Fluorometholone Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: fluorometholone ophthalmic suspension, usp 0.1% sterile
- Brand Name: FML
side effects drug center fml (fluorometholone ophthalmic suspension, usp 0.1% sterile) drug
Drug Description
What is Fluorometholone and how is it used?
Fluorometholone is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of Ocular Inflammation. Fluorometholone may be used alone or with other medications.
Fluorometholone belongs to a class of drugs called Antivirals, Ophthalmic; Corticosteroids, Opthalmic.
It is not known if Fluorometholone is safe and effective in children younger than 2 years of age.
What are the possible side effects of Fluorometholone?
Fluorometholone may cause serious side effects including:
- pain behind your eyes,
- sudden vision changes,
- slow healing after your eye surgery,
- eye pain,
- tunnel vision,
- seeing halos around lights, and
- signs of a new eye infection (swelling, draining, or crusting of your eyes)
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Fluorometholone include:
- mild stinging or burning in your eyes,
- feeling like something is in your eye,
- red or puffy eye lids,
- blurred vision, and
- drooping eye lids
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Fluorometholone. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
DESCRIPTION
FML® (fluorometholone ophthalmic suspension, USP) 0.1% is a sterile, topical anti-inflammatory agent for ophthalmic use.
Chemical Name
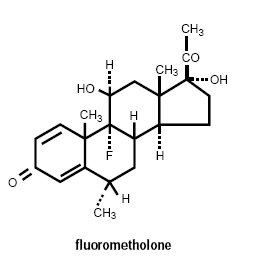
Fluorometholone: 9-Fluoro-11ß,17-dihydroxy-6α-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione.
Structural Formula
 |
Contains
Active: fluorometholone 0.1%. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.004%. Inactives: edetate disodium; polysorbate 80; polyvinyl alcohol 1.4%; purified water; sodium chloride; sodium phosphate, dibasic; sodium phosphate, monobasic; and sodium hydroxide to adjust pH. FML® suspension is formulated with a pH from 6.2 to 7.5. It has an osmolality range of 290-350 mOsm/kg.
Drug Description FML®
(fluorometholone) Ophthalmic Suspension, USP 0.1% sterile
DESCRIPTION
FML® (fluorometholone ophthalmic suspension, USP) 0.1% is a sterile, topical anti-inflammatory agent for ophthalmic use.
Chemical Name
Fluorometholone: 9-Fluoro-11ß,17-dihydroxy-6α-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione.
Structural Formula
 |
Contains
Active: fluorometholone 0.1%. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.004%. Inactives: edetate disodium; polysorbate 80; polyvinyl alcohol 1.4%; purified water; sodium chloride; sodium phosphate, dibasic; sodium phosphate, monobasic; and sodium hydroxide to adjust pH. FML® suspension is formulated with a pH from 6.2 to 7.5. It has an osmolality range of 290-350 mOsm/kg.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
FML® suspension is indicated for the treatment of corticosteroid-responsive inflammation of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea and anterior segment of the globe.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Shake well before using. Instill one drop into the conjunctival sac two to four times daily. During the initial 24 to 48 hours, the dosing frequency may be increased to one application every four hours. Care should be taken not to discontinue therapy prematurely.
If signs and symptoms fail to improve after two days, the patient should be re-evaluated (see PRECAUTIONS).
The dosing of FML® suspension may be reduced, but care should be taken not to discontinue therapy prematurely. In chronic conditions, withdrawal of treatment should be carried out by gradually decreasing the frequency of applications.
HOW SUPPLIED
FML® (fluorometholone ophthalmic suspension, USP) 0.1% is supplied sterile in opaque white LDPE plastic bottles with white high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps as follows:
5 mL in 10 mL bottle - NDC 11980-211-05
10 mL in 15 mL bottle - NDC 11980-211-10
15 mL in 15 mL bottle - NDC 11980-211-15
Storage
Store at 2° - 25°C (36°-77°F); protect from freezing. Store in an upright position.
Irvine, CA 92612, U.S.A. ® marks owned by Allergan, Inc. Made in the U.S.A. Revised: 02/2013
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
Adverse reactions include, in decreasing order of frequency, elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP) with possible development of glaucoma and infrequent optic nerve damage, posterior subcapsular cataract formation, and delayed wound healing.
Although systemic effects are extremely uncommon, there have been rare occurrences of systemic hypercorticoidism after use of topical dermatologic steroids applied to the skin.
Corticosteroid-containing preparations have also been reported to cause acute anterior uveitis and perforation of the globe. Keratitis, conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, mydriasis, conjunctival hyperemia, loss of accommodation and ptosis have occasionally been reported following local use of corticosteroids.
The development of secondary ocular infection (bacterial, fungal and viral) has occurred. Fungal and viral infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term applications of steroids. The possibility of fungal invasion should be considered in any persistent corneal ulceration where steroid treatment has been used (see WARNINGS).
Transient burning and stinging upon instillation and other minor symptoms of ocular irritation have been reported with the use of FML® suspension. Other adverse events reported with the use of fluorometholone include: allergic reactions; foreign body sensation; erythema of eyelid; eyelid edema/eye swelling; eye discharge; eye pain; eye pruritus; lacrimation increased; rash; taste perversion; visual disturbance (blurry vision); and visual field defect.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No information provided.
Warnings
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may increase intraocular pressure in susceptible individuals, resulting in glaucoma with damage to the optic nerve, defects in visual acuity and fields of vision, and in posterior subcapsular cataract formation. Prolonged use may also suppress the host immune response and thus increase the hazard of secondary ocular infections.
Various ocular diseases and long-term use of topical corticosteroids have been known to cause corneal and scleral thinning. Use of topical corticosteroids in the presence of thin corneal or scleral tissue may lead to perforation.
Acute purulent infections of the eye may be masked or activity enhanced by the presence of corticosteroid medication.
If this product is used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be routinely monitored even though it may be difficult in children and uncooperative patients. Steroids should be used with caution in the presence of glaucoma. Intraocular pressure should be checked frequently.
The use of steroids after cataract surgery may delay healing and increase the incidence of bleb formation.
Use of ocular steroids may prolong the course and may exacerbate the severity of many viral infections of the eye (including herpes simplex). Employment of a corticosteroid medication in the treatment of patients with a history of herpes simplex requires great caution; frequent slit lamp microscopy is recommended.
Precautions
General
The initial prescription and renewal of the medication order beyond 20 milliliters of FML® suspension should be made by a physician only after examination of the patient with the aid of magnification, such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining. If signs and symptoms fail to improve after two days, the patient should be re-evaluated.
As fungal infections of the cornea are particularly prone to develop coincidentally with long-term local corticosteroid applications, fungal invasion should be suspected in any persistent corneal ulceration where a corticosteroid has been used or is in use. Fungal cultures should be taken when appropriate.
If this product is used for 10 days or longer, intraocular pressure should be monitored (see WARNINGS).
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies have been conducted in animals or in humans to evaluate the possibility of these effects with fluorometholone.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects - Pregnancy Category C
Fluorometholone has been shown to be embryocidal and teratogenic in rabbits when administered at low multiples of the human ocular dose. Fluorometholone was applied ocularly to rabbits daily on days 6-18 of gestation, and dose-related fetal loss and fetal abnormalities including cleft palate, deformed rib cage, anomalous limbs and neural abnormalities such as encephalocele, craniorachischisis, and spina bifida were observed. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of fluorometholone in pregnant women, and it is not known whether fluorometholone can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Fluorometholone should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether topical ophthalmic administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Systemically-administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from fluorometholone, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in infants below the age of two years have not been established.
Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
No information provided.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
FML® suspension is contraindicated in most viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva, including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, and varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye, and fungal diseases of ocular structures.
FML® suspension is also contraindicated in individuals with known or suspected hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients of this preparation and to other corticosteroids.
Clinical Pharmacology
Corticosteroids inhibit the inflammatory response to a variety of inciting agents and probably delay or slow healing. They inhibit the edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilation, leukocyte migration, capillary proliferation, fibroblast proliferation, deposition of collagen, and scar formation associated with inflammation.
There is no generally accepted explanation for the mechanism of action of ocular corticosteroids. However, corticosteroids are thought to act by the induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins, collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting the release of their common precursor, arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
Corticosteroids are capable of producing a rise in intraocular pressure. In clinical studies of documented steroid-responders, fluorometholone demonstrated a significantly longer average time to produce a rise in intraocular pressure than dexamethasone phosphate; however, in a small percentage of individuals, a significant rise in intraocular pressure occurred within one week. The ultimate magnitude of the rise was equivalent for both drugs.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
If inflammation or pain persists longer than 48 hours or becomes aggravated, the patient should be advised to discontinue use of the medication and consult a physician.
This product is sterile when packaged. To prevent contamination, care should be taken to avoid touching the bottle tip to eyelids or to any other surface. The use of this bottle by more than one person may spread infection. Keep bottle tightly closed when not in use. Keep out of the reach of children.
The preservative in FML® suspension, benzalkonium chloride, may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Patients wearing soft contact lenses should be instructed to wait at least 15 minutes after instilling FML® suspension to insert soft contact lenses.
