Exondys 51 Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: eteplirsen injection
- Brand Name: Exondys 51
side effects drug center exondys 51 (eteplirsen injection) drug
Drug Description
What Is Exondys 51 and how is it used?
Exondys 51 is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Exondys 51 may be used alone or with other medications.
Exondys 51 belongs to a class of drugs called Neurologics, Antisense Oligonucleotides.
It is not known if Exondys 51 is safe and effective in children.
What are the possible side effects of Exondys 51?
Exondys 51 may cause serious side effects including:
- hives,
- difficulty breathing,
- swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat,
- fever,
- flushing,
- cough,
- rash,
- itching, and
- severe dizziness
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Exondys 51 include:
- pain, bruising, itching, skin rash, or other irritation where the medicine was injected,
- dizziness,
- vomiting, and
- joint pain
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Exondys 51. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
DESCRIPTION
EXONDYS 51 (eteplirsen) injection is a sterile, aqueous, preservative-free, concentrated solution for dilution prior to intravenous administration. EXONDYS 51 is clear and colorless, and may have some opalescence. EXONDYS 51 is supplied in single dose vials containing 100 mg or 500 mg eteplirsen (50 mg/mL). EXONDYS 51 is formulated as an isotonic, phosphate buffered saline solution with an osmolality of 260 to 320 mOsm and a pH of 7.5. Each milliliter of EXONDYS 51 contains 50 mg eteplirsen; 0.2 mg potassium chloride, 0.2 mg potassium phosphate monobasic, 8 mg sodium chloride, and 1.14 mg sodium phosphate dibasic, anhydrous, in water for injection. The product may contain hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH.
Eteplirsen is an antisense oligonucleotide of the phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) subclass. PMOs are synthetic molecules in which the five-membered ribofuranosyl rings found in natural DNA and RNA are replaced by a six-membered morpholino ring. Each morpholino ring is linked through an uncharged phosphorodiamidate moiety rather than the negatively charged phosphate linkage that is present in natural DNA and RNA. Each phosphorodiamidate morpholino subunit contains one of the heterocyclic bases found in DNA (adenine, cytosine, guanine, or thymine). Eteplirsen contains 30 linked subunits. The molecular formula of eteplirsen is C364H569N177O122P30 and the molecular weight is 10305.7 daltons.
The structure and base sequence of eteplirsen are:
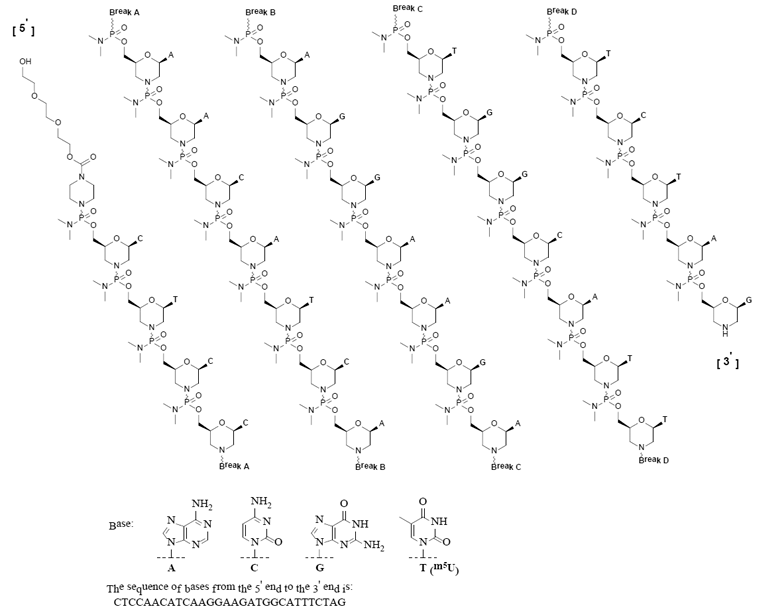 |
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
EXONDYS 51 is indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in patients who have a confirmed mutation of the DMD gene that is amenable to exon 51 skipping. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on an increase in dystrophin in skeletal muscle observed in some patients treated with EXONDYS 51 [see Clinical Studies]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification of a clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosing Information
The recommended dose of EXONDYS 51 is 30 milligrams per kilogram administered once weekly as a 35 to 60 minute intravenous infusion via an in-line 0.2 micron filter.
If a dose of EXONDYS 51 is missed, it may be administered as soon as possible after the scheduled time.
Preparation Instructions
EXONDYS 51 is supplied in single-dose vials as a preservative-free concentrated solution that requires dilution prior to administration. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Use aseptic technique.
- Calculate the total dose of EXONDYS 51 to be administered based on the patient’s weight and the recommended dose of 30 milligrams per kilogram. Determine the volume of EXONDYS 51 needed and the correct number of vials to supply the full calculated dose.
- Allow vials to warm to room temperature. Mix the contents of each vial by gently inverting 2 or 3 times. Do not shake.
- Visually inspect each vial of EXONDYS 51. EXONDYS 51 is a clear, colorless solution that may have some opalescence, and may contain trace amounts of small, white to off-white amorphous particles. Do not use if the solution in the vials is cloudy, discolored or contains extraneous particulate matter other than trace amounts of small, white to off-white amorphous particles.
- With a syringe fitted with a 21-gauge or smaller non-coring needle, withdraw the calculated volume of EXONDYS 51 from the appropriate number of vials.
- Dilute the withdrawn EXONDYS 51 in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, to make a total volume of 100-150 mL. Visually inspect the diluted solution. Do not use if the solution is cloudy, discolored or contains extraneous particulate matter other than trace amounts of small, white to off-white amorphous particles.
- Administer the diluted solution via an in-line 0.2 micron filter.
- EXONDYS 51 contains no preservatives and should be administered immediately after dilution. Complete infusion of diluted EXONDYS 51 solution within 4 hours of dilution. If immediate use is not possible, the diluted solution may be stored for up to 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not freeze. Discard unused EXONDYS 51.
Administration Instructions
Application of a topical anesthetic cream to the infusion site prior to administration of EXONDYS 51 may be considered.
EXONDYS 51 is administered via intravenous infusion. Flush the intravenous access line with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, prior to and after infusion.
Infuse the diluted EXONDYS 51 solution over 35 to 60 minutes via an in-line 0.2 micron filter. Do not mix other medications with EXONDYS 51 or infuse other medications concomitantly via the same intravenous access line.
If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, consider slowing the infusion or interrupting the EXONDYS 51 therapy [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and ADVERSE REACTIONS].
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
EXONDYS 51 is a clear and colorless solution that may have some opalescence, and may contain trace amounts of small, white to off-white amorphous particles, and is available as follows:
- Injection: 100 mg/2 mL (50 mg/mL) solution in a single-dose vial
- Injection: 500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL) solution in a single-dose vial
EXONDYS 51 injection is supplied in single-dose vials. The solution is clear and colorless, and may have some opalescence, and may contain trace amounts of small, white to off-white amorphous particles.
Single-dose vials containing 100 mg/2 mL (50 mg/mL) eteplirsen NDC 60923-363-02
Single-dose vials containing 500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL) eteplirsen NDC 60923-284-10
Storage And Handling
Store EXONDYS 51 at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not freeze. Protect from light and store EXONDYS 51 in the original carton until ready for use.
Manufactured for: Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. Cambridge, MA 02142 USA. Revised: Jul 2020
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In the EXONDYS 51 clinical development program, 107 patients received at least one intravenous dose of EXONDYS 51, ranging between 0.5 mg/kg (0.017 times the recommended dosage) and 50 mg/kg (1.7 times the recommended dosage). All patients were male and had genetically confirmed Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Age at study entry was 4 to 19 years. Most (89%) patients were Caucasian.
EXONDYS 51 was studied in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study for 24 weeks (Study 1), followed by an open label extension (Study 2). In Study 1, 12 patients were randomized to receive weekly intravenous infusions of EXONDYS 51 (n=8) or placebo (n=4) for 24 weeks. All 12 patients continued in Study 2 and received open-label EXONDYS 51 weekly for up to 208 weeks.
In Study 1, 4 patients received placebo, 4 patients received EXONDYS 51 30 mg/kg, and 4 patients received EXONDYS 51 50 mg/kg (1.7 times the recommended dosage). In Study 2, 6 patients received EXONDYS 51 30 mg/kg/week and 6 patients received EXONDYS 51 50 mg/kg/week [see Clinical Studies].
Adverse reactions that occurred in 2 or more patients who received EXONDYS 51 and were more frequent than in the placebo group in Study 1 are presented in Table 1 (the 30 and 50 mg/kg groups are pooled). Because of the small numbers of patients, these represent crude frequencies that may not reflect the frequencies observed in practice. The 50 mg/kg once weekly dosing regimen of EXONDYS 51 is not recommended [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION].
The most common adverse reactions were balance disorder and vomiting.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions in DMD Patients Treated with 30 or 50 mg/kg/week1 EXONDYS 51 with Incidence at Least 25% More than Placebo (Study 1)
| Adverse Reactions | EXONDYS 51 (N=8)% | Placebo (N=4)% |
| Balance disorder | 38 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 38 | 0 |
| Contact dermatitis | 25 | 0 |
| 1 50 mg/kg/week = 1.7 times the recommended dosage | ||
In the 88 patients who received ≥30 mg/kg/week of EXONDYS 51 for up to 208 weeks in clinical studies, the following events were reported in ≥10% of patients and occurred more frequently than on the same dose in Study 1: vomiting, contusion, excoriation, arthralgia, rash, catheter site pain, and upper respiratory tract infection.
Hypersensitivity reactions have occurred in patients treated with EXONDYS 51 [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No Information provided
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the PRECAUTIONS section.
PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash and urticaria, pyrexia, flushing, cough, dyspnea, bronchospasm, and hypotension, have occurred in patients who were treated with EXONDYS 51. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate medical treatment and consider slowing the infusion or interrupting the EXONDYS 51 therapy [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION].
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with eteplirsen.
Mutagenesis
Eteplirsen was negative in in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation and chromosomal aberration in CHO cells) and in vivo (mouse bone marrow micronucleus) assays.
Impairment Of Fertility
Fertility studies in animals were not conducted with eteplirsen. No effects on the male reproductive system were observed following intravenous administration of eteplirsen (0, 5, 40, or 320 mg/kg) to male monkeys once weekly for 39 weeks. Plasma eteplirsen exposure (AUC) in monkeys at the highest dose tested was 20 times that in humans at recommended human dose (30 mg/kg).
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no human or animal data available to assess the use of EXONDYS 51 during pregnancy. In the U.S. general population, major birth defects occur in 2 to 4% and miscarriage occurs in 15 to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no human or animal data to assess the effect of EXONDYS 51 on milk production, the presence of eteplirsen in milk, or the effects of EXONDYS 51 on the breastfed infant.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for EXONDYS 51 and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from EXONDYS 51 or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
EXONDYS 51 is indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in patients who have a confirmed mutation of the DMD gene that is amenable to exon 51 skipping, including pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies].
Intravenous administration of eteplirsen (0, 100, 300, or 900 mg/kg) to juvenile male rats once weekly for 10 weeks beginning on postnatal day 14 resulted in renal tubular necrosis at the highest dose tested and decreased bone densitometry parameters (mineral density, mineral content, area) at all doses. The kidney findings were associated with clinical pathology changes (increased serum urea nitrogen and creatinine, decreased urine creatinine clearance). No effects were observed on the male reproductive system, neurobehavioral development, or immune function. An overall no-effect dose was not identified. Plasma eteplirsen exposure (AUC) at the lowest dose tested (100 mg/kg) was similar to that in humans at the recommended human dose (30 mg/kg).
Geriatric Use
DMD is largely a disease of children and young adults; therefore, there is no geriatric experience with EXONDYS 51.
Patients With Renal Impairment
Renal clearance of eteplirsen is reduced in non-DMD adults with renal impairment based on estimated creatinine clearance [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY]. However, because of the effect of reduced skeletal muscle mass on creatinine measurements in DMD patients, no specific dosage adjustment can be recommended for DMD patients with renal impairment.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
There is no experience with overdose of EXONDYS 51.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
Eteplirsen is designed to bind to exon 51 of dystrophin pre-mRNA, resulting in exclusion of this exon during mRNA processing in patients with genetic mutations that are amenable to exon 51 skipping. Exon skipping is intended to allow for production of an internally truncated dystrophin protein, which was evaluated in Study 2 and Study 3 [see Clinical Studies].
Pharmacodynamics
All EXONDYS 51-treated patients evaluated (n=36) were found to produce messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) for a truncated dystrophin protein by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
In Study 2, the average dystrophin protein level in muscle tissue after 180 weeks of treatment with EXONDYS 51 was 0.93% of normal (i.e., 0.93% of the dystrophin level in healthy subjects). Because of insufficient information on dystrophin protein levels before treatment with EXONDYS 51 in Study 1, it is not possible to estimate dystrophin production in response to EXONDYS 51 in Study 1.
In Study 3, the average dystrophin protein level was 0.16% of normal before treatment, and 0.44% of normal after 48 weeks of treatment with EXONDYS 51 [see Clinical Studies]. The median increase in truncated dystrophin in Study 3 was 0.1% [see Clinical Studies].
Pharmacokinetics
Following single or multiple intravenous infusions of EXONDYS 51 in male pediatric DMD patients, plasma concentration-time profiles of eteplirsen were generally similar and showed multi-phasic decline. The majority of drug elimination occurred within 24 hours. Approximate dose-proportionality and linearity in PK properties were observed following multiple-dose studies (0.5 mg/kg/week [0.017 times the recommended dosage] to 50 mg/kg/week [1.7 times the recommended dosage]). There was no significant drug accumulation following weekly dosing across this dose range. The inter-subject variability for eteplirsen Cmax and AUC range from 20 to 55%.
Following single or multiple intravenous infusions of EXONDYS 51, the peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of eteplirsen occurred near the end of infusion (i.e., 1.1 to 1.2 hours across a dose range of 0.5 mg/kg/week to 50 mg/kg/week).
Distribution
In vitro investigation suggested that plasma protein binding of eteplirsen in human ranges between 6 to 17%. The mean apparent volume of distribution (Vss) of eteplirsen was 600 mL/kg following weekly intravenous infusion of EXONDYS 51 at 30 mg/kg.
Twenty-four hours after the end of the infusion, mean concentrations of eteplirsen were 0.07% of Cmax. Accumulation of eteplirsen during once weekly dosing has not been observed.
Elimination
The total clearance of eteplirsen was 339 mL/hr/kg following 12 weeks of therapy with 30 mg/kg/week.
Metabolism
Eteplirsen did not appear to be metabolized by hepatic microsomes of any species tested, including humans.
Excretion
Renal clearance of eteplirsen accounts for approximately two-thirds of the administered dose within 24 hours of intravenous administration. Elimination half-life (t½) of eteplirsen was 3 to 4 hours.
Specific Populations
Age
The pharmacokinetics of eteplirsen have been evaluated in male pediatric DMD patients. There is no experience with the use of EXONDYS 51 in patients 65 years of age or older.
Sex
Sex effects have not been evaluated; EXONDYS 51 has not been studied in female patients.
Race
Potential impact of race is not known because 89% of the patients in studies were Caucasians.
Patients With Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of eteplirsen was evaluated in non-DMD subjects aged 51 to 75 years with mild (n=8, creatinine clearance ≥60 mL/min and <90 mL/min) or moderate (n=8, creatinine clearance ≥30 mL/min and <60 mL/min) renal impairment and matched healthy subjects (n=9, creatinine clearance >90 mL/min). Subjects received a single 30 mg/kg intravenous dose of eteplirsen.
Subjects with mild and moderate renal impairment showed higher eteplirsen exposure compared to subjects with normal renal function. In subjects with mild and moderate renal impairment, exposure (AUC) increased approximately 1.4-fold and 2.4-fold, respectively. The effect of severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease on eteplirsen pharmacokinetics and safety has not been studied.
Estimated creatinine clearance values derived from the Cockcroft-Gault equation and the threshold definitions for mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment in otherwise healthy adults would not be generalizable to patients with DMD. Therefore, no specific dosage adjustment can be recommended for patients with renal impairment.
Patients With Hepatic Impairment
EXONDYS 51 has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro data showed that eteplirsen did not significantly inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4/5. Eteplirsen did not induce CYP2B6 or CYP3A4, and induction of CYP1A2 was substantially less than the prototypical inducer, omeprazole. Eteplirsen was not a substrate nor did it have any major inhibitory potential for any of the key human transporters tested (OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, P-gp, BCRP, MRP2 and BSEP). Based on in vitro data on plasma protein binding, CYP or drug transporter interactions, and microsomal metabolism, eteplirsen is expected to have a low potential for drug-drug interactions in humans.
Clinical Studies
EXONDYS 51 was evaluated in three clinical studies in patients who have a confirmed mutation of the DMD gene that is amenable to exon 51 skipping.
In Study 1, patients were randomized to receive weekly infusions of EXONDYS 51 (30 mg/kg, n=4); EXONDYS 51 (50 mg/kg, n=4), or placebo (n=4) for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was dystrophin production; a clinical outcome measure, the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), was also assessed. The 6MWT measures the distance that a patient can walk on a flat, hard surface in a period of 6 minutes. Patients had a mean age of 9.4 years, a mean 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) at baseline of 363 meters, and were on a stable dose of corticosteroids for at least 6 months. There was no significant difference in change in 6MWD between patients treated with EXONDYS 51 and those treated with placebo.
All 12 patients who participated in Study 1 continued treatment with open-label EXONDYS 51 weekly for an additional 4 years in Study 2. The 4 patients who had been randomized to placebo were re-randomized 1:1 to EXONDYS 51 30 or 50 mg/kg/week such that there were 6 patients on each dose. Patients who participated in Study 2 were compared to an external control group. The primary clinical efficacy outcome measure was the 6MWT. Eleven patients in Study 2 had a muscle biopsy after 180 weeks of treatment with EXONDYS 51, which was analyzed for dystrophin protein level by Western blot. Study 2 failed to provide evidence of a clinical benefit of EXONDYS 51 compared to the external control group. The average dystrophin protein level after 180 weeks of treatment with EXONDYS 51 was 0.93% of the dystrophin level in healthy subjects. Because of insufficient information on dystrophin protein levels before treatment with EXONDYS 51 in Study 1, it is not possible to estimate dystrophin production in response to EXONDYS 51 in Study 1.
In Study 3, 13 patients were treated with open-label EXONDYS 51 (30 mg/kg) weekly for 48 weeks and had a muscle biopsy at baseline and after 48 weeks of treatment. Patients had a mean age of 8.9 years and were on a stable dose of corticosteroids for at least 6 months. Dystrophin levels in muscle tissue were assessed by Western blot. In the 12 patients with evaluable results, the pre-treatment dystrophin level was 0.16% ± 0.12% (mean ± standard deviation) of the dystrophin level in a healthy subject and 0.44% ± 0.43% after 48 weeks of treatment with EXONDYS 51 (p < 0.05). The median increase after 48 weeks was 0.1%.
Individual patient dystrophin levels from Study 3 are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Western Blot Results: EXONDYS 51-Treated (Week 48) vs Pre-treatment Baseline (% Normal Dystrophin) (Study 301)
| Patient Number | Baseline % normal dystrophin | Week 48 % normal dystrophin | Change from Baseline % normal dystrophin |
| 1 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.13 |
| 2 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.01 |
| 3 | 0.06 | 0.37 | 0.31 |
| 4 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| 5 | 0.17 | 1.02 | 0.85 |
| 6 | 0.37 | 0.30 | -0.07 |
| 7 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.25 |
| 8 | 0.24 | 1.57 | 1.33 |
| 9 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 0.47 | 0.43 |
| 11 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| 12 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.03 |
| Mean | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.28; p=0.008 |
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients and/or caregivers that symptoms of hypersensitivity, including bronchospasm and hypotension, can occur with EXONDYS 51. Instruct them to seek immediate medical care should they experience signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
