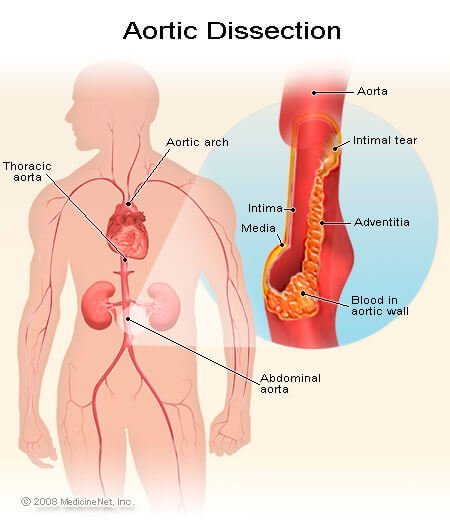
Definition of Aortic dissection
Aortic dissection: A progressive tear in the aorta. The inner lining (intima) of the aorta tears and blood surges through the tear, creating a new false channel and separating (dissecting) the middle layer (media) from the outer layer of the aorta.
Aortic dissection usually occurs in the thoracic aorta, less often the abdominal aorta. About three-fourths of aortic dissections occur in men and in people 40 to 70 years of age.
Risk factors that predispose to aortic dissection include high blood pressure, genetic disorders of connective tissue such as Marfan syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, aortic insufficiency (a leaky aortic valve), coarctation (congenital narrowing) of the aorta, and arteriosclerosis.
The key symptom of aortic dissection is sudden severe tearing pain, usually across the chest and in the back between the shoulder blades. An aortic dissection that does not stop tearing is fatal.
Treatment is often a matter of urgency. It may involve medication to lower blood pressure, surgical repair to replace the damaged portion of the blood vessel with a synthetic graft, or the placement of a stent or graft using a catheter.
Also called a dissecting aneurysm of the aorta.
Picture of Aortic Dissection