 percent.
Cardiac Disorders
Cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, atrioventricular block complete, atrioventricular block, nodal rhythm, bradycardia, angina pectoris, palpitations
Ear And Labyrinth Disorders
Eye Disorders
Vision blurred, periorbital edema, conjunctivitis
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Vomiting, abdominal pain, dysphagia, dry mouth
General Disorders And Administration Site Conditions
Chest pain, pain, injection site pain, injection site hematoma, extravasation, pyrexia, swelling, asthenia, malaise, fatigue, chills
Infections And Infestations
Injury, Poisoning, And Procedural Complications
Heart injury, vascular pseudoaneurysm
Investigations
Electrocardiogram ST segment depression, blood pressure decreased
Metabolism And Nutrition Disorders
Musculoskeletal And Connective Tissue Disorders
Muscular weakness, muscle spasms, back pain
Nervous System Disorders
Cerebral infarction, aphasia, tremor, dizziness, presyncope, headache, paraesthesia, dysgeusia
Psychiatric Disorders
Hallucination, visual hallucination, disorientation, anxiety
Renal And Urinary Disorders
Urinary retention, renal pain, polyuria
Respiratory, Thoracic, And Mediastinal Disorders
Laryngeal edema, hypoxia, pulmonary edema, dyspnea, hyperventilation, cough, sneezing, nasal congestion
Skin And Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Urticaria, rash, pruritus, swelling face, hyperhidrosis, erythema
Vascular Disorders
Hypertension, hypotension, arterial spasm, vasospasm, vasodilation, flushing
Pediatric Patients
In clinical trials involving 311 patients for pediatric angiocardiography, contrast enhanced computed tomographic imaging of the head and body, and intravenous excretory urography; 6% of patients reported an adverse reactions, with the most common adverse reactions being nausea and fever. Adverse reactions reported were similar in quality and frequency to the adverse events reported by adults..
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse drug reactions have been reported during post-approval use of Optiray. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate frequency.
Cardiac disorders: coronary artery spasm, cyanosis, arrhythmia (ventricular fibrillation, tachycardia, extrasystole), ECG abnormal.
Endocrine disorders: thyroid function tests indicative of hypothyroidism or transient thyroid suppression have been uncommonly reported following iodinated contrast media administration to adult and pediatric patients, including infants, some patients were treated for hypothyroidism.
Eye disorders: temporary blindness, conjunctivitis (including eye irritation, ocular hyperemia, watery eyes).
Gastrointestinal disorders: tongue edema, salivary hypersecretion.
General disorders and administration site conditions: injection site reactions including pain, hemorrhage, and necrosis especially after extravasation [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS], face edema, feeling hot.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions including fatal anaphylactic shock.
Nervous system disorders: seizure, loss of consciousness, somnolence, hypoesthesia, dyskinesia, amnesia.
Respiratory disorders: respiratory arrest, asthma, bronchospasm, laryngeal spasm and obstruction, throat irritation, dysphonia.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Reactions range from mild (e.g. rash, erythema, pruritus, urticaria, and skin discoloration) to severe: [e.g. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN)], acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Vascular Disorders: phlebitis, thrombosis.
Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Metformin
In patients with renal impairment, metformin can cause lactic acidosis. Iodinated contrast agents appear to increase the risk of metformin induced lactic acidosis, possibly as a result of worsening renal function. Stop metformin at the time of, or prior to, Optiray administration in patients with an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m²; in patients with a history of hepatic impairment, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast agents. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure, and reinstitute only after renal function is stable.
Radioactive Iodine
Administration of iodinated contrast agents may interfere with thyroid uptake of radioactive iodine (I-131) and decrease therapeutic efficacy in patients with carcinoma of the thyroid. The decrease in efficacy lasts for 6-8 weeks.
Oral Cholecystographic Contrast Agents
Renal toxicity has been reported in patients with liver impairment who were given oral cholecystographic agents followed by intravascular contrast agents. Administration of Optiray should be postponed in patients who have recently received a cholecystographic contrast agent.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Protein-Bound Iodine, Radioactive Iodine Determinations
The results of protein bound iodine and radioactive iodine uptake studies, which depend on iodine estimation, will not accurately reflect thyroid function for up to 16 days following administration of iodinated contrast agent. However, thyroid function tests that do not depend on iodine estimations, e.g., T3 resin uptake and total or free thyroxine (T4) assays are not affected.
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the PRECAUTIONS section.
PRECAUTIONS
Risks Associated With Inadvertent Intrathecal Administration
Optiray is indicated for intravascular use only [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION]. Inadvertent intrathecal administration can cause death, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, seizures, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Optiray can cause life-threatening or fatal hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock. Manifestations include respiratory arrest, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, angioedema, and shock. Most severe reactions develop shortly after the start of the injection (e.g. within 1 to 3 minutes), but delayed reactions may occur. There is an increased risk in patients with a history of a previous reaction to contrast agent, and known allergies (i.e., bronchial asthma, drug, or food allergies), and other hypersensitivities. Premedication with antihistamines or corticosteroids to avoid or minimize possible allergic reactions does not prevent serious life-threatening reactions, but may reduce both their incidence and severity.
Obtain a history of allergy, hypersensitivity, or prior hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast agents. Always have emergency resuscitation equipment and trained personnel available and monitor all patients for hypersensitivity reactions.
Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
Acute kidney injury, including renal failure, may occur after Optiray administration. Risk factors include: pre-existing renal impairment, dehydration, diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, advanced vascular disease, elderly age, concomitant use of nephrotoxic or diuretic medications, multiple myeloma / paraproteinaceous diseases, repetitive and/or large doses of an iodinated contrast agent.
Use the lowest necessary dose of Optiray in patients with renal impairment. Adequately hydrate patients prior to and following Optiray administration. Do not use laxatives, diuretics, or preparatory dehydration prior to Optiray administration.
Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
Optiray increases the circulatory osmotic load and may induce acute or delayed hemodynamic disturbances in patients with congestive heart failure, severely impaired renal function, combined renal and hepatic disease, combined renal and cardiac disease, particularly when repetitive or large doses are administered.
Life-threatening or fatal cardiovascular reactions have occurred with the use of Optiray, including cardiac arrest, hypotensive collapse, and shock. Most deaths occur within 10 minutes of injection; with cardiovascular disease as the main underlying factor. Cardiac decompensation, serious arrhythmias, and myocardial ischemia or infarction can occur during coronary arteriography and ventriculography.
Based upon literature reports, deaths from the administration of iodinated contrast agents range from 6.6 per 1 million (0.00066 percent) to 1 in 10,000 patients (0.01 percent). Use the lowest necessary dose of Optiray in patients with congestive heart failure and always have emergency resuscitation equipment and trained personnel available. Monitor all patients for severe cardiovascular reactions.
Thromboembolic Events
Angiocardiography
Serious, fatal, thromboembolic events causing myocardial infarction and stroke can occur during angiographic procedures with Optiray. During these procedures, increased thrombosis and activation of the complement system occurs. Risk factors for thromboembolic events include: length of procedure, catheter and syringe material, underlying disease state, and concomitant medications.
To minimize thromboembolic events use meticulous angiographic technique. Avoid blood remaining in contact with syringes containing Optiray, which increases the risk of clotting. Avoid angiocardiography in patients with homocystinuria because of the risk of inducing thrombosis and embolism [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Extravasation And Injection Site Reactions
Extravasation can occur with Optiray administration, particularly in patients with severe arterial or venous disease and can be associated with pain, hemorrhage and necrosis. Ensure intravascular placement of catheters prior to injection. Monitor patients for extravasation and advise patients to seek medical care for progression of symptoms.
Thyroid Storm In Patients With Hyperthyroidism
Optiray is contraindicated in patients with symptomatic hyperthyroidism [see CONTRAINDICATIONS]. Thyroid storm has occurred following the intravascular use of iodinated radiopaque agents in patients with hyperthyroidism or with an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. Evaluate the risk in such patients before use of Optiray.
Hypertensive Crisis In Patients With Pheochromocytoma
Hypertensive crisis has occurred after the use of iodinated radiopaque contrast agents in patient with pheochromocytoma. Closely monitor patients when administering Optiray if pheochromocytoma or catecholamine-secreting paraganglioma is suspected. Inject the minimum amount of Optiray necessary and have measures for treatment of hypertensive crisis readily available.
Sickle Cell Crisis In Patients With Sickle Cell Disease
Iodinated contrast agents may promote sickling in individuals who are homozygous for sickle cell disease. Hydrate patients prior to and following Optiray administration, use Optiray only if the necessary imaging information cannot be obtained with alternative imaging modalities, and inject the minimum amount necessary.
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) may develop from 1 hour to several weeks after intravascular contrast agent administration. These reactions include Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). Reaction severity may increase and time to onset may decrease with repeat administration of a contrast agent; prophylactic medications may not prevent or mitigate severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Avoid administering Optiray to patients with a history of a severe cutaneous adverse reaction to Optiray.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
No long term animal studies have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential. Nonclinical studies show that this drug is not mutagenic and does not affect fertility.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Postmarketing data with Optiray use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine if there is a risk of drug-associated adverse developmental outcomes. Ioversol crosses the placenta and reaches fetal tissues in small amounts [see Data]. In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed following daily intravenous administrations of ioversol to pregnant rats (from Gestation Day 7 to 17) and rabbits (Gestation Day 6 to 18) at doses 0.35 and 0.71 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of major birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 1520%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Literature reports show that ioversol crosses the placenta and is visualized in the digestive tract of exposed infants after birth.
Animal Data
Developmental toxicity studies were conducted with ioversol given intravenously at doses of 0, 0.2, 0.8, and 3.2 g iodine/kg/day from Gestation Day7 to 17 and 6 to 18, in rats and rabbits, respectively. No adverse effects on embryo-fetal development were observed in either species at the maximum dose tested (3.2 g iodine/kg/day). Maternal toxicity was observed in rabbits at 0.8 and 3.2 g iodine/kg/day.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information about the presence of ioversol in human or animal milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. However, iodinated contrast agents are excreted unchanged in human milk in very low amounts with poor absorption from the gastrointestinal tract of the breastfed infant. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Optiray and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Optiray or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Interruption of breastfeeding after exposure to iodinated contrast agents is not necessary because the potential exposure of the breastfed infant to iodine is small. However, a lactating woman may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breast milk for 8 hours (approximately 5 elimination half-lives) after Optiray administration in order to minimize drug exposure to a breast fed infant.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have been established for the use of Optiray 350 and Optiray 320 in angiocardiography; and for Optiray 320 in contrast enhanced computed tomographic imaging of the head and body, and intravenous excretory urography. Use of Optiray 350 and Optiray 320 in these age groups is based on controlled clinical trials involving 159 patients for pediatric angiocardiography; contrast enhanced computed tomographic imaging of the head and body, and intravenous excretory urography. In general, the types of adverse reactions reported are similar to those of adults [see ADVERSE REACTIONS].
Safety and effectiveness of Optiray 350 and Optiray 320 have not been established in pediatric patients less than 1 month of age. Safety and effectiveness of Optiray 300 has not been established in pediatric patients.
Pediatric patients at higher risk of experiencing adverse reactions to Optiray include patients with: asthma, sensitivity to medication and/or allergens, congestive heart failure, serum creatinine greater than 1.5 mg/dL, or age less than 12 months. Thyroid function tests indicative of hypothyroidism or transient thyroid suppression have been uncommonly reported following iodinated contrast media administration in pediatric patients, including infants. Some patients were treated for hypothyroidism [See ADVERSE REACTIONS].
Geriatric Use
Optiray is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to Optiray may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, dose selection should be cautious usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Renal Impairment
In patients with impaired renal function, the elimination half-life is prolonged. Ioversol can be removed by dialysis.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
The adverse effects of overdosage are life-threatening and affect mainly the pulmonary and cardiovascular system. Treatment of an overdosage is directed toward the support of all vital functions and prompt institution of symptomatic therapy.
Ioversol does not bind to plasma or serum protein and is, therefore, dialyzable.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Symptomatic hyperthyroidism.
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
Intravascular injection of ioversol opacifies those vessels in the path of the flow of the contrast medium, permitting radiographic visualization of the internal structures until significant hemodilution occurs.
In imaging of the body, iodinated contrast agents diffuse from the vascular into the extravascular space. In normal brain with an intact blood-brain barrier, contrast does not diffuse into the extravascular space. In patients with a disrupted blood-brain barrier, contrast agent accumulates in the interstitial space in the region of disruption.
Pharmacodynamics
Following administration of Optiray, the degree of enhancement is directly related to the iodine content in an administered dose. Peak iodine plasma levels occur immediately following rapid injection. The time to maximum contrast enhancement can vary, depending on the organ, from the time that peak blood iodine concentrations are reached to one hour after intravenous bolus administration. When a delay between peak blood iodine concentrations and peak contrast is present, it suggests that radiographic contrast enhancement is at least in part dependent on the accumulation of iodine-containing medium within the lesion and outside the blood pool.
For angiography, contrast enhancement is greatest immediately (15 seconds to 120 seconds) after rapid injection. Iodinated contrast agents may be visualized in the renal parenchyma within 30-60 seconds following rapid intravenous injection. Opacification of the calyces and pelves in patients with normal renal function becomes apparent within 1-3 minutes, with optimum contrast occurring within 5-15 minutes.
Pharmacokinetics
Based on the blood clearance curves for 12 healthy volunteers (6 receiving 50 mL and 6 receiving 150 mL of Optiray 320), the biological half-life was 1.5 hours for both doses.
Distribution
In an in vitro human plasma study, ioversol did not bind to protein. The volume of distribution in adults was 0.26 L/kg body weight, consistent with distribution to the extracellular space.
Elimination
Metabolism
Ioversol does not undergo significant metabolism, deiodination or biotransformation.
Excretion
Greater than 95% of the administered dose was excreted in urine within the first 24 hours, with the peak urine concentration occurring in the first two hours after administration.
Animal Toxicology And/Or Pharmacology
Animal studies indicate that ioversol does not cross the blood-brain barrier.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
Patients receiving iodinated intravascular contrast agents should be instructed to:
- Inform your physician if you are pregnant.
- Inform your physician if you are diabetic or if you have multiple myeloma, pheochromocytoma, homozygous sickle cell disease or known thyroid disorder (see WARNINGS).
- Inform your physician if you are allergic to any drugs or food, or if you had any reactions to previous injections of dyes used for x-ray procedures (see PRECAUTIONS, General).
- Inform your physician about any other medications you are currently taking including non-prescription drugs.
