Milprosa Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: progesterone vaginal system
- Brand Name: Milprosa
side effects drug center milprosa (progesterone vaginal system) drug
Drug Description
What is Milprosa?
- Milprosa is a vaginal system that contains the hormone progesterone. Milprosa is for infertile women who need extra progesterone while undergoing treatment in an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) program. Progesterone is one of the hormones essential for helping you to become and to stay pregnant. If you are undergoing ART treatment, your healthcare provider may prescribe Milprosa to provide the progesterone your body needs.
- It is not known if Milprosa is safe and effective in children.
- It is not known if Milprosa is effective in women 35 years of age and older.
- It is not known if Milprosa is safe and effective in women with a high body mass index (BMI) greater than 38 kg/m2.
What are the possible side effects of Milprosa?
Milprosa may cause serious side effects, including:
- blood clots. Milprosa can increase your chance of getting blood clots. Blood clots can be serious and lead to death. Serious blood clots can happen in the:
- legs (thrombophlebitis)
- lungs (pulmonary embolus)
- eyes (loss of eyesight)
- heart (heart attack)
- brain (stroke)
Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have:
- leg pain that does not go away
- sudden shortness of breath
- sudden changes in vision or blindness
- severe pain or pressure in your chest
- blood in your spit when you cough
- sudden severe headache
- vomiting
- dizziness or feeling faint
- weakness in an arm or leg
- trouble speaking
- yellowing of the skin or the white of the eyes
- depression. Tell your healthcare provider if your symptoms of depression get worse while using Milprosa.
- toxic shock syndrome (TSS). Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if youhave the following symptoms:
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- muscles pain
- dizziness
- fainting
- a sunburn-like rash on your face and body
Common side effects of Milprosa include:
- headache
- vaginal discharge
- nausea
- breast tenderness
- discomfort after inserting the vaginal system
- stomach bloating
- stomach pain
- pelvic pain
- constipation
Other side effects of progesterone use include:
- mood swings
- irritability
- drowsiness
Call your healthcare provider immediately if you have abnormal vaginal bleeding.
These are not all the possible side effects of Milprosa. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
MILPROSA™
(progesterone) Vaginal System
DESCRIPTION
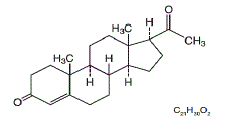
MILPROSA (progesterone) vaginal system is a white to off-white, flexible, non-biodegradable silicone ring (toroidalshaped) containing 1.78 grams of progesterone. MILPROSA has a cross-sectional diameter of approximately 8.5 mm, and an outer and inner diameter of approximately 55 mm and 38 mm, respectively.
The chemical name for progesterone is pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione. It has an empirical formula of C21H30O2 and a molecular weight of 314.5. Progesterone has a melting point of 126-131°C.
The structural formula is:
 |
When placed in the vagina, each vaginal system is estimated to provide an average release rate of 11 mg/day of progesterone over 7 days.
The inactive components of the vaginal system are light mineral oil and silicone elastomer.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
MILPROSA™ is indicated to support embryo implantation and early pregnancy (up to 10 weeks post-embryo transfer) by supplementation of corpus luteal function as part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) treatment program for infertile women up to and including 34 years of age.
Limitation Of Use
Efficacy in women 35 years of age and older has not been established.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Important Dosage And Administration Information
MILPROSA is not recommended for use with other vaginal products (such as antifungal products, vaginal lubricants, diaphragms, and condoms) because this concomitant use has not been studied and may alter the progesterone release and absorption from the vaginal system [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and DRUG INTERACTIONS].
Recommended Dosage And Administration
Insert one MILPROSA vaginal system starting on the day after oocyte retrieval. Leave in place continuously (for a minimum of 23 hours per day) for 7 days, then remove the used MILPROSA and insert a new MILPROSA. Replace MILPROSA weekly for up to 10 weeks.
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
Vaginal System
1.78 grams of progesterone in a white to off-white, flexible, non-biodegradable silicone ring (toroidalshape). MILPROSA has a cross-sectional diameter of approximately 8.5 mm, and an outer and inner diameter of approximately 55 mm and 38 mm, respectively. Each MILPROSA releases an average of 11 mg/day of progesterone when placed in the vagina over a 7-day period.
Storage And Handling
Each MILPROSA (progesterone) vaginal system is a white to off-white, flexible, non-biodegradable silicone ring (toroidal-shaped), which contains 1.78 grams of progesterone and releases an average of 11 mg/day of progesterone over a 7-day period of use. MILPROSA vaginal system has an inner and outer diameter of approximately 38 mm and 55 mm, respectively, and a cross-sectional diameter of approximately 8.5 mm.
Each MILPROSA is packed individually in a sealed foil pouch. These pouches are available in cartons packed:
- 2 vaginal systems per carton (NDC 55566-9400-1)
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not refrigerate or freeze and avoid excessive heat.
After use, place in pouch and discard via a drug take-back option if available; otherwise, mix with something undesirable, such as used coffee grounds, dirt, or cat litter to make it less appealing to children and pets. Place the mixture in something that can be closed (a re-sealable zipper storage bag, empty can, or other container) and discard in the household trash. DO NOT flush down toilet. See drug disposal information at www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for more information.
Manufactured For: Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. Parsippany, NJ 07054 USA. Revised: Apr 2020
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiovascular or Cerebrovascular Disorders [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Depression [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Toxic Shock Syndrome [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Clinical Study Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described in Table 1 reflect exposure to MILPROSA (up to 10 weeks) in 647 infertile women (80% Caucasian, 8% African-American, 5% Hispanic, 5% Asian) in a single prospective, randomized, active concurrently-controlled clinical trial of progesterone supplementation in women undergoing in-vitro fertilization (IVF) in the U.S. [see Clinical Studies]. Adverse reactions that occurred at a rate greater than or equal to 2% in the MILPROSA treatment group are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Number and Frequency of Adverse Reactions in Women Treated with MILPROSA in an Assisted Reproductive Technology Study (≥2%)
| Preferred Term | MILPROSA (N=647) |
| Headache | 44 (7%) |
| Vaginal discharge | 26 (4%) |
| Nausea | 25 (4%) |
| Breast tenderness | 24 (4%) |
| Post procedural discomfort | 24 (4%) |
| Abdominal distension | 22 (3%) |
| Abdominal pain | 19 (3%) |
| Pelvic pain | 19 (3%) |
| Constipation | 17 (3%) |
Additional safety data following exposure to MILPROSA was collected in a multi-center, non-comparative, open-label, single-arm study of women undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology in the U.S. The population consisted of 254 infertile women 18-34 years of age (83% Caucasian, 7% African-American, 9% Asian,1% American Indian) who were exposed up to 10 weeks. The adverse reaction profile was consistent with previous observations.
Adverse reactions associated with other drugs containing progesterone include bloating, mood swings, irritability, and drowsiness.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No formal drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted for MILPROSA. Drugs known to induce the hepatic CYP3A4 enzyme (such as rifampin, carbamazepine) may increase the elimination of progesterone. The effect of concomitant vaginal products on the exposure of progesterone from MILPROSA has not been assessed. MILPROSA is not recommended for use with other vaginal products (such as antifungal products, vaginal lubricants, diaphragms and condoms) as this may alter progesterone release and absorption from the vaginal system [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the "PRECAUTIONS" Section
PRECAUTIONS
Cardiovascular Or Cerebrovascular Disorders
Be alert to early signs of myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disorders, arterial or venous thromboembolism (venous thromboembolism or pulmonary embolism), thrombophlebitis, or retinal thrombosis in women using MILPROSA. Discontinue MILPROSA if any of these are suspected.
Depression
Observe closely women with a history of depression who use MILPROSA. Discontinue MILPROSA if symptoms of depression worsen.
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Cases of toxic shock syndrome (TSS) have been reported in women using vaginal systems with and without tampon use. No causal relationship between the use of MILPROSA and TSS has been established. Warning signs of TSS include fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain, dizziness, faintness or a sunburn-like rash on face and body. Discontinue MILPROSA if TSS is suspected. and initiate appropriate medical evaluation and treatment.
Use Of Other Vaginal Products
Concomitant use of MILPROSA with other vaginal products (such as antifungal products, vaginal lubricants, diaphragms and condoms) has not been studied; these products may alter progesterone release and absorption from MILPROSA [see DRUG INTERACTIONS]. If possible, avoid use of other vaginal products with MILPROSA.
Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Inform women:
- Of the importance of reporting irregular vaginal bleeding to their doctor as soon as possible.
- Of the possible side effects of progesterone therapy such as headaches, abdominal pain, breast tenderness, bloating, mood swings, irritability, and drowsiness.
- To leave the vaginal system in place continuously (for a minimum of 23 hours per day) [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION]. It may be removed for sexual intercourse, although this is not necessary.
- MILPROSA is not recommended for use with other vaginal products (such as antifungal products, vaginal lubricants, diaphragms, and condoms) as this concomitant use has not been studied and may alter the progesterone release and absorption from the vaginal system [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and DRUG INTERACTIONS].
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Nonclinical toxicity studies to determine the potential of MILPROSA to cause carcinogenicity or mutagenicity have not been performed. The effect of MILPROSA on fertility has not been evaluated in animals.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
MILPROSA is indicated to support embryo implantation and early pregnancy as part of an assisted reproductive technology treatment program in vitro fertilization (IVF) with or without intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and embryo transfer for infertile women. Maternal risks are discussed throughout the labeling.
In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
MILPROSA has been used to support embryo implantation during the first trimester of pregnancy and to maintain clinical pregnancy as part of an ART regimen. Exposure in pregnancy with use of MILPROSA occurs from implantation of an embryo through week 10 of pregnancy when the placenta takes over production of progesterone.
In clinical trials, among 813 women less than 35 years of age who were treated with MILPROSA, 75 (9.2%) had a spontaneous abortion and 6 (0.7%) had an ectopic pregnancy. Of the 813 women less than 35 years of age, 559 (68.8%) were planned to be followed through birth. Among the 559 to be followed through birth, 263 (47.0%) had livebirths consisting of 154 (58.6%) singletons, 102 (38.8%) twins, and 7 (2.7%) triplets. In this same cohort of treatment, 10 (1.8%) had a second or third trimester loss. Neonatal birth defects were reported in 8 (2.1%) of infants based on 379 liveborn infants. In the 2.1% of live born infants with birth defects for women less than 35 years of age treated with MILPROSA the following were noted: Turner’s syndrome; Tetralogy of Fallot; and congenital anomalies including left foot deformity, hypospadias, pyloric stenosis, spina bifida, multiple congenital anomalies, and multiple congenital anomalies with VACTERL association.
Lactation
Risk Summary
Detectable amounts of progesterone have been identified in the milk of nursing mothers. The effect of this on the nursing infant has not been determined. A published study reported no adverse effects of progesterone on milk production or infant growth during the first postpartum year. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for MILPROSA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from MILPROSA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of MILPROSA have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of MILPROSA did not include women 65 years of age and older. MILPROSA is not indicated in this population.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
The safety and efficacy of MILPROSA in women with a BMI >38 kg/m2 has not been studied.
Hepatic Impairment
MILPROSA has not been studied in women with hepatic impairment.
Overdosage & ContraindicationsWhat is Milprosa?
- Milprosa is a vaginal system that contains the hormone progesterone. Milprosa is for infertile women who need extra progesterone while undergoing treatment in an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) program. Progesterone is one of the hormones essential for helping you to become and to stay pregnant. If you are undergoing ART treatment, your healthcare provider may prescribe Milprosa to provide the progesterone your body needs.
- It is not known if Milprosa is safe and effective in children.
- It is not known if Milprosa is effective in women 35 years of age and older.
- It is not known if Milprosa is safe and effective in women with a high body mass index (BMI) greater than 38 kg/m2.
What are the possible side effects of Milprosa?
Milprosa may cause serious side effects, including:
- blood clots. Milprosa can increase your chance of getting blood clots. Blood clots can be serious and lead to death. Serious blood clots can happen in the:
- legs (thrombophlebitis)
- lungs (pulmonary embolus)
- eyes (loss of eyesight)
- heart (heart attack)
- brain (stroke)
Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have:
- leg pain that does not go away
- sudden shortness of breath
- sudden changes in vision or blindness
- severe pain or pressure in your chest
- blood in your spit when you cough
- sudden severe headache
- vomiting
- dizziness or feeling faint
- weakness in an arm or leg
- trouble speaking
- yellowing of the skin or the white of the eyes
- depression. Tell your healthcare provider if your symptoms of depression get worse while using Milprosa.
- toxic shock syndrome (TSS). Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if youhave the following symptoms:
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- muscles pain
- dizziness
- fainting
- a sunburn-like rash on your face and body
Common side effects of Milprosa include:
- headache
- vaginal discharge
- nausea
- breast tenderness
- discomfort after inserting the vaginal system
- stomach bloating
- stomach pain
- pelvic pain
- constipation
Other side effects of progesterone use include:
- mood swings
- irritability
- drowsiness
Call your healthcare provider immediately if you have abnormal vaginal bleeding.
These are not all the possible side effects of Milprosa. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
OVERDOSE
No Information Provided
CONTRAINDICATIONS
MILPROSA is contraindicated in women with:
- Known sensitivity to progesterone or any of the ingredients of MILPROSA [see DESCRIPTION]
- Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding
- Severe hepatic impairment or disease
- Known or suspected malignancy of the breast
- Active arterial or venous thromboembolism or severe thrombophlebitis, or a history of these events
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
Progesterone is a naturally occurring steroid that is secreted by the ovary, placenta, and adrenal gland. In the presence of adequate estrogen, progesterone transforms a proliferative endometrium into a secretory endometrium. Progesterone is necessary to increase endometrial receptivity for implantation of an embryo. Once an embryo is implanted, progesterone acts to maintain a pregnancy.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Progesterone plasma concentrations increased following the administration of MILPROSA vaginal system to 30 healthy postmenopausal females (inserted once a week for two weeks) (MILPROSA is not indicated in postmenopausal females). The 30 subjects were pre-treated with 1 mg oral estradiol tablets once a day for 28 days prior to MILPROSA treatment and during MILPROSA treatment to manage postmenopausal vaginal atrophy. Steady state concentrations were attained 96 hours after initiation of treatment with MILPROSA. After reaching steady state, MILPROSA provided average baseline-adjusted plasma concentrations of progesterone exceeding 8 ng/mL. The pharmacokinetic results are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Mean (± Standard Deviation) Baseline-Adjusted Plasma Progesterone Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | MILPROSA |
| First MILPROSA Vaginal System (n=30), 0 to 168 hours | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 9.33 ± 2.80 |
| Tmax (hr) | 134.80 ± 49.17 |
| AUC0-168 hr (ng•hr/mL) | 1188.41 ± 374.25 |
| Cavg,ss 96-168hr (ng/mL) | 8.05 ± 2.50 |
| Second MILPROSA Vaginal System (n=27, *n=22), 168 to 336 hours | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 10.66 ± 2.72 |
| Tmax (hr) | 206.15 ± 56.33 |
| Cmin (ng/mL) | 6.33 ± 1.80 |
| Cavg,ss 168-336hr (ng/mL) | 8.20 ± 2.15 |
| AUC168-336 hr (ng•hr/mL) | 1377.59 ± 362.00 |
| AUC168-inf (ng•hr/mL) | 1382.62 ± 387.81 |
| Kel (hr-1) | 0.07 ± 0.02 |
| T1/2 (hr) | 10.82 ± 4.27 |
| Cmax Maximum progesterone concentration. Tmax Time to maximum progesterone concentration. Cavg Average progesterone concentration at steady state. AUC0-168hr Area under the drug concentration versus time curve from 0-168 hours post dose. AUC168-336 hr Area under the drug concentration versus time curve from 168 hours to 336 hours after initiation of treatment AUC168-inf Area under the drug concentration versus time curve from 168 hours after initiation of treatment to infinite time Kel Elimination rate constant T1/2 Terminal elimination half-life Cmin Minimum progesterone concentration. | |
Distribution
Progesterone is approximately 95% to 98% bound to serum proteins, primarily to serum albumin and corticosteroid binding globulin.
Elimination
The mean (± standard deviation) elimination half-life of progesterone delivered by MILPROSA is 10.82 ± 4.27 hours.
Metabolism
Progesterone is metabolized primarily by the liver largely to pregnanediols and pregnanolones, which are conjugated to glucuronide and sulfate metabolites [See CONTRAINDICATIONS].
Excretion
Progesterone undergoes both biliary and renal elimination. Following an intravenous injection of labeled progesterone, 50%-60% of the excretion of metabolites occurs via the kidney; approximately 10% occurs via the bile and feces. Overall recovery of the labeled material accounts for 70% of an administered dose. Only 0.1% of unchanged progesterone is excreted in the bile.
Clinical Studies
Luteal Supplementation During Assisted Reproductive Treatment Trial
A single prospective, randomized, assessor-blind, active concurrently -controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of 10 weeks of treatment with MILPROSA for support of implantation and early pregnancy in infertile women participating in an Assisted Reproductive Technology treatment program. Women were eligible for the trial if there was tubal, idiopathic, male factor, ovulatory dysfunction or endometriosis-linked infertility, documentation of a normal uterine cavity within 1 year of screening, and a source of fresh or frozen sperm meeting standard criteria. Women were not included in the trial if they had conditions which contraindicated the use of progesterone; hypersensitivity or intolerance to silicone; history of pelvic irradiation, endometrial cancer, toxic shock syndrome, more than one failed fresh in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycle, more than two consecutive clinically recognized miscarriages, or HIV/AIDS; uncontrolled hypertension, hyperprolactinemia, or hypothyroidism; body mass index (BMI) greater than 38 kg/m2, clinically significant endometrial pathology or a communicating hydrosalpinx; and a male partner with non-obstructive azoospermia for couples using fresh sperm.
Prior to IVF with or without intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), eligible women were started on an ovarian down-regulation protocol which begin during the cycle immediately prior to the embryo transfer cycle. Ovarian stimulation with gonadotropins products was begun once down-regulation was achieved. The length of stimulation was individualized per the trial investigational site’s standard protocol(s), and/or the trial investigator’s clinical judgment. During stimulation, the participating woman was monitored to determine when to trigger ovulation with human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Egg retrieval occurred approximately 35 to 37 hours after hCG administration. On the day after egg retrieval, at the time of consent, eligible women were stratified by age and randomized in a 1:1 ratio to MILPROSA, one vaginal insert every week, or the active comparator once daily. Embryo transfer occurred 3 to 5 days after egg retrieval. A serum pregnancy test was conducted 2 weeks after egg retrieval. Women whose serum ß-hCG was less than 5 mIU were discontinued from the study. Those with a serum ß-hCG greater than 5 continued dosing with MILPROSA or active comparator for up to a total of 10 weeks (i.e., through 12 weeks of pregnancy).
Efficacy was assessed by the co-primary endpoints of clinically recognized pregnancy rate, defined as the presence of at least one fetal heartbeat seen on ultrasound at 6 weeks and at 10 weeks post-embryo transfer. The trial randomized 646 infertile women to the MILPROSA vaginal system arm and 651 infertile women to the active control arm. Women receiving MILPROSA were 80% Caucasian, 8% African-American, 5% Hispanic, 5% Asian) and between 20 and 42 years of age (mean age 31.7) with a body mass index of 38 kg/m2 or less at screening. Women in the active control arm demonstrated similar demographics.
The primary efficacy analysis set was the modified intent-to-treat population (MITT), which included all women having successful egg retrieval and having at least one dose of progesterone. Women who terminated the study prior to 6 weeks after egg retrieval were considered treatment failures at both 6 and 10 weeks. The clinical pregnancy rates at Weeks 6 and 10 were compared between the MILPROSA arm and the active comparator arm at a one-sided alpha of 0.025. The 95% confidence interval (CI) for the difference in pregnancy rate was calculated using the normal approximation method. Treatment with MILPROSA was declared non-inferior to the active comparator if the lower bound of the 95% CI for the difference in pregnancy rate was greater than -10% based on MITT population. The results with the MILPROSA treatment are shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Clinical Pregnancy Rates in Patients Receiving MILPROSA for Luteal Supplementation and Early Pregnancy While in an Assisted Reproductive Technology Treatment Program (NCT00615251).
| MILPROSA (N=646) | |
| 6 weeks post-embryo transfer | |
| Clinical Pregnancy: n (%) | 310 (48.0%) |
| Pregnancy rate percentage difference between MILPROSA and comparator | 0.8% |
| 95% Confidence Interval for difference vs. comparator | (-4.6%, 6.3%) |
| 10 weeks post-embryo transfer | |
| Clinical Pregnancy: n (%) | 300 (46.4%) |
| Pregnancy rate percentage difference between MILPROSA and comparator | 1.3% |
| 95% Confidence Interval for difference vs. comparator | (-4.1%, 6.7%) |
The pregnancy rates at Week 6 and Week 10 post embryo transfer for women treated with MILPROSA were non-inferior to those for women treated with the active comparator.
Women participating in the trial were stratified at randomization by age. The co-primary endpoints of the clinical pregnancy rate at Weeks 6 and 10 post embryo transfer were also evaluated by age groups 18-34 and 35-42. In women under the age of 35, the pregnancy rates with MILPROSA were 49.3 % and 48.2% respectively at Weeks 6 and 10 post embryo transfer and these rates were non-inferior to the rates for women treated with the active comparator and evaluated at the same time points. The trial was insufficiently powered to provide meaningful comparisons for women age 35 and older.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
MILPROSA
(mil-PRO-sah)
(progesterone) vaginal system
Read this Patient Information before you start using MILPROSA and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. Your healthcare provider may do a physical examination before prescribing MILPROSA.
What is MILPROSA?
- MILPROSA is a vaginal system that contains the hormone progesterone. MILPROSA is for infertile women who need extra progesterone while undergoing treatment in an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) program. Progesterone is one of the hormones essential for helping you to become and to stay pregnant. If you are undergoing ART treatment, your healthcare provider may prescribe MILPROSA to provide the progesterone your body needs.
- It is not known if MILPROSA is safe and effective in children.
- It is not known if MILPROSA is effective in women 35 years of age and older.
- It is not known if MILPROSA is safe and effective in women with a high body mass index (BMI) greater than 38 kg/m2.
Do not use MILPROSA if you:
- are allergic to progesterone or any ingredients in MILPROSA. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients.
- have unusual vaginal bleeding that has not been evaluated by your healthcare provider.
- have or have had liver disease.
- have known or suspected breast cancer.
- have or have had blood clots in the legs, lungs, eyes, or anywhere else in your body.
Before you use MILPROSA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have a history of heart problems or heart disease including a heart attack, stroke, and blood clots.
- have a history of depression.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. MILPROSA may pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you use MILPROSA.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Some medicines may affect MILPROSA.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you:
- use other vaginal products, such as antifungal products, vaginal lubricants, diaphragms, and condoms.
- take CYP inducers such as rifampin and carbamazepine.
Talk with your healthcare provider if you are not sure if you take these medicines. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use MILPROSA?
- Read the Instructions for Use at the end of this Patient Information that comes with MILPROSA for information about the right way to insert, remove, and throw away MILPROSA.
- Use MILPROSA exactly as prescribed. The usual dose of MILPROSA is 1 system placed in your vagina for 7 continuous days, and replaced weekly for a total of 10 weeks, unless your healthcare provider tells you something different.
- MILPROSA should remain in place for a minimum of 23 hours each day. It may be removed for sexual intercourse, although this is not necessary.
- Do not use any other vaginal products such as antifungal products, vaginal lubricants, diaphragms, and condoms when using the MILPROSA vaginal system.
What are the possible side effects of MILPROSA?
MILPROSA may cause serious side effects, including:
- blood clots. MILPROSA can increase your chance of getting blood clots. Blood clots can be serious and lead to death. Serious blood clots can happen in the:
- legs (thrombophlebitis)
- lungs (pulmonary embolus)
- eyes (loss of eyesight)
- heart (heart attack)
- brain (stroke)
Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have:
- leg pain that does not go away
- sudden shortness of breath
- sudden changes in vision or blindness
- severe pain or pressure in your chest
- blood in your spit when you cough
- sudden severe headache
- vomiting
- dizziness or feeling faint
- weakness in an arm or leg
- trouble speaking
- yellowing of the skin or the white of the eyes
- depression. Tell your healthcare provider if your symptoms of depression get worse while using MILPROSA.
- toxic shock syndrome (TSS). Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if youhave the following symptoms:
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- muscles pain
- dizziness
- fainting
- a sunburn-like rash on your face and body
Common side effects of MILPROSA include:
- headache
- vaginal discharge
- nausea
- breast tenderness
- discomfort after inserting the vaginal system
- stomach bloating
- stomach pain
- pelvic pain
- constipation
Other side effects of progesterone use include:
- mood swings
- irritability
- drowsiness
Call your healthcare provider immediately if you have abnormal vaginal bleeding.
These are not all the possible side effects of MILPROSA. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store MILPROSA?
- Store MILPROSA at room temperature between 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Do not put MILPROSA in the refrigerator.
- Do not freeze MILPROSA.
- Avoid excessive heat.
- Keep MILPROSA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of MILPROSA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. Do not use MILPROSA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give MILPROSA to other women, even if they have the same condition as you do. It may harm them.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about MILPROSA that is written for healthcare professionals.
What are the ingredients in MILPROSA?
Active ingredient: progesterone.
Inactive ingredients: light mineral oil, silicone elastomer.
Instructions for Use
MILPROSA
(mil-PRO-sah)
(progesterone) vaginal system
Read this Instructions for Use carefully before you use MILPROSA and each time you get a refill. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider who specializes in women’s health. If you have any questions about MILPROSA, ask your healthcare provider.
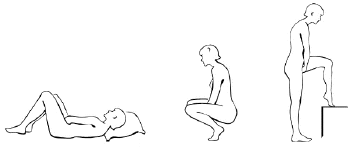
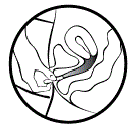
Follow the steps below to insert MILPROSA:
 |
 |
 |
 |
You do not need to use anything else to place MILPROSA in the correct position. MILPROSA will change shape to fit your body. The exact position of MILPROSA is not important. The muscles of your vagina will keep MILPROSA securely in place. If you have difficulty inserting MILPROSA, it is fine to rinse the MILPROSA with cool to lukewarm (not hot) water before inserting it.
- Wash and dry your hands.
- Remove the MILPROSA vaginal system from its foil pouch. Keep the foil pouch so you can place your used MILPROSA in it before you throw it away. See “To throw away (dispose of) MILPROSA” instructions at the end of this Instructions for Use.
- Choose the position that is most comfortable for you such as lying down, squatting, or standing with 1 leg up.
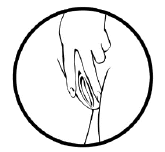
- Hold MILPROSA between your thumb and index finger and gently squeeze the sides of MILPROSA together.
- Use your other hand and hold open the folds of skin around your vagina.
- Place the tip of MILPROSA in the vaginal opening and then use your index finger to push the folded MILPROSA gently into your vagina. Push MILPROSA up towards your lower back as far as you can. If you can feel MILPROSA, it may not be placed back far enough in your vagina. Use your index finger to push MILPROSA back a bit further. Put MILPROSA where it is comfortable for you. There is no danger of MILPROSA being pushed too far up in the vagina or getting lost.
In 7 days remove the old MILPROSA and replace with a new MILPROSA.
MILPROSA should remain in place for a minimum of 23 hours each day. You can remove MILPROSA for sexual intercourse, although this is not necessary.
If MILPROSA is expelled, removed, or dropped, it should be rinsed with cool to lukewarm (not hot) water and reinserted as soon as possible, except if MILPROSA touches or has feces on it. If MILPROSA touches or has feces on it, replace it with a new MILPROSA.
To remove MILPROSA:
- Wash your hands.
- Choose the position that is the most comfortable for you such as lying down, squatting, or standing with 1 leg up.
- Put a finger into your vagina and hook it through MILPROSA.
- Gently pull downwards and forward to remove MILPROSA.
 |
To throw away (dispose of) MILPROSA:
- Place the used MILPROSA in the foil pouch. If available, throw it away through a drug take-back option.
or - Place the used MILPROSA in the foil pouch and mix it with coffee grounds, dirt or cat litter.
- Place the foil pouch mixture in something that can be closed like a zipper storage bag, empty can, or other container and throw it away in your household trash out of the reach of children and pets.
- Do not flush the foil pouch down the toilet.
For more information on drug disposal see www.fda.gov/drugdisposal.
If you have other questions call your healthcare provider.
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
