Anal Reflex
Definition and Clinical Testing
The anal reflex, also known as the anal wink or perineal reflex, is the reflexive contraction of the external anal sphincter upon stimulation of the perianal skin. To elicit the reflex, the skin around the anus is gently scratched with a dull object, which should cause a visible contraction or "wink" of the sphincter.
Alternatively, the external anal sphincter response to coughing and sniffing is a highly consistent and easily elicited polysynaptic reflex with similar characteristics to the traditional scratch-induced reflex.
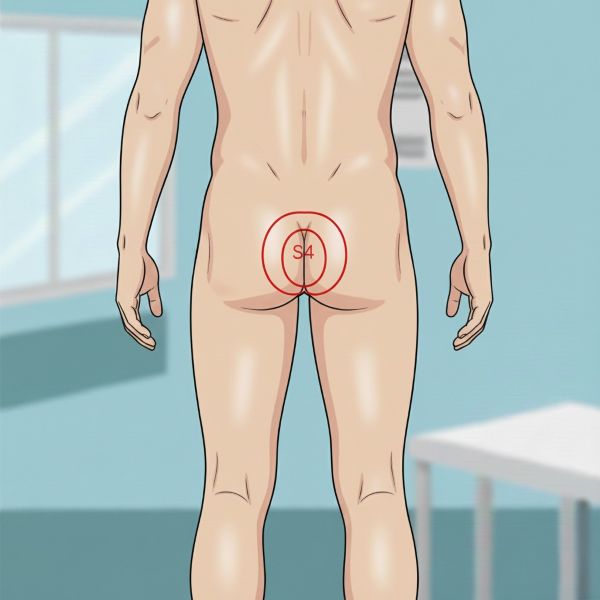
The anal reflex is a superficial reflex that tests the integrity of the S4 and S5 sacral nerve roots and the lower spinal cord.
Neural Pathway and Clinical Significance
The reflex arc for the anal reflex is mediated by the S4 and S5 sacral nerve roots. Its presence confirms the integrity of this lower part of the spinal cord and its nerve roots.
The absence of the anal reflex is a significant finding in cases of suspected cauda equina syndrome, spinal cord injury below the S4 level, or other sacral nerve pathologies. However, it is important to note that the reflex may be absent in some normal elderly individuals, and its absence does not always correlate with urinary incontinence.
References
Swash M, Chan CLH, Ponsford S. The anal reflex can be elicited by cough and sniff – validation of a clinical sign. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 2004; 75: 521 (abstract 027)
Cross References
