What Is the Main Cause of Eczema?
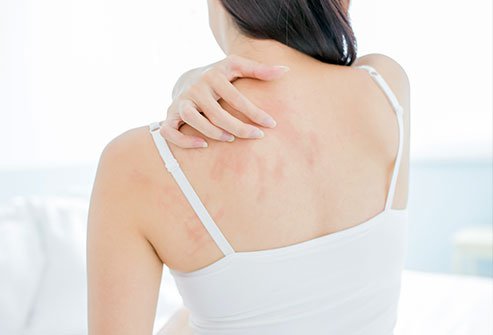
The exact cause of eczema is unknown. It is caused due to an overactive immune system that responds aggressively when exposed to triggers. Certain conditions such as asthma are seen in many patients with eczema. There are different types of eczema, and they tend to have different triggers. Common triggers of eczema flare-ups are as follows:
- Skin contact to chemical irritant, for example, soaps and detergents
- Certain fabrics such as rough fabrics
- Synthetic fabrics
- Increased body temperature
- Sweating
- Temperature changes
- Stress
- Food allergies
- Animal fur
- Upper respiratory infections and other systemic infections
- Asthma
What is eczema?
Eczema is an inflammatory condition characterized by patches on the skin with severe itching, redness, and dryness/oozing. Eczema can occur in children, teenagers, or adults. Eczema is not contagious.
What are the types of eczema?
There are five main types of eczema:
- Atopic dermatitis: This is the most common and chronic type of eczema. Hence, eczema is often called atopic dermatitis. It presents with dry, itchy, red rashes on the skin. It is often seen in babies and is associated with sensitive skin.
- Contact dermatitis: This is caused by contact with irritants that cause reaction on the skin. Burning, itching, and redness occur. The inflammation disappears when the irritant is removed.
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis: This affects the fingers, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. There are red, itchy, scaly patches on the skin that can be painful and cause the skin to crack. Sweat collection and using metal jewelry may cause such type of rash.
- Nummular dermatitis: This presents with dry, round patches of skin, which usually occur during winter and commonly appear on the legs.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Also called dandruff, this presents with itchy, red, scaly rashes typically on the scalp and other hair borne areas such as the eyebrows or eyelids.
What are the symptoms of eczema?
The main symptom of eczema is red, itchy, dry, rough, and irritated skin. Oozing may be seen due to repeated scratching. It is a lifelong condition with multiple flare-ups and periods of remission (symptom free periods).
Eczema can occur anywhere over the body, depending on the type. The signs and symptoms may vary with the type of eczema and age group of the patient.
Common symptoms are as follows:
- Intense itching
- Red or brownish-gray patches
- Multiple small, raised bumps that may ooze fluid when scratched
- Crusting due to dried-up fluid
- Pus discharge due to secondary infection
- Thick skin
- Dry, scaly, cracked skin
- Worsening of eczema following scratching
Symptoms in infants:
- Rashes on the scalp and cheeks
- Rashes that may blister and leak fluid
- Severe itching affecting sleep
- Symptoms in children (above two years):
- Rashes appear behind the elbows or knees, neck, wrists, ankles, and between the buttocks
- Bumpy rashes
- Lichenification (thickening) of the skin, leading to permanent itching
Symptoms in adults:
- Rashes are scalier than those in children
- Rashes that commonly appear in the creases of the elbows or knees or the nape of the neck
- Rashes that may cover most of the body
- Very dry skin
- Rashes that are permanently itchy
- Secondary skin infections
What are the complications of eczema?
Complications due to eczema include the following:
- Infection
- Scarring
- Sleep disturbance because of intense itching
How to prevent flare-ups of eczema?
Complications and flare-ups can be prevented in the following ways:
- Moisturizing the skin frequently with moisturizers (free of chemicals, artificial colors, and fragrances)
- Avoiding sudden changes in temperature or humidity
- Avoiding sweating
- Physical and emotional stress management
- Avoiding wearing rough fabric materials such as wool
- Avoiding direct skin contact with harsh soaps, detergents, and chemicals
- Avoiding food triggers
- Using a humidifier in the house and bedroom
