Akten Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel
- Brand Name: Akten
side effects drug center akten (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) drug
Drug Description
What is Akten and how is it used?
Akten is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of Ocular Surface Anesthesia. Akten may be used alone or with other medications.
Akten belongs to a class of drugs called Anesthetics, Ophthalmic.
What are the possible side effects of Akten?
Akten may cause serious side effects including:
- hives,
- difficulty breathing,
- swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat,
- weight gain (especially in your face or upper back and torso),
- slow wound healing,
- thinning skin,
- increased body hair,
- irregular menstrual periods,
- changes in sexual function,
- muscle weakness,
- tired feeling,
- depression,
- anxiety, and
- irritableness
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Akten include:
- redness or swelling of treated skin,
- thinning of treated skin, and
- numbness on areas where the medicine is accidentally applied
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Akten. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
DESCRIPTION
Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 3.5% is a sterile, preservative-free, single patient use ophthalmic gel preparation for topical ocular anesthesia. Lidocaine hydrochloride is designated chemically as acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl) monohydrochloride with a molecular formula of C14H22N2O HCl and molecular weight of 270.8. The structural formula of the active ingredient is:
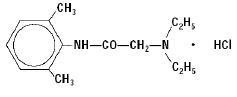 |
Akten™ contains 35 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride per mL as the active ingredient. Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) also contains Hypromellose, Sodium Chloride, and Purified Water as inactive ingredients. The pH may be adjusted to 5.5 to 7.5 with Hydrochloric Acid and/or Sodium Hydroxide.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) is a local anesthetic indicated for ocular surface anesthesia during ophthalmologic procedures.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose of Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) is 2 drops applied to the ocular surface in the area of the planned procedure. Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) may be reapplied to maintain anesthetic effect.
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage forms and Strength
Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) Ophthalmic Gel, 3.5% contains 35 mg per mL of lidocaine hydrochloride for topical ophthalmic administration.
Storage And Handling
Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 3.5% is supplied as a clear gel for single patient use as follows:
5mL fill in a 10mL natural, round plastic dropper bottle
(NDC 17478-792-10).
Storage
Store at 15° to 25° C (59° to 77° F)
Keep container closed and protected from light in the original carton until use. Discard after use.
Manufactured by: Akorn Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045. Rev. 09/08. FDA revision date: 10/7/2008
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
Most common adverse reactions are conjunctival hyperemia, corneal epithelial changes, headache, and burning upon instillation.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No information provided.
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the PRECAUTIONS section.
PRECAUTIONS
- Not for Injection.
- Corneal Opacification. Prolonged use of a topical ocular anesthetic may produce permanent corneal opacification and ulceration with accompanying visual loss.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, Impairment of fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) .
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy. Pregnancy Category B.
Reproduction< studies for lidocaine have been performed in both rats and rabbits. There was no evidence of harm to the fetus at subcutaneous doses up to 50 mg/kg lidocaine (more than 800 fold greater than the human dose on a body weight basis) in the rat model. There are however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used in pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Lidocaine is secreted in human milk. The clinical significance of this observation is unknown. Although no systemic exposure is expected with administration of Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) , caution should be exercised when Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients has been extrapolated from studies in older subjects and studies in pediatric patients using different formulations of lidocaine.
Geriatric Use
No overall clinical differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between the elderly and other adult patients.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
Prolonged use of a topical ocular anesthetic may produce permanent corneal opacification and ulceration with accompanying visual loss.
Acute emergencies from local anesthetics are generally related to high plasma levels encountered during therapeutic use of local anesthetics or to unintended subarachnoid injection of local anesthetic solution. However, topical ocular application of Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) is not expected to result in systemic exposure.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) is a local anesthetic agent that stabilizes the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses, thereby effecting local anesthetic action. Anesthesia generally occurs between 20 seconds to 1 minute and persists for 5 to 30 minutes.
Pharmacokinetics
Lidocaine may be absorbed following topical administration to mucous membranes. Its rate and extent of absorption depend upon various factors such as concentration, the specific site of application, viscosity of the agent, and duration of exposure.
The plasma binding of lidocaine is dependent on drug concentration, and the fraction bound decreases with increasing concentration. At concentrations of 1 to 4 mcg of free base per mL, 60 to 80 percent of lidocaine is protein bound. Binding is also dependent on the plasma concentration of the alpha-1-acid glycoprotein.
Lidocaine is metabolized rapidly by the liver, and metabolites and unchanged drug are excreted by the kidneys. Biotransformation includes oxidative Ndealkylation, ring hydroxylation, cleavage of the amide linkage, and conjugation. N-dealkylation, a major pathway of biotransformation, yields the metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide and glycinexylidide. The pharmacologic/toxicologic actions of these metabolites are similar to, but less potent than, those of lidocaine. Approximately 90% of lidocaine administered is excreted in the form of various metabolites, and less than 10% is excreted unchanged. The primary metabolite in urine is a conjugate of 4-hydroxy-2, 6-dimethylaniline.
Studies of lidocaine metabolism following intravenous bolus injections have shown that the elimination half-life of this agent is typically 1.5 to 2 hours. Because of the rate at which lidocaine is metabolized, any condition that affects liver function may alter lidocaine kinetics. The half-life may be prolonged twofold or more in patients with liver dysfunction. Renal dysfunction does not affect lidocaine kinetics but may increase the accumulation of metabolites.
Clinical Studies
The effect of Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) on ocular anesthesia was studied in a multi-center, randomized, controlled, double-blind study.
A total of 209 subjects were enrolled, with 54, 51, 53, and 51 subjects randomized to the sham, Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 1.5%, Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 2.5%, and Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 3.5% groups, respectively. Ocular anesthesia was achieved within 5 minutes of anesthetic application by 47 of 51 subjects (92%) in the Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 3.5% group.
The mean time to anesthesia onset ranged from 20 seconds to 5 minutes was not affected by Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) dose. The mean time to anesthesia onset was approximately 60 seconds, with a median onset time of 40 seconds for the Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 3.5% group. Among the subjects in the Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) groups who achieved anesthesia within 5 minutes, approximately 90% had achieved anesthesia within 60 seconds of application.
The duration of anesthesia generally ranged from approximately 5 minutes to 30 minutes, with mean anesthesia durations of approximately 15 minutes for the Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 3.5% group.
Approximately 84% of the subjects in the Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) 3.5% group experienced anesthesia for at least 5 minutes, approximately 55% of subjects experienced anesthesia for 10 minutes or longer and 27% experienced anesthesia for 15 minutes or longer. The anesthetic effect of additional applications of Akten™ (lidocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel) has not been evaluated.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
No information provided. Please refer to the PRECAUTIONS section.
