ProHance Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: gadoteridol injection solution
- Brand Name: ProHance
- Drug Class: How Do Gadolinium Containing Contrast Agents Work?
side effects drug center prohance (gadoteridol injection solution) drug
Drug Description
What is PROHANCE and how is it used?
- PROHANCE is a prescription medicine called a gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA). PROHANCE, like other GBCAs, is used with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner.
- An MRI exam with a GBCA, including PROHANCE, helps your doctor to see problems better than an MRI exam without a GBCA.
- Your doctor has reviewed your medical records and has determined that you would benefit from using a GBCA with your MRI exam.
What are the possible side effects of PROHANCE?
- See “What is the most important information I should know about PROHANCE?”
- Allergic reactions. PROHANCE can cause allergic reactions that can sometimes be serious. Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely for symptoms of an allergic reaction.
The most common side effects of PROHANCE include: nausea, taste perversion, headache, feeling hot, or burning at the injection site.
These are not all the possible side effects of PROHANCE.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
WARNING
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating systemic fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
- The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
- chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2), or
- acute kidney injury.
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g. age > 60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
- For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended ProHance dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to re-administration (see WARNINGS).
DESCRIPTION
ProHance (Gadoteridol) Injection is a nonionic contrast medium for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), available as a 0.5M sterile clear colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution in vials and syringes for intravenous injection.
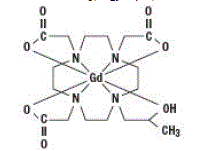
Gadoteridol is the gadolinium complex of 10-(2-hydroxy-propyl)-1,4,7,10tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triacetic acid with a molecular weight of 558.7, an empirical formula of C17H29N4O7Gd and has the following structural formula:
 |
Each mL of ProHance contains 279.3 mg gadoteridol, 0.23 mg calteridol calcium, 1.21 mg tromethamine and water for injection. ProHance contains no antimicrobial preservative. ProHance has a pH of 6.5 to 8.0. Pertinent physicochemical data are noted below:
PARAMETER
| Osmolality (mOsmol/kg water) | |
| @ 37° C | 630 |
| Viscosity (cP) | |
| @ 20° C | 2.0 |
| @ 37° C | 1.3 |
| Specific Gravity | |
| @ 25° C | 1.140 |
| Density | |
| (g/mL) @ 25° C | 1.137 |
| Octanol: H2O coefficient | -3.68 ± 0.02 |
ProHance has an osmolality 2.2 times that of plasma (285 mOsmol/kg water) and is hypertonic under conditions of use.
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
MRI Of The Central Nervous System (CNS)
ProHance is indicated for use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in adults and pediatric patients over 2 years of age to visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine and associated tissues.
MRI Of Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues
ProHance is indicated for use in MRI in adults to visualize lesions in the head and neck.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosing And Imaging Instructions
MRI Of The CNS
Adults
- Recommended dose is 0.1 mmol/kg (0.2 mL/kg) administered as a rapid intravenous infusion (10 mL/min-60 mL/min) or bolus (> 60 mL/min)
- A supplementary dose of 0.2 mmol/kg (0.4 mL/kg) may be given up to 30 minutes after the first dose in patients with normal renal function suspected of having poorly enhancing lesions, in the presence of negative or equivocal scans
- Immediately after injection, inject at least a 5 mL normal saline flush to ensure complete administration of contrast medium
- Imaging procedure should be completed within 1 hour of the first injection of ProHance
Pediatric Use (2-17 years)
- Recommended dose is 0.1 mmol/kg (0.2 mL/kg) administered as a rapid intravenous infusion (10 mL/min-60 mL/min) or bolus (> 60 mL/min)
- Safety and efficacy of doses > 0.1 mmol/kg, and sequential and/or repeat procedures have not been studied
- Follow injection by at least a 5 mL normal saline flush
MRI Of Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues
Adults
- Recommended dose 0.1 mmol/kg (0.2 mL/kg) administered as a rapid intravenous infusion (10 mL/min-60 mL/min) or bolus (> 60 mL/min)
- To ensure complete injection of the contrast medium, the injection should be followed by at least a 5 mL normal saline flush
Pediatric Use
- Safety and efficacy for extracranial/extraspinal tissues have not been established.
Administration
- Visually inspect ProHance for particulate matter and discoloration prior to use
- Do not administer the solution if it is discolored or particulate matter is present
- Concurrent medications or parenteral nutrition should not be physically mixed with contrast agents and should not be administered in the same intravenous line because of the potential for chemical incompatibility
Directions For Proper Use Of Pharmacy Bulk Package
Not For Direct Infusion
The pharmacy bulk package is used as a multiple dose container with an appropriate transfer device to fill empty sterile syringes. Use the following procedures when transferring ProHance from the pharmacy bulk package to individual syringes:
- Use of this product is restricted to a suitable work area, such as a laminar flow hood, utilizing aseptic technique
- Prior to entering the vial, remove the seal and cleanse the rubber closure with a suitable antiseptic agent
- The container closure may be penetrated only one time, utilizing a suitable transfer device or dispensing set that allows measured dispensing of the contents
- Once the pharmacy bulk package is punctured, it should not be removed from the aseptic work area during the entire period of use
- Withdrawal of container contents should be accomplished without delay. A maximum time of 8 hours from initial closure entry is permitted to complete fluid transfer operations
- Any unused contents must be discarded by 8 hours after initial puncture of the bulk package
- Once drawn into syringe, administer transferred agent promptly
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
ProHance Multipack is supplied as a sterile, nonpyrogenic, and colorless to slightly yellow solution available in a 50 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package for intravenous administration. Each mL contains 279.3 mg of gadoteridol for injection.
ProHance Multipack (gadoteridol) injection is a colorless to slightly yellow solution containing 279.3 mg/mL of gadoteridol in rubber stoppered vials. ProHance Multipack is supplied in boxes of five 50 mL Pharmacy Bulk Packages (NDC 0270-1111-70).
Storage And Handling
Store at 25°C (77° F). Excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light. DO NOT FREEZE. Should freezing occur in the vial, ProHance Multipack should be brought to room temperature before use. If allowed to stand at room temperature for a minimum of 60 minutes, ProHance Multipack (Gadoteridol) Injection should return to a clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution. Before use, examine the product to assure that all solids are redissolved and that the container and closure have not been damaged. Should solids persist, discard vial.
Manufactured by: BIPSO GmbH-78224 Singen (Germany). Revised: Aug 2018
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis [see BOX WARNING and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The adverse events described in this section were observed in clinical trials involving 1,251 patients (670 males and 581 females). Adult patients ranged in age from 18 to 91 yrs. Pediatric patients ranged from 2 to 17 years. The racial breakdown was 83% Caucasian, 8% Black, 3% Hispanic, 2% Asian, and 1% other. In 2% of the patients, race was not reported.
The most commonly noted adverse experiences were nausea and taste perversion with an incidence of 1.4%.
These events were mild to moderate in severity.
The following additional adverse events occurred in less than 1% of the patients:
Body as a Whole: Facial Edema; Neck Rigidity; Pain; Pain at Injection Site; Injection Site Reaction; Chest Pain; Headache; Fever; Itching; Watery Eyes; Abdominal Cramps; Tingling Sensation in Throat; Laryngismus; Flushed Feeling; Vasovagal Reaction; Anaphylactoid Reactions (characterized by cardiovascular, respiratory and cutaneous symptoms)
Cardiovascular: Prolonged P-R Interval; Hypotension; Elevated Heart Rate; A-V Nodal Rhythm
Digestive: Edematous and/or itching tongue; Gingivitis; Dry Mouth; Loose Bowel; Vomiting
Nervous System: Anxiety; Dizziness; Paresthesia; Mental Status Decline; Loss of Coordination in Arm; Staring Episode; Seizure; Syncope
Respiratory System: Dyspnea; Rhinitis; Cough
Skin and Appendages: Pruritus; Rash; Rash Macular Papular; Urticaria; Hives; Tingling Sensation of Extremity and Digits
Special Senses: Tinnitus
Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of ProHance that were not observed in the clinical trials. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
General Disorders and Administration Site ConditionsAdverse events with variable onset and duration have been reported after GBCA administration [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]. These include fatigue, asthenia, pain syndromes, and heterogeneous clusters of symptoms in the neurological, cutaneous, and musculoskeletal systems.
Body as a Whole: Generalized Edema; Laryngeal Edema; Malaise; Anaphylactoid Reactions (characterized by cardiovascular, respiratory and cutaneous symptoms, and rarely resulting in Death)
Cardiovascular: Cardiac Arrest; Bradycardia; Hypertension; and Death in association with pre-existing cardiovascular disorders
Digestive: Increased Salivation; Dysphagia
Nervous System: Stupor; Tremor; Loss of Consciousness
Skin and Appendages: Gadolinium associated plaques, Sweating; and Cyanosis
Special Senses: Voice Alteration; Transitory Deafness
Urogenital: Urinary Incontinence
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No human drug interaction studies have been performed.
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the "PRECAUTIONS" Section
PRECAUTIONS
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF)
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced MRI or other modalities. The GBCA-associated NSF risk appears highest for patients with chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2) as well as patients with acute kidney injury. The risk appears lower for patients with chronic, moderate kidney disease (GFR 30-59 mL/min/1.73m2) and little, if any, for patients with chronic, mild kidney disease (GFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73m2). NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. Report any diagnosis of NSF following ProHance Multipack administration to Bracco Diagnostics (1-800-257-5181) or FDA (1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch).
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. Features of acute kidney injury consist of rapid (over hours to days) and usually reversible decrease in kidney function, commonly in the setting of surgery, severe infection, injury or drug-induced kidney toxicity. Serum creatinine levels and estimated GFR may not reliably assess renal function in the setting of acute kidney injury. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, diabetes mellitus or chronic hypertension), estimate the GFR through laboratory testing.
Among the factors that may increase the risk for NSF are repeated or higher than recommended doses of a GBCA and the degree of renal impairment at the time of exposure. Record the specific GBCA and the dose administered to a patient. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended ProHance dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug prior to readministration. For patients receiving hemodialysis, physicians may consider the prompt initiation of hemodialysis following the administration of a GBCA in order to enhance the contrast agent’s elimination. The usefulness of hemodialysis in the prevention of NSF is unknown. [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe and fatal hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been observed with administration of gadolinium products, including ProHance. Prior to ProHance administration, ensure the availability of trained personnel and medications to treat hypersensitivity reactions. Patients with a history of allergy, drug reactions or other hypersensitivity-like disorders should be closely monitored during the procedure and for several hours after drug administration. If a reaction occurs, stop ProHance and immediately begin appropriate therapy including resuscitation.
Gadolinium Retention
Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations (nanomoles per gram of tissue) have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (e.g. brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen). The duration of retention also varies by tissue and is longest in bone. Linear GBCAs cause more retention than macrocyclic GBCAs. At equivalent doses, retention varies among the linear agents with Omniscan (gadodiamide) and Optimark (gadoversetamide) causing greater retention than other linear agents [Eovist (gadoxetate disodium), Magnevist (gadopentetate dimeglumine), MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine)]. Retention is lowest and similar among the macrocyclic GBCAs [Dotarem (gadoterate meglumine), Gadavist (gadobutrol), ProHance (gadoteridol)].
Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established. Pathologic and clinical consequences of GBCA administration and retention in skin and other organs have been established in patients with impaired renal function [see Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF)]. There are rare reports of pathologic skin changes in patients with normal renal function. Adverse events involving multiple organ systems have been reported in patients with normal renal function without an established causal link to gadolinium retention[see ADVERSE REACTIONS].
While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions. Consider the retention characteristics of the agent when choosing a GBCA for these patients. Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies when possible.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent; administer the lowest dose necessary for adequate imaging.
Patient Counseling Information
- Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (PATIENT INFORMATION).
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
Instruct patients to inform their physician if they:
- have a history of kidney disease
- have recently received a GBCA
GBCAs increase the risk for NSF in patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. To counsel patients at risk for NSF:
- describe the clinical manifestations of NSF
- describe procedures to screen for the detection of renal impairment
Instruct the patients to contact their physician if they develop signs or symptoms of NSF following ProHance administration, such as burning, itching, swelling, scaling, hardening and tightening of the skin; red or dark patches on the skin; stiffness in joints with trouble moving, bending or straightening the arms, hands, legs or feet; pain in the hip bones or ribs; or muscle weakness.
General Precautions
Instruct patients to inform their physician if they;
- are pregnant or breast feeding
- have a history of renal disease or heart disease, seizure, asthma or allergic respiratory diseases
Gadolinium Retention
- Advise patients that gadolinium is retained for months or years in brain, bone, skin, and other organs in patients with normal renal function. The clinical consequences of retention are unknown. Retention depends on multiple factors and is greater following administration of linear GBCAs than following administration of macrocyclic GBCAs [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
No animal studies have been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of gadoteridol or potential effects on fertility.
Gadoteridol did not demonstrate genotoxic activity in: bacterial reverse mutation assays using Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli; a mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay; an in vitro cytogenetic assay measuring chromosomal aberration frequencies in Chinese hamster ovary cells; and an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay at intravenous doses up to 5.0 mmol/kg.
Use In Specific Population
Pregnancy
GBCAs cross the placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. The human data on the association between GBCAs and adverse fetal outcomes are limited and inconclusive. Because of the potential risks of gadolinium to the fetus, use ProHance only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed. Contrast enhancement is visualized in the human placenta and fetal tissues after maternal GBCA administration.
Cohort studies and case reports on exposure to GBCAs during pregnancy have not reported a clear association between GBCAs and adverse effects in the exposed neonates. However, a retrospective cohort study, comparing pregnant women who had a GBCA MRI to pregnant women who did not have an MRI, reported a higher occurrence of stillbirths and neonatal deaths in the group receiving GBCA MRI. Limitations of this study include a lack of comparison with non-contrast MRI and lack of information about the maternal indication for MRI. Overall, these data preclude a reliable evaluation of the potential risk of adverse fetal outcomes with the use of GBCAs in pregnancy.
GBCAs administered to pregnant non-human primates (0.1 mmol/kg on gestational days 85 and 135) result in measurable gadolinium concentration in the offspring in bone, brain, skin, liver, kidney, and spleen for at least 7 months. GBCAs administered to pregnant mice (2 mmol/kg daily on gestational days 16 through 19) result in measurable gadolinium concentrations in the pups in bone, brain, kidney, liver, blood, muscle, and spleen at one month postnatal age.
Gadoteridol administered to rats at 10 mmol/kg/day (33 times the maximum recommended human dose of 0.03 mmol/kg or 6 times the human dose based on a mmol/m2 comparison) for 12 days during gestation doubled the incidence of postimplantation loss. When rats were administered 6.0 or 10.0 mmol/ kg/day for 12 days, an increase in spontaneous locomotor activity was observed in the offspring. Gadoteridol increased the incidence of spontaneous abortion and early delivery in rabbits administered 6 mmol/ kg/day (20 times the maximum recommended human dose or 7 times the human dose based on a mmol/m2 comparison) for 13 days during gestation.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ProHance is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients under the age of 2 years have not been established. The safety and efficacy of > 0.1 mmol/kg; and sequential and/or repeat procedures have not been studied in pediatric patients [see INDICATIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION].
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of 2673 adult subjects in clinical studies of ProHance, 22% were 65 and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between these elderly subjects and the younger subjects.
ProHance is known to be substantially excreted by the kidneys, and the risk of toxic reactions from ProHance may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
Clinical consequences of overdose with ProHance have not been reported.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ProHance is contraindicated in patients with known allergic or hypersensitivity reactions to ProHance [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
Gadoteridol is a paramagnetic agent and, as such, develops a magnetic moment when placed in a magnetic field. The relatively large magnetic moment produced by the paramagnetic agent results in a relatively large local magnetic field, which can enhance the relaxation rates of water protons in the vicinity of the paramagnetic agent.
In MRI, visualization of normal and pathologic brain tissue depends, in part, on variations in the radiofrequency signal intensity that occur with: 1) differences in proton density; 2) differences of the spin-lattice or longitudinal relaxation times (T1); and 3) differences in the spin-spin or transverse relaxation time (T2). When placed in a magnetic field, gadoteridol decreases T1 relaxation times in the target tissues. At recommended doses, the effect is observed with greatest sensitivity in the T1-weighted sequences.
Pharmacodynamics
Gadoteridol affects proton relaxation times and consequently the MR signal. The enhancement of the signal intensity is effected by the dose and relaxivity of the gadoterate molecule. Consistently, for all gadolinium based contrast agents, the relaxivity of gadoteridol decreases with the increase of the magnetic field strength used in clinical MRI (0.2 –3.0T).
Disruption of the blood-brain barrier or abnormal vascularity allows accumulation of gadoteridol in lesions such as neoplasms, abscesses, and subacute infarcts. The pharmacokinetics of gadoteridol in various lesions is not known.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered gadoteridol in normal subjects conforms to a two-compartment open model with mean distribution and elimination half-lives (reported as mean ± SD) of about 0.20 ± 0.04 hours and 1.57 ± 0.08 hours, respectively. Following GBCA administration, gadolinium is present for months or years in brain, bone, skin, and other organs [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Elimination
Gadoteridol is eliminated in the urine with 94.4 ± 4.8% (mean ± SD) of the dose excreted within 24 hours post-injection. It is unknown if biotransformation or decomposition of gadoteridol occur in vivo. The renal and plasma clearance rates (1.41 ± 0.33 mL/ min/kg and 1.50 ± 0.35 mL/ min/kg, respectively) of gadoteridol are essentially identical, indicating no alteration in elimination kinetics on passage through the kidneys and that the drug is essentially cleared through the kidney. The volume of distribution (204 ± 58 mL/kg) is equal to that of extracellular water, and clearance is similar to that of substances which are subject to glomerular filtration.
It is unknown if protein binding of gadoteridol occurs in vivo.
Clinical Studies
ProHance was evaluated in two blinded read trials in a total of 133 adults who had an indication for head and neck extracranial or extraspinal MRI. These 133 adults (74 men, 59 women) had a mean age of 53 with a range of 19 to 76 years. Of these patients, 85% were Caucasian, 13% Black, 2% Asian, and < 1% other. The results of the non-contrast and gadoteridol MRI scans were compared. In this database, approximately 75-82% of the scans were enhanced, 45-48% of the scans provided additional diagnostic information, and 8-25% of the diagnoses were changed. The relevance of the findings to disease sensitivity and specificity has not been fully evaluated.
ProHance was evaluated in a multicenter clinical trial of 103 pediatric patients who had an indication for a brain or spine MRI. These 103 pediatric patients, (54 boys and 49 girls) had a mean age of 8.7 years with an age range of 2 to 20 years. Of these 103 pediatric patients, 54 were between 2 and 12 years of age. Also, of these 103 pediatric patients, 74% were Caucasian, 11% Black, 12% Hispanic, 2% Asian, and 2% other. The results of the non-contrast and gadoteridol MRI scans were compared. ProHance was given in one single 0.1 mmol/kg dose. Repeat dosing was not studied. In this database, MRI enhancement was noted in approximately 60% of the scans and additional diagnostic information in 30-95% of the scans.
In early studies, ProHance was evaluated in two multicenter trials of 310 evaluable patients suspected of having neurological pathology. After the administration of ProHance 0.1 mmol/kg IV, the results were similar to those described above.
In another multicenter study of 49 evaluable adult patients with known intracranial tumor with high suspicion of having cerebral metastases, two doses of ProHance were administered. First ProHance 0.1 mmol/kg was injected followed 30 minutes later with 0.2 mmol/kg. In comparison to the 0.1 mmol/kg dose alone, the addition of the 0.2 mmol/kg dose improved visualization in 67% and improved border definition in 56% of patients. In comparison to non-contrast MRI, the number of lesions after 0.1 mmol/kg increased in 34% of patients. After ProHance 0.2 mmol/kg, this increased to 44%.
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
PROHANCE®
(pro-han(t)s)
(Gadoteridol)
Injection for intravenous use
What is PROHANCE?
- PROHANCE is a prescription medicine called a gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA). PROHANCE, like other GBCAs, is used with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner.
- An MRI exam with a GBCA, including PROHANCE, helps your doctor to see problems better than an MRI exam without a GBCA.
- Your doctor has reviewed your medical records and has determined that you would benefit from using a GBCA with your MRI exam.
What is the most important information I should know about PROHANCE?
- PROHANCE contains a metal called gadolinium. Small amounts of gadolinium can stay in your body including the brain, bones, skin and other parts of your body for a long time (several months to years).
- It is not known how gadolinium may affect you, but so far, studies have not found harmful effects in patients with normal kidneys.
- Rarely, patients have reported pains, tiredness, and skin, muscle or bone ailments for a long time, but these symptoms have not been directly linked to gadolinium.
- There are different GBCAs that can be used for your MRI exam. The amount of gadolinium that stays in the body is different for different gadolinium medicines. Gadolinium stays in the body more after Omniscan or Optimark than after Eovist, Magnevist, or MultiHance. Gadolinium stays in the body the least after Dotarem, Gadavist, or ProHance.
- People who get many doses of gadolinium medicines, women who are pregnant and young children may be at increased risk from gadolinium staying in the body.
- Some people with kidney problems who get gadolinium medicines can develop a condition with severe thickening of the skin, muscles and other organs in the body (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis). Your healthcare provider should screen you to see how well your kidneys are working before you receive PROHANCE.
Do not receive PROHANCE if you have had a severe allergic reaction to PROHANCE.
Before receiving PROHANCE, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have had any MRI procedures in the past where you received a GBCA. Your healthcare provider may ask you for more information including the dates of these MRI procedures.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if PROHANCE can harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the possible risks to an unborn baby if a GBCA such as PROHANCE is received during pregnancy
- have kidney problems, diabetes, or high blood pressure
- have had an allergic reaction to dyes (contrast agents) including GBCAs
What are the possible side effects of PROHANCE?
- See “What is the most important information I should know about PROHANCE?”
- Allergic reactions. PROHANCE can cause allergic reactions that can sometimes be serious. Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely for symptoms of an allergic reaction.
The most common side effects of PROHANCE include: nausea, taste perversion, headache, feeling hot, or burning at the injection site.
These are not all the possible side effects of PROHANCE.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of PROHANCE.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your healthcare provider for information about PROHANCE that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in PROHANCE?
Active ingredient: gadoteridol
Inactive ingredients: calteridol calcium, tromethamine
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
