Tussigon Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: hydrocodone bitartrate and homatropine methylbromide tablets
- Brand Name: Tussigon
side effects drug center tussigon (hydrocodone bitartrate and homatropine methylbromide tablets) drug
Drug Description
TUSSIGON®
(hydrocodone bitartrate and homatropine methylbromide)
Tablets
DESCRIPTION
Tussigon contains hydrocodone (dihydrocodeinone) bitartrate, a semi-synthetic centrally-acting narcotic antitussive. Homatropine methylbromide is included in a subtherapeutic amount to discourage deliberate overdosage.
Each TUSSIGON tablet contains: Hydrocodone Bitartrate USP 5 mg Homatropine Methylbromide USP 1.5 mg.
The hydrocodone component is 4,5á- Epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan -6-one-tartrate (1:1) hydrate (2:5), a fine white crystal or crystalline powder which is derived from the opium alkaloid, thebaine, has a molecular weight of (494.50) and may be represented by the following structural formula:
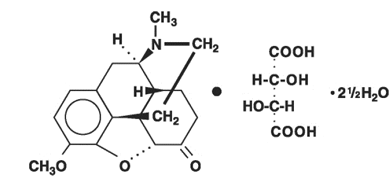 |
C18H21N03•C4H606•2½H20
Hydrocodone Bitartrate
Homatropine methylbromide is 8- Azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 3-[(hydroxy phenylacetyl)oxy]-8, 8- dimethyl-,bromide, endo-, a white crystal or fine white crystalline powder, with a molecular weight of (370.29).
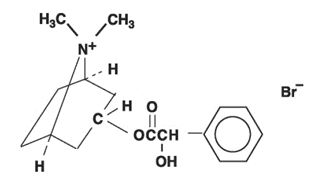 |
C17H24BrN03
Homatropine Methylbromide
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
TUSSIGON is indicated for the symptomatic relief of cough.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adult
One (1) tablet every 4 to 6 hours as needed; do not exceed six (6) tablets in 24 hours.
Children 6 To 12 Years Of Age
One-half (1/2) tablet every 4 to 6 hours as needed; do not exceed three (3) tablets in 24 hours.
HOW SUPPLIED
Each blue, scored tablet contains 5 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 1.5 mg homatropine methylbromide and is available in:
Bottles of 100 NDC 61570-102-01
Store at controlled room temperature 15°–30°C (59°–86°F). Oral prescription where permitted by state law.
This product's label may have been updated. For current full prescribing information, please visit www.pfizer.com.
Distributed by: Pfizer Inc, New York,NY 10017.Revised: Aug 2016.
Side Effects
Central Nervous System
Sedation, drowsiness, mental clouding, lethargy, impairment of mental and physical performance, anxiety, fear, dysphoria, dizziness, psychic dependence, mood changes.
Gastrointestinal System
Nausea and vomiting may occur; they are more frequent in ambulatory than in recumbent patients.
Prolonged administration of TUSSIGON may produce constipation.
Genitourinary System
Ureteral spasm, spasm of vesicle sphincters and urinary retention have been reported with opiates.
Respiratory Depression
TUSSIGON may produce dose-related respiratory depression by acting directly on brain stem respiratory centers (see OVERDOSE).
Dermatological
Skin rash, pruritus.
Drug Interactions
Patients receiving narcotics, antihistamines, antipsychotics, antianxiety agents or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with TUSSIGON may exhibit an additive CNS depression. When combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced.
The use of MAO inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants with hydrocodone preparations may increase the effect of either the antidepressants or hydrocodone.
Drug Abuse And Dependence
TUSSIGON is a Schedule II narcotic. Psychic dependence, physical dependence and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of narcotics; therefore, TUSSIGON should be prescribed and administered with caution. However, psychic dependence is unlikely to develop when TUSSIGON is used for a short time for the treatment of cough. Physical dependence, the condition in which continued administration of the drug is required to prevent the appearance of a withdrawal syndrome, assume clinically significant proportions only after several weeks of continued oral narcotic use, although some mild degree of physical dependence may develop after a few days of narcotic therapy.
Warnings
Hydrocodone can produce drug dependence of the morphine type and, therefore, has the potential for being abused. Psychic dependence, physical dependence and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of TUSSIGON and it should be prescribed and administered with the same degree of caution appropriate to the use of other narcotic drugs (see Drug Abuse And Dependence).
Respiratory Depression
TUSSIGON produces dose-related respiratory depression by directly acting on brain stem respiratory centers. If respiratory depression occurs, it may be antagonized by the use of naloxone hydrochloride and other supportive measures when indicated.
Head Injury And Increased Intracranial Pressure
The respiratory depression properties of narcotics and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions, or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, narcotics produce adverse reactions which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries.
Acute Abdominal Conditions
The administration of TUSSIGON or other narcotics may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Pediatric Use
In young children, as well as adults, the respiratory center is sensitive to the depressant action of narcotic cough suppressants in a dose-dependent manner. Benefit to risk ratio should be carefully considered especially in children with respiratory embarrassment (e.g. croup).
Precautions
General
Before prescribing medication to suppress or modify cough, it is important to ascertain that the underlying cause of cough is identified, that modification of cough does not increase the risk of clinical or physiological complications, and that appropriate therapy for the primary disease is provided.
Special Risk Patients
TUSSIGON should be given with caution to certain patients such as the elderly or debilitated, and those with severe impairment of hepatic or renal functions, hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture, asthma, and narrow-angle glaucoma.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Studies of TUSSIGON in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic and mutagenic potential and the effect on fertility have not been conducted.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with TUSSIGON. It is also not known whether TUSSIGON can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. TUSSIGON should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Babies born to mothers who have been taking opioids regularly prior to delivery will be physically dependent. The withdrawal signs include: irritability and excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, increased respiratory rate, increased stools, sneezing, yawning, vomiting and fever. The intensity of the syndrome does not always correlate with the duration of maternal opioid use or dose.
Labor And Delivery
As with all narcotics, administration of TUSSIGON to the mother shortly before delivery may result in some degree of respiratory depression in the newborn, especially if higher doses are used.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from TUSSIGON, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TUSSIGON in children under six have not been established.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
Signs And Symptoms
Serious overdosage with hydrocodone is characterized by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis), extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin and sometimes bradycardia and hypotension. In severe overdosage apnea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest and death may occur. The ingestion of very large amounts of TUSSIGON may, in addition, result in acute homatropine intoxication.
Treatment
Primary attention should be given to the reestablishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and the institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. The narcotic antagonist naloxone hydrochloride is a specific antidote for respiratory depression which may result from overdosage or unusual sensitivity to narcotics including hydrocodone. Therefore, an appropriate dose of naloxone hydrochloride should be administered, preferably by the intravenous route, simultaneously with efforts at respiratory resuscitation. For further information, see full prescribing information for naloxone hydrochloride. An antagonist should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory depression. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, vasopressors and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated. Gastric emptying may be useful in removing unabsorbed drug.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
TUSSIGON should not be administered to patients who are hypersensitive to hydrocodone or homatropine methylbromide.
Clinical Pharmacology
Hydrocodone is a semisynthetic narcotic antitussive and analgesic with multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of codeine. The precise mechanism of action of hydrocodone and other opiates is not known; however, hydrocodone is believed to act directly on the cough center. In excessive doses, hydrocodone like other opium derivatives, will depress respiration. The effects of hydrocodone in therapeutic doses on the cardiovascular system are insignificant. Hydrocodone can produce miosis, euphoria, physical and psychological dependence.
Following a 10 mg oral dose of hydrocodone administered to five adult male subjects, the mean peak concentration was 23.6 ± 5.2 ng/ml. Maximum serum levels were achieved at 1.3± 0.3 hours and the half-life was determined to be 3.8 ± 0.3 hours. Hydrocodone exhibits a complex pattern of metabolism including 0-demethylation, N-demethylation and 6-keto reduction to the corresponding 6-á and 6-â- hydroxymetabolites.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
Hydrocodone may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. The patient using TUSSIGON should be cautioned accordingly.
