Benzonatate Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: benzonatate softgels
- Brand Name: Benzonatate
side effects drug center benzonatate (benzonatate softgels) drug
Drug Description
What is Benzonatate and how is it used?
Benzonatate is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of cough. Benzonatate may be used alone or with other medications.
Benzonatate belongs to a class of drugs called Antitussives.
It is not known if Benzonatate is safe and effective in children younger than 10 years of age.
What are the possible side effects of Benzonatate?
Benzonatate may cause serious side effects including:
- confusion,
- difficulty breathing,
- difficulty speaking,
- visual hallucinations,
- shortness of breath,
- tightness in the chest, and
- wheezing
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Benzonatate include:
- drowsiness,
- dizziness,
- headache,
- stomach upset,
- constipation,
- stuffy nose,
- hypersensitivity reactions,
- confusion,
- visual hallucinations,
- nausea,
- itching,
- skin breakouts,
- burning in the eyes, and
- chills
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Benzonatate. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
WARNING
Hypersensitivity
Severe hypersensitivity reactions (including bronchospasm, laryngospasm and cardiovascular collapse) have been reported which are possibly related to local anesthesia from sucking or chewing the capsule instead of swallowing it. Severe reactions have required intervention with vasopressor agents and supportive measures.
Psychiatric Effects
Isolated instances of bizarre behavior, including mental confusion and visual hallucinations, have also been reported in patients taking benzonatate in combination with other prescribed drugs.
Accidental Ingestion And Death In Children
Keep benzonatate out of reach of children.
Accidental ingestion of benzonatate resulting in death has been reported in children below age 10.
Signs and symptoms of overdose have been reported within 15 to 20 minutes and death has been reported within one hour of ingestion. If accidental ingestion occurs, seek medical attention immediately (see OVERDOSE).
DESCRIPTION
Benzonatate, a non-narcotic antitussive agent, is 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23, 26-nonaoxaoctacosan-28-yl p-(butylamino) benzoate; with a molecular weight of 603.7.
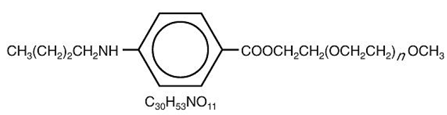 |
Benzonatate Capsules, USP contain 100 mg or 200 mg of benzonatate, USP.
Benzonatate Capsules also contain: D&C Yellow No. 10, gelatin, glycerin, methylparaben sodium and propylparaben sodium.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
Benzonatate is indicated for the symptomatic relief of cough.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults and Children over 10 years of age:
Usual dose is one 100 mg or 200 mg capsule three times a day as needed for cough. If necessary to control cough, up to 600 mg daily in three divided doses may be given. Benzonatate should be swallowed whole. Benzonatate Capsules are not to be broken, chewed, dissolved, cut or crushed.
HOW SUPPLIED
Benzonatate Capsules, USP are available as:
100 mg (oval, yellow) soft gelatin capsules with imprint “A5”.
NDC 62332-426-31 Bottles of 100
NDC 62332-426-71 Bottles of 500
200 mg (oblong, yellow) soft gelatin capsules with imprint “A6”.
NDC 62332-427-31 Bottles of 100
NDC 62332-427-71 Bottles of 500
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excurs ions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alembic Pharmaceuticals Limited at 1-866-210-9797 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Manufactured by: Swiss Caps AG Kirchberg, Switzerland. Revised: Nov 2018
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
Potential Adverse Reactions to benzonatate may include:
Hypersens itivity reactions including bronchospasm, laryngospasm, cardiovascular collapse possibly related to local anesthesia from chewing or sucking the capsule.
CNS: sedation; headache; dizziness; mental confusion; visual hallucinations.
GI: constipation, nausea, GI upset.
Dermatologic: pruritus; skin eruptions.
Other: nasal congestion; sensation of burning in the eyes; vague “chilly” sensation; numbness of the chest; hypersensitivity.
Deliberate or accidental overdose has resulted in death, particularly in children.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No Information Provided
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
No Information Provided
PRECAUTIONS
Benzonatate is chemically related to anesthetic agents of the para-amino-benzoic acid class (e.g., procaine; tetracaine) and has been associated with adverse CNS effects possibly related to a prior sensitivity to related agents or interaction with concomitant medication.
Usage In Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with benzonatate. It is also not known whether benzonatate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Benzonatate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when benzonatate is administered to a nursing woman.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and reproduction studies have not been conducted with benzonatate.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of 10 has not been established. Accidental ingestion resulting in death has been reported in children below age 10. Keep out of reach of children.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
Intentional and unintentional overdose may result in death, particularly in children.
The drug is chemically related to tetracaine and other topical anesthetics and shares various aspects of their pharmacology and toxicology. Drugs of this type are generally well absorbed after ingestion.
Signs And Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of overdose of benzonatate have been reported within 15 to 20 minutes. If capsules are chewed or dissolved in the mouth, oropharyngeal anesthesia will develop rapidly, which may cause choking and airway compromise.
CNS stimulation may cause restlessness and tremors which may proceed to clonic convulsions followed by profound CNS depression. Convulsions, coma, cerebral edema and cardiac arrest leading to death have been reported within 1 hour of ingestion.
Treatment
In case of overdose, seek medical attention immediately. Evacuate gastric contents and administer copious amounts of activated charcoal slurry. Even in the conscious patient, cough and gag reflexes may be so depressed as to necessitate special attention to protection against aspiration of gastric contents and orally administered materials. Convulsions should be treated with a short-acting barbiturate given intravenously and carefully titrated for the smallest effective dosage. Intensive support of respiration and cardiovascular-renal function is an essential feature of the treatment of severe intoxication from overdosage.
Do not use CNS stimulants.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to benzonatate or related compounds.
Clinical Pharmacology
Benzonatate acts peripherally by anesthetizing the stretch receptors located in the respiratory passages, lungs, and pleura by dampening their activity and thereby reducing the cough reflex at its source. It begins to act within 15 to 20 minutes and its effect lasts for 3 to 8 hours. Benzonatate has no inhibitory effect on the respiratory center in recommended dosage.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
Swallow benzonatate capsules whole. Do not break, chew, dissolve, cut, or crush benzonatate capsules. Release of benzonatate from the capsule in the mouth can produce a temporary local anesthesia of the oral mucosa and choking could occur. If numbness or tingling of the tongue, mouth, throat, or face occurs, refrain from oral ingestion of food or liquids until the numbness has resolved. If the symptoms worsen or persist, seek medical attention.
Keep benzonatate out of reach of children. Accidental ingestion resulting in death has been reported in children. Signs and symptoms of overdose have been reported within 15 to 20 minutes and death has been reported within one hour of ingestion. Signs and symptoms may include restlessness, tremors, convulsions, coma and cardiac arrest. If accidental ingestion occurs, seek medical attention immediately.
Overdosage resulting in death may occur in adults.
Do not exceed a single dose of 200 mg and a total daily dose of 600 mg. If you miss a dose of benzonatate, skip that dose and take the next dose at the next scheduled time. Do not take 2 doses of benzonatate at one time.
