Cosmetic Procedures: Botox, Laser, Peels Before and After Photos
Mirror, Mirror on the Wall

Stopping the aging process and living eternally has been an enduring human desire, sought by Egyptian pharaohs, Chinese emperors, and Ponce de Leon's search for the Fountain of Youth. Cosmetic medicine has developed several nonsurgical procedures that can camouflage the effects of sun exposure and the passing of time.
Botox Basics
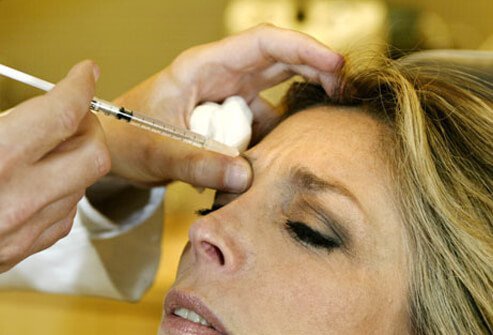
Three different forms of botulinum toxin are available (Botox Cosmetic, Dysport, and Xeomin) for the injection of facial muscles. This bacterial protein temporarily paralyzes the muscle that receives the injection. Certain types of wrinkles, such as those on the forehead and at the corners of the eyes, diminish if the muscles producing them cannot contract normally. A thin needle and a small volume of toxin minimize the pain of the injection.
Botox: Before and After
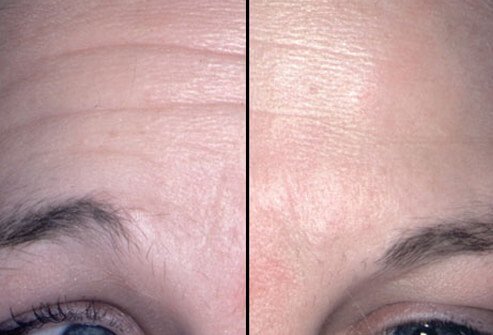
After toxin injection, there is a gradual loss of muscular control, which usually takes up to a week to reach maximum effect; the areas of the affected face appear calm and unexpressive. The paralysis lasts about four months so patients must receive injections at regular intervals for maintenance.
Chemical Peel Basics
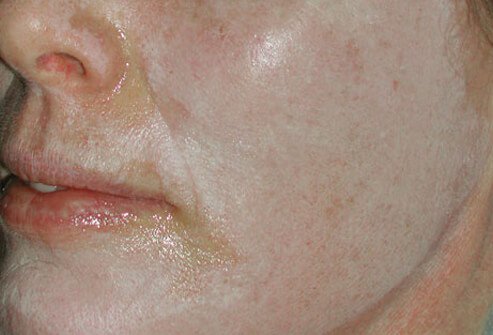
Chemical peels use a variety of substances to damage the skin in order to exfoliate the outer layers. The depth of the peel depends on the type of chemical, its concentration, and the length of time it remains on the skin. Glycolic acid, lactic acid, salicylic acid, trichloroacetic acid (TCA), and phenol are some of the chemicals used in cosmetic peels. There is an improvement over the skin's pre-peel state after the skin heals.
Chemical Peel: Before and After
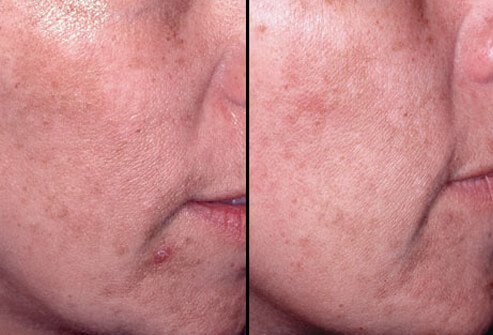
Mild peels may be repeated every few weeks for the desired effect. Deeper peels may cause some initial discomfort as well as swelling and crusting of the face. Moderate or deep facial peels can be repeated at 6- to 12-month intervals. It is important for patients to choose a physician who has plenty of experience with the chosen procedure, since the results of chemical peels are technique dependent. The doctor will be able to choose the best approach for the particular cosmetic issue.
Microdermabrasion Basics
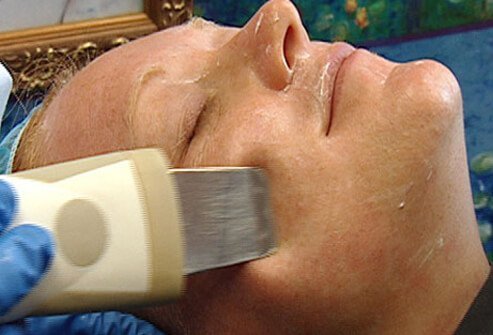
Microdermabrasion is a procedure whereby silicon crystals (grains of sand) are propelled by air onto the skin surface, producing a small amount of inflammation. The minimal swelling produced by this technique can improve the appearance of superficial wrinkles. The results are modest, temporary, and must be repeated at frequent intervals. On the other hand, there are few side effects.
Microdermabrasion: After
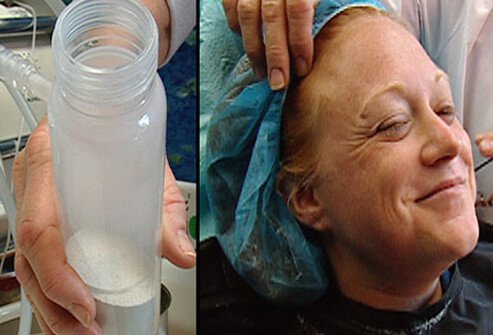
The irritation produced by microdermabrasion initially looks like a sunburn and feels tight, but this effect goes away within one day. Multiple treatments may be necessary.
Thermage Basics
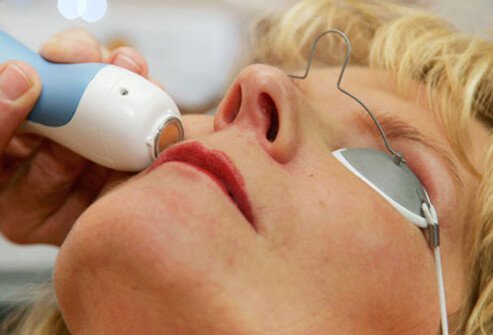
Radio waves can improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin. It is believed that either changes produced by directly heating skin collagen produces tightening of loosened skin, or new collagen synthesized after heating is responsible for the improvement, or both. Devices (for example, Thermage) used to generate the radio energy can produce enough heat in the skin to be painful, but a single treatment is all that is generally needed.
Thermage: Before and After – Eyelids
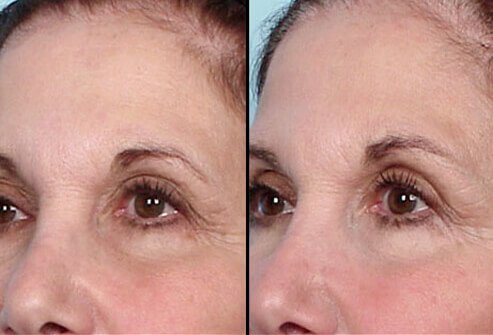
Droopiness of the eyelids is one condition often treated by Thermage. Results are not visible until four to six months after the procedure.
Nonablative Laser (Fraxel) Basics
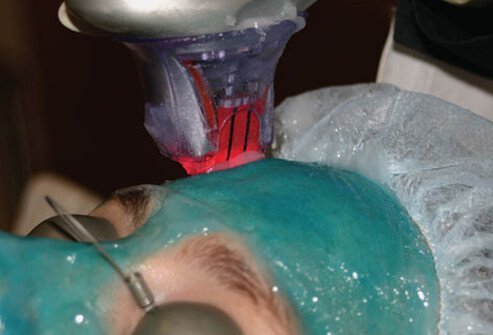
The idea of nonablative lasers like Fraxel is to protect the outer layers of the skin (the epidermis) while damaging only the deeper dermis. Topical anesthetic reduces the pain associated with the procedure. Since the surface layers are preserved while the deeper layers of the skin sustain the damage, scarring is unlikely to occur, and new collagen is generated.
Nonablative Laser: Before and After
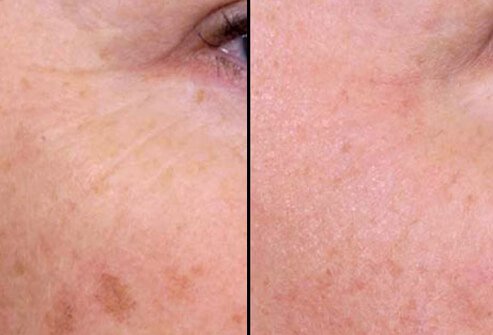
One of the advantages of nonablative laser therapy is that it does not require significant time away from work or daily activities. The skin may be mildly reddened after the treatment, but this quickly improves. Most people undergo four to six treatments over a period of several months.
Nonablative Laser for Melasma
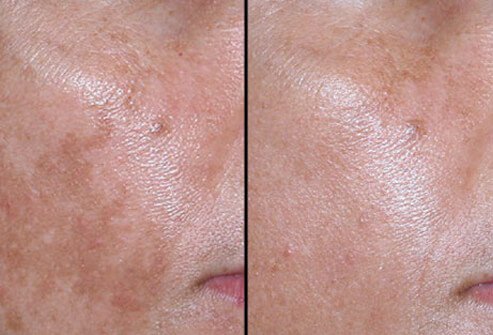
The use of lasers is just one of many approaches to the treatment of brown spots or patches, including "pregnancy mask" (melasma). The doctor will determine the best treatment depending on the patient's skin color, the extent of discoloration, and their experience.
Diode Laser Basics
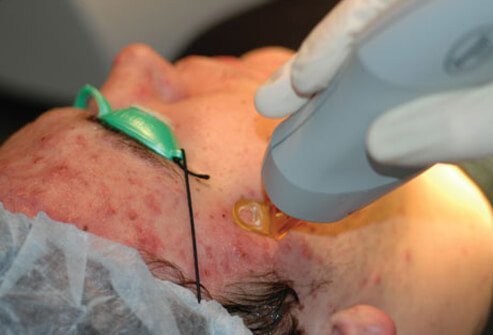
Diode laser is a technique that can achieve improvements by destroying oil-producing glands for those with severe acne. Similar to Fraxel laser therapy, diode lasers penetrate below the surface layer of skin without damaging the outermost layer. Side effects are temporary and include redness and inflammation.
Diode Laser: Before and After
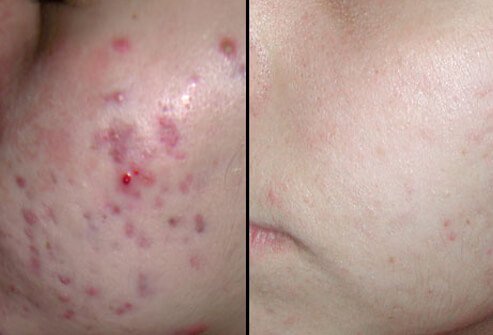
Diode laser therapy for acne may require several treatments. This image shows skin that has improved after a series of five diode laser treatments.
Intense Pulse Light (IPL)
Intense pulsed light (IPL) technology exposes human tissues to broad spectrum (non-laser) light sources that produce enough heat to destroy colored molecules that can absorb the light. In the case of human tissue, this involves melanin (skin pigment) and hemoglobin (blood pigment). When used appropriately on aged or pigmented skin, IPL can improve the skin's appearance.
IPL: Before and After
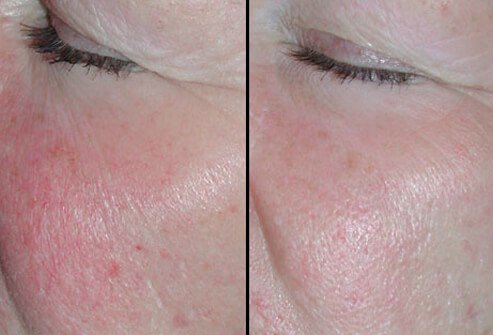
Since IPL relies upon the absorption by hemoglobin and melanin, it can work on skin discolorations that are red or brown. It may be effective in patients with dark spots (melasma), redness (rosacea), dilated blood vessels (telangiectasia), and aged skin. IPL also stimulates the production of collagen.
Cosmetic Filler Basics
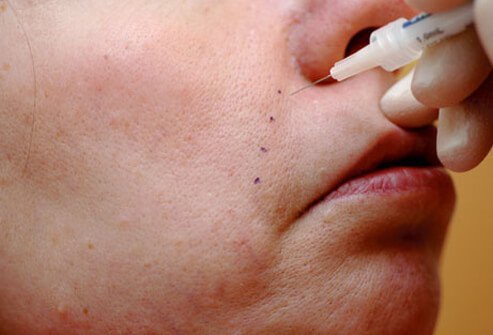
Cosmetic fillers add substance to skin in order to lift up areas that are sinking. Certain wrinkles, depressed scars, and hollows can be camouflaged using this technique. The substances that have been used are varied and include one's own fat or fibroblasts, poly-L-lactic acid, hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxyapatite, polymethylmethacrylate beads, and even silicone. Some of these substances produce improvement by enhancing collagen in the area injected, which adds volume to the tissue beneath the skin, and helps smooth the appearance of lines or wrinkles.
Cosmetic Filler: Before and After

Many, but not all, fillers disappear over a period of months, so it is necessary to reinject them to retain the desired appearance. The benefit of this is if too much of the filler is injected, producing an undesirable puffiness to the tissue, this swelling will diminish over a period of months. On the other hand, repeated treatments are needed to maintain the desired look. Injection with fat cells often yields permanent results. Polymethylmethacrylate is another filler that produces permanent results.
Cosmetic Filler: Beyond Wrinkles
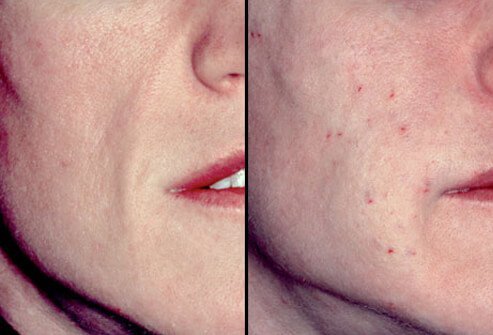
The anatomy of the aging face is now better understood than in the past. Aside from increased wrinkling, there is a loss of fat in the cheeks and temples, and an increase in fat in the neck. As shown in this photograph, a filler has been used to plump a woman's sunken cheek area.
Cosmetic Filler for Dark Circles: Before and After
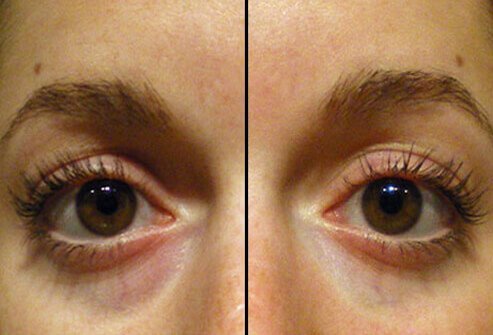
Physicians may use fillers in the hollow area around the eye socket to minimize dark circles and bags under the eyes.
Cosmetic Filler for Lips: Before and After
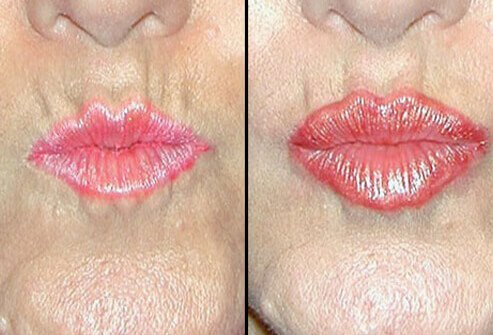
Health-care professionals may use the same fillers that plump wrinkles and minimize dark circles to plump the lips. Fat-cell injections may have permanent results, but collagen and hyaluronic acid fillers produce a temporary effect.
Making the Decision

The perception that nonsurgical cosmetic procedures are less risky than conventional scalpel surgery is not entirely accurate. The choice of the best procedure requires careful consideration by both the patient and physician. It is important for the patient to have realistic expectations regarding the outcome.
Be very careful in choosing who you will trust to do any cosmetic work on your face (or on any part of your body). Your primary care doctor and/ or friends that have had a good outcome by an experienced caregiver are potential sources to help choose the best qualified person to do such procedures.
Cosmetic Procedures: Botox, Laser, Peels Before and After Photos
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
- Jutta Klee/fStop
- Don Murray/Stringer
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- WebMD Video
- WebMD Video
- Andreas Rentz/Getty
- Photo courtesy of Dr. Karyn Grossman/grossmandermatology.com
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- “Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology”; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- “Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology”; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- WebMD Video
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- "Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology"; Marc R. Avram, Sandy Tsao, Zeina Tannous, Mathew M. Avram; Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
- Photo courtesy of Dr. Alexander Rivkin/westsidemedicalspa.com
- Courtesy of Dr. Geoffrey Leber/bevhillsdoc.com
- DigitalVision/Getty
REFERENCES:
- Aesthetic Surgery Journal
- American Board of Cosmetic Surgery: "How to Find the Right Cosmetic Surgeon for You," ""Non-Surgical Procedures."
- American Journal of Clinical Dermatology
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons: "Chemical Peel," "Microdermabrasion."
- Clinics in Geriatric Medicine
- Color Atlas of Cosmetic Dermatology
- Dermatologic Surgery
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Journal of Drugs in Dermatology
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America
- Systemic Reviews Journal
© 1996-2022 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved.
Source slideshow on OnHealth
