Heart Disease:, Signs, and Causes
Understanding How the Heart Works
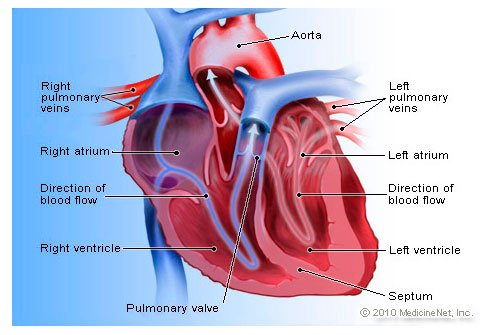
The heart is the hardest working muscle in your body. The average heart beats 100,000 times a day, day and night, to supply oxygen and nutrients throughout your body. Blood pumped by the heart also shuttles waste products such as carbon dioxide to the lungs so it can be eliminated from your body. Proper heart function is essential to support life.
What is Heart Disease?
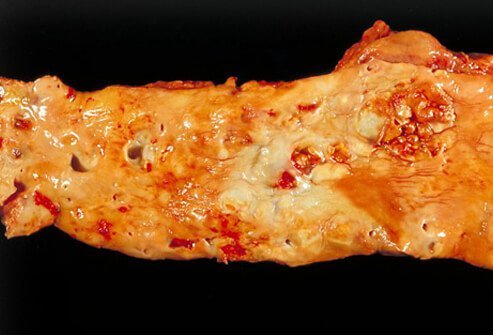
Coronary artery disease (CAD), commonly known as heart disease, is a condition in which cholesterol, calcium, and other fats accumulate in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. It is the most common type of heart disease. This material hardens forming a plaque that blocks blood flow to the heart. When a coronary artery narrows due to plaque buildup or some other cause, the heart muscle is starved for oxygen and a person experiences chest pain known as angina. CAD
The Link Between Heart Disease and Heart Attack

Sometimes a piece of a fatty plaque in a coronary artery breaks off or ruptures. When this happens, a blood clot forms in the area in response to the injury. The clot may block the flow of blood through the artery, causing a heart attack. Sadly, some heart attacks lead to the heart stopping completely, a situation known as sudden cardiac arrest. The heart may also start to beat in a very dangerous rhythm called ventricular tachycardia, which is potentially fatal.
Heart Disease: The Number-One Killer

Heart disease is the leading killer in the United States and affects an estimated 14 million adults. Heart disease is responsible for more deaths in the U.S. than the 2nd through 7th leading causes of death combined.
What Are the Risk Factors for Heart Disease?

Certain risk factors increase the chances of developing heart disease. More common heart disease risk factors include:
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Heart disease in a close blood relative
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
What Are Lifestyle Risk Factors for Heart Disease?

Certain lifestyle factors and choices increase the risk of heart disease including:
- Eating a diet high in fat
- Being "type A" (impatient, aggressive, and/or competitive)
- Being physically inactive
- Experiencing emotional distress or being "stressed out"
Sudden Cardiac Death - A Fatal Consequence of Heart Disease

Heart disease symptoms differ from person to person. Those who experience chest pain or shortness of breath have a chance to receive life-saving treatment in a hospital. For others, unfortunately, sudden cardiac arrest and death are the first symptoms of heart disease they experience.
What Are Common Symptoms of Heart Disease?

Many people with heart disease notice symptoms during physical exertion or exercise. The heart needs more oxygen and nutrients during physical exertion, so people with heart disease may notice symptoms when they are active. Symptoms of heart disease may include:
- Jaw pain
- Chest pain
- Back pain (typically left-sided)
- Shortness of breath
What Are Other Symptoms of Heart Disease?

Symptoms of heart disease may also include:
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness, dizziness
- Abdominal pain
- Irregular heartbeat
- Weakness (especially at rest)
What Are the Heart Disease Symptoms in Women, Seniors, and People with Diabetes?

Certain groups of people with heart disease experience atypical symptoms. Many women, people with diabetes, and elderly individuals do not experience pain as a symptom of heart disease. People in those groups are more likely to report fatigue or a general feeling of malaise as a symptom of heart disease.
What is an Electrocardiogram (EKG)?

Electricity flows through heart cells to stimulate contraction of the heart muscle. People who have heart disease have hearts that do not conduct electricity normally. An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a quick, painless, noninvasive test that assesses the electrical behavior of the heart. An EKG is able to detect many heart conditions including:
- Current heart attack
- Past history of heart attack
- Heart rhythm disturbances
- Blood electrolyte abnormalities
- Unstable angina
- Congenital heart defects
- Conditions involving cardiac inflammation (pericarditis and myocarditis)
What is a Stress Test?

Symptoms of heart disease are often present during physical exertion, because the heart is stressed and doesn't receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients. A stress test observes the behavior of the heart while the patient is walking or running on a treadmill. The patient is hooked up to an EKG machine to detect the heart's activity before, during, and after the stress test. The test is 60% to 70% accurate in detecting blocked coronary arteries. Sometimes, a patient may be too weak or deconditioned to perform a stress test. In that case, the doctor can administer medications that simulate the heart activity during exercise. The patient remains stationary. The doctor may also use nuclear imaging or ultrasound to visualize the behavior of the heart.
What is Echocardiography?
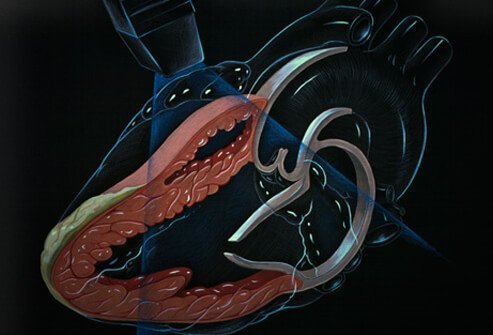
An echocardiogram is an image of the heart that is created with sound waves. This test can detect heart disease and observe the function of the heart. A normal, healthy heart pumps 50% to 60% of the blood with each heartbeat into the body. A weaker heart will pump less blood with each heartbeat. This is detectable with an echocardiogram and may be a sign of heart disease.
Why Use Computerized Tomography Tests (CT scans)?

A cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan is a test that uses X-rays to obtain detailed images of cardiac blood vessels. The test can detect narrowing of blood vessels and is useful in showing the absence of heart disease.
What Makes Coronary Angiography a Superior Test Compared to the Others?
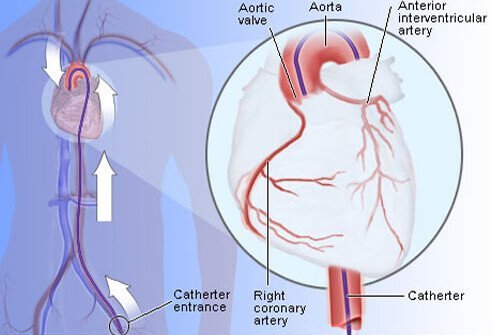
A coronary angiogram is a test that provides sophisticated X-ray images of the heart. During the test, doctors advance a catheter into the heart after it is inserted into a vein in the groin. A substance called contrast is injected into the coronary arteries so that they can be imaged with X-rays. These X-ray images show the location and severity of blockages in coronary arteries.
There is No Single Treatment Method for Heart Disease

Heart disease treatment differs from person to person. There is no such thing as one uniform treatment that works for everyone who has heart disease. Most heart disease patients are treated with a combination of diet, exercise, and other lifestyle changes in addition to medication.
What are Some Common Medications Used to Treat Heart Disease?

A variety of medications may be used to treat heart disease. Medication options include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors decrease strain on the heart by opening blood vessels.
- Beta blockers reduce strain on the heart by decreasing heart rate and blood pressure.
- Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) increase the efficiency of the heart and decrease heart rate.
- Nitroglycerin opens arteries in the heart allowing for increased blood flow.
- Statins alter blood lipids (fats in the blood that make up cholesterol) and decrease the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries.
What Are Some of the Procedures Performed to Treat Heart Disease?

In addition to lifestyle changes and medications, several procedures may be used to treat heart disease including:
- Coronary (balloon) angioplasty is a procedure in which a balloon-tipped catheter is advanced to the site of the blockage and expanded to open the clogged artery. This procedure improves blood flow.
- A stent is a small metallic tube that is placed during coronary balloon angioplasty to keep a newly-opened coronary artery open.
The Key to Preventing Heart Disease is Through a Healthy Lifestyle, Starting with a Healthy Diet.

Some heart disease risk factors, such as genetics, cannot be controlled. However, many other heart disease risk factors can be modified. Eating heart-healthy foods can reduce the risk of heart disease. Heart-healthy foods include fruits, and vegetables. Cholesterol-lowering foods such as beans, soy, chickpeas, garlic, avocados, and olive oil are beneficial. Boost levels of HDL "good" cholesterol by eating nuts. Walnuts, pecans, and almonds are good choices, but limit your serving to a small handful as nuts are high in calories. It's a good idea to eat fish and seafood a few times a week to boost intake of heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Avoid sugary foods as they promote heart disease and other chronic conditions.
Lifestyle Changes: Using Alcohol in Moderation and Quitting Smoking

Controlling your alcohol intake and avoiding smoking are two easy ways to reduce the risk of heart disease. To optimize levels of HDL "good" cholesterol, women should have no more than one alcoholic drink per day while men should have no more than two alcoholic drinks per day. A person who smokes and then quits reduces his or her risk of heart disease to the level of that of a nonsmoker 3 years after quitting.
Lower the Risk of Heart Disease with Exercise, Aspirin, and by Controlling High Blood Pressure and diabetes.
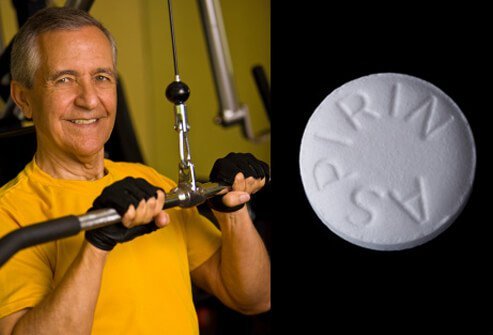
A few simple measures can help reduce heart disease risk. Speak with your doctor before implementing these measures to make sure they are safe for you.
- Daily low-dose aspirin therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of heart attack.
- Exercise for at least 30 minutes 3 to 5 days a week to optimize blood lipids (lowers "bad" LDL and raises "good" HDL cholesterol), lower blood pressure, and strengthen the heart muscle.
- If you have diabetes or high blood pressure (or both), control them. High blood pressure and high blood sugar are damaging to the heart.
Heart Disease: Symptoms, Signs, and Causes
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
- MedicineNet
- CDC/Dr. Edwin P. Ewing Jr.
- MedicineNet
- iStockPhoto / Rene Mansi
- iStockPhoto / Rhoberazzi
BigStockPhoto / Milan Radulovic
iStockPhoto / Sergey Lavrentev
iStockPhoto / Brian Toro - iStockPhoto / Spauln
BigStockPhoto / John Young
iStockPhoto / Tulay Over
BigStockPhoto / Vladimir Mucibabic - iStockPhoto / Lisa F. Young
- iStockPhoto / Jan Tyler
iStockPhoto / Renee Lee
iStockPhoto / Robert Kyllo - iStockPhoto / Eduardo Jose Bernardino
- BigStockPhoto / Fred Goldstein
- MedicineNet
- BlueOctane at en.wikipedia
- Wikimedia Commons - Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator
- iStockPhoto / Joel Johndro
- MedicineNet
- BigStockPhoto / Vitalii Gu
iStockPhoto / Anne Clark
iStockPhoto / Michael Krinke
BigStockPhoto / Rob Marmion - BigStockPhoto / David Gallaher
- MedicineNet
- BigStockPhoto / Rohit Seth
- iStockPhoto / Webphotographeer
iStockPhoto / Stock Photo NYC - iStockPhoto / Derek Latta
iStockPhoto / Jim DeLillo
REFERENCES:
- CDC: "About Heart Disease." Jan. 13, 2021.
- CDC: "Heart Disease Facts." Sept. 8, 2020. CDC: "Know Your Heart Disease Risk." Dec. 9, 2019.
- American Heart Association: "Prevention and Treatment of High Cholesterol." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): "Million Hearts: Prevalence of Leading Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors — United States, 2005–2012."
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "How Can Coronary Heart Disease Be Prevented or Delayed?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "How Is Coronary Heart Disease Treated?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "How the Heart Works." National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Coronary Heart Disease?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "What Does an Electrocardiogram Show??"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "What Is an Electrocardiogram?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "What Is Cardiac CT?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "What Is Coronary Angiography?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "What Is Coronary Heart Disease?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "What Is Echocardiography?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "What Is Stress Testing?"
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): "Who Is at Risk for Coronary Heart Disease?"
© 1996-2022 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved.
Source slideshow on OnHealth
