Dextenza Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: dexamethasone ophthalmic insert
- Brand Name: Dextenza
side effects drug center dextenza (dexamethasone ophthalmic insert) drug
Drug Description
What is Dextenza and how is it used?
Dextenza is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of Ocular Pain and Inflammation. Dextenza may be used alone or with other medications.
Dextenza belongs to a class of drugs called Corticosteroids, Ophthalmic.
It is not known if Dextenza is safe and effective in children.
What are the possible side effects of Dextenza?
Dextenza may cause serious side effects including:
- hives,
- difficulty breathing,
- swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat,
- eye pain or redness,
- blurred vision,
- tunnel vision,
- seeing halos around lights,
- cloudy or hazy vision,
- eyebrow pain,
- changes in the shape of your pupil,
- increased sensitivity of your eyes to light,
- swelling of the eye,
- redness in the eye,
- severe discomfort in the eye, and
- crusting or drainage from the eye
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Dextenza include:
- vision problems,
- seeing “floaters” in your vision,
- eye pain or redness,
- feeling like something is in your eye,
- eyelid swelling,
- dry eyes,
- headache, and
- your eyes may be more sensitivity to light
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Dextenza. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
DESCRIPTION
DEXTENZA (dexamethasone ophthalmic insert) is a fluorescent yellow, 3 mm cylindrical-shaped, resorbable, sterile insert for intracanalicular use. DEXTENZA contains 0.4 mg dexamethasone in a polyethylene glycol (PEG) based hydrogel conjugated with fluorescein. DEXTENZA does not contain an antimicrobial preservative. The active ingredient is represented by the chemical structure:
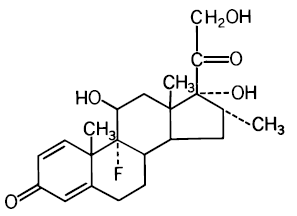 |
The chemical name for dexamethasone is 9-Fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16α-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione. It has a molecular formula of C22H29FO5 and a molecular weight of 392.47 g/mol. Dexamethasone is a crystalline powder.
Each DEXTENZA Contains
Active Ingredients
0.4 mg dexamethasone.
Inactive Ingredients
4-arm polyethylene glycol (PEG) N-hydroxysuccinimidyl glutarate (20K), trilysine acetate, N-hydroxysuccinimide-fluorescein, sodium phosphate dibasic, sodium phosphate monobasic, water for injection.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
DEXTENZA® (dexamethasone ophthalmic insert) is a corticosteroid indicated for the treatment of ocular inflammation and pain following ophthalmic surgery (1).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
General Dosing Information
DEXTENZA is an ophthalmic insert that is inserted in the lower lacrimal punctum into the canaliculus. A single DEXTENZA insert releases a 0.4 mg dose of dexamethasone for up to 30 days following insertion.
DEXTENZA is resorbable and does not require removal. Saline irrigation or manual expression can be performed to remove the insert if necessary. DEXTENZA is intended for single-use only.
Administration
Do not use if pouch has been damaged or opened. Do not re-sterilize.
- Carefully remove foam carrier and transfer to a clean and dry area.
- If necessary, dilate the punctum with an ophthalmic dilator. Care should be taken not to perforate the canaliculus during dilation or insertion of DEXTENZA. If perforation occurs, do not insert DEXTENZA.
- After drying the punctal area, using blunt (non-toothed) forceps, grasp DEXTENZA and insert into the lower lacrimal canaliculus. DEXTENZA should be placed just below the punctal opening. Excessive squeezing of DEXTENZA may cause deformation.
- To aid in the hydration of DEXTENZA, 1 to 2 drops of balanced salt solution can be instilled into the punctum. DEXTENZA hydrates quickly upon contact with moisture. If DEXTENZA begins to hydrate before fully inserted, discard the product and use a new DEXTENZA.
- DEXTENZA can be visualized when illuminated by a blue light source (e.g., slit lamp or hand held blue light) with yellow filter.
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
Ophthalmic insert: fluorescent yellow, 3 mm cylindrical-shaped insert containing dexamethasone, 0.4 mg.
Storage And Handling
DEXTENZA is supplied sterile in a foam carrier within a foil laminate pouch containing:
NDC 70382-204-10 - Carton containing 10 pouches (10 inserts)
NDC 70382-204-01 - Carton containing 1 pouch (1 insert)
Do not use if pouch has been damaged or broken.
DEXTENZA is intended for single dose only.
Storage
Store refrigerated, between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F). Do not freeze. Protect from light, keep in package until use.
Manufactured by: Ocular Therapeutix, Inc. Bedford, MA 01730 USA. Revised: Jun 2019
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Intraocular Pressure Increase [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Bacterial Infection [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Viral Infection [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Fungal Infection [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Delayed Healing [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. Adverse reactions associated with ophthalmic steroids include elevated intraocular pressure, which may be associated with optic nerve damage, visual acuity and field defects, posterior subcapsular cataract formation; delayed wound healing; secondary ocular infection from pathogens including herpes simplex, and perforation of the globe where there is thinning of the cornea or sclera [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
DEXTENZA was studied in four randomized, vehicle-controlled studies (n = 567). The mean age of the population was 68 years (range 35 to 87 years), 59% were female, and 83% were white. Forty-seven percent had brown iris color and 30% had blue iris color. The most common ocular adverse reactions that occurred in patients treated with DEXTENZA were: anterior chamber inflammation including iritis and iridocyclitis (10%); intraocular pressure increased (6%); visual acuity reduced (2%); cystoid macular edema (1%); corneal edema (1%); eye pain (1%) and conjunctival hyperemia (1%).
The most common non-ocular adverse reaction that occurred in patients treated with DEXTENZA was headache (1%).
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No Information Provided
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the "PRECAUTIONS" Section
PRECAUTIONS
Intraocular Pressure Increase
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may result in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision. Steroids should be used with caution in the presence of glaucoma. Intraocular pressure should be monitored during the course of the treatment.
Bacterial Infection
Corticosteroids may suppress the host response and thus increase the hazard for secondary ocular infections. In acute purulent conditions, steroids may mask infection and enhance existing infection [see CONTRAINDICATIONS].
Viral Infections
Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex) [see CONTRAINDICATIONS].
Fungal Infections
Fungus invasion must be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where a steroid has been used or is in use. Fungal culture should be taken when appropriate [see CONTRAINDICATIONS].
Delayed Healing
The use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
No adequate studies in animals have been conducted to determine whether DEXTENZA has the potential for carcinogenesis.
Dexamethasone was not mutagenic in the Ames/Salmonella assay, both with and without metabolic activation. Dexamethasone was genotoxic in two in vitro assays using human lymphocytes (chromosomal aberration assay and sister chromatid exchange assay) and was genotoxic in two mouse in vivo assays (micronucleus assay and sister chromatid exchange assay).
Fertility studies have not been conducted in animals using DEXTENZA.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate or well-controlled studies with DEXTENZA in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. In animal reproduction studies, administration of topical ocular dexamethasone to pregnant mice and rabbits during organogenesis produced embryofetal lethality, cleft palate and multiple visceral malformations [see Animal Data].
Data
Animal Data
Topical ocular administration of 0.15% dexamethasone (0.75 mg/kg/day) on gestational days 10 to 13 produced embryofetal lethality and a high incidence of cleft palate in a mouse study. A daily dose of 0.75 mg/kg/day in the mouse is approximately 5 times the entire dose of dexamethasone in the DEXTENZA product, on a mg/m2 basis. In a rabbit study, topical ocular administration of 0.1% dexamethasone throughout organogenesis (0.36 mg /day, on gestational day 6 followed by 0.24 mg/day on gestational days 7-18) produced intestinal anomalies, intestinal aplasia, gastroschisis and hypoplastic kidneys. A daily dose of 0.24 mg/day is approximately 6 times the entire dose of dexamethasone in the DEXTENZA product, on a mg/m2 basis.
Lactation
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth and interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production; however the systemic concentration of dexamethasone following administration of DEXTENZA is low [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY]. There is no information regarding the presence of DEXTENZA in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or the effects of the drug on milk production to inform risk of DEXTENZA to an infant during lactation. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for DEXTENZA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from DEXTENZA.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
No Information Provided
CONTRAINDICATIONS
DEXTENZA is contraindicated in patients with active corneal, conjunctival or canalicular infections, including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, varicella; mycobacterial infections; fungal diseases of the eye, and dacryocystitis.
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
Dexamethasone, a corticosteroid, has been shown to suppress inflammation by inhibiting multiple inflammatory cytokines resulting in decreased edema, fibrin deposition, capillary leakage and migration of inflammatory cells.
Pharmacokinetics
Plasma samples were obtained from 16 healthy volunteers prior to insertion of DEXTENZA and on Day 1 (at 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 hours), 2 (24 hours), 4, 8, 15, 22 and 29 following the insertion of DEXTENZA.
Plasma concentrations of dexamethasone were detectable (above 50 pg/mL, the lower limit of quantification of the assay) in 11% of samples (21 of 189), and ranged from 0.05 ng/mL to 0.81 ng/mL.
Clinical Studies
In three randomized, multicenter, double-masked, parallel group, vehicle-controlled trials, patients received DEXTENZA or its vehicle immediately upon completion of cataract surgery. In all three trials, DEXTENZA had a higher proportion of patients than the vehicle group who were pain free on post-operative Day 8. On post-operative Day 14, in two of the three studies, DEXTENZA had a higher proportion of patients than the vehicle group who had an absence of anterior chamber cells that was statistically significant. Results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1: Percentage of Patients with Absence of Anterior Chamber Cells
| Study 1 | Study 2 | Study 3 | |||||||
| Visit | DEXTENZA (N=164) n (%) |
Vehicle (N=83) n (%) |
Difference (95% CI) |
DEXTENZA (N=161) n (%) |
Vehicle (N=80) n (%) |
Difference (95% CI) |
DEXTENZA (N=216) n (%) |
Vehicle (N=222) n (%) |
Difference (95% CI) |
| Day 14 | 54 (33%) | 12 (14%) | 18% (8%, 29%) | 63 (39%) | 25 (31%) | 8% (-5%, 21%) | 113 (52%) | 69 (31%) | 21 % (12%, 30%) |
Table 2: Percentage of Patients with Absence of Pain
| Study 1 | Study 2 | Study 3 | |||||||
| Visit | DEXTENZA (N=164) n (%) |
Vehicle (N=83) n (%) |
Difference (95% CI) |
DEXTENZA (N=161) n (%) |
Vehicle (N=80) n (%) |
Difference (95% CI) |
DEXTENZA (N=216) n (%) |
Vehicle (N=222) n (%) |
Difference (95% CI) |
| Day 8 | 131 (80%) | 36 (43%) | 37% (24%, 49%) | 124 (77%) | 47 (59%) | 18% (6%, 31%) | 172 (80%) | 136 (61%) | 18% (10%, 27%) |
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
Advise patients to consult their surgeon if pain, redness, or itching develops.
