Brilinta
Brilinta (Ticagrelor Tablets for Oral Administration) side effects drug center
Brilinta Side Effects Center
What Is Brilinta?
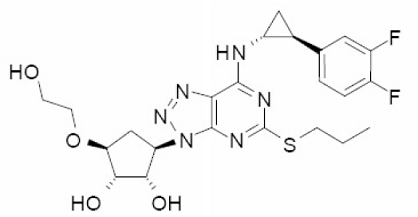
Brilinta (ticagrelor) is a blood-thinner used to reduce cardiovascular death and heart attack in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS). Brilinta works by preventing the formation of new blood clots, thus maintaining blood flow in the body to help reduce the risk of another cardiovascular event.
What Are Side Effects for Brilinta?
Common side effects of Brilinta include:
- bruising
- bleeding more easily
- nosebleeds
- headache
- dizziness
- cough
- nausea
- diarrhea
- irregular heartbeat
- high blood pressure
- back pain
- low blood pressure
- fatigue, and
- chest pain.
Tell your doctor if you experience serious side effects of Brilinta including:
- severe bleeding or uncontrollable bleeding,
- shortness of breath,
- colored urine (pink, red, or brown),
- red or black stools (looks like tar),
- coughing or vomiting that produces blood or blood clots, or
- vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- myocardial infarction,
- stent thrombosis, and
- death
- slow heartbeats;
- nosebleeds, or any bleeding that will not stop;
- shortness of breath even with mild exertion or while lying down;
- easy bruising, unusual bleeding, purple or red spots under your skin;
- red, pink, or brown urine;
- black, bloody, or tarry stools; or
- coughing up blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds.
- bleeding; or
- shortness of breath.
- Bleeding [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Dyspnea [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Dosage for Brilinta
Brilinta should be started with two 90 mg tablets as a loading dose, continuing treatment with 90 mg twice daily. After the initial loading dose of aspirin (usually 325 mg), use Brilinta with a daily maintenance dose of aspirin of 75-100 mg. A patient who misses a dose of Brilinta should take one 90 mg tablet (their next dose) at its scheduled time.
What Drugs, Substances, or Supplements Interact with Brilinta?
Patients who have received a loading dose of clopidogrel may be started on Brilinta.
Brilinta During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Brilinta use in pregnant women. Brilinta should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. It is not known whether ticagrelor or its active metabolites are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Brilinta, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Additional Information
Patients should avoid interruption of Brilinta treatment. If Brilinta must be temporarily discontinued, restart it as soon as possible. Discontinuation of Brilinta will increase the risk of:
Our Brilinta Side Effects Drug Center provides a comprehensive view of available drug information on the potential side effects when taking this medication.

IMAGES
See Images
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Call your doctor at once if you have:
Common side effects may include:
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Read the entire detailed patient monograph for Brilinta (Ticagrelor Tablets for Oral Administration)
Brilinta Professional Information
SIDE EFFECTS
The following adverse reactions are also discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
BRILINTA has been evaluated for safety in more than 58,000 patients.
Bleeding In PLATO (Reduction In Risk Of Thrombotic Events In ACS)
Figure 1 is a plot of time to the first non-CABG major bleeding event.
Figure 1 - Kaplan-Meier estimate of time to first non-CABG PLATO-defined major bleeding event (PLATO)
 |
Frequency of bleeding in PLATO is summarized in Tables 1 and 2. About half of the non-CABG major bleeding events were in the first 30 days.
Table 1 – Non-CABG related bleeds (PLATO)
| BRILINTA* N=9235 | Clopidogrel N=9186 | |
| n (%) patients with event | n (%) patients with event | |
| PLATO Major + Minor | 713 (7.7) | 567 (6.2) |
| Major | 362 (3.9) | 306 (3.3) |
| Fatal/Life-threatening | 171 (1.9) | 151 (1.6) |
| Fatal | 15 (0.2) | 16 (0.2) |
| Intracranial hemorrhage (Fatal/Life-threatening) | 26 (0.3) | 15 (0.2) |
| PLATO Minor bleed: requires medical intervention to stop or treat bleeding. PLATO Major bleed: any one of the following: fatal; intracranial; intrapericardial with cardiac tamponade; hypovolemic shock or severe hypotension requiring intervention; significantly disabling (e.g., intraocular with permanent vision loss); associated with a decrease in Hb of at least 3 g/dL (or a fall in hematocrit (Hct) of at least 9%); transfusion of 2 or more units. PLATO Major bleed, fatal/life-threatening: any major bleed as described above and associated with a decrease in Hb of more than 5 g/dL (or a fall in hematocrit (Hct) of at least 15%); transfusion of 4 or more units. Fatal: A bleeding event that directly led to death within 7 days. | ||
| * 90 mg BID | ||
No baseline demographic factor altered the relative risk of bleeding with BRILINTA compared to clopidogrel.
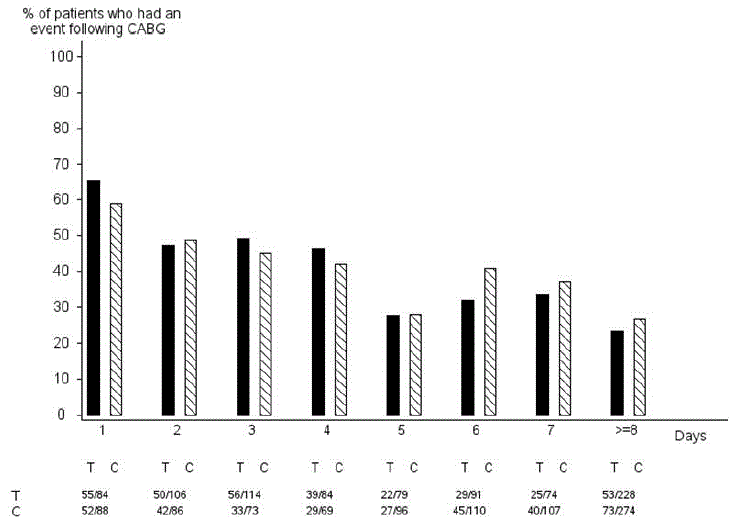
In PLATO, 1584 patients underwent CABG surgery. The percentages of those patients who bled are shown in Figure 2 and Table 2.
Figure 2 – ‘Major fatal/life-threatening’ CABG-related bleeding by days from last dose of study drug to CABG procedure (PLATO)
 |
| X-axis is days from last dose of study drug prior to CABG. The PLATO protocol recommended a procedure for withholding study drug prior to CABG or other major surgery without unblinding. If surgery was elective or non-urgent, study drug was interrupted temporarily, as follows: If local practice was to allow antiplatelet effects to dissipate before surgery, capsules (blinded clopidogrel) were withheld 5 days before surgery and tablets (blinded ticagrelor) were withheld for a minimum of 24 hours and a maximum of 72 hours before surgery. If local practice was to perform surgery without waiting for dissipation of antiplatelet effects capsules and tablets were withheld 24 hours prior to surgery and use of aprotinin or other haemostatic agents was allowed. If local practice was to use IPA monitoring to determine when surgery could be performed both the capsules and tablets were withheld at the same time and the usual monitoring procedures followed. T Ticagrelor; C Clopidogrel. |
Table 2 – CABG-related bleeding (PLATO)
| BRILINTA* N=770 | Clopidogrel N=814 | |
| n (%) patients with event | n (%) patients with event | |
| PLATO Total Major | 626 (81.3) | 666 (81.8) |
| Fatal/Life-threatening | 337 (43.8) | 350 (43.0) |
| Fatal | 6 (0.8) | 7 (0.9) |
| PLATO Major bleed: any one of the following: fatal; intracranial; intrapericardial with cardiac tamponade; hypovolemic shock or severe hypotension requiring intervention; significantly disabling (e.g., intraocular with permanent vision loss); associated with a decrease in Hb of at least 3 g/dL (or a fall in hematocrit (Hct) of at least 9%); transfusion of 2 or more units. PLATO Major bleed, fatal/life-threatening: any major bleed as described above and associated with a decrease in Hb of more than 5 g/dL (or a fall in hematocrit (Hct) of at least 15%); transfusion of 4 or more units. | ||
| * 90 mg BID | ||
When antiplatelet therapy was stopped 5 days before CABG, major bleeding occurred in 75% of BRILINTA treated patients and 79% on clopidogrel.
Other Adverse Reactions In PLATO
Adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of 4% or more in PLATO are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 – Percentage of patients reporting non-hemorrhagic adverse reactions at least 4% or more in either group and more frequently on BRILINTA (PLATO)
| BRILINTA* N=9235 | Clopidogrel N=9186 | |
| Dyspnea | 13.8 | 7.8 |
| Dizziness | 4.5 | 3.9 |
| Nausea | 4.3 | 3.8 |
| * 90 mg BID | ||
Bleeding In PEGASUS (Secondary Prevention In Patients With A History Of Myocardial Infarction)
Overall outcome of bleeding events in the PEGASUS study are shown in Table 4.
Table 4 – Bleeding events (PEGASUS)
| BRILINTA* N=6958 | Placebo N=6996 | |
| Events / 1000 patient years | Events / 1000 patient years | |
| TIMI Major | 8 | 3 |
| Fatal | 1 | 1 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 2 | 1 |
| TIMI Major or Minor | 11 | 5 |
| TIMI Major: Fatal bleeding, OR any intracranial bleeding, OR clinically overt signs of hemorrhage associated with a drop in hemoglobin (Hgb) of ≥5 g/dL, or a fall in hematocrit (Hct) of ≥15%. Fatal: A bleeding event that directly led to death within 7 days. TIMI Minor: Clinically apparent with 3-5 g/dL decrease in hemoglobin. * 60 mg BID | ||
The bleeding profile of BRILINTA 60 mg compared to aspirin alone was consistent across multiple pre-defined subgroups (e.g., by age, gender, weight, race, geographic region, concurrent conditions, concomitant therapy, stent, and medical history) for TIMI Major and TIMI Major or Minor bleeding events.
Other Adverse Reactions In PEGASUS
Adverse reactions that occurred in PEGASUS at rates of 3% or more are shown in Table 5.
Table 5 – Non-hemorrhagic adverse reactions reported in >3.0% of patients in the ticagrelor 60 mg treatment group (PEGASUS)
| BRILINTA* N=6958 | Placebo N=6996 | |
| Dyspnea | 14.2% | 5.5% |
| Dizziness | 4.5% | 4.1% |
| Diarrhea | 3.3% | 2.5% |
| *60 mg BID | ||
Bleeding In THEMIS (Prevention Of Major CV Events In Patients With CAD And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus)
The Kaplan-Meier curve of time to first TIMI Major bleeding event is presented in Figure 3.
Figure 3 - Time to first TIMI Major bleeding event (THEMIS)
 |
| T = Ticagrelor; P = Placebo; N = Number of patients |
The bleeding events in THEMIS are shown below in Table 6.
Table 6 – Bleeding events (THEMIS)
| BRILINTA N=9562 | Placebo N=9531 | |
| Events / 1000 patient years | Events / 1000 patient years | |
| TIMI Major | 9 | 4 |
| TIMI Major or Minor | 12 | 5 |
| TIMI Major or Minor or Requiring medical attention | 46 | 18 |
| Fatal bleeding | 1 | 0 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 3 | 2 |
Bleeding In THALES (Reduction In Risk Of Stroke In Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke Or TIA)
The Kaplan-Meier curve of time course of GUSTO severe bleeding events is presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4 - Time course of GUSTO severe bleeding events
 |
| KM%: Kaplan-Meier percentage evaluated at Day 30; T = Ticagrelor; P = placebo; N = Number of patients GUSTO Severe: Any one of the following: fatal bleeding, intracranial bleeding (excluding asymptomatic hemorrhagic transformations of ischemic brain infarctions and excluding microhemorrhages < 10 mm evident only on gradient-echo magnetic resonance imaging), bleeding that caused hemodynamic compromise requiring intervention (eg, systolic blood pressure <90 mmg Hg that required blood or fluid replacement, or vasopressor/inotropic support, or surgical intervention). |
Intracranial Bleeding and Fatal Bleeding in THALES
In total, there were 21 intracranial hemorrhages (ICHs) for BRILINTA and 6 ICHs for placebo. Fatal bleedings, almost all ICH, occurred in 11 for BRILINTA and in 2 for placebo.
Bradycardia
In a Holter substudy of about 3000 patients in PLATO, more patients had ventricular pauses with BRILINTA (6.0%) than with clopidogrel (3.5%) in the acute phase; rates were 2.2% and 1.6%, respectively, after 1 month. PLATO, PEGASUS, THEMIS and THALES excluded patients at increased risk of bradycardic events (e.g., patients who have sick sinus syndrome, 2nd or 3rd degree AV block, or bradycardic-related syncope and not protected with a pacemaker).
Lab Abnormalities
Serum Uric Acid
In PLATO, serum uric acid levels increased approximately 0.6 mg/dL from baseline on BRILINTA 90 mg and approximately 0.2 mg/dL on clopidogrel. The difference disappeared within 30 days of discontinuing treatment. Reports of gout did not differ between treatment groups in PLATO (0.6% in each group).
In PEGASUS, serum uric acid levels increased approximately 0.2 mg/dL from baseline on BRILINTA 60 mg and no elevation was observed on aspirin alone. Gout occurred more commonly in patients on BRILINTA than in patients on aspirin alone (1.5%, 1.1%). Mean serum uric acid concentrations decreased after treatment was stopped.
Serum Creatinine
In PLATO, a >50% increase in serum creatinine levels was observed in 7.4% of patients receiving BRILINTA 90 mg compared to 5.9% of patients receiving clopidogrel. The increases typically did not progress with ongoing treatment and often decreased with continued therapy. Evidence of reversibility upon discontinuation was observed even in those with the greatest on treatment increases. Treatment groups in PLATO did not differ for renal-related serious adverse events such as acute renal failure, chronic renal failure, toxic nephropathy, or oliguria.
In PEGASUS, serum creatinine concentration increased by >50% in approximately 4% of patients receiving BRILINTA 60 mg, similar to aspirin alone. The frequency of renal related adverse events was similar for ticagrelor and aspirin alone regardless of age and baseline renal function.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of BRILINTA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of an unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) has been rarely reported with the use of BRILINTA. TTP is a serious condition which can occur after a brief exposure (<2 weeks) and requires prompt treatment.
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema [see CONTRAINDICATIONS].
Respiratory Disorders: Central sleep apnea, Cheyne-Stokes respiration
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash
Read the entire FDA prescribing information for Brilinta (Ticagrelor Tablets for Oral Administration)
© Brilinta Patient Information is supplied by Cerner Multum, Inc. and Brilinta Consumer information is supplied by First Databank, Inc., used under license and subject to their respective copyrights.

