Danocrine Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: danazol
- Brand Name: Danocrine
side effects drug center danocrine (danazol) drug
Drug Description
DANOCRINE®
(Danazol) Capsules, USP
DESCRIPTION
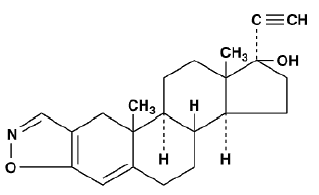
DANOCRINE, brand of danazol, is a synthetic steroid derived from ethisterone. It is a white to pale yellow crystalline powder, practically insoluble or insoluble in water, and sparingly soluble in alcohol. Chemically, danazol is 17α-Pregna-2,4-dien-20-yno [2,3-d]isoxazol-17-ol. The molecular formula is C22H27NO2. It has a molecular weight of 337.46 and the following structural formula:
 |
Danocrine capsules for oral administration contain 50 mg, 100 mg or 200 mg danazol.
Inactive Ingredients: Corn Starch, Lactose, Magnesium Stearate, Talc. Capsules 50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg contain D&C Yellow #10, FD&C Red #40, Gelatin, Silicon Dioxide, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Titanium Dioxide. The 50 mg and 200 mg capsules also contain D&C Red #28.
Indications
Endometriosis
DANOCRINE is indicated for the treatment of endometriosis amenable to hormonal management.
Fibrocystic Breast Disease
Most cases of symptomatic fibrocystic breast disease may be treated by simple measures (e.g., padded brassieres and analgesics).
In infrequent patients, symptoms of pain and tenderness may be severe enough to warrant treatment by suppression of ovarian function. DANOCRINE is usually effective in decreasing nodularity, pain, and tenderness. It should be stressed to the patient that this treatment is not innocuous in that it involves considerable alterations of hormone levels and that recurrence of symptoms is very common after cessation of therapy.
Hereditary Angioedema
DANOCRINE is indicated for the prevention of attacks of angioedema of all types (cutaneous, abdominal, laryngeal) in males and females.
Dosage
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Endometriosis
In moderate to severe disease, or in patients infertile due to endometriosis, a starting dose of 800 mg given in two divided doses is recommended. Amenorrhea and rapid response to painful symptoms is best achieved at this dosage level. Gradual downward titration to a dose sufficient to maintain amenorrhea may be considered depending upon patient response. For mild cases, an initial daily dose of 200 mg to 400 mg given in two divided doses is recommended and may be adjusted depending on patient response.
Therapy should begin during menstruation. Otherwise, appropriate tests should be performed to ensure that the patient is not pregnant while on therapy with DANOCRINE. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS.) It is essential that therapy continue uninterrupted for 3 to 6 months but may be extended to 9 months if necessary. After termination of therapy, if symptoms recur, treatment can be reinstituted.
Fibrocystic Breast Disease
The total daily dosage of DANOCRINE for fibrocystic breast disease ranges from 100 mg to 400 mg given in two divided doses depending upon patient response. Therapy should begin during menstruation. Otherwise, appropriate tests should be performed to ensure that the patient is not pregnant while on therapy with DANOCRINE. A nonhormonal method of contraception is recommended when DANOCRINE is administered at this dose, since ovulation may not be suppressed.
In most instances, breast pain and tenderness are significantly relieved by the first month and eliminated in 2 to 3 months. Usually elimination of nodularity requires 4 to 6 months of uninterrupted therapy. Regular menstrual patterns irregular menstrual patterns and amenorrhea each occur in approximately one-third of patients treated with 100 mg of DANOCRINE. Irregular menstrual patterns and amenorrhea are observed more frequently with higher doses. Clinical studies have demonstrated that 50% of patients may show evidence of recurrence of symptoms within one year. In this event, treatment may be reinstated.
Hereditary Angioedema
The dosage requirements for continuous treatment of hereditary angioedema with DANOCRINE should be individualized on the basis of the clinical response of the patient. It is recommended that the patient be started on 200 mg, two or three times a day. After a favorable initial response is obtained in terms of prevention of episodes of edematous attacks, the proper continuing dosage should be determined by decreasing the dosage by 50% or less at intervals of one to three months or longer if frequency of attacks prior to treatment dictates. If an attack occurs, the daily dosage may be increased by up to 200 mg. During the dose adjusting phase, close monitoring of the patient's response is indicated, particularly if the patient has a history of airway involvement.
HOW SUPPLIED
Capsules of 200 mg (orange), bottles of 60 (NDC 0024-0305-60).
Capsules of 200 mg (orange), bottles of 100 (NDC 0024-0305-06).
Capsules of 100 mg (yellow), bottles of 100 (NDC 0024-0304-06).
Capsules of 50 mg (orange and white), bottles of 100 (NDC 0024-0303-06).
Store at controlled room temperature, 15° C to 30° C (59° F to 86° F).
sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC Bridgewater, New Jersey 08807. Revised December 2011.
Side Effects
The following events have been reported in association with the use of DANOCRINE:
Androgen like effects include weight gain, acne and seborrhea. Mild hirsutism, edema, hair loss, voice change, which may take the form of hoarseness, sore throat or of instability or deepening of pitch, may occur and may persist after cessation of therapy. Hypertrophy of the clitoris is rare.
Other possible endocrine effects are menstrual disturbances including spotting, alteration of the timing of the cycle and amenorrhea. Although cyclical bleeding and ovulation usually return within 60-90 days after discontinuation of therapy with DANOCRINE, persistent amenorrhea has occasionally been reported.
Flushing, sweating, vaginal dryness and irritation and reduction in breast size, may reflect lowering of estrogen. Nervousness and emotional lability have been reported. In the male a modest reduction in spermatogenesis may be evident during treatment. Abnormalities in semen volume, viscosity, sperm count, and motility may occur in patients receiving long-term therapy.
Hepatic dysfunction, as evidenced by reversible elevated serum enzymes and/or jaundice, has been reported in patients receiving a daily dosage of DANOCRINE of 400 mg or more. It is recommended that patients receiving DANOCRINE be monitored for hepatic dysfunction by laboratory tests and clinical observation. Serious hepatic toxicity including cholestatic jaundice, peliosis hepatis, and hepatic adenoma have been reported. (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.)
Abnormalities in laboratory tests may occur during therapy with DANOCRINE including CPK, glucose tolerance, glucagon, thyroid binding globulin, sex hormone binding globulin, other plasma proteins, lipids and lipoproteins.
The following reactions have been reported, a causal relationship to the administration of DANOCRINE has neither been confirmed nor refuted; allergic: urticaria, pruritus and rarely, nasal congestion; CNS effects: headache, nervousness and emotional lability, dizziness and fainting, depression, fatigue, sleep disorders, tremor, paresthesias, weakness, visual disturbances, and rarely, benign intracranial hypertension, anxiety, changes in appetite, chills, and rarely convulsions, Guillain-Barre syndrome; gastrointestinal: gastroenteritis, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and rarely, pancreatitis and splenic peliosis; musculoskeletal: muscle cramps or spasms, or pains, joint pain, joint lockup, joint swelling, pain in back, neck, or extremities, and rarely, carpal tunnel syndrome which may be secondary to fluid retention; genitourinary: hematuria, prolonged posttherapy amenorrhea; hematologic: an increase in red cell and platelet count. Reversible erythrocytosis, leukocytosis or polycythemia may be provoked. Eosinophilia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia have also been noted. Skin: rashes (maculopapular, vesicular, papular, purpuric, petechial), and rarely, sun sensitivity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme; other: increased insulin requirements in diabetic patients, change in libido, myocardial infarction, palpitation, tachycardia, elevation in blood pressure, interstitial pneumonitis, and rarely, cataracts, bleeding gums, fever, pelvic pain, nipple discharge. Malignant liver tumors have been reported in rare instances, after long-term use.
Drug Interactions
Prolongation of prothrombin time occurs in patients stabilized on warfarin.
Therapy with danazol may cause an increase in carbamazepine levels in patients taking both drugs.
Danazol can cause insulin resistance. Caution should be exercised when used with antidiabetic drugs.
Danazol may raise the plasma levels of cyclosporin and tacrolimus, leading to an increase of the renal toxicity of these drugs. Monitoring of systemic concentrations of these drugs and appropriate dose adjustments may be needed when used concomitantly with danazol.
Danazol can increase the calcemic response to synthetic vitamin D analogs in primary hypoparathyroidism.
The risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis is increased by concomitant administration of danazol with statins such as simvastatin, atorvastatin and lovastatin. Caution should be exercised if used concomitantly. Consult the product labeling for statin drugs for specific information on dose restrictions in presence of danazol.
Laboratory Tests
Danazol treatment may interfere with laboratory determinations of testosterone, androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone. Other metabolic events include a reduction in thyroid binding globulin and T4 with increased uptake of T3, but without disturbance of thyroid stimulating hormone or of free thyroxin index.
Warnings
Use of danazol in pregnancy is contraindicated. A sensitive test (e.g., beta subunit test if available) capable of determining early pregnancy is recommended immediately prior to start of therapy. Additionally a non-hormonal method of contraception should be used during therapy. If a patient becomes pregnant while taking danazol, administration of the drug should be discontinued and the patient should be apprised of the potential risk to the fetus. Exposure to danazol in utero may result in androgenic effects on the female fetus; reports of clitoral hypertrophy, labial fusion, urogenital sinus defect, vaginal atresia, and ambiguous genitalia have been received. (See PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy, Teratogenic Effects.)
Thromboembolism, thrombotic and thrombophlebitic events including sagittal sinus thrombosis and life-threatening or fatal strokes have been reported.
Experience with long-term therapy with danazol is limited. Peliosis hepatis and benign hepatic adenoma have been observed with long-term use. Peliosis hepatis and hepatic adenoma may be silent until complicated by acute, potentially life-threatening intraabdominal hemorrhage. The physician therefore should be alert to this possibility. Attempts should be made to determine the lowest dose that will provide adequate protection. If the drug was begun at a time of exacerbation of hereditary angioneurotic edema due to trauma, stress or other cause, periodic attempts to decrease or withdraw therapy should be considered.
Danazol has been associated with several cases of benign intracranial hypertension also known as pseudotumor cerebri. Early signs and symptoms of benign intracranial hypertension include papilledema, headache, nausea and vomiting, and visual disturbances. Patients with these symptoms should be screened for papilledema and, if present, the patients should be advised to discontinue danazol immediately and be referred to a neurologist for further diagnosis and care.
A temporary alteration of lipoproteins in the form of decreased high density lipoproteins and possibly increased low density lipoproteins has been reported during danazol therapy. These alterations may be marked, and prescribers should consider the potential impact on the risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease in accordance with the potential benefit of the therapy to the patient.
Before initiating therapy of fibrocystic breast disease with DANOCRINE, carcinoma of the breast should be excluded. However, nodularity, pain, tenderness due to fibrocystic breast disease may prevent recognition of underlying carcinoma before treatment is begun. Therefore, if any nodule persists or enlarges during treatment, carcinoma should be considered and ruled out.
Patients should be watched closely for signs of androgenic effects some of which may not be reversible even when drug administration is stopped.
Precautions
Because DANOCRINE may cause some degree of fluid retention, conditions that might be influenced by this factor, such as epilepsy, migraine, or cardiac or renal dysfunction, polycythemia and hypertension require careful observation. Use with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Since hepatic dysfunction manifested by modest increases in serum transaminases levels has been reported in patients treated with DANOCRINE, periodic liver function tests should be performed (see WARNINGS and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Administration of danazol has been reported to cause exacerbation of the manifestations of acute intermittent porphyria. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Laboratory monitoring of the hematologic state should be considered.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Current data are insufficient to assess the carcinogenicity of danazol.
Pregnancy, Teratogenic Effects
(See CONTRAINDICATIONS.) Pregnancy Category X. DANOCRINE administered orally to pregnant rats from the 6th through the 15th day of gestation at doses up to 250 mg/kg/day (7-15 times the human dose) did not result in drug-induced embryotoxicity or teratogenicity, nor difference in litter size, viability or weight of offspring compared to controls. In rabbits, the administration of DANOCRINE on days 6-18 of gestation at doses of 60 mg/kg/day and above (2-4 times the human dose) resulted in inhibition of fetal development.
Nursing Mothers
(See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of DANOCRINE did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine the safety and effectiveness of Danocrine in elderly patients.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
No information provided.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
DANOCRINE should not be administered to patients with:
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding.
- Markedly impaired hepatic, renal, or cardiac function.
- Pregnancy. (See WARNINGS.)
- Breast feeding.
- Porphyria-DANOCRINE can induce ALA synthetase activity and hence porphyrin metabolism.
- Androgen-dependent tumor.
- Active thrombosis or thromboembolic disease and history of such events.
- Hypersensitivity to danazol.
SIDE EFFECTS
The following events have been reported in association with the use of DANOCRINE:
Androgen like effects include weight gain, acne and seborrhea. Mild hirsutism, edema, hair loss, voice change, which may take the form of hoarseness, sore throat or of instability or deepening of pitch, may occur and may persist after cessation of therapy. Hypertrophy of the clitoris is rare.
Other possible endocrine effects are menstrual disturbances including spotting, alteration of the timing of the cycle and amenorrhea. Although cyclical bleeding and ovulation usually return within 60-90 days after discontinuation of therapy with DANOCRINE, persistent amenorrhea has occasionally been reported.
Flushing, sweating, vaginal dryness and irritation and reduction in breast size, may reflect lowering of estrogen. Nervousness and emotional lability have been reported. In the male a modest reduction in spermatogenesis may be evident during treatment. Abnormalities in semen volume, viscosity, sperm count, and motility may occur in patients receiving long-term therapy.
Hepatic dysfunction, as evidenced by reversible elevated serum enzymes and/or jaundice, has been reported in patients receiving a daily dosage of DANOCRINE of 400 mg or more. It is recommended that patients receiving DANOCRINE be monitored for hepatic dysfunction by laboratory tests and clinical observation. Serious hepatic toxicity including cholestatic jaundice, peliosis hepatis, and hepatic adenoma have been reported. (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.)
Abnormalities in laboratory tests may occur during therapy with DANOCRINE including CPK, glucose tolerance, glucagon, thyroid binding globulin, sex hormone binding globulin, other plasma proteins, lipids and lipoproteins.
The following reactions have been reported, a causal relationship to the administration of DANOCRINE has neither been confirmed nor refuted; allergic: urticaria, pruritus and rarely, nasal congestion; CNS effects: headache, nervousness and emotional lability, dizziness and fainting, depression, fatigue, sleep disorders, tremor, paresthesias, weakness, visual disturbances, and rarely, benign intracranial hypertension, anxiety, changes in appetite, chills, and rarely convulsions, Guillain-Barre syndrome; gastrointestinal: gastroenteritis, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and rarely, pancreatitis and splenic peliosis; musculoskeletal: muscle cramps or spasms, or pains, joint pain, joint lockup, joint swelling, pain in back, neck, or extremities, and rarely, carpal tunnel syndrome which may be secondary to fluid retention; genitourinary: hematuria, prolonged posttherapy amenorrhea; hematologic: an increase in red cell and platelet count. Reversible erythrocytosis, leukocytosis or polycythemia may be provoked. Eosinophilia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia have also been noted. Skin: rashes (maculopapular, vesicular, papular, purpuric, petechial), and rarely, sun sensitivity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme; other: increased insulin requirements in diabetic patients, change in libido, myocardial infarction, palpitation, tachycardia, elevation in blood pressure, interstitial pneumonitis, and rarely, cataracts, bleeding gums, fever, pelvic pain, nipple discharge. Malignant liver tumors have been reported in rare instances, after long-term use.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Prolongation of prothrombin time occurs in patients stabilized on warfarin.
Therapy with danazol may cause an increase in carbamazepine levels in patients taking both drugs.
Danazol can cause insulin resistance. Caution should be exercised when used with antidiabetic drugs.
Danazol may raise the plasma levels of cyclosporin and tacrolimus, leading to an increase of the renal toxicity of these drugs. Monitoring of systemic concentrations of these drugs and appropriate dose adjustments may be needed when used concomitantly with danazol.
Danazol can increase the calcemic response to synthetic vitamin D analogs in primary hypoparathyroidism.
The risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis is increased by concomitant administration of danazol with statins such as simvastatin, atorvastatin and lovastatin. Caution should be exercised if used concomitantly. Consult the product labeling for statin drugs for specific information on dose restrictions in presence of danazol.
Laboratory Tests
Danazol treatment may interfere with laboratory determinations of testosterone, androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone. Other metabolic events include a reduction in thyroid binding globulin and T4 with increased uptake of T3, but without disturbance of thyroid stimulating hormone or of free thyroxin index.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
No information provided. Please refer to the WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS sections.
