Aimovig Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: erenumab-aooe injection, for subcutaneous use
- Brand Name: Aimovig
- Drug Class: CGRP Monoclonal Antibodies
side effects drug center aimovig (erenumab-aooe injection, for subcutaneous use) drug
Drug Description
What is Aimovig and how is it used?
Aimovig (erenumab-aooe) Injection is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
What are side effects of Aimovig?
Common side effects of Aimovig include:
- injection site reactions (pain or redness),
- constipation, and
- muscle spasms or
- cramps
DESCRIPTION
Erenumab-aooe is a human immunoglobulin G2 (IgG2) monoclonal antibody that has high affinity binding to the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor. Erenumab-aooe is produced using recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. It is composed of 2 heavy chains, each containing 456 amino acids, and 2 light chains of the lambda subclass, each containing 216 amino acids, with an approximate molecular weight of 150 kDa.
AIMOVIG (erenumab-aooe) injection is supplied as a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent, colorless to light yellow solution for subcutaneous administration. Each 1 mL single-dose prefilled autoinjector and single-dose prefilled glass syringe contains 70 mg erenumab-aooe, acetate (1.5 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.10 mg), and sucrose (73 mg). Enclosed within the autoinjector is a single-dose, prefilled glass syringe. The solution of AIMOVIG has a pH of 5.2.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
AIMOVIG is indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosing
The recommended dosage of AIMOVIG is 70 mg injected subcutaneously once monthly. Some patients may benefit from a dosage of 140 mg injected subcutaneously once monthly.
If a dose of AIMOVIG is missed, administer as soon as possible. Thereafter, AIMOVIG can be scheduled monthly from the date of the last dose.
Important Administration Instructions
AIMOVIG is for subcutaneous use only.
The needle shield within the white or orange cap of the AIMOVIG prefilled autoinjector and gray needle cap of the AIMOVIG prefilled syringe contain dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex), which may cause allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to latex.
AIMOVIG is intended for patient self-administration. Prior to use, provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on how to prepare and administer AIMOVIG using the single-dose prefilled autoinjector or single-dose prefilled syringe, including aseptic technique [see INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE]:
- Prior to subcutaneous administration, allow AIMOVIG to sit at room temperature for at least 30 minutes protected from direct sunlight [see HOW SUPPLIED]. This is important for administering the entire dose and helps minimize discomfort. Do not warm by using a heat source such as hot water or a microwave.
- Do not shake the product.
- Inspect visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration [see Dosage Forms And Strengths]. Do not use if the solution is cloudy or discolored or contains flakes or particles.
- Administer AIMOVIG in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm subcutaneously. Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard.
- Both prefilled autoinjector and prefilled syringe are single-dose and deliver the entire contents.
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
AIMOVIG is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to light yellow solution available as follows:
Injection
70 mg/mL in a single-dose prefilled SureClick® autoinjector
Injection
140 mg/mL in a single-dose prefilled SureClick® autoinjector
Injection
70 mg/mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe
Injection
140 mg/mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe
AIMOVIG (erenumab-aooe) injection is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to light yellow solution for subcutaneous administration.
The needle shield within the white or orange cap of the AIMOVIG prefilled autoinjector and gray needle cap of the AIMOVIG prefilled syringe contain dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex). Each single-dose prefilled SureClick® autoinjector or single-dose prefilled syringe of AIMOVIG contains a Type 1 glass syringe and stainless steel needle and delivers 1 mL of 70 mg/mL or 140 mg/mL solution.
AIMOVIG is supplied as follows:
SureClick® Autoinjector
- Pack of 1 autoinjector: 70 mg/mL single-dose prefilled autoinjector
NDC 55513-841-01 - Pack of 1 autoinjector: 140 mg/mL single-dose prefilled autoinjector
NDC 55513-843-01
Syringe
- Pack of 1 syringe: 70 mg/mL single-dose prefilled syringe
NDC 55513-840-01 - Pack of 1 syringe: 140 mg/mL single-dose prefilled syringe
NDC 55513-842-01
Storage And Handling
- Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light until time of use.
- If removed from the refrigerator, AIMOVIG should be kept at room temperature (up to 25°C [77°F]) in the original carton and must be used within 7 days. Throw away AIMOVIG that has been left at room temperature for more than 7 days.
- Do not freeze.
- Do not shake.
Manufactured by: Amgen Inc. One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799 USA. Revised: May 2021
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Constipation with Serious Complications [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Hypertension [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of AIMOVIG has been evaluated in 2537 patients with migraine who received at least one dose of AIMOVIG, representing 2310 patient-years of exposure. Of these, 2057 patients were exposed to 70 mg or 140 mg once monthly for at least 6 months, 1198 patients were exposed for at least 12 months, and 287 patients were exposed for at least 18 months.
In placebo-controlled clinical studies (Studies 1, 2, and 3) of 2184 patients, 787 patients received at least one dose of AIMOVIG 70 mg once monthly, 507 patients received at least one dose of AIMOVIG 140 mg once monthly, and 890 patients received placebo during 3 months or 6 months of double-blind treatment [see Clinical Studies]. Approximately 84% were female, 91% were white, and the mean age was 42 years at study entry.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 3% and more often than placebo) in the migraine studies were injection site reactions and constipation. Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred during the first 3 months in the migraine studies (Studies 1, 2, and 3).
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring with an Incidence of at Least 2% for Either Dose of AIMOVIG and at Least 2% Greater than Placebo During the First 3 Months in Studies 1, 2, and 3
| Adverse Reaction | AIMOVIG 70 mg Once Monthly N = 787 % |
AIMOVIG 140 mg Once Monthly N = 507 % |
Placebo N = 890 % |
| Injection site reactionsa,b | 6 | 5 | 3 |
| Constipation | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Cramps, muscle spasms | <1 | 2 | <1 |
| aInjection site reactions include multiple adverse reactions related terms, such as injection site pain and injection site erythema. b The rate of injection site reactions reported in Table 1 is with the prefilled syringe. |
|||
In Studies 1, 2, and 3, 1.3% of patients treated with AIMOVIG discontinued double-blind treatment because of adverse events. The most frequent injection site reactions were injection site pain, injection site erythema, and injection site pruritus.
Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation, including neutralizing antibodies, is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to erenumab-aooe in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
The immunogenicity of AIMOVIG has been evaluated using an immunoassay for the detection of binding anti-erenumab-aooe antibodies. For patients whose sera tested positive in the screening immunoassay, an in vitro biological assay was performed to detect neutralizing antibodies.
In controlled studies with AIMOVIG, the incidence of anti-erenumab-aooe antibody development was 6.2% (48/778) in patients receiving AIMOVIG 70 mg once monthly (2 of whom had in vitro neutralizing activity) and 2.6% (13/504) in patients receiving AIMOVIG 140 mg once monthly (none of whom had in vitro neutralizing activity). The neutralizing anti-erenumab-aooe antibody positive rate may be underestimated because of limitations of the assay. Although these data do not demonstrate an impact of anti-erenumab-aooe antibody development on the efficacy or safety of AIMOVIG in these patients, the available data are too limited to make definitive conclusions.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of AIMOVIG. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, angioedema, and anaphylaxis [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Constipation with serious complications [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS], oral mucosal ulceration.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Rash, alopecia.
Vascular Disorders: Hypertension [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No Information Provided
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the "PRECAUTIONS" Section
PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, angioedema, and anaphylaxis, have been reported with AIMOVIG in postmarketing experience. Most hypersensitivity reactions were not serious and occurred within hours of administration, although some occurred more than one week after administration. If a serious or severe hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue administration of AIMOVIG and initiate appropriate therapy [see CONTRAINDICATIONS, and PATIENT INFORMATION].
Constipation With Serious Complications
Constipation with serious complications has been reported following the use of AIMOVIG in the postmarketing setting. There were cases that required hospitalization, including cases where surgery was necessary. In a majority of these cases, the onset of constipation was reported after the first dose of AIMOVIG; however, patients have also presented with constipation later on in treatment. AIMOVIG was discontinued in most reported cases of constipation with serious complications. Constipation was one of the most common (up to 3%) adverse reactions reported in clinical studies [see ADVERSE REACTIONS].
Monitor patients treated with AIMOVIG for severe constipation and manage as clinically appropriate [see PATIENT INFORMATION]. The concurrent use of medications associated with decreased gastrointestinal motility may increase the risk for more severe constipation and the potential for constipation-related complications.
Hypertension
Development of hypertension and worsening of pre-existing hypertension have been reported following the use of AIMOVIG in the postmarketing setting. Many of the patients had pre-existing hypertension or risk factors for hypertension. There were cases requiring pharmacological treatment and, in some cases, hospitalization. Hypertension may occur at any time during treatment but was most frequently reported within seven days of dose administration. In the majority of the cases, the onset or worsening of hypertension was reported after the first dose. AIMOVIG was discontinued in many of the reported cases.
Monitor patients treated with AIMOVIG for new-onset hypertension, or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, and consider whether discontinuation of AIMOVIG is warranted if evaluation fails to establish an alternative etiology.
Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (PATIENT INFORMATION and Instructions for Use).
Information On Preparation And Administration
Provide guidance to patients and caregivers on proper subcutaneous administration technique, including aseptic technique, and how to use the single-dose prefilled autoinjector or single-dose prefilled syringe [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION]. Instruct patients and/or caregivers to read and follow the Instructions for Use each time they use AIMOVIG.
Advise latex-sensitive patients that the needle shield within the white or orange cap of the AIMOVIG prefilled autoinjector and gray needle cap of the AIMOVIG prefilled syringe contain dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex) that may cause allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to latex [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION].
Advise patients to let AIMOVIG sit at room temperature for at least 30 minutes prior to administration [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptoms of serious or severe hypersensitivity reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Constipation With Serious Complications
Advise patients that constipation with serious complications can occur with AIMOVIG and that they should contact their healthcare providers if they experience severe constipation [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Hypertension
Advise patients that development of hypertension and worsening of pre-existing hypertension can occur with AIMOVIG and that they should contact their healthcare providers if they experience elevation in their blood pressure [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
The carcinogenic potential of erenumab-aooe has not been assessed.
Mutagenesis
Genetic toxicology studies of erenumab-aooe have not been conducted.
Impairment Of Fertility
Mating studies have not been conducted on erenumab-aooe. No histopathological changes in male or female reproductive organs were observed in monkeys administered erenumab-aooe (0, 25, or 150 mg/kg) by subcutaneous injection twice weekly for up to 6 months. Serum erenumab-aooe exposures (AUC) at the higher dose tested were more than 100 times that in humans at a dose of 140 mg once monthly.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of AIMOVIG in pregnant women. No adverse effects on offspring were observed when pregnant monkeys were administered erenumab-aooe throughout gestation [see Data]. Serum erenumab-aooe exposures in pregnant monkeys were greater than those in humans at clinical doses.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively. The estimated rate of major birth defects (2.2%-2.9%) and miscarriage (17%) among deliveries to women with migraine are similar to rates reported in women without migraine.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Published data have suggested that women with migraine may be at increased risk of preeclampsia during pregnancy.
Data
Animal Data
In a study in which female monkeys were administered erenumab-aooe (0 or 50 mg/kg) twice weekly by subcutaneous injection throughout pregnancy (gestation day 20-22 to parturition), no adverse effects on offspring were observed. Serum erenumab-aooe exposures (AUC) in pregnant monkeys were approximately 20 times that in humans at a dose of 140 mg once monthly.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of erenumab-aooe in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for AIMOVIG and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from AIMOVIG or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of AIMOVIG did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
No Information Provided
CONTRAINDICATIONS
AIMOVIG is contraindicated in patients with serious hypersensitivity to erenumab-aooe or to any of the excipients. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
Erenumab-aooe is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor and antagonizes CGRP receptor function.
Pharmacodynamics
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in healthy volunteers, concomitant administration of erenumab-aooe (140 mg intravenous, single-dose) with sumatriptan (12 mg subcutaneous, given as two 6 mg doses separated by one hour) had no effect on resting blood pressure compared with sumatriptan alone. AIMOVIG is for subcutaneous use only.
Pharmacokinetics
Erenumab-aooe exhibits non-linear kinetics as a result of binding to the CGRP receptor. The Cmax mean and AUClast mean following subcutaneous administration of a 70 mg once monthly and a 140 mg once monthly dose in healthy volunteers or migraine patients are included in Table 2.
Less than 2-fold accumulation was observed in trough serum concentrations (Cmin) for episodic and chronic migraine patients following subcutaneous administration of 70 mg once monthly and 140 mg once monthly doses (see Table 2). Serum trough concentrations approached steady state by 3 months of dosing. The effective half-life of erenumab-aooe is 28 days.
Table 2: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of AIMOVIG
| AIMOVIG 70 mg Subcutaneously Once Monthly |
AIMOVIG 140 mg Subcutaneously Once Monthly |
|
| Cmax mean (SD)a,b | 6.1 (2.1) mcg/mL | 15.8 (4.8) mcg/mL |
| AUClast mean (SD)a,b | 159 (58) day*mcg/mL | 505 (139) day*mcg/mL |
| Cmin (SD) | ||
| Episodic migraine | 5.7 (3.1) mcg/mL | 12.8 (6.5) mcg/mL |
| Chronic migraine | 6.2 (2.9) mcg/mL | 14.9 (6.5) mcg/mL |
| a SD = standard deviation b from a single-dose study |
||
Absorption
Following a single subcutaneous dose of 70 mg or 140 mg erenumab-aooe administered to healthy adults, median peak serum concentrations were attained in approximately 6 days, and estimated absolute bioavailability was 82%.
Distribution
Following a single 140 mg intravenous dose, the mean (SD) volume of distribution during the terminal phase (Vz) was estimated to be 3.86 (0.77) L.
Metabolism And Excretion
Two elimination phases were observed for erenumab-aooe. At low concentrations, the elimination is predominantly through saturable binding to target (CGRP receptor), while at higher concentrations the elimination of erenumab-aooe is largely through a non-specific, non-saturable proteolytic pathway.
Specific Populations
The pharmacokinetics of erenumab-aooe were not affected by age, gender, race, or subtypes of migraine spectrum (episodic or chronic migraine) based on population pharmacokinetics analysis.
Patients With Renal Or Hepatic Impairment
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of integrated data from the AIMOVIG clinical studies did not reveal a difference in the pharmacokinetics of erenumab-aooe in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment relative to those with normal renal function. Patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) have not been studied. No dedicated clinical studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic impairment or renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of erenumab-aooe. Renal or hepatic impairment is not expected to affect pharmacokinetics of erenumab-aooe.
Drug Interaction Studies
P450 Enzymes
Erenumab-aooe is not metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes; therefore, interactions with concomitant medications that are substrates, inducers, or inhibitors of cytochrome P450 enzymes are unlikely.
Oral Contraceptives
In an open-label drug interaction study in healthy female volunteers, erenumab-aooe (140 mg subcutaneous, single-dose) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of a combined oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate.
Sumatriptan
In a study in healthy volunteers, concomitant administration of erenumab-aooe with sumatriptan had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of sumatriptan [see Pharmacodynamics].
Clinical Studies
The efficacy of AIMOVIG was evaluated as a preventive treatment of episodic or chronic migraine in three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies: two studies in patients with episodic migraine (4 to 14 migraine days per month) (Study 1 and Study 2) and one study in patients with chronic migraine (≥ 15 headache days per month with ≥ 8 migraine days per month) (Study 3). The studies enrolled patients with a history of migraine, with or without aura, according to the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-III) diagnostic criteria.
Episodic Migraine
Study 1 (NCT 02456740) was a randomized, multi-center, 6-month, placebo-controlled, double-blind study evaluating AIMOVIG for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine. A total of 955 patients with a history of episodic migraine were randomized to receive either AIMOVIG 70 mg (N = 317), AIMOVIG 140 mg (N = 319), or placebo (N = 319) by subcutaneous injection once monthly (QM) for 6 months. Patients were allowed to use acute headache treatments including migraine-specific medications (i.e., triptans, ergotamine derivatives) and NSAIDs during the study.
The study excluded patients with medication overuse headache as well as patients with myocardial infarction, stroke, transient ischemic attacks, unstable angina, coronary artery bypass surgery, or other revascularization procedures within 12 months prior to screening.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline in mean monthly migraine days over months 4 to 6. Secondary endpoints included the achievement of a ≥ 50% reduction from baseline in mean monthly migraine days over months 4 to 6 (“≥ 50% MMD responders”), the change from baseline in mean monthly acute migraine-specific medication days over months 4 to 6, and the change from baseline in mean Migraine Physical Function Impact Diary (MPFID) over months 4 to 6. The MPFID measures the impact of migraine on everyday activities (EA) and physical impairment (PI) using an electronic diary administered daily. Monthly MPFID scores are averaged over 28 days, including days with and without migraine; scores are scaled from 0 to 100. Higher scores indicate worse impact on EA and PI. Reductions from baseline in MPFID scores indicate improvement.
A total of 858 (90%) patients completed the 6-month double-blind study. Patients had a median age of 42 years (range: 18 to 65 years), 85% were female, and 89% were white. Three percent of patients were taking concomitant preventive treatments for migraine. The mean migraine frequency at baseline was approximately 8 migraine days per month and was similar across treatment groups.
AIMOVIG treatment demonstrated statistically significant improvements for key efficacy endpoints compared to placebo, as summarized in Table 3.
Table 3: Efficacy Endpoints Over Months 4 to 6 in Study 1
| AIMOVIG 70 mg Once Monthly N = 312 |
AIMOVIG 140 mg Once Monthly N = 318 |
Placebo N = 316 |
|
| Monthly Migraine Days (MMD) | |||
| Change from baseline | -3.2 | -3.7 | -1.8 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.4 | -1.9 | |
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |
| ≥ 50% MMD responders | |||
| % Responders | 43.3% | 50.0% | 26.6% |
| Difference from placebo | 16.7% | 23.4% | |
| Odds ratio relative to placebo | 2.1 | 2.8 | |
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |
| Monthly acute migraine-specific medication days | |||
| Change from baseline | -1.1 | -1.6 | -0.2 |
| Difference from placebo | -0.9 | -1.4 | |
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |
Figure 1: Change from Baseline in Monthly Migraine Days in Study 1a
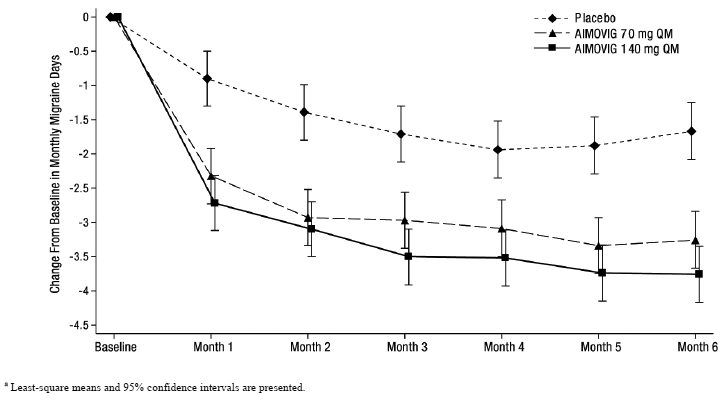 |
| a Least-square means and 95% confidence intervals are presented. |
Figure 2 shows the distribution of change from baseline in mean monthly migraine days over months 4 to 6 in bins of 2 days by treatment group. A treatment benefit over placebo for both doses of AIMOVIG is seen across a range of changes from baseline in monthly migraine days.
Figure 2: Distribution of Change from Baseline in Mean Monthly Migraine Days Over Months 4 to 6 by Treatment Group in Study 1
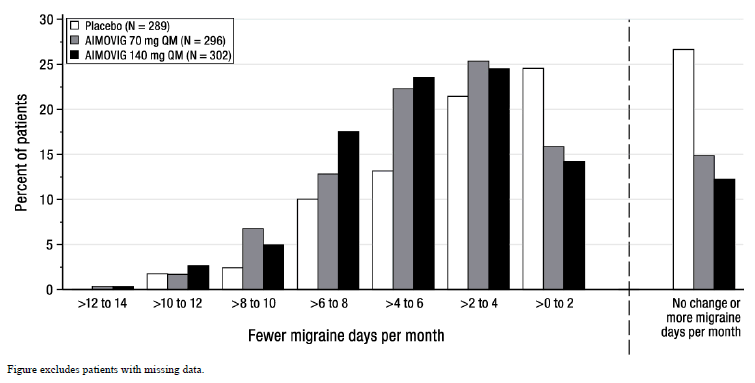 |
| Figure excludes patients with missing data. |
Compared to placebo, patients treated with AIMOVIG 70 mg once monthly and 140 mg once monthly showed greater reductions from baseline in mean monthly MPFID everyday activity scores averaged over months 4 to 6 [difference from placebo: −2.2 for AIMOVIG 70 mg and −2.6 for AIMOVIG 140 mg; p-value < 0.001 for both], and in mean monthly MPFID physical impairment scores averaged over months 4 to 6 [difference from placebo: −1.9 for AIMOVIG 70 mg and −2.4 for AIMOVIG 140 mg; p-value < 0.001 for both].
Study 2 (NCT 02483585) was a randomized, multi-center, 3-month, placebo-controlled, double-blind study evaluating AIMOVIG for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine. A total of 577 patients with a history of episodic migraine were randomized to receive either AIMOVIG 70 mg (N = 286) or placebo (N = 291) by subcutaneous injection once monthly for 3 months. Patients were allowed to use acute headache treatments including migraine-specific medications (i.e., triptans, ergotamine derivatives) and NSAIDs during the study.
The study excluded patients with medication overuse headache as well as patients with myocardial infarction, stroke, transient ischemic attacks, unstable angina, coronary artery bypass surgery, or other revascularization procedures within 12 months prior to screening.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline in monthly migraine days at month 3. Secondary endpoints included the achievement of a ≥ 50% reduction from baseline in monthly migraine days (“≥ 50% MMD responders”), the change from baseline in monthly acute migraine-specific medication days at month 3, and the proportion of patients with at least a 5-point score reduction from baseline in MPFID at month 3.
A total of 546 (95%) patients completed the 3-month double-blind study. Patients had a median age of 43 years (range: 18 to 65 years), 85% were female, and 90% were white. Six to seven percent of patients were taking concomitant preventive migraine treatment. The mean migraine frequency at baseline was approximately 8 migraine days per month and was similar between treatment groups.
AIMOVIG treatment demonstrated statistically significant improvements for key efficacy endpoints compared to placebo, as summarized in Table 4.
Table 4: Efficacy Endpoints at Month 3 for Study 2
| AIMOVIG 70 mg Once Monthly N = 282 |
Placebo N = 288 |
|
| Monthly Migraine Days (MMD) | ||
| Change from baseline | -2.9 | -1.8 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.0 | |
| p-value | < 0.001 | |
| ≥ 50% MMD responders | ||
| % Responders | 39.7% | 29.5% |
| Difference from placebo | 10.2% | |
| Odds ratio relative to placebo | 1.6 | |
| p-value | 0.010 | |
| Monthly acute migraine-specific medication days | ||
| Change from baseline | -1.2 | -0.6 |
| Difference from placebo | -0.6 | |
| p-value | 0.002 | |
Figure 3: Change from Baseline in Monthly Migraine Days in Study 2a
 |
| a Least-square means and 95% confidence intervals are presented. |
Figure 4 shows the distribution of change from baseline in monthly migraine days at month 3 in bins of 2 days by treatment group. A treatment benefit over placebo for AIMOVIG is seen across a range of changes from baseline in monthly migraine days.
Figure 4: Distribution of Change from Baseline in Monthly Migraine Days at Month 3 by Treatment Group in Study 2
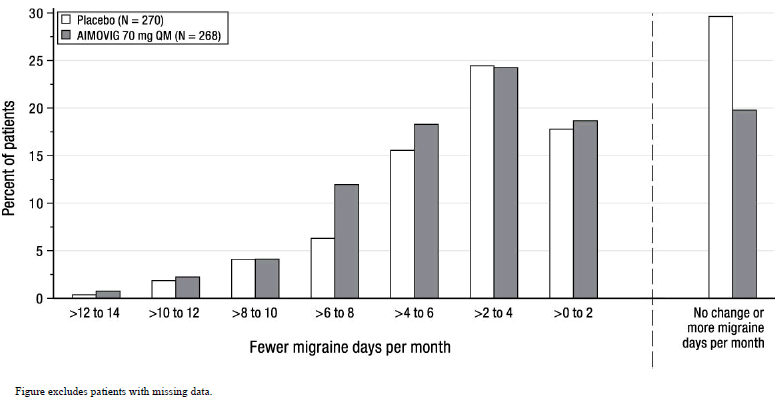 |
| Figure excludes patients with missing data. |
The pre-specified analysis for the MPFID was based on at least a 5-point reduction within-patient responder definition. AIMOVIG 70 mg once monthly was not significantly better than placebo for the proportion of responders for everyday activity [difference from placebo: 4.7%; odds ratio = 1.2; p-value = 0.26] and physical impairment [difference from placebo: 5.9%; odds ratio = 1.3; p-value = 0.13]. In an exploratory analysis of the change from baseline in the mean MPFID scores at month 3, patients treated with AIMOVIG 70 mg, as compared to placebo, showed nominally greater reductions of physical impairment scores [difference from placebo: -1.3; p-value = 0.021], but not of everyday activities scores [difference from placebo: -1.1; p-value = 0.061].
Chronic Migraine
Study 3 (NCT 02066415) was a randomized, multi-center, 3-month, placebo-controlled, double-blind study evaluating AIMOVIG as a preventive treatment of chronic migraine. A total of 667 patients with a history of chronic migraine with or without aura were randomized to receive AIMOVIG 70 mg (N = 191), AIMOVIG 140 mg (N = 190), or placebo (N = 286) by subcutaneous injections once monthly for 3 months. Patients were allowed to use acute headache treatments including migraine-specific medications (i.e., triptans, ergotamine derivatives) and NSAIDs during the study.
The study excluded patients with medication overuse headache caused by opiate overuse and patients with concurrent use of migraine preventive treatments. Patients with myocardial infarction, stroke, transient ischemic attacks, unstable angina, coronary artery bypass surgery, or other revascularization procedures within 12 months prior to screening were also excluded.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline in monthly migraine days at month 3. Secondary endpoints included the achievement of a ≥ 50% reduction from baseline in monthly migraine days (“≥ 50% MMD responders”) and change from baseline in monthly acute migraine-specific medication days at month 3.
A total of 631 (95%) patients completed the 3-month double-blind study. Patients had a median age of 43 years (range: 18 to 66 years), 83% were female, and 94% were white. The mean migraine frequency at baseline was approximately 18 migraine days per month and was similar across treatment groups.
AIMOVIG treatment demonstrated statistically significant improvements for key efficacy outcomes compared to placebo, as summarized in Table 5.
Table 5: Efficacy Endpoints at Month 3 in Study 3
| AIMOVIG 70 mg Once Monthly N = 188 |
AIMOVIG 140 mg Once Monthly N = 187 |
Placebo N = 281 |
|
| Monthly Migraine Days (MMD) | |||
| Change from baseline | -6.6 | -6.6 | -4.2 |
| Difference from placebo | -2.5 | -2.5 | |
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |
| ≥ 50% MMD responders | |||
| % Responders | 39.9% | 41.2% | 23.5% |
| Difference from placebo | 16.4% | 17.7% | |
| Odds ratio relative to placebo | 2.2 | 2.3 | |
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |
| Monthly acute migraine-specific medication days | |||
| Change from baseline | -3.5 | -4.1 | -1.6 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.9 | -2.6 | |
| p-value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |
Figure 5: Change from Baseline in Monthly Migraine Days in Study 3a
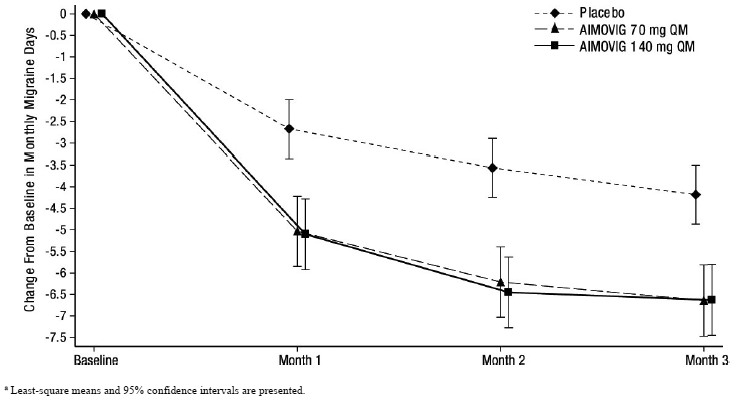 |
| a Least-square means and 95% confidence intervals are presented. |
Figure 6 shows the distribution of change from baseline in monthly migraine days at month 3 in bins of 3 days by treatment group. A treatment benefit over placebo for both doses of AIMOVIG is seen across a range of changes from baseline in migraine days.
Figure 6: Distribution of Change from Baseline in Monthly Migraine Days at Month 3 by Treatment Group in Study 3
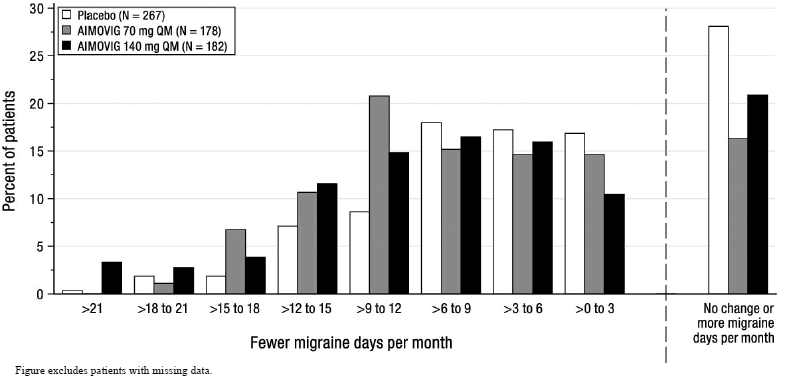 |
| Figure excludes patients with missing data. |
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
AIMOVIG®
(AIM-oh-vig)
(erenumab-aooe) injection, for subcutaneous use
What is AIMOVIG?
AIMOVIG is a prescription medicine used for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
It is not known if AIMOVIG is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age.
Who should not use AIMOVIG?
Do not use AIMOVIG if you are allergic to erenumab-aooe or any of the ingredients in AIMOVIG. See the end of this Patient Information for a complete list of ingredients in AIMOVIG.
Before you start using AIMOVIG, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you are:
- Allergic to rubber or latex. The needle shield within the white or orange cap of the single-dose prefilled SureClick® autoinjectors and the gray needle cap of the single-dose prefilled syringes contain dry natural rubber.
- Pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if AIMOVIG will harm your unborn baby.
- Breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if AIMOVIG passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while using AIMOVIG.
Tell your pharmacist or healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including any prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements.
How should I take AIMOVIG?
- See the detailed “Instructions for Use” on complete information on how to take AIMOVIG.
- Take AIMOVIG exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Before you inject, always check the label of your single-dose prefilled autoinjector or single-dose prefilled syringe to make sure you have the correct medicine and the correct dose of AIMOVIG.
- Also, before you inject, leave AIMOVIG at room temperature for at least 30 minutes protected from direct sunlight.
- AIMOVIG is injected under your skin (subcutaneously) 1 time each month.
- AIMOVIG comes in 2 different types of devices: a single-dose (1 time) prefilled autoinjector or a single-dose (1 time) prefilled syringe. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the type and dose that is best for you.
- If you forget to take AIMOVIG or are not able to take the dose at the regular time, take your missed dose as soon as you remember. After that, you can continue to take AIMOVIG 1 time each month from the date of your last dose.
What are possible side effects of AIMOVIG?
AIMOVIG may cause serious side effects, including:
- Allergic reactions. Allergic reactions, including rash or swelling can happen after receiving AIMOVIG. This can happen within hours to days after using AIMOVIG. Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- swelling of the face, mouth, tongue, or throat
- trouble breathing
- Constipation with serious complications. Severe constipation can happen after receiving AIMOVIG. In some cases, people have been hospitalized or needed surgery. Contact your healthcare provider if you have severe constipation.
