Gvoke Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: glucagon injection
- Brand Name: Gvoke
side effects drug center gvoke (glucagon injection) drug
Drug Description
What is Gvoke and how is it used?
Gvoke is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of severe Hypoglycemia. Gvoke may be used alone or with other medications.
Gvoke belongs to a class of drugs called Diagnostics, Gastrointestinal; Glucose-Elevating Agents; Hypoglycemia Antidotes.
It is not known if Gvoke is safe and effective in children younger than 2 years of age.
What are the possible side effects of Gvoke?
Gvoke may cause serious side effects including:
- hives,
- difficulty breathing,
- swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat,
- fast or slow heartbeat, and
- redness, itching, blistering, crusting, scaling, or other skin sores or lesions on your face, legs, groin, or genital area
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Gvoke include:
- nausea,
- vomiting, and
- swelling where the injection was given
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Gvoke. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
DESCRIPTION
GVOKE contains glucagon, an antihypoglycemic agent used to treat severe hypoglycemia. Glucagon is a single chain containing 29 amino acid residues and has a molecular weight of 3483 and is identical to human glucagon. Glucagon is produced by solid phase synthesis with subsequent purification.
Its molecular formula is C153H225N43O49S with the following structure:
 |
GVOKE is a clear, colorless to pale yellow, sterile solution for subcutaneous injection available in 0.5 mg per 0.1 mL or 1 mg per 0.2 mL auto-injector or pre-filled syringe.
Each 0.2 mL of GVOKE contains 1 mg of glucagon, 11.1 mg of trehalose dihydrate USP and 1.2 mg of 1N sulfuric acid, NF in dimethyl sulfoxide diluent.
Each 0.1 mL of GVOKE contains 0.5 mg of glucagon, 5.6 mg of trehalose dihydrate USP and 0.6 mg of 1N sulfuric acid, NF in dimethyl sulfoxide diluent.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
GVOKE is indicated for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in pediatric and adult patients with diabetes ages 2 years and above.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Important Administration Instructions
GVOKE auto-injector and pre-filled syringe are for subcutaneous injection only.
Instruct patients and their caregivers on the signs and symptoms of severe hypoglycemia. Because severe hypoglycemia requires the help of others to recover, instruct the patient to inform those around them about GVOKE and its Instructions for Use. Administer GVOKE as soon as possible when severe hypoglycemia is recognized.
Instruct the patient or caregiver to read the Instructions for Use at the time they receive a prescription for GVOKE. Emphasize the following instructions to the patient or caregiver:
- Do not open foil pouch until ready to administer GVOKE.
- Administer GVOKE according to the printed instructions on the foil pouch label, carton, or the Instructions for Use.
- Visually inspect GVOKE prior to administration. The solution should appear clear and colorless to pale yellow and be free of particles. If the solution is discolored or contains particulate matter, do not use.
- Administer the injection in the lower abdomen, outer thigh, or outer upper arm.
- Call for emergency assistance immediately after administering the dose.
- When the patient has responded to treatment, give oral carbohydrates to restore the liver glycogen and prevent recurrence of hypoglycemia.
- Do not attempt to reuse GVOKE. Each GVOKE device contains a single dose of glucagon and cannot be reused.
Dosage In Adults And Pediatric Patients Aged 2 years And Above
Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 12 and Older
- The recommended dose of GVOKE is 1 mg administered by subcutaneous injection into lower abdomen, outer thigh, or outer upper arm.
- If there has been no response after 15 minutes, an additional 1 mg dose of GVOKE from a new device may be administered while waiting for emergency assistance.
Pediatric Patients Aged 2 To Under 12 Years Of Age
- The recommended dose for pediatric patients who weigh less than 45 kg is 0.5 mg GVOKE administered by subcutaneous injection into the lower abdomen, outer thigh, or outer upper arm.
- The recommended dose for pediatric patients who weigh 45 kg or greater is 1 mg GVOKE administered by subcutaneous injection into the lower abdomen, outer thigh, or outer upper arm.
- If there has been no response after 15 minutes, an additional weight appropriate dose of GVOKE from a new device may be administered while waiting for emergency assistance.
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
GVOKE injection is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution available as follows:
- 0.5 mg/0.1 mL single-dose pre-filled HypoPen auto-injector
- 1 mg/0.2 mL single-dose pre-filled HypoPen auto-injector
- 0.5 mg/0.1 mL single-dose pre-filled syringe
- 1 mg/0.2 mL single-dose pre-filled syringe
Storage And Handling
GVOKE injection is supplied as a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution in the following configurations:
| GVOKE | Strength | Packaging Size | NDC number |
| HypoPen | 0.5 mg per 0.1 mL | 1 single-dose auto-injector | 72065-120-11 |
| HypoPen | 0.5 mg per 0.1 mL | 2 single-dose auto-injectors | 72065-120-12 |
| HypoPen | 1 mg per 0.2 mL | 1 single-dose auto-injector | 72065-121-11 |
| HypoPen | 1 mg per 0.2 mL | 2 single-dose auto-injectors | 72065-121-12 |
| PFS | 0.5 mg per 0.1 mL | 1 single-dose pre-filled syringe | 72065-130-11 |
| PFS | 0.5 mg per 0.1 mL | 2 single-dose pre-filled syringes | 72065-130-12 |
| PFS | 1 mg per 0.2 mL | 1 single-dose pre-filled syringe | 72065-131-11 |
| PFS | 1 mg per 0.2 mL | 2 single-dose pre-filled syringes | 72065-131-12 |
- Store at Controlled Room Temperature, 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F). Do not refrigerate or freeze.
- Store in original sealed foil pouch until time of use.
- Do not expose to extreme temperatures.
- Do not use GVOKE after the expiration date printed on the carton and foil pouch.
Manufactured for : Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc. by Pyramid Laboratories Inc., Costa Mesa, CA 92626. For information contact: Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 180 North LaSalle Street, Suite 1600, Chicago, IL 60601, 1-877-XERIS-37 (1-877-937-4737) www.xerispharma.com. Revised: Sep 2019
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in labeling:
- Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions [ see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
- Necrolytic Migratory Erythema [ see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of GVOKE cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of other drugs and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions In Adult Patients
The safety of GVOKE was evaluated in two randomized, blinded, 2-way crossover studies conducted in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. In total, 154 patients received an injection of GVOKE [ see Clinical Studies].
The most common adverse reactions occurring in 2% or more of adult subjects treated with GVOKE during clinical trials are listed in Table 1.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring ≥ 2% in Adult Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with GVOKE
| GVOKE 1 mg dose (N= 154) | |
| Nausea | 30% |
| Vomiting | 16% |
| Injection site edema raised 1 mm or greater | 7% |
| Headache | 5% |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Beta-Blockers
Patients taking beta-blockers may have a transient increase in pulse and blood pressure when given GVOKE.
Indomethacin
In patients taking indomethacin, GVOKE may lose its ability to raise blood glucose or may even produce hypoglycemia.
Warfarin
GVOKE may increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
Patients taking beta-blockers may have a transient increase in pulse and blood pressure when given GVOKE.
Indomethacin
In patients taking indomethacin, GVOKE may lose its ability to raise blood glucose or may even produce hypoglycemia.
Warfarin
GVOKE may increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the PRECAUTIONS section.
PRECAUTIONS
Catecholamine Release In Patients With Pheochromocytoma
GVOKE is contraindicated in patients with pheochromocytoma because glucagon may stimulate the release of catecholamines from the tumor [ see CONTRAINDICATIONS]. If the patient develops a dramatic increase in blood pressure and a previously undiagnosed pheochromocytoma is suspected, 5 to 10 mg of phentolamine mesylate, administered intravenously, has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure.
Hypoglycemia In Patients With Insulinoma
In patients with insulinoma, administration of glucagon may produce an initial increase in blood glucose; however, glucagon administration may directly or indirectly (through an initial rise in blood glucose) stimulate exaggerated insulin release from an insulinoma and cause hypoglycemia. GVOKE is contraindicated in patients with insulinoma [ see CONTRAINDICATIONS]. If a patient develops symptoms of hypoglycemia after a dose of GVOKE, give glucose orally or intravenously.
Hypersensitivity And Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions have been reported with glucagon, these include generalized rash, and in some cases anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties and hypotension. GVOKE is contraindicated in patients with a prior hypersensitivity reaction [see CONTRAINDICATIONS].
Lack Of Efficacy In Patients With Decreased Hepatic Glycogen
GVOKE is effective in treating hypoglycemia only if sufficient hepatic glycogen is present. Patients in states of starvation, with adrenal insufficiency or chronic hypoglycemia may not have adequate levels of hepatic glycogen for GVOKE administration to be effective. Patients with these conditions should be treated with glucose.
Necrolytic Migratory Erythema
Necrolytic migratory erythema (NME), a skin rash commonly associated with glucagonomas (glucagon-producing tumors) and characterized by scaly, pruritic erythematous plaques, bullae, and erosions, has been reported postmarketing following continuous glucagon infusion. NME lesions may affect the face, groin, perineum and legs or be more widespread. In the reported cases NME resolved with discontinuation of the glucagon, and treatment with corticosteroids was not effective. Should NME occur, consider whether the benefits of continuous glucagon infusion outweigh the risks.
Hypoglycemia In Patients With Glucagonoma
Glucagon administered to patients with glucagonoma may cause secondary hypoglycemia. Test patients suspected of having glucagonoma for blood levels of glucagon prior to treatment, and monitor for changes in blood glucose levels during treatment. If a patient develops symptoms of hypoglycemia after a dose of Glucagon for Injection, give glucose orally or intravenously.
Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient and family members or caregivers to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Recognition Of Severe Hypoglycemia
Inform patient and family members or caregivers on how to recognize the signs and symptoms of severe hypoglycemia and the risks of prolonged hypoglycemia.
Administration
Review the Patient Information and Instructions for Use with the patient and family members or caregivers.
Serious Hypersensitivity
Inform patients that allergic reactions can occur with GVOKE. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptoms of serious hypersensitivity reactions [ see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Long term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been performed. Recombinant glucagon was positive in the bacterial Ames assay. It was determined that an increase in colony counts was related to technical difficulties in running this assay with peptides. Studies in rats have shown that glucagon does not cause impaired fertility.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from case reports and a small number of observational studies with glucagon use in pregnant women over decades of use have not identified a drugassociated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Multiple small studies have demonstrated a lack of transfer of pancreatic glucagon across the human placental barrier during early gestation. In a rat reproduction study, no embryofetal toxicity was observed with glucagon administered by injection during the period of organogenesis at doses representing up to 40 times the human dose, based on body surface area (mg/m²) (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In pregnant rats given animal sourced glucagon twice-daily by injection at doses up to 2 mg/kg (up to 40 times the human dose based on body surface area extrapolation, mg/m²) during the period of organogenesis, there was no evidence of increased malformations or embryofetal lethality.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information available on the presence of glucagon in human or animal milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. However, glucagon is a peptide and would be expected to be broken down to its constituent amino acids in the infant's digestive tract and is therefore, unlikely to cause harm to an exposed infant.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of GVOKE for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes have been established in pediatric patients ages 2 years and above. Use of GVOKE for this indication is supported by evidence from a study in 31 pediatric patients ages 2 and older with type 1 diabetes mellitus [ see Clinical Studies].
The safety and effectiveness of GVOKE have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of GVOKE did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Limited clinical trial experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
If overdosage occurs, the patient may experience nausea, vomiting, inhibition of GI tract motility, increase in blood pressure, and pulse rate. In case of suspected overdosing, serum potassium may decrease and should be monitored and corrected if needed. If the patient develops a dramatic increase in blood pressure, phentolamine mesylate has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure for the short time that control would be needed.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GVOKE is contraindicated in patients with:
- Pheochromocytoma [ see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Insulinoma [ see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS] because of the risk of hypoglycemia
- Known hypersensitivity to glucagon or to any of the excipients in GVOKE. Allergic reactions have been reported with glucagon and include anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties and hypotension [ see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
Glucagon increases blood glucose concentration by activating hepatic glucagon receptors, thereby stimulating glycogen breakdown and release of glucose from the liver. Hepatic stores of glycogen are necessary for glucagon to produce an antihypoglycemic effect.
Pharmacodynamics
After administration of 1 mg GVOKE in adult patients with diabetes, the mean maximum glucose increase from baseline was 176 mg/dL.
Figure 1: Mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM) Plasma Glucose vs. Time from 1 mg GVOKE Injection in Adult Subjects with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
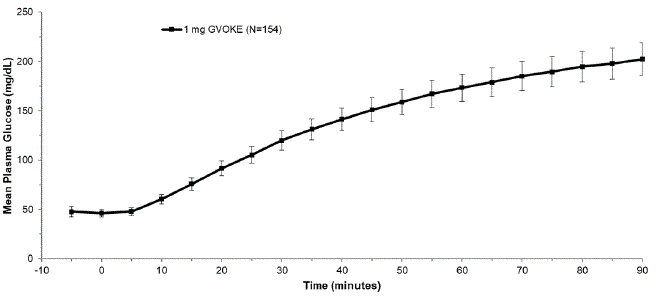 |
In pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes (2 to less than 18 years), the mean maximum glucose increase from baseline was 134 mg/dL (2 to less than 6 years), 145 mg/dL (6 to less than 12 years), and 123 mg/dL (12 to less than 18 years).
Figure 2: Mean (± SEM) Plasma Glucose vs. Time from GVOKE Injection in Pediatric Subjects with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
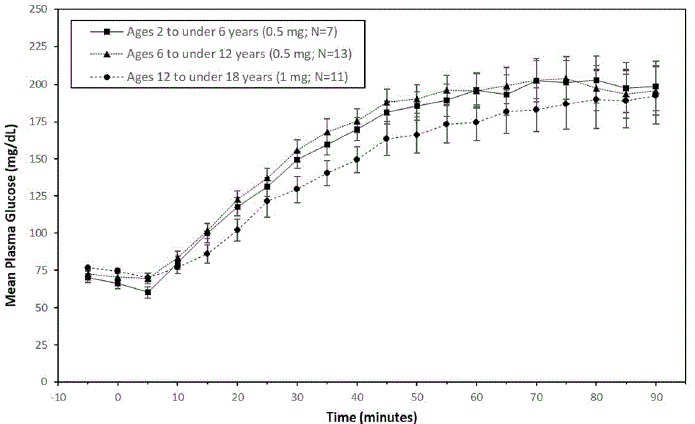 |
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Subcutaneous injection of 1 mg GVOKE in adult type 1 diabetes mellitus subjects resulted in a mean glucagon Cmax of 2481.3 pg/mL, tmax of 50 minutes and AUC0-240min of 3454.6 pg*min/mL.
Figure 3: Mean (± SEM) Plasma Glucagon Concentration vs. Time for 1 mg GVOKE Injection in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
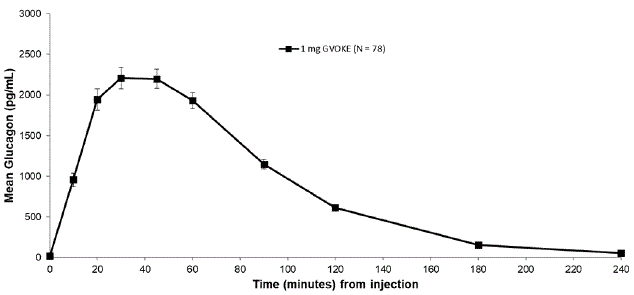 |
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution was in the range of 137-2425 L.
Elimination
The half-life of GVOKE was determined to be 32 minutes.
Metabolism
Glucagon is extensively degraded in liver, kidney, and plasma.
Excretion
Urinary excretion of intact glucagon has not been measured.
Specific Populations
Pediatrics
Subcutaneous injection of 0.5 mg GVOKE in subjects ages 2 to under 6 years resulted in a mean glucagon Cmax of 2300 pg/mL, tmax of 41 minutes, and AUC0-180min of 1389 pg/mL*min. Subcutaneous injection of 0.5 mg GVOKE in subjects ages 6 to under 12 years resulted in a mean Cmax of 1600 pg/mL, median tmax of 34 minutes and AUC0-180min of 1047 pg/mL*min. Subcutaneous injection of 1 mg GVOKE in subjects ages 12 to less than 18 years resulted in a mean Cmax of 1900 pg/mL, tmax of 51 minutes AUC0-180min of 1343 pg/mL*min. Mean plasma glucagon levels were similar across the age groups following age appropriate doses of GVOKE.
Figure 4: Mean (± SEM) Plasma Glucagon Concentration vs. Time from GVOKE Injection in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
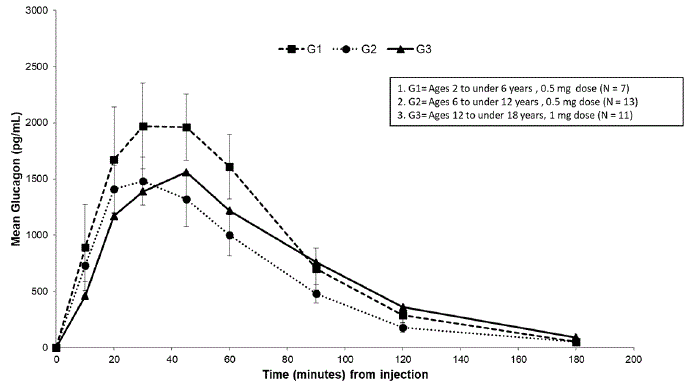 |
Clinical Studies
Adult Patients Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
GVOKE was evaluated in adult patients aged 18 to 74 years with type 1 diabetes in two multi-center 2-way crossover studies, Study A was double-blinded with 80 patients, and Study B was single-blinded with 81 patients. Both studies involved 2 clinic visits 7 to 28 days apart, with random assignment to receive GVOKE 1 mg during one session and GEK 1 mg during the other. 154 subjects received an injection of GVOKE and 157 subjects received an injection of GEK. A total of 152 subjects received both GVOKE and GEK.
The efficacy of GVOKE was compared to GEK in subjects who were in a state of insulin-induced hypoglycemia via insulin infusion with target plasma glucose less than 50 mg/dL. In Study A, mean plasma glucose at time of glucagon administration was 44.8 mg/dL and 45.2 mg/dL for GVOKE and GEK, respectively. In Study B, mean plasma glucose at time of glucagon administration was 47.7 mg/dL and 48.7 mg/dL for GVOKE and GEK, respectively.
Treatment ‘success’ was defined as plasma glucose increase from mean value at time of glucagon administration to absolute value greater than 70 mg/dL or relative increase of 20 mg/dL or greater, at 30 minutes after glucagon administration. In a pooled analysis of Study A and Study B, the proportion of patients who achieved treatment ‘success’ was 98.7 % in the GVOKE group and 100% in the GEK group and the comparison between groups met the pre-specified non-inferiority margin. A summary of treatment ‘success’ rates is shown in Table 3.
The mean time to treatment ‘success’ was 13.8 minutes in the GVOKE group and 10 minutes in the GEK group.
Table 3: Adult Patients Meeting Treatment Success in Studies A and B Combined
| Study A (n=80) | Study B (n=81) | Pooled Studies A and B (n=161)2 | ||||
| GVOKE | GEK | GVOKE | GEK | GVOKE | GEK | |
| Treatment Success-n (%) 1 | 76 (97%) | 79 (100%) | 76 (100%) | 78 (100%) | 152 (99%) | 157 (100%) |
| Glucose criteria met- n (%) | 74 (95%) | 79 (100%) | 76 (100%) | 78 (100%) | 150(97%) | 157(100%) |
| 20 mg/dL or greater increase from baseline | 76 (97%) | 79 (100%) | 76 (100%) | 78 (100%) | 152(99%) | 157(100%) |
| 1 - Treatment success is defines as blood glucose greater than 70 mg/dL or an increase of blood glucose by 20 mg/dL or greater from baseline. The efficacy analysis population consisted of all patients who received both doses of the study drug. 2 - Percentage based on number of patients from both studies. | ||||||
Pediatric Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
GVOKE was evaluated in a study in 31 pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Patients were administered insulin to induce a plasma glucose of less than 80 mg/dL. Patients ages 2 to under 6 years and 6 to under 12 years of age then received a 0.5 mg dose of GVOKE. Patients ages 12 and older received a 0.5 mg or 1 mg dose of GVOKE.
All evaluable pediatric patients (30/30) achieved a target glucose increase of at least 25 mg/dL. Following administration, plasma glucose levels over time showed similar glucose responses for patients in each age group. A summary of plasma glucose results are shown in Table 4.
Table 4: Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Plasma Glucose by Age Group
| Age Group | Plasma Glucose Mean (SD) | |||
| GVOKE Dose | Baseline | (mg/dL) 30 minutes | Change | |
| 2 to under 6 years (n=7) | 0.5 mg | 68.1 (8.3) | 149.6 (15.2) | 81.4 (18.3) |
| 6 to under 12 years (n=13) | 0.5 mg | 71.6 (7.6) | 155.8 (26.5) | 84.2 (25.3) |
| 12 to under 18 years (n=11) | 0.5 mg | 75.2 (2.1) | 128.1 (20.46) | 52.9 (19.88) |
| 1 mg | 74.5 (4.84) | 129.5 (29.5) | 55 (27.3) | |
| SD=standard deviation | ||||
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
Gvoke HypoPen™
(glucagon injection) Instructions for Use
- Become familiar with the following instructions before an emergency happens.
- Do not use this auto-injector past the expiration date printed on the device. Replace GVOKE HypePen before the expiration date on the box.
- If you have questions regarding the use of this product, talk to a healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Make sure that relatives, close friends or caregivers know that if you become unconscious, they should call for emergency medical help right away. The GVOKE HypoPen may have been prescribed so that relatives, close friends and caregivers can give the injection if you become hypoglycemic (severe low blood sugar) and are unable to take sugar by mouth. If you are unconscious, the GVOKE HypoPen can be given while awaiting medical assistance.
Show your relatives, close friends or caregivers where you store the GVOKE HypoPen and how to use it. They need to know how to use the GVOKE HypoPen before an emergency situation happens.
Indications for Use
GVOKE HypoPen is for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in pediatric and adult patients with diabetes ages 2 years and above. Symptoms of severe hypoglycemia include, unconsciousness, and seizures or convulsions.
Give the GVOKE HypoPen if:
- the patient is unconscious,
- the patient is unable to eat sugar or a sugar-sweetened product,
- the patient is having a seizure, or
- you have tried to give the patient sugar or drinks that are high in sugar such as a regular soft drink (soda) or fruit juice and the patient does not get better.
Milder cases of hypoglycemia should be treated promptly by eating sugar or a sugar-sweetened product. (See Information on Hypoglycemia for more information on the symptoms of low blood sugar.) The GVOKE HypoPen will not work when taken by mouth (orally).
Understanding the GVOKE HypoPen
The adult GVOKE HypoPen contains a 1 mg dose of glucagon and is in a foil pouch. Below is a picture of the pouch. See the GVOKE HypoPen package for a full view of the Quick-Use Guide.
Adult GVOKE HypoPen (1 mg dose)
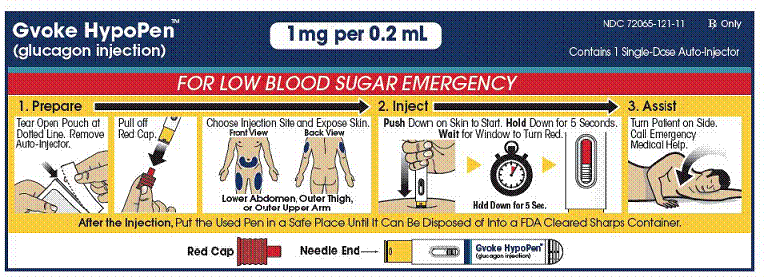 |
The pediatric GVOKE HypoPen contains a 0.5 mg dose of glucagon and is in a foil pouch. Below is a picture of the pouch. Below is a picture of the pouch. See the GVOKE HypoPen package for a full view of the Quick-Use guide.
Pediatric GVOKE HypoPen (0.5 mg dose)
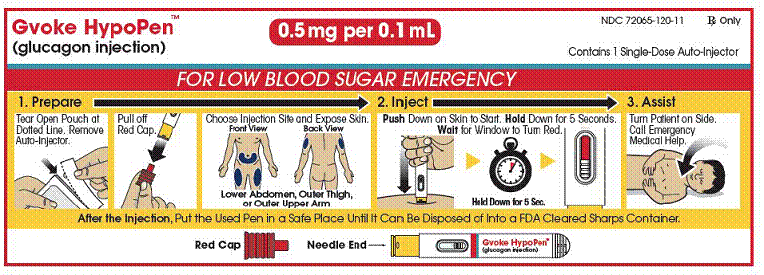 |
 |
Note: Each GVOKE HypoPen should be used one time and then thrown away (discarded).
Storage Information
- Store in sealed original foil pouch until time of use.
- Store at room temperature, 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Information on Hypoglycemia
Early symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) include:
- sweating
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- sleep disturbances
- palpitation
- anxiety
- tremor
- blurred vision
- hunger
- slurred speech
- depressed mood
- tingling in the hands, feet, lips, or tongue
- irritability
- light-headedness
- abnormal behavior
- inability to concentrate
- unsteady movement
- headache
- personality changes
If not treated, the patient may progress to severe hypoglycemia which can include:
- confusion
- seizures
- unconsciousness
- death
The occurrence of early symptoms calls for quick and, if necessary, repeated administration of some form of carbohydrate. Patients should always carry a quick source of sugar, such as candy mints or glucose tablets. The prompt treatment of mild hypoglycemic symptoms can prevent severe hypoglycemic reactions. If the patient does not improve or if administration of carbohydrate is impossible, the GVOKE HypoPen should be given or the patient should be treated with intravenous glucose by a medical professional.
Possible Problems with GVOKE HypoPen Treatment
Common side effects in adults and pediatric patients are nausea and vomiting. The product may cause serious side effects including serious allergic reactions, fast heart beat and high blood pressure.
People may be allergic to glucagon or to one of the inactive ingredients in GVOKE HypoPen or may experience fast heart-beat for a short while.
If you experience any other reactions that may have been caused by the GVOKE HypoPen, please contact your healthcare provider.
Important:
- Act quickly. Prolonged unconsciousness may be harmful.
- After the injection is complete, turn the unconscious patient on his or her side to prevent them from choking in case they throw up (vomit).
- Carefully read and follow these instructions. Have a healthcare provider show you the right way to use the GVOKE HypoPen.
Important Warnings
- Do not open pouch until time of use.
- Do not use after the expiration date has passed.
- Do not use if the red needle cap has been removed or is damaged.
- Do not remove the red cap until you are ready to inject.
- Do not put or press thumb, fingers, or hand over the yellow needle guard.
- Call a healthcare provider as soon as glucagon has been injected.
- If the patient does not awaken within 15 minutes, give another dose of GVOKE HypoPen and call for emergency medical help right away.
- Feed the patient as soon as he or she awakens and is able to swallow.
Read and become familiar with the following instructions before an emergency happens. If you have questions about using the GVOKE HypoPen, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
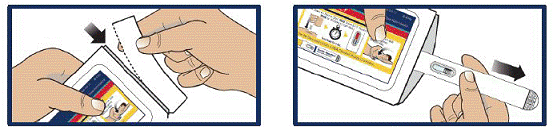
Remove GVOKE HypoPen from Pouch
- Tear open pouch at the dotted line and carefully remove the GVOKE HypoPen (see Figure 1).
Figure 1
 |
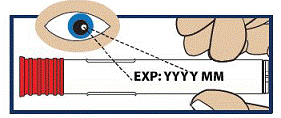
Check the Expiration Date
- Check the expiration date printed on the label of the GVOKE HypoPen (see Figure 2).
Important:
Do not use the GVOKE HypoPen if the expiration date has passed. If the GVOKE HypoPen is expired, throw it away in an FDA cleared sharps container and use a new GVOKE HypoPen.
Figure 2
 |
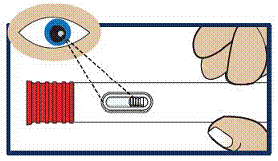
Inspect the Solution
- Look at the liquid medicine through the viewing window. It must be clear and colorless, or a pale yellow (see Figure 3).
Important:
Do not use GVOKE HypoPen or inject if the liquid contains lumps, flakes, or particles.
Do not inject if solution is not visible in the viewing window.
If you do not have another GVOKE HypoPen to use, call for emergency medical help right away.
Figure 3
 |
Pull off Red Cap
- Pull the red needle cap straight off of the device (see Figure 4).
Important:
Do not put your thumb, fingers, or hand on or near the needle guard or needle opening to help prevent accidental needle sticks.
Figure 4
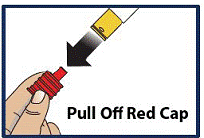 |
Choose Injection Site and Expose Bare Skin
- Choose the lower abdomen, outer thigh, or outer upper arm for your injection site (see Figure 5).
- Remove any clothing covering the injection site (see Figure 6). The injection must be performed straight into the skin.
Important:
- Do not inject through clothing.
Figure 5 and 6
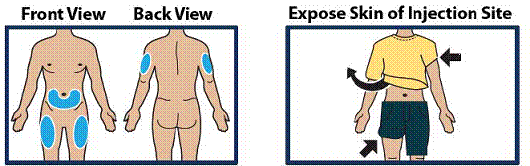 |
Push and Hold to Start Injection
- Push and hold the GVOKE HypoPen straight Down against the injection site. Listen for a “Click”
- Continue to hold the device down and count slowly to 5 (see Figure 7).
- When the injection is complete, the viewing window will be red (see Figure 8).
Important:
Do not lift up the GVOKE HypoPen until the injection is complete.
Figure 7 And 8
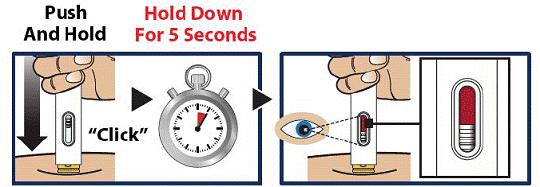 |
Lift Away from Skin
- Lift the device straight up from the injection site (see Figure 9).
- The yellow needle guard will lock over the needle.
Figure 9
 |
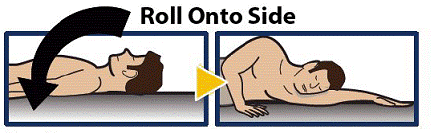
Turn Patient onto Side
- When an unconscious person wakes up, he or she may throw up (vomit).
- Turn the patient on their side to prevent choking (see Figure 10).
Figure 10
 |
Make Sure Patient Receives Immediate Medical Attention After Use
- Call for emergeny medical help right after the GVOKE HypoPen has been injected.
- Even if the GVOKE HypoPen helps the patient to wake up, you should still call for emergency medical help right away.
- The patients’s healthcare provider should also be notified whenever a severe drop in blood sugar (hypoglycemic reactions) happens. Hypoglycemia may happen again after receiving an injection from the GVOKE HypoPen. The patient’s diabetes medication may need to be changed.
- Feed the patient as soon as he or she wakes up and is able to swallow. Give the patient a fast-acting source of sugar (such as a regular soft drink or fruit juice) and a long-acting source of sugar (such as crackers and cheese or a meat sandwich). If the patient does not wake up within 15 minutes, give another dose of glucagon and notify emergency medical services right away.
Re-Cap and Dispose of the GVOKE HypoPen in a FDA Cleared Sharps Disposal Container
If a puncture-resistant sharps container is not available, carefully re-cap and store the GVOKE HypoPen in a safe place until it can be disposed of into a FDA cleared sharps container (see Figure 11). Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
If you do not have a FDA cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic
- can be closed with a tight-fitting puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
- upright and stable during use
- leak-resistant
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this.
Always keep the sharps container out of the reach of children.
If needed, make sure to get a refill of your GVOKE HypoPen.
Figure 11
 |
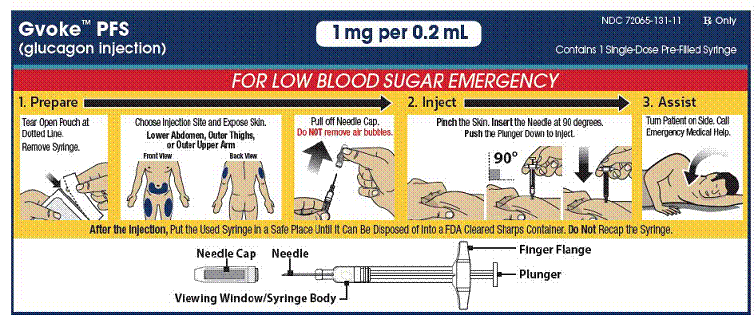
Gvoke™ PFS
(glucagon injection) Instructions for Use
Gvoke™ PFS
(glucagon injection) Instructions for Use
- Become familiar with the following instructions before an emergency happens.
- Do not use this product past the expiration date printed on the device. Replace GVOKE PFS before the expiration date on the box.
- If you have questions regarding the use of this product, talk to a healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Make sure that relatives, close friends or caregivers know that if you become unconscious, they should call for emergency medical help right away. The GVOKE PFS may have been prescribed so that relatives, close friends and caregivers can give the injection if you become hypoglycemic (severe low blood sugar) and are unable to take sugar by mouth. If you are unconscious, the GVOKE PFS can be given while awaiting medical assistance.
Show your relatives, close friends or caregivers where you store the GVOKE PFS and how to use it. They need to know how to use the GVOKE PFS before an emergency situation happens.
Indications for Use
GVOKE PFS is for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in pediatric and adult patients with diabetes ages 2 years and above. Symptoms of severe hypoglycemia include unconsciousness, and seizures or convulsions.
Give the GVOKE PFS if:
- the patient is unconscious,
- the patient is unable to eat sugar or a sugar-sweetened product,
- the patient is having a seizure, or
- you have tried to give the patient sugar or drinks that are high in sugar such as a regular soft drink (soda) or fruit juice and the patient does not get better.
Milder cases of hypoglycemia should be treated promptly by eating sugar or a sugar-sweetened product. (See Information on Hypoglycemia for more information on the symptoms of low blood sugar.) The GVOKE PFS will not work when taken by mouth (orally).
Understanding the GVOKE PFS
The adult GVOKE PFS contains a 1 mg dose of glucagon and is in a foil pouch. Below is a picture of the pouch. See the GVOKE PFS package for a full view of the Quick-Use Guide.
Adult GVOKE PFS (1 mg dose)
 |
The pediatric GVOKE PFS contains a 0.5 mg dose of glucagon and is in a foil pouch. Below is a picture of the pouch. See the GVOKE PFS package for a full view of the Quick-Use Guide.
Pediatric GVOKE PFS (0.5 mg dose)
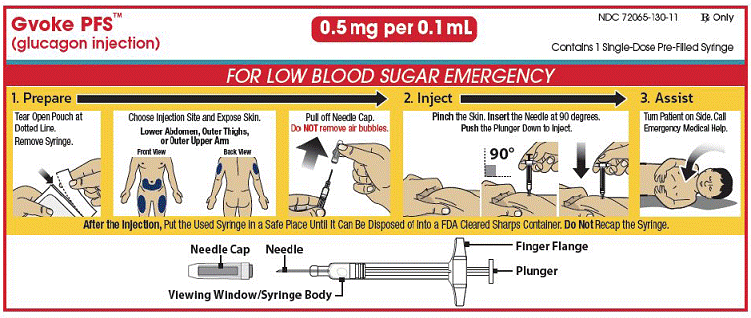 |
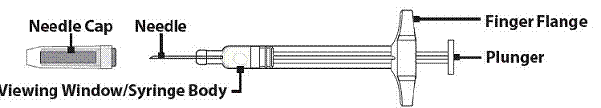 |
Note: Each GVOKE PFS should be used one time and then thrown away (discarded).
Storage Information
- Store in sealed original foil pouch until time of use.
- Store at room temperature, 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Information on Hypoglycemia
Early symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) include:
- sweating
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- sleep disturbances
- palpitation
- anxiety
- tremor
- blurred vision
- hunger
- slurred speech
- depressed mood
- tingling in the hands, feet, lips, or tongue
- irritability
- light-headedness
- abnormal behavior
- inability to concentrate
- unsteady movement
- headache
- personality changes
If not treated, the patient may progress to severe hypoglycemia which can include:
- confusion
- seizures
- unconsciousness
- death
The occurrence of early symptoms calls for quick and, if necessary, repeated administration of some form of carbohydrate. Patients should always carry a quick source of sugar, such as candy mints or glucose tablets. The prompt treatment of mild hypoglycemic symptoms can prevent severe hypoglycemic reactions. If the patient does not improve or if administration of carbohydrate is impossible, the GVOKE PFS should be given or the patient should be treated with intravenous glucose by a medical professional.
Possible Problems with GVOKE PFS Treatment
Common side effects in adults and pediatric patients are nausea and vomiting. The product may cause serious side effects including serious allergic reactions, fast heart beat and high blood pressure.
People may be allergic to glucagon or to one of the inactive ingredients in GVOKE PFS, or may experience fast heart-beat for a short while.
If you experience any other reactions that may have been caused by the GVOKE PFS, please contact your healthcare provider.
Important:
- Act quickly. Prolonged unconsciousness may be harmful.
- After the injection is complete, turn the unconscious patient on his or her side to prevent them from choking in case they throw up (vomit).
- Carefully read and follow these instructions. Have a healthcare provider show you the right way to use the Gvoke PFS.
Important Warnings
- Do not open pouch until time of use.
- Do not use after the expiration date has passed.
- Do not use if the red needle cap has been removed or is damaged.
- Do not remove the red cap until you are ready to inject.
- Do not remove the finger flange from the syringe.
- Call a healthcare provider as soon as GVOKE PFS has been injected.
- If the patient does not awaken within 15 minutes, give another dose of glucagon and call for emergency medical help right away.
- Feed the patient as soon as he or she awakens and is able to swallow.
Read and become familiar with the following instructions before an emergency happens. If you have questions about using the GVOKE PFS, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Remove GVOKE PFS from Pouch
- Tear open pouch at the dotted line and carefully remove the GVOKE PFS (see Figure 1).
Figure 1
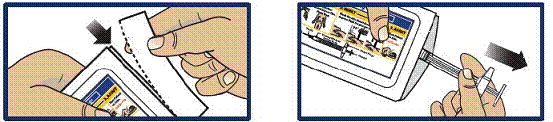 |
Check the Expiration Date
- Check the expiration date printed on the label of the GVOKE PFS (see Figure 2).
Important:
Do not use the GVOKE PFS if the expiration date has passed. If the GVOKE PFS is expired, throw it away in an FDA cleared sharps container and use a new GVOKE PFS.
Figure 2
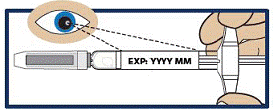 |
Inspect the Solution
- Look at the liquid medicine through the viewing window. It must be clear and colorless, or a pale yellow (see Figure 3).
- It is normal to see air bubbles in the medicine.
Important:
- Do not try to remove air bubbles before injecting.
- Do not use GVOKE PFS or inject if the liquid contains lumps, flakes, or particles.
- Do not inject if solution is not visible in the viewing window.
- If you do not have another GVOKE PFS to use call for emergency medical help right away.
Figure 3
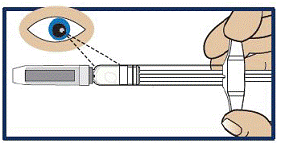 |
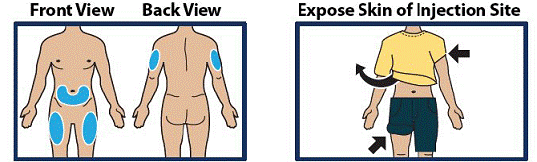
Choose Injection Site and Expose Bare Skin
- Choose the lower abdomen, outer thigh, or outer upper arm for your injection site (see Figure 4).
- Remove any clothing covering the injection site (see Figure 5). The injection must be performed straight into the skin.
Important:
Do not inject through clothing
Figure 4 and 5
 |
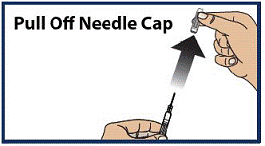
Pull off the Needle Cap
- Pull the red needle cap straight off of the syringe (see Figure 6).
Important:
Do not put your thumb, fingers, or hand on or near the needle guard or needle opening to help prevent accidental needle sticks.
Figure 6
 |
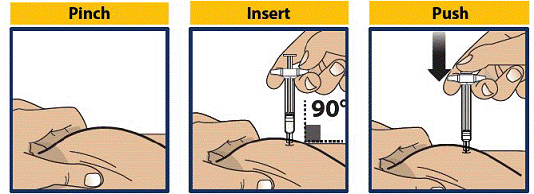
Pinch, Insert and Push to Start Injection
- Pinch the skin directly around the chosen injection site and keep pinching for the entire injection (see Figure 7). This is recommended to make sure a subcutaneous (under the skin) injection is given and to prevent injection into the muscle.
- Without touching the plunger, insert the needle into the skin at the injection site at a 90-degree angle (see Figure 8).
- Push the plunger down as far as it will go to inject all of the liquid medicine into the skin (see Figure 9). You want to inject the medicine very fast to help decrease the pain.
Important:
Do not aspirate (pull back on plunger rod) after inserting the needle.
Push the plunger down as far as it will go.
Do not lift up the GVOKE PFS until the injection is complete.
Figure 7, 8 and 9
 |
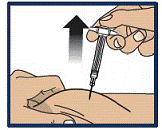
Lift Away from Skin
- Lift the syringe straight up from the injection site (see Figure 10).
Important:
Do not re-cap the syringe.
Figure 10
 |
Turn Patient onto Side
- When an unconscious person wakes up, he or she may throw up (vomit).
- Turn the unconscious patient on their side to prevent choking (see Figure 11).
Figure 11
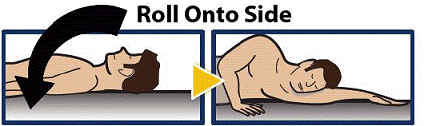 |
Make Sure Patient Receives Immediate Medical Attention After Use
- Call for emergeny medical help right after the GVOKE PFS has been injected.
- Even if the GVOKE PFS helps the patient to wake up, you should still call for emergency medical help right away.
- The patients’s healthcare provider should also be notified whenever a severe drop in blood sugar (hypoglycemic reactions) happens. Hypoglycemia may happen again after receiving an injection from the GVOKE PFS. The patient’s diabetes medication may need to be changed.
- Feed the patient as soon as he or she wakes up and is able to swallow. Give the patient a fast-acting source of sugar (such as a regular soft drink or fruit juice) and a long-acting source of sugar (such as crackers and cheese or a meat sandwich). If the patient does not wake up within 15 minutes, give another dose of glucagon and notify emergency medical services right away.
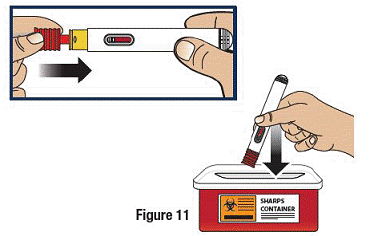
Dispose of the GVOKE PFS in a FDA Cleared Sharps Disposal Container
To prevent injury caused from contact with the used needle, put the used syringe in a safe place until it can be disposed of into a FDA cleared sharps container right away after use (see Figure 12). Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
If you do not have a FDA cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic
- can be closed with a tight-fitting puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
- upright and stable during use
- leak-resistant
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this.
Always keep the sharps container out of the reach of children.
If needed, make sure to get a refill of your GVOKE PFS.
Figure 12
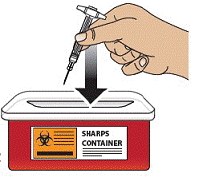 |
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
