Definition of Breast
Breast: The breast refers to the front of the chest or, more specifically, to the mammary gland. The mammary gland is a milk producing gland. It is composed largely of fat. Within the mammary gland is a complex network of branching ducts. These ducts exit from sac-like structures called lobules, which can produce milk in females. The ducts exit the breast at the nipple.
The breast has been viewed as an organ designed to produce milk. The lobules are the glands that produce the breast milk. The ducts are tubes or channels which transport the milk from these glands out to the nipple. The nipple becomes erect because of cold, breast feeding and sexual activity. The pigmented area around the nipple is called the areola.
The lobules and ducts are supported in the breast by surrounding fatty tissue and ligaments. There are no muscles in the breast.
There are blood vessels and lymphatics in the breast. The lymphatics are thin channels similar to blood vessels; they do not carry blood but collect and carry tissue fluid which ultimately reenters the blood stream. Breast tissue fluid drains through the lymphatics into the lymph nodes located in the underarm (axilla) and behind the breast bone (sternum).
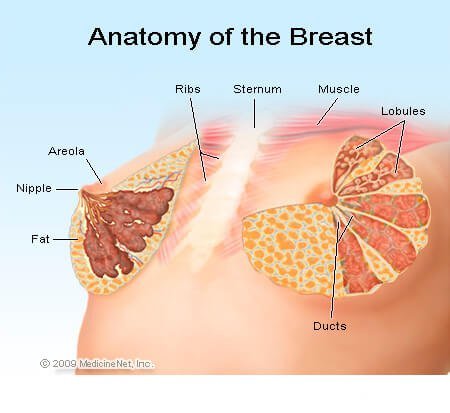
Picture of the anatomy of the breast
