Hoarseness Symptoms
Hoarseness is a harsh, rough, raspy quality to the voice. Hoarseness is generally caused by irritation of, or injury to, the vocal cords. This trauma to the vocal cords leads to a change in the pitch of the voice. The voice box, or larynx, is the portion of the respiratory (breathing) tract containing the vocal cords that produce sound. It is located between the pharynx and the trachea. The larynx, also called the voice box, is a 2-inch-long, tube-shaped organ in the neck.

We use the larynx when we breathe, talk, or swallow. Its outer wall of cartilage forms the area of the front of the neck referred to as the "Adams apple." The vocal cords are two bands of muscle that form a "V" inside the larynx.
Hoarseness can be caused by a number of conditions. The most common cause of hoarseness is inflammation of the vocal cords from virus infection related to the common cold or upper respiratory infection. Hoarseness can also be caused by bacterial infection, overuse of the voice (such as from yelling and voice abuse or singing), trauma to the vocal cords or larynx, inhalation of irritants (smoking, etc.), chronic sinusitis, allergy, reflux of acid from the stomach (GERD), tuberculosis, syphilis, stroke and neurologic disorders (Parkinson's disease), rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid problems (hypothyroidism), and cancer of (or that has spread to) the larynx.
Cough suppressants are sometimes used to prevent recurrent irritation of the vocal cords from coughing. Hoarseness that persists for longer than two weeks should be evaluated by doctor.
Other causes of hoarseness
- After Breathing Tube for Ventilator Is Removed
- Bacterial Laryngitis
- Cancer That Spread to the Larynx
- Overuse (Yelling, Singing, Etc.)
- Polyp
- Viral Laryngitis
- Vocal Cord Paralysis
- Vocal Nodules
- Voice Disorders
Causes of Hoarseness
-

Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious allergic reaction that affects a number of different areas of the body at one time, and can be fatal. Causes of anaphylaxis can be food allergy, latex allergy, allergy to insect or but stings/bites, asthma, or other materials or conditions. Symptoms include flushing, itching, hives, anxiety, rapid or irregular pulse. Severe symptoms may be throat and tongue swelling, swallowing, and difficulty breathing. Some disorders appear similar to anaphylaxis such as fainting, panic attacks, blood clots in the lungs, heart attacks, and septic shock. If you think that you may be having an anaphylactic reaction, seek emergency care or call 911 immediately.
-

Common Cold
The common cold (viral upper respiratory tract infection) is a contagious illness that may be caused by various viruses. Symptoms include a stuffy nose, headache, cough, sore throat, and maybe a fever. Antibiotics have no effect upon the common cold, and there is no evidence that zinc and vitamin C are effective treatments.
-

Cough: 19 Tips on How to Stop a Cough
Coughing is a reflex that helps a person clear their airways of irritants. There are many causes of an excessive or severe cough including irritants like cigarette and secondhand smoke, pollution, air fresheners, medications like beta blockers and ACE inhibitors, the common cold, GERD, lung cancer, and heart disease.Natural and home remedies to help cure and soothe a cough include stay hydrated, gargle saltwater, use cough drops or lozenges, use herbs and supplements like ginger, mint, licorice, and slippery elm, and don't smoke. Over-the-counter products (OTC)to cure and soothe a cough include cough suppressants and expectorants, and anti-reflux drugs. Prescription drugs that help cure a cough include narcotic medications, antibiotics, inhaled steroids, and anti-reflux drugs like proton pump inhibitors or PPIs, for example, omeprazole (Prilosec), rabeprazole (Aciphex), and pantoprazole (Protonix).
-

Croup
Croup is a contagious viral infection that affects children's respiratory systems. Symptoms include a barking cough, stridor, fever, and difficulty breathing. Treatment may incorporate the use of a humidifier, saline nasal spray, and pain relievers such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
-
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the esophagus. Risk factors of cancer of the esophagus include smoking, heavy alcohol use, Barrett's esophagus, being male and being over age 60. Severe weight loss, vomiting, hoarseness, coughing up blood, painful swallowing, and pain in the throat or back are symptoms. Treatment depends upon the size, location and staging of the cancer and the health of the patient.
-

Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma
Gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma is cancer that forms in the area where the esophagus joins the stomach. Having GERD and Barrett's esophagus increases one's odds of developing gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Symptoms and signs of GE junction adenocarcinoma include dysphagia, weight loss, black stool, cough, nausea, and vomiting. Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
-

GERD (Acid Reflux, Heartburn)
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) is a condition in which the acidified liquid contents of the stomach backs up into the esophagus. The symptoms of uncomplicated GERD are: heartburn, regurgitation, and nausea. Effective treatment is available for most patients with GERD.
-
Hereditary Angioedema (HAE)
Hereditary angioedema or HAE is a genetic disease that causes swelling of the skin and tissues beneath it. Symptoms of HAE include shortness of breath, mood changes, laryngeal edema (a medical emergency), swelling of the hands and feet, muscle aches, and skin tingling. Treatment of HAE includes medication and avoidance of triggers.
-

How Long Does Laryngitis Last?
What is laryngitis, and how do you know if you have laryngitis? Learn the signs of laryngitis and how to care for your throat if you have laryngitis.
-

Hunter Syndrome (Mucopolysaccharidosis II, MPS II)
Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis II, MPS II) is an inherited or genetic disease. Signs and symptoms of Hunter syndrome include diarrhea, voice changes, facial changes, and distended abdomen. Treatment for Hunter syndrome is geared toward symptoms of the disease with idursulfase or Elaprase (enzyme replacement therapy).
-

Insect Sting Allergies
The majority of stinging insects in the United States are from bees, yellow jackets, hornets, wasps, and fire ants. Severity of reactions to stings varies greatly. Avoidance and prompt treatment are essential. In selected cases, allergy injection therapy is highly effective.
-
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the voice box (vocal cords). The most common cause of acute laryngitis is infection, which inflames the vocal cords. Symptoms may vary from degree of laryngitis and age of the person (laryngitis in infants and children is more commonly caused by croup). Common symptoms include a "barky" cough, a hoarse cough, fever, cold, runny nose, dry cough, and loss of voice. Chronic laryngitis generally lasts more than three weeks. Causes other than infection include smoking, excess coughing, GERD, and more. Treatment depends on the cause of laryngitis.
-
Larynx Cancer (Throat Cancer)
Symptoms and signs of cancer of the larynx, the organ at the front of the neck, include hoarseness, a lump in the neck, sore throat, cough, problems breathing, bad breath, earache, and weight loss. Treatment for larynx cancer depends on the stage (the extent) of the disease. Radiation therapy, surgery, and chemotherapy are all forms of treatment for laryngeal cancer.
-

Pregnancy (Week by Week, Trimesters)
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy vary by stage (trimester). The earliest pregnancy symptom is typically a missed period, but others include breast swelling and tenderness, nausea and sometimes vomiting, fatigue, and bloating. Second trimester symptoms include backache, weight gain, itching, and possible stretch marks. Third trimester symptoms are additional weight gain, heartburn, hemorrhoids, swelling of the ankles, fingers, and face, breast tenderness, and trouble sleeping. Eating a healthy diet, getting a moderate amount of exercise, also are recommended for a healthy pregnancy. Information about the week by week growth of your baby in the womb are provided.
-

Reflux Laryngitis (Diet, Home Remedies, Medicine)
Reflux laryngitis is caused by acid refluxing back up through the esophagus and voice box. Reflux laryngitis causes irritation and inflammation of the lining of the esophagus, larynx, and throat; and can lead to symptoms, signs, and other problems like esophagitis, sinusitis, strictures, throat clearing, swallowing problems, asthma, chronic cough, and growths on the vocal cords. Typical symptoms of reflux laryngitis include heartburn, hoarseness, or a sensation of a foreign body in the throat. Reflux laryngitis can be treated with diet chanes, OTC medication, prescription medication, and lifestyle changes.
-
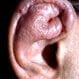
Relapsing Polychondritis
Relapsing polychondritis is an uncommon, chronic disorder of the cartilage that is characterized by recurrent episodes of inflammation of the cartilage of various tissues of the body. Tissues containing cartilage that can become inflamed include the ears, nose, joints, spine, and windpipe (trachea). Tissues that have a biochemical makeup similar to that of cartilage such as the eyes, heart, and blood vessels, can also be affected. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) is used as treatment for mild cases of the disease. Steroid-related medications also are usually required.
-
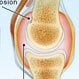
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease resulting in chronic inflammation of the joints, the tissue around the joints, as well as other organs in the body. Early RA signs and symptoms include anemia, both sides of the body affected (symmetric), depression, fatigue, fever, joint deformity, joint pain, joint redness, joint stiffness, joint swelling, joint tenderness, joint warmth, limping, loss of joint function, loss of joint range of motion, and polyarthritis.
-

Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are among the most common infectious diseases in the United States. STDs can be spread through any type of sexual activity involving the sex organs, the anus or mouth, or through contact with blood during sexual activity. Examples of STDs include, chancroid, chlamydia, gonorrhea, granuloma inguinale, lymphogranuloma venereum, syphilis, genital herpes, genital warts, trichomoniasis, pubic lice (crabs), and scabies. Treatment is generally with antibiotics; however, some STDs that go untreated can lead to death.
-

Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
Sinus infection (sinusitis) is caused by allergies, infection, and chemicals or other irritants of sinuses. Signs and symptoms are headache, fever, and facial tenderness, pressure, or pain. Treatments of sinus infections are generally with antibiotics and at times, home remedies.
-

Sjogren's Syndrome
Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disease involving the abnormal production of extra antibodies that attack the glands and connective tissue. Sjögren's syndrome with gland inflammation (resulting dry eyes and mouth, etc.) that is not associated with another connective tissue disease is referred to as primary Sjögren's syndrome. Sjögren's syndrome that is also associated with a connective tissue disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, or scleroderma, is referred to as secondary Sjögren's syndrome. Though there is no cure for Sjögren's syndrome, the symptoms may be treated by using lubricating eye ointments, drinking plenty of water, humidifying the air, and using glycerin swabs. Medications are also available to treat dry eye and dry mouth.
-
Small Cell Lung Cancer vs. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) consist of large cell carcinomas, adenocarcinomas, and squamous cell carcinomas. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) usually starts in the bronchi and typically appears in those who smoke. SCLC and NSCLC are staged in different manners, and SCLC tends to metastasize more quickly than NSCLC. Signs and symptoms of NSCLC and SCLC include shortness of breath, coughing up blood, recurring lung infections, and chest pain. Treatment may involve radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery.
-
Smoking (How to Quit Smoking)
Smoking is an addiction. More than 430,000 deaths occur each year in the U.S. from smoking related illnesses. Secondhand smoke or "passive smoke" also harm family members, coworkers, and others around smokers. There are a number of techniques available to assist people who want to quit smoking.
-

Syphilis in Women
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a spiral-shaped type of bacteria known as a spirochete. There are three stages of syphilis with distinct symptoms. During first stage of syphilis, a painless ulcer known as a chancre forms. Irreversible organ damage can occur during the late stage of syphilis. Special blood tests are used to diagnose syphilis. Syphilis infection is treated with penicillin. Condom use can often prevent syphilis.
-
Thyroid Cancer
There are four major types of thyroid cancer: papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Tumors on the thyroid are referred to as thyroid nodules. Symptoms of thyroid cancer include swollen lymph nodes, pain in the throat, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, and a lump near the Adam's apple. Treatment usually involves chemotherapy, surgery, radioactive iodine, hormone treatment or external radiation and depends upon the type of thyroid cancer, the patient's age, the tumor size, and whether the cancer has metastasized.
-

Tuberculosis (TB)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that causes tuberculosis (TB). Symptoms and signs of TB include bloody sputum, fever, cough, weight loss, and chest pain. Treatment depends upon the type of TB infection.
Examples of Medications for Hoarseness
- Hoarseness
- Anaphylaxis
- Common Cold
- Cough: 19 Tips on How to Stop a Cough
- Croup
- Esophageal Cancer
- Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma
- GERD (Acid Reflux, Heartburn)
- Hereditary Angioedema (HAE)
- How Long Does Laryngitis Last?
- Hunter Syndrome (Mucopolysaccharidosis II, MPS II)
- Insect Sting Allergies
- Laryngitis
- Larynx Cancer (Throat Cancer)
- Pregnancy (Week by Week, Trimesters)
- Reflux Laryngitis (Diet, Home Remedies, Medicine)
- Relapsing Polychondritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
- Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
- Sjogren's Syndrome
- Small Cell Lung Cancer vs. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Smoking (How to Quit Smoking)
- Syphilis in Women
- Thyroid Cancer
- Tuberculosis (TB)

