Mavyret Drug Description: Detailed Datasheet
- Generic Name: glecaprevir and pibrentasvir
- Brand Name: Mavyret
- Drug Class: HCV NS3/4A Protease Inhibitors
side effects drug center mavyret (glecaprevir and pibrentasvir) drug
Drug Description
What is MAVYRET and how is it used?
MAVYRET is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 3 years of age and older with:
- chronic (lasting a long time) hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis.
- HCV genotype 1 infection and have been previously treated with a regimen that contained an HCV NS5A inhibitor or an NS3/4A protease inhibitor (PI), but not both.
MAVYRET contains the two medicines: glecaprevir and pibrentasvir.
It is not known if MAVYRET is safe and effective in children under 3 years of age.
What are the possible side effects of MAVYRET?
MAVYRET can cause serious side effects, including:
- Hepatitis B virus reactivation. See “What is the most important information I should know about MAVYRET?”
- In people who had or have advanced liver problems before starting treatment with MAVYRET: rare risk of worsening liver problems, liver failure and death. Your healthcare provider will check you for signs and symptoms of worsening liver problems during treatment with MAVYRET. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following signs and symptoms:
- nausea
- tiredness
- yellowing of your skin or white part of your eyes
- bleeding or bruising more easily than normal
- confusion
- dark, black, or bloody stool
- loss of appetite
- diarrhea
- dark or brown (tea-colored) urine
- swelling or pain on the upper right side of your stomach area (abdomen)
- sleepiness
- vomiting of blood
- lightheadedness
The most common side effects of MAVYRET include headache and tiredness.
These are not all the possible side effects of MAVYRET.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
WARNING
RISK OF HEPATITIS B VIRUS REACTIVATION IN PATIENTS COINFECTED WITH HCV AND HBV
Test all patients for evidence of current or prior hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection before initiating treatment with MAVYRET. HBV reactivation has been reported in HCV/HBV coinfected patients who were undergoing or had completed treatment with HCV direct-acting antivirals and were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy. Some cases have resulted in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death. Monitor HCV/HBV coinfected patients for hepatitis flare or HBV reactivation during HCV treatment and post-treatment follow-up. Initiate appropriate patient management for HBV infection as clinically indicated [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
DESCRIPTION
MAVYRET is a fixed-dose combination tablet containing glecaprevir and pibrentasvir for oral administration. Glecaprevir is a HCV NS3/4A PI, and pibrentasvir is a HCV NS5A inhibitor.
Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir Film-Coated Immediate Release Tablets
Each tablet contains 100 mg of glecaprevir and 40 mg of pibrentasvir. Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir are presented as a co-formulated, fixed-dose combination, immediate release bilayer tablet.
The tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, copovidone (type K 28), croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose 2910, iron oxide red, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol 3350, propylene glycol monocaprylate (type II), sodium stearyl fumarate, titanium dioxide, and vitamin E (tocopherol) polyethylene glycol succinate.
The tablets do not contain gluten.
Glecaprevir Drug Substance
The chemical name of glecaprevir is (3aR,7S,10S,12R,21E,24aR)-7-tert-butyl-N-{(1R,2R)-2(difluoromethyl)-1-[(1-methylcyclopropane-1-sulfonyl)carbamoyl]cyclopropyl}-20,20-difluoro5,8-dioxo-2,3,3a,5,6,7,8,11,12,20,23,24a-dodecahydro-1H,10H-9,12methanocyclopenta[18,19][1,10,17,3,6]trioxadiazacyclononadecino[11,12-b]quinoxaline-10carboxamide hydrate.
The molecular formula is C38H46F4N6O9S (anhydrate) and the molecular weight for the drug substance is 838.87 g/mol (anhydrate). The strength of glecaprevir is based on anhydrous glecaprevir. Glecaprevir is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a solubility of less than 0.1 to 0.3 mg/mL across a pH range of 2–7 at 37°C and is practically insoluble in water, but is sparingly soluble in ethanol. Glecaprevir has the following molecular structure:
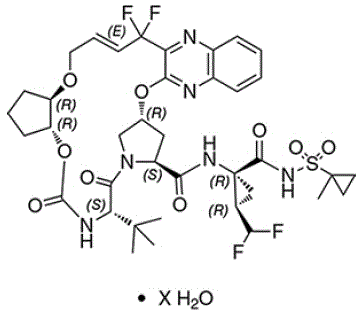 |
Pibrentasvir Drug Substance
The chemical name of pibrentasvir is Methyl {(2S,3R)-1-[(2S)-2-{5-[(2R,5R)-1-{3,5-difluoro-4[4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]phenyl}-5-(6-fluoro-2-{(2S)-1-[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-Omethyl-L-threonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)pyrrolidin-2-yl]-6-fluoro-1Hbenzimidazol-2-yl}pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methoxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl}carbamate.
The molecular formula is C57H65F5N10O8 and the molecular weight for the drug substance is 1113.18 g/mol. Pibrentasvir is a white to off-white to light yellow crystalline powder with a solubility of less than 0.1 mg/mL across a pH range of 1–7 at 37°C and is practically insoluble in water, but is freely soluble in ethanol. Pibrentasvir has the following molecular structure:
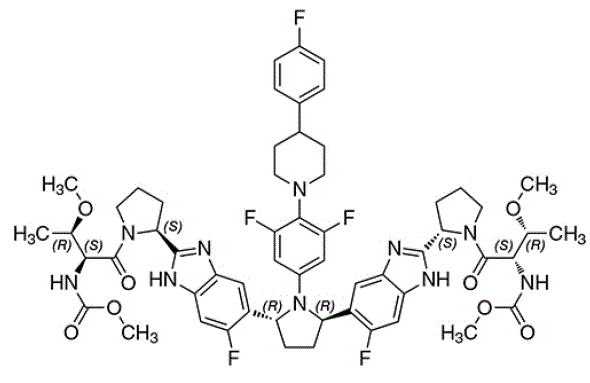 |
Indications & Dosage
INDICATIONS
MAVYRET is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older or weighing at least 45 kg with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A).
MAVYRET is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older or weighing at least 45 kg with HCV genotype 1 infection, who previously have been treated with a regimen containing an HCV NS5A inhibitor or an NS3/4A protease inhibitor (PI), but not both [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and Clinical Studies].
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Testing Prior To The Initiation Of Therapy
Test all patients for evidence of current or prior HBV infection by measuring hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) before initiating HCV treatment with MAVYRET [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ].
Recommended Dosage In Adult And Pediatric Patients 12 Years And Older Or Weighing At Least 45 Kg
MAVYRET is a fixed-dose combination product containing glecaprevir 100 mg and pibrentasvir 40 mg in each tablet.
The recommended oral dosage of MAVYRET is 3 tablets taken at the same time once daily with food (total daily dose: glecaprevir 300 mg and pibrentasvir 120 mg) [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Tables 1 and 2 provide the recommended MAVYRET treatment duration based on the patient population in HCV mono-infected and HCV/HIV-1 co-infected patients with compensated liver disease (with or without cirrhosis) and with or without renal impairment including patients receiving dialysis [see CONTRAINDICATIONS and Clinical Studies]. Refer to Drug Interactions (7) for dosage recommendations for concomitant HIV-1 antiviral drugs.
Table 1. Recommended Duration for Treatment-Naïve Patients
| HCV Genotype | Treatment Duration | |
| No Cirrhosis | Compensated Cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) |
|
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 | 8 weeks | 12 weeks |
Table 2. Recommended Duration for Treatment-Experienced Patients
| Treatment Duration | |||
| HCV Genotype | Patients Previously Treated with a Regimen Containing: |
No Cirrhosis | Compensated Cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) |
| 1 | An NS5A inhibitor1 without prior treatment with an NS3/4A protease inhibitor (PI) | 16 weeks | 16 weeks |
| An NS3/4A PI2 without prior treatment with an NS5A inhibitor | 12 weeks | 12 weeks | |
| 1, 2, 4, 5, or 6 | PRS3 | 8 weeks | 12 weeks |
| 3 | PRS3 | 16 weeks | 16 weeks |
|
1. In clinical trials, subjects were treated with prior regimens containing ledipasvir and sofosbuvir or daclatasvir with (peg)interferon and ribavirin. 2. In clinical trials, subjects were treated with prior regimens containing simeprevir and sofosbuvir, or simeprevir, boceprevir, or telaprevir with (peg)interferon and ribavirin. 3. PRS=Prior treatment experience with regimens containing (peg)interferon, ribavirin, and/or sofosbuvir, but no prior treatment experience with an HCV NS3/4A PI or NS5A inhibitor. |
|||
Liver Or Kidney Transplant Recipients
MAVYRET is recommended for 12 weeks in adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older or weighing at least 45 kg who are liver or kidney transplant recipients. A 16-week treatment duration is recommended in genotype 1-infected patients who are NS5A inhibitor-experienced without prior treatment with an NS3/4A protease inhibitor or in genotype 3-infected patients who are PRS treatment-experienced [see Clinical Studies].
Hepatic Impairment
MAVYRET is not recommended in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) and is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see CONTRAINDICATIONS, Use In Specific Populations and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
Each MAVYRET tablet contains 100 mg of glecaprevir and 40 mg of pibrentasvir. The tablets are pink, oblong-shaped, film-coated, and debossed with “NXT” on one side.
Storage And Handling
MAVYRET is dispensed in a 4-week (monthly) or an 8-week carton. Each weekly carton contains seven daily dose wallets. Each monthly carton contains four weekly cartons. Each 8-week carton contains 2 monthly cartons. Each child resistant daily dose wallet contains three 100 mg/40 mg glecaprevir/pibrentasvir tablets. MAVYRET tablets are pink-colored, film-coated, oblong biconvex shaped, debossed with “NXT” on one side.
The NDC numbers are:
- 4-Week Carton: 0074-2625-28
- 8-Week Carton: 0074-2625-56
Store at or below 30°C (86°F).
Manufactured by AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL 60064. Revised: Apr 2019
Side Effects
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of MAVYRET cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Overall Adverse Reactions In HCV-Infected Adults Without Cirrhosis Or With Compensated Cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A)
The adverse reactions data for MAVYRET in subjects without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) were derived from nine registrational Phase 2 and 3 trials which evaluated approximately 2,300 subjects infected with genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 HCV who received MAVYRET for 8, 12 or 16 weeks [see Clinical Studies].
The overall proportion of subjects who permanently discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions was 0.1% for subjects who received MAVYRET for 8, 12 or 16 weeks.
The most common adverse reactions, all grades, observed in greater than or equal to 5% of subjects receiving 8, 12, or 16 weeks of treatment with MAVYRET were headache (13%), fatigue (11%), and nausea (8%). In subjects receiving MAVYRET who experienced adverse reactions, 80% had an adverse reaction of mild severity (Grade 1). One subject experienced a serious adverse reaction.
Adverse reactions (type and severity) were similar for subjects receiving MAVYRET for 8, 12 or 16 weeks. The type and severity of adverse reactions in subjects with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) were similar to those seen in subjects without cirrhosis.
Adverse Reactions In HCV-Infected Adults Without Cirrhosis Treated With MAVYRET In Controlled Trials
ENDURANCE-2
Among 302 treatment-naive or PRS treatment-experienced, HCV genotype 2-infected adults without cirrhosis enrolled in ENDURANCE-2, adverse reactions (all intensity) occurring in at least 5% of subjects treated with MAVYRET for 12 weeks are presented in Table 3. In subjects treated with MAVYRET for 12 weeks, 32% reported an adverse reaction, of which 98% had adverse reactions of mild or moderate severity. No subjects treated with MAVYRET or placebo in ENDURANCE-2 permanently discontinued treatment due to an adverse drug reaction.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥5% of
Treatment-Naive and PRS-Experienced Adults without Cirrhosis Receiving MAVYRET
for 12 Weeks in ENDURANCE-2
| Adverse Reaction | MAVYRET 12 Weeks (N = 202) % |
Placebo 12 Weeks (N = 100) % |
| Headache | 9 | 6 |
| Nausea | 6 | 2 |
| Diarrhea | 5 | 2 |
ENDURANCE-3
Among 505 treatment-naive, HCV genotype 3-infected adults without cirrhosis enrolled in ENDURANCE-3, adverse reactions (all intensity) occurring in at least 5% of subjects treated with MAVYRET for 8 or 12 weeks are presented in Table 4. In subjects treated with MAVYRET, 45% reported an adverse reaction, of which 99% had adverse reactions of mild or moderate severity. The proportion of subjects who permanently discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions was 0%, < 1% and 1% for the MAVYRET 8 week arm, MAVYRET 12 week arm and DCV + SOF arm, respectively.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥5% of
Treatment-Naive Adults without Cirrhosis Receiving MAVYRET for 8 Weeks or 12
Weeks in ENDURANCE-3
| Adverse Reaction | MAVYRET* 8 Weeks (N = 157) % |
MAVYRET 12 Weeks (N = 233) % |
DCV1 + SOF2 12 Weeks (N = 115) % |
| Headache | 16 | 17 | 15 |
| Fatigue | 11 | 14 | 12 |
| Nausea | 9 | 12 | 12 |
| Diarrhea | 7 | 3 | 3 |
| 1 DCV=daclatasvir 2 SOF=sofosbuvir * The 8 week arm was a non-randomized treatment arm. |
|||
Adverse Reactions In Subjects With Compensated Cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A)
The safety of MAVYRET in HCV GT 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 adults with compensated cirrhosis is based on data from 288 subjects from the Phase 2/3 registrational trials treated with MAVYRET for 12 or more weeks and 343 subjects from EXPEDITION-8 treated with MAVYRET for 8 weeks. The adverse reactions observed were generally consistent with those observed in clinical studies of MAVYRET in non-cirrhotic subjects [see Clinical Studies].
In the Phase 2/3 registrational trials, the adverse reactions reported in greater than or equal to 5% of compensated cirrhotic subjects (n=288) treated across all durations of MAVYRET were fatigue (15%), headache (14%), nausea (8%), diarrhea (6%), and pruritus (6%). In EXPEDITION-8, the adverse reactions reported in greater than or equal to 5% of compensated cirrhotic subjects (n=343) were fatigue (8%), pruritus (7%), and headache (6%). No subjects with compensated cirrhosis in the Phase 2/3 registrational trials (without severe renal impairment) or in EXPEDITION-8 discontinued treatment with MAVYRET due to an adverse reaction.
Adverse Reactions In HCV-Infected Adults With Severe Renal Impairment Including Subjects On Dialysis
The safety of MAVYRET in subjects with chronic kidney disease (Stage 4 or Stage 5 including subjects on dialysis) with genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 chronic HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) was assessed in 104 subjects (EXPEDITION-4) who received MAVYRET for 12 weeks. The most common adverse reactions observed in greater than or equal to 5% of subjects receiving 12 weeks of treatment with MAVYRET were pruritus (17%), fatigue (12%), nausea (9%), asthenia (7%), and headache (6%). In subjects treated with MAVYRET who reported an adverse reaction, 90% had adverse reactions of mild or moderate severity (Grade 1 or 2). The proportion of subjects who permanently discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions was 2%.
Adverse Reactions In HCV/HIV-1 Co-infected Subjects
The safety of MAVYRET in subjects with HIV-1 co-infection with genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4 or 6 chronic HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) was assessed in 153 subjects (EXPEDITION-2) who received MAVYRET for 8 or 12 weeks. Thirty-three subjects with HIV-1 coinfection also received 8 or 12 weeks of therapy in ENDURANCE-1.
The overall safety profile in HCV/HIV-1 co-infected subjects (ENDURANCE-1 and EXPEDITION-2) was similar to that observed in HCV mono-infected subjects. Adverse reactions observed in greater than or equal to 5% of subjects receiving MAVYRET in EXPEDITION-2 for 8 or 12 weeks were fatigue (10%), nausea (8%), and headache (5%).
Adverse Reactions In Subjects With Liver Or Kidney Transplant
The safety of MAVYRET was assessed in 100 post-liver or -kidney transplant recipients with genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 chronic HCV infection without cirrhosis (MAGELLAN-2). The overall safety profile in transplant recipients was similar to that observed in subjects in the Phase 2 and 3 studies, without a history of transplantation. Adverse reactions observed in greater than or equal to 5% of subjects receiving MAVYRET for 12 weeks were headache (17%), fatigue (16%), nausea (8%) and pruritus (7%). In subjects treated with MAVYRET who reported an adverse reaction, 81% had adverse reactions of mild severity. Two percent of subjects experienced a serious adverse reaction, and no subjects permanently discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions.
Adverse Reactions In Adolescent Subjects
The safety of MAVYRET in HCV GT1, 2, 3, or 4 infected adolescents is based on data from a Phase 2/3 open-label trial in 47 subjects aged 12 years to less than 18 years without cirrhosis treated with MAVYRET for 8 or 16 weeks (DORA-Part 1). The adverse reactions observed were consistent with those observed in clinical studies of MAVYRET in adults [see Clinical Studies]. The only adverse drug reaction observed in greater than or equal to 5% of subjects receiving MAVYRET was fatigue (6%). No subjects discontinued or interrupted treatment with MAVYRET due to an adverse reaction.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Serum Bilirubin Elevations
Elevations of total bilirubin at least 2 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 3.5% of subjects treated with MAVYRET versus 0% in placebo; these elevations were observed in 1.2% of subjects across the Phase 2 and 3 trials.
In subjects with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A), 17% experienced early, transient post-baseline elevations of bilirubin above the upper limit of normal. These bilirubin elevations were typically less than two times the upper limit of normal, generally occurred within the first 2 weeks of treatment and resolved with continued treatment. The subjects with compensated cirrhosis and bilirubin elevations did not have concurrent increases in ALT or AST, or signs of liver decompensation or failure, and these laboratory events did not lead to treatment discontinuation. MAVYRET inhibits OATP1B1/3 and is a weak inhibitor of UGT1A1 and may have the potential to impact bilirubin transport and metabolism, including direct and indirect bilirubin. Few subjects experienced jaundice or ocular icterus and total bilirubin levels decreased after completing MAVYRET.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of MAVYRET. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Angioedema
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatic decompensation, hepatic failure [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Drug Interactions
Mechanisms For The Potential Effect Of MAVYRET On Other Drugs
Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir are inhibitors of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), and organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1/3. Coadministration with MAVYRET may increase plasma concentration of drugs that are substrates of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1 or OATP1B3. Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir are weak inhibitors of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A, CYP1A2, and uridine glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1.
Mechanisms For The Potential Effect Of Other Drugs On MAVYRET
Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir are substrates of P-gp and/or BCRP. Glecaprevir is a substrate of OATP1B1/3. Coadministration of MAVYRET with drugs that inhibit hepatic P-gp, BCRP, or OATP1B1/3 may increase the plasma concentrations of glecaprevir and/or pibrentasvir.
Coadministration of MAVYRET with drugs that induce P-gp/CYP3A may decrease glecaprevir and pibrentasvir plasma concentrations.
Carbamazepine, phenytoin, efavirenz, and St. John's wort may significantly decrease plasma concentrations of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir, leading to reduced therapeutic effect of MAVYRET. The use of these agents with MAVYRET is not recommended [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Established And Other Potential Drug Interactions
Clearance of HCV infection with direct-acting antivirals may lead to changes in hepatic function, which may impact the safe and effective use of concomitant medications. For example, altered blood glucose control resulting in serious symptomatic hypoglycemia has been reported in diabetic patients in postmarketing case reports and published epidemiological studies. Management of hypoglycemia in these cases required either discontinuation or dose modification of concomitant medications used for diabetes treatment.
Frequent monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters (e.g. International Normalized Ratio [INR] in patients taking warfarin, blood glucose levels in diabetic patients) or drug concentrations of concomitant medications such as CYP P450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index (e.g. certain immunosuppressants) is recommended to ensure safe and effective use. Dose adjustments of concomitant medications may be necessary.
Table 5 provides the effect of MAVYRET on concentrations of coadministered drugs and the effect of coadministered drugs on glecaprevir and pibrentasvir [see CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Table 5: Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
Identified in Drug Interaction Studies
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration | Clinical Comments |
| Antiarrhythmics: | ||
| Digoxin | ↑ digoxin | Measure serum digoxin concentrations before initiating MAVYRET. Reduce digoxin concentrations by decreasing the dose by approximately 50% or by modifying the dosing frequency and continue monitoring. |
| Anticoagulants: | ||
| Dabigatran etexilate | ↑dabigatran | If MAVYRET and dabigatran etexilate are coadministered, refer to the dabigatran etexilate prescribing information for dabigatran etexilate dose modifications in combination with P-gp inhibitors in the setting of renal impairment. |
| Anticonvulsants: | ||
| Carbamazepine | ↓ glecaprevir ↓pibrentasvir |
Coadministration may lead to reduced therapeutic effect of MAVYRET and is not recommended. |
| Antimycobacterials: | ||
| Rifampin | ↓ glecaprevir ↓ pibrentasvir |
Coadministration is contraindicated because of potential loss of therapeutic effect [see CONTRAINDICATIONS]. |
| Ethinyl Estradiol-Containing Products: | ||
| Ethinyl estradiol-containing medications such as combined oral contraceptives | ↔ glecaprevir ↔ pibrentasvir |
Coadministration of MAVYRET may increase the risk of ALT elevations and is not recommended. |
| Herbal Products: | ||
| St. John’s wort (hypericum perforatum) | ↓ glecaprevir ↓ pibrentasvir |
Coadministration may lead to reduced therapeutic effect of MAVYRET and is not recommended. |
| HIV-Antiviral Agents: | ||
| Atazanavir | ↑glecaprevir ↑ pibrentasvir |
Coadministration is contraindicated due to increased risk of ALT elevations [see CONTRAINDICATIONS]. |
| Darunavir Lopinavir Ritonavir | ↑ glecaprevir ↑ pibrentasvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
| Efavirenz | ↓ glecaprevir ↓ pibrentasvir |
Coadministration may lead to reduced therapeutic effect of MAVYRET and is not recommended. |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: | ||
| Atorvastatin Lovastatin Simvastatin | ↑ atorvastatin ↑ lovastatin ↑ simvastatin |
Coadministration may increase the concentration of atorvastatin, lovastatin, and simvastatin. Increased statin concentrations may increase the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Coadministration with these statins is not recommended. |
| Pravastatin | ↑ pravastatin | Coadministration may increase the concentration of pravastatin. Increased statin concentrations may increase the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Reduce pravastatin dose by 50% when coadministered with MAVYRET. |
| Rosuvastatin | ↑ rosuvastatin | Coadministration may significantly increase the concentration of rosuvastatin. Increased statin concentrations may increase the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Rosuvastatin may be administered with MAVYRET at a dose that does not exceed 10 mg. |
| Fluvastatin Pitavastatin | ↑ fluvastatin ↑ pitavastatin |
Coadministration may increase the concentrations of fluvastatin and pitavastatin. Increased statin concentrations may increase the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Use the lowest approved dose of fluvastatin or pitavastatin. If higher doses are needed, use the lowest necessary statin dose based on a risk/benefit assessment. |
| Immunosuppressants: | ||
| Cyclosporine | ↑ glecaprevir ↑pibrentasvir |
MAVYRET is not recommended for use in patients requiring stable cyclosporine doses > 100 mg per day. |
| See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Tables 8 and 9. ↑= increase; ↓= decrease; ↔ = no effect |
||
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) For Opioid Use Disorder
No buprenorphine/naloxone or methadone dosage adjustment is required when used concomitantly with MAVYRET. There is insufficient information to make a recommendation regarding the concomitant use of naltrexone with MAVYRET.
Drugs With No Observed Clinically Significant Interactions With MAVYRET
No dose adjustment is required when MAVYRET is coadministered with the following medications: abacavir, amlodipine, caffeine, dextromethorphan, dolutegravir, elvitegravir/cobicistat, emtricitabine, felodipine, lamivudine, lamotrigine, losartan, midazolam, norethindrone or other progestin-only contraceptives, omeprazole, raltegravir, rilpivirine, sofosbuvir, tacrolimus, tenofovir alafenamide, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, tolbutamide, and valsartan.
Warnings & Precautions
WARNINGS
Included as part of the PRECAUTIONS section.
PRECAUTIONS
Risk Of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation In Patients Coinfected With HCV And HBV
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation has been reported in HCV/HBV coinfected patients who were undergoing or had completed treatment with HCV direct-acting antivirals, and who were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy. Some cases have resulted in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure and death. Cases have been reported in patients who are HBsAg positive and also in patients with serologic evidence of resolved HBV infection (i.e., HBsAg negative and anti-HBc positive). HBV reactivation has also been reported in patients receiving certain immunosuppressant or chemotherapeutic agents; the risk of HBV reactivation associated with treatment with HCV direct-acting antivirals may be increased in these patients.
HBV reactivation is characterized as an abrupt increase in HBV replication manifesting as a rapid increase in serum HBV DNA level. In patients with resolved HBV infection reappearance of HBsAg can occur. Reactivation of HBV replication may be accompanied by hepatitis, i.e., increase in aminotransferase levels and, in severe cases, increases in bilirubin levels, liver failure, and death can occur.
Test all patients for evidence of current or prior HBV infection by measuring HBsAg and anti- HBc before initiating HCV treatment with MAVYRET. In patients with serologic evidence of HBV infection, monitor for clinical and laboratory signs of hepatitis flare or HBV reactivation during HCV treatment with MAVYRET and during post-treatment follow-up. Initiate appropriate patient management for HBV infection as clinically indicated.
Risk Of Hepatic Decompensation/Failure In Patients With Evidence Of Advanced Liver Disease
Postmarketing cases of hepatic decompensation/failure, including those with fatal outcomes, have been reported in patients treated with HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor-containing regimens, including MAVYRET. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The majority of patients with severe outcomes had evidence of advanced liver disease with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) prior to initiating therapy with MAVYRET, including some patients reported as having compensated cirrhosis with mild liver impairment (Child-Pugh A) at baseline but with a prior decompensation event (i.e., prior history of ascites, variceal bleeding, encephalopathy). Rare cases of hepatic decompensation/failure were reported in patients without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A); many of these patients had evidence of portal hypertension. Events also occurred in patients taking a concomitant medication not recommended for coadministration, or in patients with confounding factors such as serious liver-related medical or surgical comorbidities. Cases typically occurred within the first 4 weeks of treatment (median of 27 days).
In patients with compensated cirrhosis (Child Pugh A) or evidence of advanced liver disease such as portal hypertension, perform hepatic laboratory testing as clinically indicated; and monitor for signs and symptoms of hepatic decompensation such as the presence of jaundice, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and variceal hemorrhage. Discontinue MAVYRET in patients who develop evidence of hepatic decompensation/failure.
MAVYRET is contraindicated in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) or those with any history of prior hepatic decompensation [see CONTRAINDICATIONS, ADVERSE REACTIONS, Use In Specific Populations, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Risk Of Reduced Therapeutic Effect Due To Concomitant Use Of MAVYRET With Carbamazepine, Efavirenz Containing Regimens, Or St. John’s Wort
Carbamazepine, efavirenz, and St. John’s wort may significantly decrease plasma concentrations of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir, leading to reduced therapeutic effect of MAVYRET. The use of these agents with MAVYRET is not recommended.
Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (PATIENT INFORMATION).
Risk Of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation In Patients Coinfected With HCV And HBV
Inform patients that HBV reactivation can occur in patients coinfected with HBV during or after treatment of HCV infection. Advise patients to tell their healthcare provider if they have a history of hepatitis B virus infection [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Risk Of Hepatic Decompensation/Failure In Patients With Evidence Of Advanced Liver Disease
Advise patients to seek medical evaluation immediately for symptoms of worsening liver problems such as nausea, tiredness, yellowing of the skin or white part of the eyes, bleeding or bruising more easily than normal, confusion, loss of appetite, diarrhea, dark or brown urine, dark or bloody stool, swelling of the stomach area (abdomen) or pain in the upper right side of the stomach area, sleepiness, or vomiting of blood [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
Drug Interactions
Inform patients that MAVYRET may interact with some drugs; therefore, patients should be advised to report to their healthcare provider the use of any prescription, non-prescription medication or herbal products [see CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS and DRUG INTERACTIONS].
Administration
Inform patients it is important to take all three tablets at the same time once daily with food as directed. Inform patients that it is important not to miss or skip doses and to take MAVYRET for the duration that is recommended by the physician [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION].
If a dose is missed and it is:
- Less than 18 hours from the usual time that MAVYRET should have been taken – advise the patient to take the dose as soon as possible and then to take the next dose at the usual time.
- More than 18 hours from the usual time that MAVYRET should have been taken – advise the patient not to take the missed dose and to take the next dose at the usual time.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis And Mutagenesis
Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir were not genotoxic in a battery of in vitro or in vivo assays, including bacterial mutagenicity, chromosome aberration using human peripheral blood lymphocytes and in vivo rodent micronucleus assays.
Carcinogenicity studies with glecaprevir and pibrentasvir have not been conducted.
Impairment Of Fertility
No effects on mating, female or male fertility, or early embryonic development were observed in rodents at up to the highest dose tested. Systemic exposures (AUC) to glecaprevir and pibrentasvir were approximately 63 and 102 times higher, respectively, than the exposure in humans at the recommended dose.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
No adequate human data are available to establish whether or not MAVYRET poses a risk to pregnancy outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed when the components of MAVYRET were administered separately during organogenesis at exposures up to 53 times (rats; glecaprevir) or 51 and 1.5 times (mice and rabbits, respectively; pibrentasvir) the human exposures at the recommended dose of MAVYRET (see Data). No definitive conclusions regarding potential developmental effects of glecaprevir could be made in rabbits, since the highest achieved glecaprevir exposure in this species was only 7% (0.07 times) of the human exposure at the recommended dose. There were no effects with either compound in rodent pre/post-natal developmental studies in which maternal systemic exposures (AUC) to glecaprevir and pibrentasvir were approximately 47 and 74 times, respectively, the exposure in humans at the recommended dose (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Glecaprevir
Glecaprevir was administered orally to pregnant rats (up to 120 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (up to 60 mg/kg/day) during the period of organogenesis (gestation days (GD) 6 to 18, and GD 7 to 19, respectively). No adverse embryo-fetal effects were observed in rats at dose levels up to 120 mg/kg/day (53 times the exposures in humans at the recommended human dose (RHD)). In rabbits, the highest glecaprevir exposure achieved was 7% (0.07 times) of the exposure in humans at RHD. As such, data in rabbits during organogenesis are not available for glecaprevir systemic exposures at or above the exposures in humans at the RHD.
In the pre/post-natal developmental study in rats, glecaprevir was administered orally (up to 120 mg/kg/day) from GD 6 to lactation day 20. No effects were observed at maternal exposures 47 times the exposures in humans at the RHD.
Pibrentasvir
Pibrentasvir was administered orally to pregnant mice and rabbits (up to 100 mg/kg/day) during the period of organogenesis (GD 6 to 15, and GD 7 to 19, respectively). No adverse embryo-fetal effects were observed at any studied dose level in either species. The systemic exposures at the highest doses were 51 times (mice) and 1.5 times (rabbits) the exposures in humans at the RHD.
In the pre/post-natal developmental study in mice, pibrentasvir was administered orally (up to 100 mg/kg/day) from GD 6 to lactation day 20. No effects were observed at maternal exposures approximately 74 times the exposures in humans at the RHD.
Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether the components of MAVYRET are excreted in human breast milk, affect human milk production, or have effects on the breastfed infant. When administered to lactating rodents, the components of MAVYRET were present in milk, without effect on growth and development observed in the nursing pups (see Data).
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for MAVYRET and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from MAVYRET or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
No significant effects of glecaprevir or pibrentasvir on growth and post-natal development were observed in nursing pups at the highest doses tested (120 mg/kg/day for glecaprevir and 100 mg/kg/day for pibrentasvir). Maternal systemic exposure (AUC) to glecaprevir and pibrentasvir was approximately 47 or 74 times the exposure in humans at the RHD. Systemic exposure in nursing pups on post-natal day 14 was approximately 0.6 to 2.2 % of the maternal exposure for glecaprevir and approximately one quarter to one third of the maternal exposure for pibrentasvir.
Glecaprevir or pibrentasvir was administered (single dose; 5 mg/kg oral) to lactating rats, 8 to 12 days post parturition. Glecaprevir in milk was 13 times lower than in plasma and pibrentasvir in milk was 1.5 times higher than in plasma. Parent drug (glecaprevir or pibrentasvir) represented the majority (>96%) of the total drug-related material in milk.
Pediatric Use
No dosage adjustment of MAVYRET is required in pediatric patients 12 years and older or weighing at least 45 kg [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and Clinical Studies].
The safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of MAVYRET in HCV GT1, 2, 3, or 4 infected pediatric patients 12 years and older or weighing at least 45 kg is based on data from an open-label trial in 47 subjects without cirrhosis aged 12-18 years who were either treatment naive (n=36) or treatment experienced (n=11) and received MAVYRET for 8 or 16 weeks (DORA-Part 1). The safety and efficacy results observed in this trial were consistent with those observed in clinical studies of MAVYRET in adults.
In pediatric patients with cirrhosis, history of a kidney and/or liver transplant, or HCV GT5 or 6 infection, the safety and efficacy of MAVYRET are supported by the comparable glecaprevir and pibrentasvir exposures observed between adolescents and adults [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
The safety and effectiveness of MAVYRET in children less than 12 years of age have not been studied.
Geriatric Use
In clinical trials of MAVYRET, 328 subjects were age 65 years and over (14% of the total number of subjects in the Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials) and 47 subjects were age 75 and over (2%). No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger subjects. No dosage adjustment of MAVYRET is warranted in geriatric patients [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of MAVYRET is required in patients with mild, moderate or severe renal impairment, including those on dialysis [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and Clinical Studies].
Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of MAVYRET is required in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A). MAVYRET has not been evaluated and is contraindicated in HCV-infected patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or Child-Pugh C) or those with any history of prior hepatic decompensation [see CONTRAINDICATIONS]. Postmarketing cases of hepatic decompensation/failure have been reported in these patients [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS]. Higher exposures of both glecaprevir and pibrentasvir occur in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Overdosage & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
In case of overdose, the patient should be monitored for any signs and symptoms of toxicities. Appropriate symptomatic treatment should be instituted immediately. Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir are not significantly removed by hemodialysis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- MAVYRET is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Use In Specific Populations and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
- MAVYRET is contraindicated with atazanavir or rifampin [see DRUG INTERACTIONS and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY].
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism Of Action
MAVYRET is a fixed-dose combination of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir, which are direct-acting antiviral agents against the hepatitis C virus [see Microbiology].
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of doses up to glecaprevir 600 mg (2 times the recommended dosage) with doses up to pibrentasvir 240 mg (2 times the recommended dosage) on QTc interval was evaluated in an active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) thorough QT study. At 20-fold of glecaprevir and 5-fold of pibrentasvir therapeutic concentrations, the glecaprevir and pibrentasvir combination does not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic properties of the components of MAVYRET in healthy subjects are provided in Table 6. The steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir in HCV-infected subjects without cirrhosis are provided in Table 7.
Table 6: Pharmacokinetic Properties of the Components
of MAVYRET in Healthy Subjects
| Glecaprevir | Pibrentasvir | |
| Absorption | ||
| Tmax (h)a | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Effect of meal (relative to fasting)b | ↑83-163% | ↑ 40-53% |
| Distribution | ||
| % Bound to human plasma proteins | 97.5 | >99.9 |
| Blood-to-plasma ratio | 0.57 | 0.62 |
| Elimination | ||
| t½ (h) | 6 | 13 |
| Metabolism | secondary, CYP3A | None |
| Major route of excretion | biliary-fecal | biliary-fecal |
| % of dose excreted in urinec | 0.7 | 0 |
| % of dose excreted in fecesc | 92.1 | 96.6 |
| a Median Tmax following single doses of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir in healthy subjects. b. Mean systemic exposures with moderate to high fat meals. c. Single dose administration of radiolabeled glecaprevir or pibrentasvir in mass balance studies. |
||
Table 7: Steady-State Pharmacokinetic Parameters of
Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir Following Administration of MAVYRET in
Non-Cirrhotic HCV-Infected Subjects
| Pharmacokinetic Parameter | Glecaprevirb | Pibrentasvirc |
| Cmax (ng/mL)a | 597 (114) | 110 (49) |
| AUC24,ss (ng•h/mL)a | 4800 (122) | 1430 (57) |
| a Geometric mean (%CV) of individual-estimated Cmax and
AUC24,ss values b Relative to healthy subjects, glecaprevir Cmax was 51% lower and AUC24,ss was similar (10% difference) in HCV-infected subjects without cirrhosis, respectively c Relative to healthy subjects, pibrentasvir Cmax and AUC24,ss were 63% and 34% lower, respectively in HCV-infected subjects without cirrhosis, respectively |
||
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
Exposures [geometric mean (%CV)] of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir in 14 pediatric patients 12 years of age and older receiving a daily dose of MAVYRET (300 mg glecaprevir and 120 mg pibrentasvir) were 4790 (72) and 1380 (40) ng•h/mL for AUC24,ss, and 1040 (86) and 174 (36) ng/mL for Cmax, respectively, and were comparable to those in adults who received the same dose. The pharmacokinetics of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir have not been established in children less than 12 years of age.
Subjects With Renal Impairment
Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir AUC were increased ≤ 56% in non-HCV infected subjects with mild, moderate, severe, or end-stage renal impairment (GFR estimated using Modification of Diet in Renal Disease) not on dialysis compared to subjects with normal renal function. Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir AUC were similar with and without dialysis (≤ 18% difference) in dialysis-dependent non-HCV infected subjects. In HCV-infected subjects, 86% higher glecaprevir and 54% higher pibrentasvir AUC were observed for subjects with end stage renal disease, with or without dialysis, compared to subjects with normal renal function.
Subjects With Hepatic Impairment
Following administration of MAVYRET in HCV infected subjects with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A), exposure of glecaprevir was approximately 2-fold and pibrentasvir exposure was similar to non-cirrhotic HCV infected subjects.
At the clinical dose, compared to non-HCV infected subjects with normal hepatic function, glecaprevir AUC was 100% higher in Child-Pugh B subjects, and increased 11-fold in Child-Pugh C subjects. Pibrentasvir AUC was 26% higher in Child-Pugh B subjects, and 114% higher in Child-Pugh C subjects.
Age/Gender/Race/Body Weight
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of glecaprevir or pibrentasvir were observed based on age [12-88 years], sex, race/ethnicity or body weight.
Drug Interaction Studies
Drug interaction studies were performed with glecaprevir/pibrentasvir and other drugs that are likely to be coadministered and with drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interactions. Tables 8 and 9 summarize the pharmacokinetic effects when glecaprevir/pibrentasvir was coadministered with other drugs which showed potentially clinically relevant changes. Significant interactions are not expected when MAVYRET is coadministered with substrates of CYP3A, CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, UGT1A1, or UGT1A4.
Table 8: Drug Interactions: Changes in Pharmacokinetic
Parameters of Glecaprevir (GLE) or Pibrentasvir (PIB) in the Presence of
Coadministered Drug
| Co- administered Drug | Regimen of Coadministered Drug (mg) | Regimen of GLE/PIB (mg) | N | DAA | Central Value Ratio (90% CI) | ||
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | |||||
| Atazanavir + ritonavir | 300+ 100 once daily | 300/120 once dailya | 12 | GLE | ≥4.06 (3.15, 5.23) |
≥6.53 (5.24, 8.14) |
≥14.3 (9.85, 20.7) |
| PIB | ≥1.29 (115, 1.45) |
≥1.64 (148, 1.82) |
≥2.29 (1.95, 2.68) |
||||
| Carbamazepine | 200 twice daily | 300/120 single dose | 10 | GLE | 0.33 (0.27, 0.41) |
0.34 (0.28, 0.40) |
-- |
| PIB | 0.50 (0.42, 0.59) |
0.49 (0.43, 0.55) |
-- | ||||
| Cyclosporine | 100 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 12 | GLEb | 1.30 (0.95, 1.78) |
1.37 (113, 1.66) |
1.34 (1.12, 1.60) |
| PIB | ↔ | ↔ | 1.26 (1.15, 1.37) |
||||
| 400 single dose | 300/120 single dose | 11 | GLE | 4.51 (3.63, 6.05) |
5.08 (4.11, 6.29) |
-- | |
| PIB | ↔ | 1.93 (178, 2.09) |
-- | ||||
| Darunavir + ritonavir | 800+ 100 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 8 | GLE | 3.09 (2.26, 4.20) |
4.97 (3.62, 6.84) |
8.24 (4.40, 15.4) |
| PIB | ↔ | ↔ | 1.66 (1.25, 2.21) |
||||
| Elvitegravir/ cobicistat/ emtricitabine/ tenofovir alafenamide | 150/150/ 200/10 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 11 | GLE | 2.50 (2.08, 3.00) |
3.05 (2.55, 3.64) |
4.58 (3.15,6.65) |
| PIB | ↔ | 1.57 (139, 1.76) |
1.89 (1.63, 2.19) |
||||
| Omeprazole | 20 once daily | 300/120 single dose | 9 | GLE | 0.78 (0.60, 1.00) |
0.71 (0.58, 0.86) |
-- |
| PIB | ↔ | ↔ | -- | ||||
| 40 once daily (1 hour before GLE/PIB) |
300/120 single dose | 12 | GLE | 0.36 (0.21, 0.59) |
0.49 (0.35, 0.68) |
||
| PIB | ↔ | ↔ | -- | ||||
| Rifampin | 600 (first dose) |
300/120 single dose | 12 | GLE | 6.52 (5.06, 8.41) |
8.55 (7.01, 10.4) |
|
| PIB | ↔ | ↔ | -- | ||||
| 600 once daily | 300/120 single dosec | 12 | GLE | 0.14 (0.11, 0.19) |
0.12 (0.09, 0.15) |
-- | |
| PIB | 0.17 (0.14, 0.20) |
0.13 (0.11, 0.15) |
-- | ||||
| Lopinavir/ ritonavir | 400/100 twice daily | 300/120 once daily | 9 | GLE | 2.55 (184, 3.52) |
4.38 (3.02, 6.36) |
18.6 (10.4, 33.5) |
| PIB | 1.40 (1.17,1.67) |
2.46 (2.07,2.92) |
5.24(4.18, 6.58) | ||||
| ↔ = No change (central value ratio 0.80 to 1.25) a. Effect of atazanavir and ritonavir on the first dose of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir is reported. b. HCV-infected transplant recipients who received cyclosporine dose of 100 mg or less per day had mean glecaprevir exposures 2.4-fold of those not receiving cyclosporine. c. Effect of rifampin on glecaprevir and pibrentasvir 24 hours after final rifampin dose. |
|||||||
Table 9: Drug Interactions: Pharmacokinetic Parameters
for Coadministered Drug in the Presence of Combination of
Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir (GLE/PIB)
| Co- administered Drug | Regimen of Coadministered Drug (mg) | Regimen of GLE/PIB (mg) | N | Central Value Ratio (90% CI) | ||
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| Abacavir | ABC/DTG/3TC 600/50/300 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 12 | ↔ | ↔ | 1.31 (1.05, 1.63) |
| Atorvastatin | 10 once daily | 400/120 once daily | 11 | 22.0 (16.4, 29.6) |
8.28 (6.06, 11.3) |
-- |
| Caffeine | 100 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 12 | ↔ | 1.35 (1.23, 1.48) |
-- |
| Dabigatran | Dabigatran etexilate 150 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 11 | 2.05 (1.72, 2.44) |
2.38 (2.11, 2.70) |
-- |
| Darunavir | DRV + RTV 800+ 100 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 1.30 (1.21, 1.40) |
1.29 (1.18, 1.42) |
↔ |
| Ritonavir | 2.03 (1.78, 2.32) |
1.87 (1.74, 2.02) |
↔ | |||
| Dextro- methorphan | Dextromethorphan hydrobromide 30 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 0.70 (0.61, 0.81) |
0.75 (0.66, 0.85) |
-- |
| Digoxin | 0.5 single dose | 400/120 once daily | 12 | 1.72 (1.45, 2.04) |
1.48 (1.40, 1.57) |
-- |
| Ethinyl estradiol (EE) |
EE/ Norgestimate 35 ng/250 |ig once daily | 300/120 once daily | 11 | 1.31 (1.24, 1.38) |
1.28 (1.23, 1.32) |
1.38 (1.25, 1.52) |
| Norgestrel | 1.54 (1.34, 1.76) |
1.63 (1.50, 1.76) |
1.75 (1.62, 1.89) |
|||
| Norgestromin | ↔ | 1.44 (1.34, 1.54) |
1.45 (1.33, 1.58) |
|||
| Ethinyl estradiol | EE/ Levonorgestrel | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 1.30 (1.18, 1.44) |
1.40 (1.33, 1.48) |
1.56 (1.41, 1.72) |
| Norgestrel | 20 ng/100 |ig once daily | 1.37 (1.23, 1.52) |
1.68 (1.57, 1.80) |
1.77 (1.58, 1.98) |
||
| Elvitegravir | EVG/COBI/FTC/ TAF 150/ 150/200/10 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 1.36 (1.24, 1.49) |
1.47 (1.37, 1.57) |
1.71 (1.50, 1.95) |
| Tenofovir | ↔ | ↔ | ↔ | |||
| Felodipine | 2.5 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 11 | 1.31 (1.05, 1.62) |
1.31 (1.08, 1.58) |
-- |
| Losartan | 50 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 2.51 (2.00, 3.15) |
1.56 (1.28, 1.89) |
-- |
| Losartan carboxylic acid | 2.18 (1.88, 2.53) |
↔ | -- | |||
| Lovastatin | Lovastatin 10 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 12 | ↔ | 1.70 (1.40, 2.06) |
-- |
| Lovastatin acid | 5.73 (4.65, 7.07) |
4.10 (3.45, 4.87) |
-- | |||
| Midazolam | 1 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 12 | ↔ | 1.27 (1.11, 1.45) |
-- |
| Omeprazole | 20 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 0.57 (0.43, 0.75) |
0.79 (0.70, 0.90) |
-- |
| Pravastatin | 10 once daily | 400/120 once daily | 12 | 2.23 (1.87, 2.65) |
2.30 (1.91, 2.76) |
-- |
| Raltegravir | 400 twice daily | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 1.34 (0.89, 1.98) |
1.47 (1.15, 1.87) |
2.64 (1.42, 4.91) |
| Rilpivirine | 25 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 2.05 (1.73, 2.43) |
1.84 (1.72, 1.98) |
1.77 (1.59, 1.96) |
| Rosuvastatin | 5 once daily | 400/120 once daily | 11 | 5.62 (4.80, 6.59) |
2.15 (1.88, 2.46) |
-- |
| Simvastatin | Simvastatin 5 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 1.99 (1.60, 2.48) |
2.32 (1.93, 2.79) |
-- |
| Simvastatin acid | 10.7 (7.88, 14.6) |
4.48 (3.11, 6.46) |
-- | |||
| Sofosbuvir | Sofosbuvir 400 once daily | 400/120 once daily | 8 | 1.66 (1.23, 1.22) |
2.25 (1.86, 2.72) |
-- |
| GS-331007 | ↔ | ↔ | 1.85 (1.67, 2.04) |
|||
| Tacrolimus | 1 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 10 | 1.50 (1.24, 1.82) |
1.45 (1.24, 1.70) |
-- |
| Tenofovir | EFV/FTC/TDF 300/200/300 once daily | 300/120 once daily | 12 | ↔ | 1.29 (1.23, 1.35) |
1.38 (1.31, 1.46) |
| Valsartan | 80 single dose | 300/120 once daily | 12 | 1.36 (1.17, 1.58) |
1.31 (1.16, 1.49) |
-- |
| ↔ = No change (central value ratio 0.80 to 1.25) 3TC – lamivudine; ABC – abacavir; COBI – cobicistat; DRV – darunavir; DTG – dolutegravir; EFV – efavirenz; EVG – elvitegravir; FTC – emtricitabine; RTV – ritonavir; TAF – tenofovir alafenamide; TDF – tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
||||||
Microbiology
Mechanism Of Action
Glecaprevir
Glecaprevir is an inhibitor of the HCV NS3/4A protease, which is necessary for the proteolytic cleavage of the HCV encoded polyprotein (into mature forms of the NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B proteins) and is essential for viral replication. In a biochemical assay, glecaprevir inhibited the proteolytic activity of recombinant NS3/4A enzymes from clinical isolates of HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a, 4a, 5a, and 6a with IC50 values ranging from 3.5 to 11.3 nM.
Pibrentasvir
Pibrentasvir is an inhibitor of HCV NS5A, which is essential for viral RNA replication and virion assembly. The mechanism of action of pibrentasvir has been characterized based on cell culture antiviral activity and drug resistance mapping studies.
Antiviral Activity
In HCV replicon assays, glecaprevir had median EC50 values of 0.08-4.6 nM against laboratory and clinical isolates from subtypes 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a, 4a, 4d, 5a, and 6a. Pibrentasvir had median EC50 values of 0.5-4.3 pM against laboratory and clinical isolates from subtypes 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a, 4a, 4b, 4d, 5a, 6a, 6e and 6p.
Combination Antiviral Activity
Evaluation of combination of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir showed no antagonism in antiviral activity in HCV genotype 1 replicon cell culture assays.
Resistance
In Cell Culture
Selection of HCV genotype 1a, 1b, 2a, 3a, 4a or 6a replicons for reduced susceptibility to glecaprevir resulted in the emergence of amino acid substitutions most commonly at NS3 positions A156 or D/Q168. Individual substitutions at NS3 amino acid position A156 introduced into HCV replicons by site-directed mutagenesis generally caused the greatest reductions (>100-fold) in susceptibility to glecaprevir. Individual substitutions at NS3 position D/Q168 had varying effects on glecaprevir susceptibility depending on HCV genotype/subtype and specific amino acid change, with the greatest reductions (>30-fold) observed in genotypes 1a (D168F/Y), 3a (Q168R) and 6a (D168A/G/H/V/Y). Combinations of NS3 Y56H plus D/Q168 substitutions resulted in greater reductions in glecaprevir susceptibility. An NS3 Q80R substitution in genotype 3a caused a 21-fold reduction in glecaprevir susceptibility, while Q80 substitutions in genotypes 1a and 1b (including genotype 1a Q80K) did not reduce glecaprevir susceptibility.
Individual amino acid substitutions associated with resistance to other HCV protease inhibitors at positions 36, 43, 54, 55, 56, 155, 166, or 170 in NS3 generally did not reduce susceptibility to glecaprevir.
Selection of HCV genotype 1a, 2a or 3a replicons for reduced susceptibility to pibrentasvir resulted in the emergence of amino acid substitutions at known NS5A inhibitor resistance-associated positions, including Q30D/deletion, Y93D/H/N or H58D +Y93H in genotype 1a replicons, F28S + M31I or P29S + K30G in genotype 2a replicons, and Y93H in genotype 3a replicons. The majority of individual amino acid substitutions associated with resistance to other HCV NS5A inhibitors at positions 24, 28, 30, 31, 58, 92, or 93 in NS5A did not reduce susceptibility to pibrentasvir. Individual NS5A amino acid substitutions that reduced susceptibility to pibrentasvir include M28G or Q30D in a genotype 1a replicon (244- and 94-fold, respectively), and P32-deletion in a genotype 1b replicon (1,036-fold). Some combinations of two or more NS5A inhibitor resistance-associated amino acid substitutions may result in greater reductions in pibrentasvir susceptibility.
In Clinical Studies
Studies In Treatment-Naive And (peg)Interferon, Ribavirin And/Or Sofosbuvir Treatment-Experienced Subjects With Or Without Cirrhosis
In pooled analyses of NS3/4A PI- and NS5A inhibitor-naive subjects who received MAVYRET for 8, 12, or 16 weeks in the registrational Phase 2 and 3 clinical studies (including EXPEDITION-2 and MAGELLAN-2), treatment-emergent resistance analyses were conducted for 24 subjects who experienced virologic failure (2 with genotype 1, 2 with genotype 2, 20 with genotype 3 infection). No subjects with HCV genotype 4, 5 or 6 infection experienced virologic failure.
Among the two genotype 1-infected subjects who experienced virologic failure, both subjects had a subtype 1a infection. One subject had treatment-emergent substitutions A156V in NS3, and Q30R, L31M and H58D in NS5A (Q30R and L31M were also detected at a low frequency at baseline). One subject had treatment-emergent Q30R and H58D (while Y93N was present at baseline and post-treatment) in NS5A.
Among the two genotype 2-infected subjects who experienced virologic failure, both subjects had a subtype 2a infection, and no treatment-emergent substitutions were observed in NS3 or NS5A.
Among the 20 genotype 3-infected subjects who experienced virologic failure, treatment-emergent NS3 substitutions Y56H/N, Q80K/R, A156G, or Q168L/R were observed in 13 subjects. A166S or Q168R were present at baseline and post-treatment in 5 subjects. Treatment-emergent NS5A substitutions S24F, M28G/K, A30G/K, L31F, P58T, or Y93H were observed in 17 subjects, and 14 subjects had A30K (n=9) or Y93H (n=6) at baseline and post-treatment.
Studies In Subjects With Or Without Cirrhosis Who Were Treatment-Experienced To NS3/4A Protease And/Or NS5A Inhibitors
Treatment-emergent resistance analyses were conducted for 11 HCV genotype 1-infected subjects (10 genotype 1a, 1 genotype 1b) with prior NS3/4A PI or NS5A inhibitor treatment experience who experienced virologic failure with MAVYRET with or without ribavirin in the MAGELLAN-1 study. Treatment-emergent NS3 substitutions V36A/M, Y56H, R155K/T, A156G/T/V, or D168A/T were observed in 73% (8/11) of subjects. Nine of 10 subjects (90%, not including one subject missing NS5A data at failure) had treatment-emergent NS5A substitutions M28A/G (or L28M for genotype 1b), P29Q/R, Q30K/R, H58D or Y93H/N. All 11 subjects also had NS5A inhibitor resistance-associated substitutions detected at baseline, and 7/11 had NS3 PI resistance-associated substitutions detected at baseline (see Cross-Resistance for the effect of baseline resistance-associated substitutions on treatment response for NS3/4A PI or NS5A inhibitor treatment-experienced patients).
Effect Of Baseline HCV Amino Acid Polymorphisms On Treatment Response (NS3/4A PI- and NS5A Inhibitor-Naive Subjects)
A pooled analysis of NS3/4A PI- and NS5A inhibitor-naive subjects who received MAVYRET in the Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical studies was conducted to identify the HCV subtypes represented and explore the association between baseline amino acid polymorphisms and treatment outcome. Baseline polymorphisms relative to a subtype-specific reference sequence at resistance-associated amino acid positions 155, 156, and 168 in NS3, and 24, 28, 30, 31, 58, 92, and 93 in NS5A were evaluated at a 15% detection threshold by next-generation sequencing. Among subjects who received MAVYRET for 8-, 12-, or 16 weeks, baseline polymorphisms in NS3 were detected in 1% (9/845), 1% (3/398), 2% (10/613), 1% (2/164), 42% (13/31), and 3% (1/34) of subjects with HCV genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 infection, respectively. No baseline polymorphisms were detected at NS3 amino acid position 156 across all genotypes. Baseline polymorphisms in NS5A were detected in 27% (225/841), 80% (331/415), 22% (136/615), 50% (80/161), 13% (4/31), and 54% (20/37) of subjects with HCV genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 infection, respectively.
Genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6: Baseline HCV polymorphisms in genotypes 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6 had no impact on treatment outcome.
Genotype 3: Among treatment-naive, genotype 3-infected subjects without cirrhosis who received MAVYRET for 8 weeks, an NS5A A30K polymorphism was detected in 10% (18/181) of subjects, of whom 78% (14/18) achieved SVR12. Limited data are available to characterize the impact of the A30K polymorphism in genotype 3-infected subjects with cirrhosis (n=3 who received MAVYRET for 8 weeks, all achieved SVR12) or prior treatment experience (n=1 who received MAVYRET for 16 weeks, relapse). In the pooled Phase 2 and Phase 3 trials including EXPEDITION-8, all genotype 3-infected subjects (100%, 15/15) with Y93H in NS5A at baseline who received the recommended MAVYRET regimens achieved SVR12. In MAGELLAN-2 (post-transplant subjects), SVR12 was achieved in 2 of 3 (67%) genotype 3-infected subjects with the NS5A Y93H baseline polymorphism.
Cross-Resistance
Based on resistance patterns observed in cell culture replicon studies and HCV-infected subjects, cross-resistance is possible between glecaprevir and other HCV NS3/4A PIs, and between pibrentasvir and other HCV NS5A inhibitors. Cross-resistance is not expected between MAVYRET and sofosbuvir, (peg)interferon or ribavirin.
In the MAGELLAN-1 study, HCV genotype 1-infected subjects who had failed prior treatment with NS3/4A protease and/or NS5A inhibitors were treated with MAVYRET for 12 or 16 weeks. Baseline sequences were analyzed by next generation sequencing at a 15% detection threshold.
Among 23 NS3/4A PI-experienced/NS5A inhibitor-naive subjects who received MAVYRET for 12 weeks in MAGELLAN-1 (excluding 2 non-virologic failure subjects), 2 subjects each had baseline NS3 R155K or D168E/V substitutions; all 23 subjects achieved SVR12.
Among NS5A inhibitor-experienced/PI-naive subjects who received MAVYRET for 16 weeks, baseline NS5A resistance-associated substitutions [R30Q (n=1), Y93H/N (n=5), M28A+Q30R (n=1), Q30H+Y93H (n=1), Q30R+L31M (n=2), L31M+H58P (n=1)], were detected in 73% (11/15) of subjects with available data, of whom 91% (10/11) achieved SVR12. The non-SVR12 subject experienced on-treatment virologic failure and had a genotype 1a infection with baseline NS5A Q30R and L31M substitutions.
Persistence Of Resistance-Associated Substitutions
Data on the persistence of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir resistance-associated substitutions are not available. NS5A resistance-associated substitutions observed in patients treated with other NS5A inhibitors have been found to persist for longer than 1 year. In patients treated with other NS3/4A PI, viral populations with NS3 resistance-associated substitutions have been found to decline in some patients through post-treatment weeks 24 and 48. The long-term clinical impact of the emergence or persistence of virus containing glecaprevir or pibrentasvir resistance-associated substitutions is unknown.
Clinical Studies
Description Of Clinical Trials
Table 10 summarizes the clinical trials conducted to support the effectiveness of MAVYRET in subjects with HCV genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 infection and compensated liver disease (including Child-Pugh A cirrhosis) according to treatment history and cirrhosis status.
Table 10: Clinical Trials Conducted with MAVYRET in Subjects
with HCV Genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 Infection and Compensated Liver Disease
| Genotype (GT) | Clinical Trial (NCT Number) | Treatment Duration* |
| TN and PRS-TE Subjects without Cirrhosis | ||
| GT1** | ENDURANCE-1 (NCT02604017) | MAVYRET for 8 (n=351) or 12 weeks (n=352) |
| GT2 | SURVEYOR-2 (NCT02243293) | MAVYRET for 8 weeks (n=197) |
| GT3 | ENDURANCE-3 | MAVYRET for 8 (n=157) or 12 weeks (n=233) |
| (NCT02640157) | sofosbuvir + daclatasvir for 12 weeks (n=115) | |
| SURVEYOR-2 | MAVYRET for 16 (PRS-TE only) weeks (n=22) | |
| GT4, 5, 6 | ENDURANCE-5,6 (NCT02966795) | MAVYRET for 8 weeks (GT5 n=20; GT6 n=55) |
| SURVEYOR-2 | MAVYRET for 8 weeks (GT4 n=46; GT5 n=2; GT6 n=10) | |
| TN and PRS-TE Subjects with Compensated Cirrhosis | ||
| GT1, 2, 4, 5, 6 | EXPEDITION-1 (NCT02642432) | MAVYRET for 12 weeks (n=146) |
| GT1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 | EXPEDITION-8 (NCT03089944) | MAVYRET for 8 weeks (n=343) (TN only) |
| GT3 | SURVEYOR-2 | MAVYRET for 16 weeks (PRS-TE only) (n=47) |
| GT5, 6 | ENDURANCE-5,6 | MAVYRET for 12 weeks (GT 5 n=3; GT 6 n=6) |
| Subjects with CKD Stage 4 and 5 without Cirrhosis or with Compensated Cirrhosis | ||
| GT1-6 | EXPEDITION-4 (NCT02651194) | MAVYRET for 12 weeks (n=104) |
| NS5A Inhibitor or PI-Experienced Subjects without Cirrhosis or with Compensated Cirrhosis | ||
| GT1 | MAGELLAN-1 (NCT02446717) | MAVYRET for 12 (n=25) or 16 weeks (n=17) |
| HCV/HIV-1 Co-Infected Subjects without Cirrhosis or with Compensated Cirrhosis | ||
| GT1, 2, 3, 4, 6 | EXPEDITION-2 (NCT02738138) | MAVYRET for 8 (n=137) or 12 weeks (n=16) |
| Liver or Kidney Transplant Recipients without Cirrhosis | ||
| GT1, 2, 3, 4, 6 | MAGELLAN-2 (NCT02692703) | MAVYRET for 12 weeks (n=100) |
| Adolescent Subjects (12 years to less than 18 years) | ||
| GT1, 2, 3, 4 | DORA (Part 1) (NCT03067129) | MAVYRET for 8 weeks (n=44) or 16 weeks (n=3) |
| TN=treatment naive; PI=protease inhibitor; CKD=chronic
kidney disease PRS-TE= defined as prior treatment experience with regimens
containing (peg)interferon, ribavirin, and/or sofosbuvir, but no prior
treatment experience with an HCV NS3/4A PI or NS5A inhibitor. * Treatment durations for some trial arms shown in this table do not reflect recommended dosing for the respective genotypes, prior treatment history, and/or cirrhosis status. For recommended dosing in adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older or weighing at least 45 kg [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION]. ** ENDURANCE-1 included 33 subjects co-infected with HIV-1. |
||
Serum HCV RNA values were measured during the clinical trials using the Roche COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HCV test (version 2.0) with a lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of 15 IU/mL (except for SURVEYOR-2 which used the Roche COBAS TaqMan real-time reverse transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR) assay v. 2.0 with an LLOQ of 25 IU/mL). The primary endpoint across all clinical trials was sustained virologic response (SVR12), defined as HCV RNA less than LLOQ at 12 weeks after the end of treatment. Relapse was defined as HCV RNA ≥ LLOQ after end-of-treatment response among subjects who completed treatment. Subjects with missing HCV RNA data, such as those who discontinued due to an adverse event, subject withdrawal or were lost to follow-up, were counted as SVR12 failures.
Demographics And Baseline Characteristics Of Clinical Trials In Treatment-Naive Or Treatment-Experienced Adults To (peg)Interferon, Ribavirin And/Or Sofosbuvir (PRS) Without Cirrhosis Or With Compensated Cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A)
Of the 2,152 subjects without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis who were treatment-naive or treatment-experienced to combinations of (peg)interferon, ribavirin and/or sofosbuvir (PRS), treated in the registrational studies excluding EXPEDITION-4 and MAGELLAN-1, the median age was 54 years (range: 19 to 88); 73% were treatment-naive, 27% were PRS treatment-experienced; 39% were HCV genotype 1; 21% were HCV genotype 2; 29% were HCV genotype 3; 7% were HCV genotype 4; 4% were HCV genotype 5, or 6; 13% were ≥65 years; 54% were male; 5% were Black; 12% had cirrhosis; 20% had a body mass index of at least 30 kg per m²; and median baseline HCV RNA level was 6.2 log10 IU/mL.
Treatment-Naive Or PRS Treatment-Experienced Adults With HCV Genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, Or 6 Infection Without Cirrhosis
The efficacy of MAVYRET in subjects who were treatment-naive or treatment-experienced to combinations of (peg)interferon, ribavirin and/or sofosbuvir (PRS) with genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, or 6 chronic HCV infection without cirrhosis was studied in three trials using an 8 week duration: ENDURANCE-1, ENDURANCE-5,6, and SURVEYOR-2 [(Part 2 and Part 4)].
ENDURANCE-1 was a randomized (1:1), open-label, multi-national trial comparing the efficacy of 8 weeks of treatment with MAVYRET versus 12 weeks of treatment in subjects without cirrhosis with genotype 1 infection with or without HIV-1 co-infection (n=33 co-infected). Table 11 presents SVR12 in MAVYRET-treated genotype 1-infected subjects for the 8 week treatment arm. Due to numerically similar efficacy, MAVYRET is recommended for 8 weeks for treatment-naive and PRS treatment-experienced genotype 1 subjects without cirrhosis, rather than 12 weeks [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION].
Table 11: ENDURANCE-1: Efficacy in Treatment-Naive and
PRS Treatment-Experienced Adults with HCV Genotype 1 Infection without
Cirrhosis
| MAVYRET 8 Weeks GT1 N=351 |
|
| SVR12 | 99% (348/351) |
| Outcome for Subjects without SVR12 | |
| On-treatment VF | <1% (1/351) |
| Relapse | 0/349 |
| Other* | <1% (2/351) |
| VF= virologic failure * Includes subjects who discontinued due to adverse event, lost to follow-up, or subject withdrawal. |
|
The SVR12 data from the open-label trials SURVEYOR-2 (Parts 2 and 4) and ENDURANCE-5,6, are pooled by genotype, where appropriate, in Table 12 for ease of display.
Table 12: SURVEYOR-2 (Part 2 and Part 4) and
ENDURANCE-5, 6: Efficacy in Treatment-Naive and PRS Treatment-Experienced
Adults with HCV Genotypes 2, 4, 5 or 6 Infection without Cirrhosis
| MAVYRET 8 Weeks | ||||
| GT2 N=197 |
GT4 N=46 |
GT5 N=22 |
GT6 N=65 |
|
| SVR 12 | 98% (193/197) | 93% (43/46) | 95% (21/22) | 100% (65/65) |
| Outcome for Subjects without SVB12 | ||||
| On Treatment VF | 0/197 | 0/46 | 0/22 | 0/65 |
| Relapse | 1% (2/195) | 0/45 | 5% (1/22) | 0/65 |
| Other* | 1% (2/197) | 7% (3/46) | 0/22 | 0/65 |
| GT=genotype; VF= virologic failure * Includes subjects who discontinued due to adverse event, lost to follow-up, or subject withdrawal. |
||||
Treatment-Naive Adults With HCV Genotype 1-6 Infection With Compensated Cirrhosis Or PRS Treatment-Experienced Adults With HCV Genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, Or 6 Infection With Compensated Cirrhosis
The efficacy of MAVYRET in treatment-naive subjects with genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 chronic HCV infection and compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) was studied in EXPEDITION-8, a single-arm, open-label trial in 343 subjects who received MAVYRET for 8 weeks.
Table 13: EXPEDITION-8: Efficacy in Treatment-Naive
Adults with HCV Genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 Infection with Compensated
Cirrhosis
| MAVYRET 8 Weeks (N=343) |
|||||||
| Total (all GTs) (N=343) |
GT1 (N=231) |
GT2 (N=26) |
GT3 (N=63) |
GT4 (N=13) |
GT5 (N=1) |
GT6 (N=9) |
|
| SVR12 | 98% (335/343) | 98% (226/231) | 100% (26/26) | 95% (60/63) | 100% (13/13) | 100% (1/1) | 100% (9/9) |
| Outcome for Subjects without SVR12 | |||||||
| On-treatment VF | 0/343 | 0/231 | 0/26 | 0/63 | 0/13 | 0/1 | 0/9 |
| Relapse | <1% (1/336) | 0/225 | 0/26 | 2% (1/62) | 0/13 | 0/1 | 0/9 |
| Other* | 2% (7/343) | 2% (5/231) | 0/26 | 3% (2/63) | 0/13 | 0/1 | 0/9 |
| GT = genotype; VF = virologic failure * Includes subjects who discontinued due to lost to follow-up or subject withdrawal. |
|||||||
The efficacy of MAVYRET in treatment-naive or PRS treatment-experienced subjects with genotype 1, 2, 4, 5 or 6 chronic HCV infection with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) was studied in EXPEDITION-1 a single-arm, open-label trial, which included 146 subjects (TN N=110, TE-PRS N=36) treated with MAVYRET for 12 weeks, and in ENDURANCE-5, 6, an open-label trial in 84 subjects (TN N= 76, TE-PRS N=8) with genotype 5 or 6 chronic HCV infection, 9 of whom had compensated cirrhosis (GT5 N=3, GT6 N=6) and received MAVYRET for 12 weeks.
Table 14: EXPEDITION-1 and ENDURANCE-5, 6: Efficacy in
Treatment-Naive and PRS Treatment-Experienced Adults with HCV Genotype 1, 2, 4,
5 or 6 Infection with Compensated Cirrhosis
| MAVYRET 12 Weeks | ||||||
| Total (all GTs) (N=155) |
GT1 (N=90) |
GT2 (N=31) |
GT4 (N=16) |
GT5 (N=5) |
GT6 (N=13) |
|
| SVR12 | 99% (153/155) | 99% (89/90) | 100% (31/31) | 100% (16/16) | 100% (5/5) | 92% (12/13) |
| Outcome for Subjects without SVR12 | ||||||
| On-treatment VF | <1% (1/155) | 0/90 | 0/31 | 0/16 | 0/5 | 8% (1/13) |
| Relapse | <1% (1/152) | 1% (1/88) | 0/31 | 0/16 | 0/5 | 0/12 |
| GT = genotype; VF = virologic failure | ||||||
Treatment-Naive Or PRS Treatment-Experienced Adults With HCV Genotype 3 Infection Without Cirrhosis Or With Compensated Cirrhosis
The efficacy of MAVYRET in subjects who were treatment-naive or treatment-experienced to combinations of (peg)interferon, ribavirin and/or sofosbuvir (PRS) with genotype 3 chronic HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis was studied in ENDURANCE-3, EXPEDITION-8 and in SURVEYOR-2 Part 3.
ENDURANCE-3 was a partially-randomized, open-label, active-controlled trial in treatment-naive subjects without cirrhosis. Subjects were randomized (2:1) to either MAVYRET for 12 weeks or to the combination of sofosbuvir and daclatasvir for 12 weeks; subsequently the trial included a third non-randomized arm with MAVYRET for 8 weeks. The SVR12 data are summarized in Table 15. Due to numerically similar efficacy, MAVYRET is recommended for 8 weeks for treatment-naive genotype 3 subjects without cirrhosis, rather than 12 weeks [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION].
Table 15: ENDURANCE-3: Efficacy in Treatment-Naive,
HCV Genotype 3-Infected Subjects without Cirrhosis
MAVYRET1 8 Weeks |
MAVYRET 12 Weeks* (N=233) |
DCV+SOF 12 Weeks (N=115) |
|
| SVR12 | 95% (149/157) | 95% (222/233)* | 97% (111/115) |
| Outcome for Subjects without SVR12 | |||
| On-treatment VF | 1% (1/157) | <1% (1/233) | 0/115 |
| Relapse | 3% (5/150) | 1% (3/222) | 1% (1/114) |
| Other2 | 1% (2/157) | 3% (7/233) | 3% (3/115) |
| VF=virologic failure 1 MAVYRET 8 weeks was a non-randomized treatment arm. 2 Includes subjects who discontinued due to adverse event, lost to follow-up, or subject withdrawal. * Data for MAVYRET 12-week treatment is displayed to reflect the original randomized study design. The treatment difference (95% confidence interval) was -1.2% (-5.6, 3.1) between the randomized arms of MAVYRET 12 weeks and DCV + SOF 12 weeks. |
|||
The efficacy of MAVYRET in subjects who were treatment-naive with genotype 3 chronic HCV infection and compensated cirrhosis was studied in EXPEDITION-8. The SVR12 rate of the treatment-naive subjects with genotype 3 and compensated cirrhosis was 95% (60/63) and one subject experienced virologic relapse [see Clinical Studies].
SURVEYOR-2 Part 3 was an open-label trial randomizing PRS treatment-experienced subjects with genotype 3 infection without cirrhosis to 16-weeks of treatment. In addition, the trial evaluated the efficacy of MAVYRET in PRS treatment-experienced genotype 3-infected subjects with compensated cirrhosis for a 16-week duration. Among PRS treatment-experienced subjects treated with MAVYRET for 16 weeks, 49% (34/69) had failed a previous regimen containing sofosbuvir.
Table 16: SURVEYOR-2 Part 3: Efficacy in PRS
Treatment-Experienced, HCV Genotype 3-Infected Adults without Cirrhosis or with
Compensated Cirrhosis
| PRS Treatment-Experienced without Cirrhosis or with Compensated Cirrhosis | |
| MAVYRET 16 Weeks (N=69) |
|
| SVR12 | 96% (66/69) |
| Outcome for Subjects without SVR12 | |
| On-treatment VF | 1% (1/69) |
| Relapse | 3% (2/68) |
| Other* | 0/69 |
| SVR12 by Cirrhosis Status | |
| Without Cirrhosis | 95% (21/22) |
| With Compensated Cirrhosis | 96% (45/47) |
| VF=virologic failure * Includes subjects who discontinued due to adverse event, lost to follow-up, or subject withdrawal. |
|
Treatment-Naive And PRS Treatment-Experienced Adults With CKD Stage 4 And 5 And Chronic HCV Infection Without Cirrhosis Or With Compensated Cirrhosis
EXPEDITION-4 was an open-label, single-arm, multicenter trial to evaluate safety and efficacy in subjects with severe renal impairment (CKD Stages 4 and 5) with compensated liver disease (with and without Child-Pugh A cirrhosis). There were 104 subjects enrolled, 82% were on hemodialysis, and 53%, 15%, 11%, 19%, 1% and 1% were infected with HCV genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6; respectively. Overall, 19% of subjects had compensated cirrhosis and 81% of subjects were non-cirrhotic; 58% and 42% of subjects were treatment-naive and PRS treatment-experienced, respectively. The overall SVR12 rate was 98% and no subjects experienced virologic failure. The presence of renal impairment did not affect efficacy; no dose-adjustments were required during the trial.
Adults Who Are NS5A Inhibitor Or NS3/4A-Protease Inhibitor (PI)-Experienced, Without Cirrhosis Or With Compensated Cirrhosis
MAGELLAN-1 was a randomized, multipart, open-label trial in 141 genotype 1- or 4-infected subjects who failed a previous regimen containing an NS5A inhibitor and/or NS3/4A PI. Part 1 (n=50) was a randomized trial exploring 12 weeks of glecaprevir 200 mg and pibrentasvir 80 mg, glecaprevir 300 mg and pibrentasvir 120 mg, with and without ribavirin (only data from glecaprevir 300 mg plus pibrentasvir 120 mg without ribavirin are included in these analyses). Part 2 (n=91) randomized genotype 1- or 4-infected subjects without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis to 12- or 16-weeks of treatment with MAVYRET.
Of the 42 genotype 1-infected subjects treated in Parts 1 and 2, who were either NS5A inhibitor-experienced only (and treated for 16 weeks), or NS3/4A PI-experienced only (and treated for 12 weeks), the median age was 58 years (range: 34 to 70); 40% of the subjects were NS5A-treatment experienced only and 60% were PI experienced only; 24% had cirrhosis; 19% were ≥65 years, 69% were male; 26% were Black; 43% had a body mass index ≥ 30 kg/m²; 67% had baseline HCV RNA levels of at least 1,000,000 IU per mL; 79% had subtype 1a infection, 17% had subtype 1b infection and 5% had non-1a/1b infection.
Due to higher rates of virologic failure and treatment-emergent drug resistance, the data do not support labeling for treatment of HCV genotype 1-infected patients who are both NS3/4A PI and NS5A inhibitor-experienced.
Table 17: MAGELLAN-1: Efficacy in HCV Genotype
1-Infected Adults Who Are NS3/4A PI-Experienced or NS5A Inhibitor-Experienced,
without Cirrhosis or with Compensated Cirrhosis
| PI-Experienced1 (NS5A Inhibitor-naive) | NS5A Inhibitor-Experienced2 (PI-naive) | |
| MAVYRET 12 Weeks (N=25) |
MAVYRET 16 Weeks (N=17) |
|
| SVR12 | 92% (23/25) | 94% (16/17) |
| Outcome for Subjects without SVR | ||
| On-treatment Virologic Failure | 0/25 | 6% (1/17) |
| Relapse | 0/25 | 0/16 |
| Other3 | 8% (2/25) | 0/17 |
| PI= protease inhibitor 1 Includes subjects who were treated with a regimen containing an NS3/4A PI (simeprevir with sofosbuvir, or simeprevir, boceprevir, or telaprevir with (peg)interferon and ribavirin) and without prior treatment with an NS5A inhibitor. 2 Includes subjects who were treated with a regimen containing an NS5A inhibitor (ledipasvir with sofosbuvir or daclatasvir with (peg)interferon and ribavirin) and without prior treatment with an NS3/4A PI. 3 Includes subjects who discontinued due to adverse event, lost to follow-up, or subject withdrawal. |
||
Treatment-Naive Or PRS Treatment-Experienced Adults With HCV/HIV-1 Coinfection Without Cirrhosis Or With Compensated Cirrhosis
EXPEDITION-2 was an open-label study in 153 HCV/HIV-1-coinfected subjects. Subjects without cirrhosis received MAVYRET for 8 weeks and subjects with compensated cirrhosis received MAVYRET for 12 weeks. The study included subjects who were HCV treatment-naive or treatment-experienced to combinations of (peg)interferon, ribavirin, and/or sofosbuvir, with the exception of genotype 3-infected subjects who were all treatment naive.
Of the 153 subjects treated, the median age was 45 years (range: 23 to 74); 63% had HCV genotype 1, 7% had HCV genotype 2, 17% had HCV genotype 3, 11% had HCV genotype 4, 2% had HCV genotype 6; 11% had cirrhosis; 84% were male; and 16% were Black.
In EXPEDITION-2, the SVR12 rate in HCV/HIV-1 co-infected subjects was 98% (150/153). One subject experienced on-treatment virologic failure and no subjects relapsed.
Treatment-Naive Or PRS Treatment-Experienced Adults With Liver Or Kidney Transplant Without Cirrhosis
MAGELLAN-2 was a single-arm, open-label study in 100 post-liver or -kidney transplant HCV genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 infected subjects without cirrhosis who received MAVYRET for 12 weeks. The study included subjects who were HCV treatment-naive or treatment-experienced to combinations of (peg)interferon, ribavirin, and/or sofosbuvir, with the exception of genotype 3-infected subjects who were all treatment-naive.
Of the 100 subjects treated, the median age was 60 years (range: 39 to 78); 57% had HCV genotype 1, 13% had HCV genotype 2, 24% had HCV genotype 3, 4% had HCV genotype 4, 2% had HCV genotype 6; 75% were male; 8% were Black; 80% of subjects were post-liver transplant and 20% were post-kidney transplant. Immunosuppressants allowed for co-administration were cyclosporine ≤100 mg, tacrolimus, sirolimus, everolimus, azathioprine, mycophenolic acid, prednisone, and prednisolone.
The overall SVR12 rate in post-transplant subjects was 98% (98/100). There was one relapse and no on-treatment virologic failures.
Clinical Trial In Pediatric Subjects (12 Years To Less Than 18 Years)
The efficacy of MAVYRET was evaluated in an open-label study (DORA [Part 1]) that evaluated adolescent subjects 12 years to less than 18 years without cirrhosis who received MAVYRET for 8 or 16 weeks. Treatment duration was chosen to match approved adult durations based on HCV genotype and prior treatment experience.
47 subjects were enrolled in DORA (Part 1). The median age was 14 years (range: 12 to 17); 79% had HCV genotype 1, 6% had HCV genotype 2, 9% had HCV genotype 3, 6% had HCV genotype 4; 55% were female; 9% were Black; 77% were HCV treatment-naive; 23% were treatment-experienced to interferon; 4% had HIV-coinfection; none had cirrhosis; the mean weight was 59 kg (range: 32 kg to 109 kg).
The overall SVR12 rate was 100% (47/47).
Medication Guide
PATIENT INFORMATION
MAVYRET™
(MAV-ih-reht)
(glecaprevir and pibrentasvir) tablets
What is the most important information I should know about MAVYRET?
MAVYRET can cause serious side effects, including:
Hepatitis B virus reactivation. Before starting treatment with MAVYRET, your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check for hepatitis B virus infection. If you have ever had hepatitis B virus infection, the hepatitis B virus could become active again during or after treatment for hepatitis C virus with MAVYRET. Hepatitis B virus that becomes active again (called reactivation) may cause serious liver problems including liver failure and death. Your healthcare provider will monitor you if you are at risk for hepatitis B virus reactivation during treatment and after you stop taking MAVYRET.
For more information about side effects, see the section “What are the possible side effects of MAVYRET?”
What is MAVYRET?
MAVYRET is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 12 years of age and older or weighing at least 99 pounds (45 kilograms) with:
- chronic (lasting a long time) hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis.
- HCV genotype 1 infection and have been previously treated with a regimen that contained an HCV NS5A inhibitor or an NS3/4A protease inhibitor (PI), but not both.
MAVYRET contains the two medicines: glecaprevir and pibrentasvir.
It is not known if MAVYRET is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age.
Do not take MAVYRET if you
- have certain liver problems
- also take any of the following medicines:
- atazanavir
- rifampin
Before taking MAVYRET, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have had hepatitis B virus infection
- have liver problems other than hepatitis C virus infection.
- have HIV-1 infection
- have had a liver or a kidney transplant
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if MAVYRET will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if MAVYRET passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take MAVYRET.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. MAVYRET and other medicines may affect each other. This can cause you to have too much or not enough MAVYRET or other medicines in your body. This may affect the way MAVYRET or your other medicines work or may cause side effects.
Keep a list of your medicines to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
- You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with MAVYRET.
- Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take MAVYRET with other medicines.
How should I take MAVYRET?
- Take MAVYRET exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Do not change your dose unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Do not stop taking MAVYRET without first talking with your healthcare provider.
- Take 3 MAVYRET tablets at one time each day.
- Take MAVYRET with food.
- It is important that you do not miss or skip doses of MAVYRET during treatment.
- If you miss a dose of MAVYRET and it is:
- Less than 18 hours from the time you usually take MAVYRET, take the missed dose with food as soon as possible. Then take your next dose at your usual time.
- More than 18 hours from the time you usually take MAVYRET, do not take the missed dose. Take your next dose as usual with food.
- If you take too much MAVYRET, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of MAVYRET?
MAVYRET can cause serious side effects, including:
- Hepatitis B virus reactivation. See “What is the most important information I should know about MAVYRET?”
- In people who had or have advanced liver problems
before starting treatment with MAVYRET: rare risk of worsening liver
problems, liver failure and death. Your healthcare provider will check you for
signs and symptoms of worsening liver problems during treatment with MAVYRET.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following signs
and symptoms:
- nausea
- tiredness
- yellowing of your skin or white part of your eyes
- bleeding or bruising more easily than normal
- confusion
- dark, black, or bloody stool
- loss of appetite
- diarrhea
- dark or brown (tea-colored) urine
- swelling or pain on the upper right side of your stomach area (abdomen)
- sleepiness
- vomiting of blood
- lightheadedness
The most common side effects of MAVYRET include headache and tiredness.
These are not all the possible side effects of MAVYRET.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store MAVYRET?
- Store MAVYRET at or below 86°F (30°C).
- Keep MAVYRET in its original blister package until you are ready to take it.
Keep MAVYRET and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of MAVYRET
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use MAVYRET for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give MAVYRET to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about MAVYRET that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in MAVYRET?
Active ingredients: glecaprevir and pibrentasvir
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, copovidone (type K 28), croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose 2910, iron oxide red, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol 3350, propylene glycol monocaprylate (type II), sodium stearyl fumarate, titanium dioxide, and vitamin E (tocopherol) polyethylene glycol succinate. The tablets do not contain gluten.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
