What Is Embolization of a Tumor?
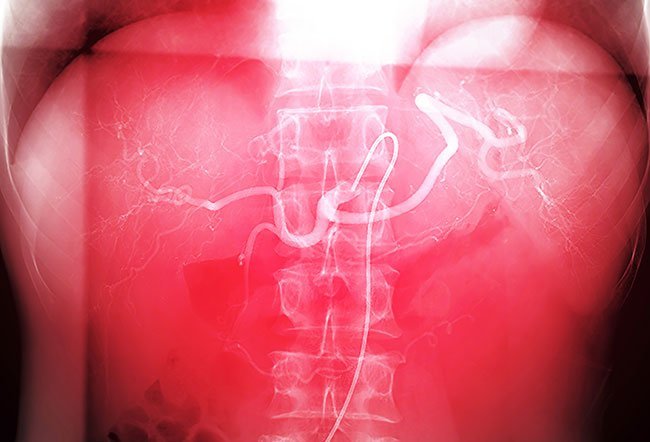
A tumor requires a continuous blood supply to grow and survive. Embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to block the blood supply to a tumor to reduce its size or cause complete cell death. This technique utilizes liquid, particles, or microspheres to obstruct blood vessels.
Embolization is mainly used to treat:
- Liver cancer
- Kidney cancer
- Neuroendocrine tumors (tumors in the cells of the endocrine and nervous system)
- Uterine fibroids
- Aneurysms (weakening of an artery wall that creates a bulge)
The three different types of embolization are:
- Arterial embolization: The physician injects small beads into the blood vessel supplying the tumor to stop the blood flow.
- Chemoembolization: In this technique, tiny beads infused with chemotherapy are sent through a blood vessel directly into a tumor.
- Radioembolization: Radiation therapy uses tiny beads with radioactive isotopes on them to directly treat tumors.
The advantages of embolization include:
- Shrinks tumor for surgical removal.
- Reducing blood loss during the surgery to remove the tumor.
- Slowing tumor growth when surgery and chemotherapy are not possible.
- Relieving symptoms of heavy bleeding in women with uterine fibroids.
What are the different conditions treated with tumor embolization?
Embolization can treat both cancerous and benign tumors, including:
- Cancerous tumors (specifically in the liver or kidney):
- Benign tumors:
- Uterine fibroids (noncancerous tumors that develop in and around the uterus)
- Angiomyolipoma of the kidney (benign tumor in the fat and muscle tissue usually found in the kidney)
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate)
- Hepatic adenoma (benign liver tumor)
- Hemangioblastoma (benign tumor formed in the lower part of the brain, spinal cord, or retina)
- Meningioma (benign tumor in the membranes of the brain and spinal cord)
- Juvenile nasal angiofibroma (benign tumor formed in the back of the nose in adolescent males)
- Aneurysmal bone cyst (highly destructive benign bone tumor)
- Paraganglioma’s (rare tumors that form near the carotid artery and other nerve pathways)
- Hemangiopericytoma (rare tumors of the blood vessels and soft tissues)
How is embolization of a tumor done?
The surgical removal of the tumor is made easier by the embolization procedure. During the embolization procedure:
- The physician makes a small incision in the groin area to access a blood vessel and carefully inserts a catheter into the vessel.
- Next, the physician injects dye into the vessel through the catheter to visualize the vessels during imaging.
- Using imaging, such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy, the physician directs the catheter to the desired site.
- After reaching the site, the physician inserts medication or agents, such as tiny plastic particles, foam, or little metal coils to seal the blood vessels that supply the tumor.
What are the complications of tumor embolization?
Some of the possible complications after the procedure include:
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Nausea
- Infection
- Blood clots in the main blood vessels
